Development and Progress in Sensors and Technologies for Human Emotion Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Contributions
- We review the state of the art development and progress in sensors and technologies for human emotion recognition. In particular, we provide a systematic study of various types of emotion recognition techniques, methods, and available applications.
- We discuss the several challenges for human emotion recognition (including monitoring and analysis of behaviour patterns, and measurement actions) to develop a flexible and efficient human emotion recognition system at scale.
- We provide a summary of the state of the trends in applying sensors in human emotion recognition and indicate the potential of employing such intelligent sensing systems for human emotion recognition in the future.
1.3. Methodology
1.4. Organization and Roadmap
2. Human Emotion Recognition
3. Sensors for Human Emotion Recognition
4. Types of Activity Monitoring and Methodologies
5. Design Challenges and Applications
6. Current Trends and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egger, M.; Ley, M.; Hanke, S. Emotion recognition from physiological signal analysis: A review. Electron. Notes Theor. Comput. Sci. 2019, 343, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzedzickis, A.; Kaklauskas, A.; Bucinskas, V. Human Emotion Recognition: Review of Sensors and Methods. Sensors 2020, 20, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Ren, F. A survey of textual emotion recognition and its challenges. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumenthaler, C.; Sander, D.; Manstead, A. Emotion recognition in simulated social interactions. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 11, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, J.; Tan, T. Affective computing: A review. In International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 981–995. [Google Scholar]
- Akgün, A.E.; Koçoğlu, İ.; İmamoğlu, S.Z. An emerging consumer experience: Emotional branding. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 99, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Álvarez-Pato, V.M.; Sánchez, C.N.; Domínguez-Soberanes, J.; Méndoza-Pérez, D.E.; Velázquez, R. A Multisensor Data Fusion Approach for Predicting Consumer Acceptance of Food Products. Foods 2020, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Sarkar, N.; Smith, C.A.; Adams, J.A. Affective communication for implicit human-machine interaction. In Proceedings of the SMC’03 Conference Proceedings. 2003 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Conference Theme-System Security and Assurance (Cat. No. 03CH37483), Washington, DC, USA, 8 October 2003; Volume 5, pp. 4896–4903. [Google Scholar]
- Murugappan, M.; Ramachandran, N.; Sazali, Y. Classification of human emotion from EEG using discrete wavelet transform. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suryadevara, N.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Determining wellness through an ambient assisted living environment. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2014, 29, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadevara, N.; Chen, C.P.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Rayudu, R. Ambient assisted living framework for elderly wellness determination through wireless sensor scalar data. In Proceedings of the 2013 Seventh International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Wellington, New Zealand, 3–5 December 2013; pp. 632–639. [Google Scholar]
- AlMejrad, A.S. Human emotions detection using brain wave signals: A challenging. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2010, 44, 640–659. [Google Scholar]
- Ghayvat, H.; Awais, M.; Pandya, S.; Ren, H.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Chandra Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chen, C.; Gope, P.; Chouhan, A.; Chen, W. Smart aging system: Uncovering the hidden wellness parameter for well-being monitoring and anomaly detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandya, S.; Ghayvat, H.; Kotecha, K.; Awais, M.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Gope, P.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Chen, W. Smart home anti-theft system: A novel approach for near real-time monitoring and smart home security for wellness protocol. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2018, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varghese, A.A.; Cherian, J.P.; Kizhakkethottam, J.J. Overview on emotion recognition system. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Soft-Computing and Networks Security (ICSNS), Coimbatore, India, 25–27 February 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, T.; Saravanan, C. Advancements and recent trends in emotion recognition using facial image analysis and machine learning models. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer, and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT), Mysuru, India, 15–16 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Alam, M.G.R.; Uddin, M.Z.; Huda, S.; Almogren, A.; Fortino, G. Human emotion recognition using deep belief network architecture. Inf. Fusion 2019, 51, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggioli, A. Online Emotion Recognition Services Are a Hot Trend. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2019, 22, 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, A.; Goronzy, S.; Schaich, P.; Williams, J. Emotion recognition using bio-sensors: First steps towards an automatic system. In Tutorial and Research Workshop on Affective Dialogue Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 36–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.; Siddiqui, M.F.H.; Javaid, A.Y. Facial emotion recognition: A survey and real-world user experiences in mixed reality. Sensors 2018, 18, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marechal, C.; Mikolajewski, D.; Tyburek, K.; Prokopowicz, P.; Bougueroua, L.; Ancourt, C.; Wegrzyn-Wolska, K. Survey on AI-Based Multimodal Methods for Emotion Detection. In High-Performance Modelling and Simulation for Big Data Applications; Kołodziej, J., González-Vélez, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11400, pp. 307–324. [Google Scholar]
- Landowska, A.; Brodny, G.; Wrobel, M.R. Limitations of Emotion Recognition from Facial Expressions in e-Learning Context; CSEDU: Gdansk, Poland, 2017; pp. 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Coito, T.; Firme, B.; Martins, M.S.; Vieira, S.M.; Figueiredo, J.; Sousa, J. Intelligent Sensors for Real-Time Decision-Making. Automation 2021, 2, 62–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, U.; Hareli, S. The influence of context on emotion recognition in humans. In Proceedings of the 2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–8 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Korkmaz, T.; Erol, H. Classification Of Human Facial Expressions For Emotion Recognition Using A Distributed Computer System. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), Diyarbakir, Turkey, 9–11 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, R.W.; Vyzas, E.; Healey, J. Toward machine emotional intelligence: Analysis of affective physiological state. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christie, I.C.; Friedman, B.H. Autonomic specificity of discrete emotion and dimensions of affective space: A multivariate approach. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2004, 51, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Jo, S. Deep physiological affect network for the recognition of human emotions. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 11, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, J.; Platt, T.; Ruch, W. Laughter and smiling in 16 positive emotions. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 8, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Sorenson, E.R.; Friesen, W.V. Pan-cultural elements in facial displays of emotion. Science 1969, 164, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckman, P. Basic Emotions, Handbook of Cognition and Emotion. In Proceedings of the Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications, Portsmouth, NH, USA, 1999; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa, R. The Rationality of Emotion; Mit Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Damasio, A.R. A second chance for emotion. In Cognitive Neuroscience of Emotion; Lane, R.D., Nadel, L., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson, B.L. What good are positive emotions? Rev. Gen. Psychol. 1998, 2, 300–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feidakis, M.; Daradoumis, T.; Caballé, S. Endowing e-learning systems with emotion awareness. In Proceedings of the 2011 Third International Conference on Intelligent Networking and Collaborative Systems, Fukuoka, Japan, 30 November–2 December 2011; pp. 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Kanjo, E.; Younis, E.M.; Sherkat, N. Towards unravelling the relationship between on-body, environmental and emotion data using sensor information fusion approach. Inf. Fusion 2018, 40, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, N.; Menicucci, D.; Sebastiani, L.; Bedini, R.; Pingitore, A.; Vanello, N.; Milanesi, M.; Landini, L.; Gemignani, A. The dynamics of EEG gamma responses to unpleasant visual stimuli: From local activity to functional connectivity. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyng, C.M.; Amin, H.U.; Saad, M.N.; Malik, A.S. The influences of emotion on learning and memory. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantic, M.; Rothkrantz, L.J.M. Automatic analysis of facial expressions: The state of the art. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1424–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elfenbein, H.A.; Ambady, N. On the universality and cultural specificity of emotion recognition: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 2002, 128, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawar, S.; Kithani, V.; Ahuja, S.; Sahu, S. Smart Home Security Using IoT and Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 16–18 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Trinh, M.H.; Phan, T.V.; Nguyen, H.D. An efficient real-time emotion detection using camera and facial landmarks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Seventh International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), Da Nang, Vietnam, 16–19 April 2017; pp. 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, P.; El Kaliouby, R. Real time facial expression recognition in video using support vector machines. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5–7 November 2003; pp. 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Daros, A.R.; Zakzanis, K.K.; Ruocco, A. Facial emotion recognition in borderline personality disorder. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Facial landmark detection by deep multi-task learning. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 94–108. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, A.; Raju, A.K.; Deb, S. Facial Emotion Detection Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), Belgaum, India, 5–7 June 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Peng, L. A Deep Learning Compensated Back Projection for Image Reconstruction of Electrical Capacitance Tomography. IEEE Sensors J. 2020, 20, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudiri, K.M.; Said, A.M.; Nayan, M.Y. Human emotion detection through speech and facial expressions. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCOINS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2016; pp. 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasomphan, S. Detecting human emotion via speech recognition by using speech spectrogram. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Paris, France, 19–21 October 2015; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Sasikumar, M. Recognizing emotions from human speech. In Thinkquest 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Kuang, Y.; Li, J. Human motion capture algorithm based on inertial sensors. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 4343797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulou, I.O.; Tsihrintzis, G.A. Emotion recognition from body movements and gestures. In Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems and Services; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, F.; Bari, A.H.; Gavrilova, M.L. Emotion Recognition From Body Movement. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 11761–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.R.; Pan, X.Y.; Zhan, Y.Z.; Shen, X.J. Using Kinect for real-time emotion recognition via facial expressions. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2015, 16, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; An, L.; Dong, J. Hand gesture monitoring using fiber-optic curvature sensors. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 7935–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalloul, N. Wearable sensors for the monitoring of movement disorders. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulliam, C.L.; Heldman, D.A.; Brokaw, E.B.; Mera, T.O.; Mari, Z.K.; Burack, M.A. Continuous assessment of levodopa response in Parkinson’s disease using wearable motion sensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 65, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, T.K.; Sherratt, R.S. Coverage of emotion recognition for common wearable biosensors. Biosensors 2018, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Pirbhulal, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Zhang, Y.T. Assessment of biofeedback training for emotion management through wearable textile physiological monitoring system. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 7087–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelopoulos, A.; Bourbakis, N. A survey on wearable biosensor systems for health monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008; pp. 4887–4890. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.; Long, S.; Yuan, H. Non-Contact Emotion Recognition Combining Heart Rate and Facial Expression for Interactive Gaming Environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11896–11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M.; Robertson, G. Perceptual user interfaces (introduction). Commun. ACM 2000, 43, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotovtsev, P. How IoT Can Integrate Biotechnological Approaches for City Applications—Review of Recent Advancements, Issues, and Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerritta, S.; Murugappan, M.; Nagarajan, R.; Wan, K. Physiological signals based human emotion recognition: A review. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 7th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications, Penang, Malaysia, 4–6 March 2011; pp. 410–415. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, J.; Barreda-Angeles, M.; Oliver, J.; Nandi, G.; Puig, D. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from electrodermal activity. In IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, P.; De Cock, P.; Munde, V.; Petry, K.; Van Den Noortgate, W.; Maes, B. The tell-tale: What do heart rate; skin temperature and skin conductance reveal about emotions of people with severe and profound intellectual disabilities? Res. Dev. Disabil. 2012, 33, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushki, A.; Fairley, J.; Merja, S.; King, G.; Chau, T. Comparison of blood volume pulse and skin conductance responses to mental and affective stimuli at different anatomical sites. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hameed, R.A.; Sabir, M.K.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Shamma, O.; Alzubaidi, L. Human emotion classification based on respiration signal. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology, Jeju Island, Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, N.; Zeng, Y.; Tong, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yan, B. Emotion recognition from EEG signals using multidimensional information in EMD domain. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8317357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardini, W.; Ali, G.A.; Magdady, E.; Al-momani, S. Detecting human emotions using electroencephalography (EEG) using dynamic programming approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 6th International Symposium on Digital Forensic and Security (ISDFS), Antalya, Turkey, 22–25 March 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, O.S.; Kim, M.J.; Ryu, Y.H.; Park, J.E. Is heart rate variability (HRV) an adequate tool for evaluating human emotions?–A focus on the use of the International Affective Picture System (IAPS). Psychiatry Res. 2017, 251, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenke, R.; Peer, A.; Buss, M. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2014, 5, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcao, S.M.; Fonseca, M.J. Emotions recognition using EEG signals: A survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 374–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, N.S.; Mountstephens, J.; Teo, J. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition: A State-of-the-Art Review of Current Trends and Opportunities. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020, 8875426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Z.; Mountstephens, J.; Teo, J. Emotion Recognition Using Eye-Tracking: Taxonomy, Review and Current Challenges. Sensors 2020, 20, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zheng, W.L.; Li, B.; Lu, B.L. Combining eye movements and eeg to enhance emotion recognition. IJCAI 2015, 15, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, D.; Ma, R.; Zhang, X.; Rao, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; Yi, F. Flexible temperature sensors based on carbon nanomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1941–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Han, L.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, P.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.P. Flexible, Highly Sensitive, and Ultrafast Responsive Pressure Sensor with Stochastic Microstructures for Human Health Monitoring. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2000902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, F.; Tang, W.l.; Jianping, S.; Yang, J.Q.; Zhu, L.Y. An review of flexible force sensors for human health monitoring. J. Adv. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Harada, S.; Yamamoto, D.; Honda, W.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Printed multifunctional flexible device with an integrated motion sensor for health care monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melzer, M.; Mönch, J.I.; Makarov, D.; Zabila, Y.; Cañón Bermúdez, G.S.; Karnaushenko, D.; Baunack, S.; Bahr, F.; Yan, C.; Kaltenbrunner, M. Wearable magnetic field sensors for flexible electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaloo, S.; Zand, M.M. Wearable electrochemical flexible biosensors: With the focus on affinity biosensors. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 32, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, S.; Al Machot, F.; Mayr, H.C. A review on applications of activity recognition systems with regard to performance and evaluation. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2016, 12, 1550147716665520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poria, S.; Majumder, N.; Mihalcea, R.; Hovy, E. Emotion recognition in conversation: Research challenges, datasets, and recent advances. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 100943–100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, F.; Kuroiwa, S. Semi-automatic emotion recognition from textual input based on the constructed emotion thesaurus. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Engineering, Wuhan, China, 30 October–1 November 2005; pp. 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, K.; Minato, J.; Ren, F.; Kuroiwa, S. Estimating human emotions using wording and sentence patterns. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Information Acquisition, Hong Kong, China, 27 June–3 July 2005; p. 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.; El-Hajj, W.; Hajj, H.; Elbassuoni, S. Emotion recognition from text based on automatically generated rules. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshop, Shenzhen, China, 14 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.W.; Kim, C.J.; Hwang, M.; Lee, E.C. Individual emotion classification between happiness and sadness by analyzing photoplethysmography and skin temperature. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fourth World Congress on Software Engineering, Hong Kong, China, 3–4 December 2013; pp. 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, H.; Lun, X.; Dan, L.; Zhijie, H.; Zhiliang, W. Cognitive emotion model for eldercare robot in smart home. China Commun. 2015, 12, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollreisz, D.; TaheriNejad, N. A simple algorithm for emotion recognition, using physiological signals of a smart watch. In Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Jeju, Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 2353–2356. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Park, J.; Shin, D.; Choi, Y. A BCI Based Alerting System for Attention Recovery of UAV Operators. Sensors 2021, 21, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.; Liu, Y. Emotion Recognition From Multi-Channel EEG Signals by Exploiting the Deep Belief-Conditional Random Field Framework. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 33002–33012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Chi, W.; Dong, E.; Song, X.; Gao, Q.; Song, Y. The fusion of electroencephalography and facial expression for continuous emotion recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 155724–155736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gao, Z.; Wang, S. Emotion recognition from peripheral physiological signals enhanced by EEG. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 2827–2831. [Google Scholar]
- Markov, K.; Matsui, T. Music genre and emotion recognition using Gaussian processes. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Yu, M.; Zhao, G.; Song, J.; Ge, Y.; Shi, Y. Real-time movie-induced discrete emotion recognition from EEG signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 9, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadevara, N.; Gaddam, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Rayudu, R. Wellness determination of inhabitant based on daily activity behaviour in real-time monitoring using sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 Fifth International Conference on Sensing Technology, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 28 November–1 December 2011; pp. 474–481. [Google Scholar]
- Survadevara, N.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Rayudu, R. Applying SARIMA time series to forecast sleeping activity for wellness model of elderly monitoring in smart home. In Proceedings of the 2012 Sixth International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Kolkata, India, 18–21 December 2012; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.J.; Yoon, C.; Jang, E.H.; Kim, D.H. Physiological signals and recognition of negative emotions. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 1074–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.; Vlasenko, B.; Eyben, F.; Wöllmer, M.; Stuhlsatz, A.; Wendemuth, A.; Rigoll, G. Cross-corpus acoustic emotion recognition: Variances and strategies. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2010, 1, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Wang, C.H.; Jung, T.P.; Wu, T.L.; Jeng, S.K.; Duann, J.R.; Chen, J.H. EEG-based emotion recognition in music listening. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.H.; Chen, H.H. Ranking-based emotion recognition for music organization and retrieval. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 19, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.V.; Pasad, V.; Sankhe, S.R.; Prajapati, K. Emotion based mood enhancing music recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT), Bangalore, India, 19–20 May 2017; pp. 1573–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanathan, R.; Kumaran, R.; Rohan, R.R.; Gupta, R.; Prabhu, V. An Intelligent Music Player Based on Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS), Bengaluru, India, 21–23 December 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; André, E. Emotion recognition based on physiological changes in music listening. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 2067–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukose, S.; Upadhya, S.S. Music player based on emotion recognition of voice signals. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT), Kerala, India, 6–7 July 2017; pp. 1751–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Attabi, Y.; Dumouchel, P. Anchor models for emotion recognition from speech. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2013, 4, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Chin, Y.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Hsieh, W.C. Hierarchical Dirichlet process mixture model for music emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 6, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, Y.G.; Li, B.; Sigal, L. Heterogeneous knowledge transfer in video emotion recognition, attribution and summarization. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2016, 9, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rengers, J. Investigating Association between Musical Features and Emotion through EEG Signal Analysis. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, R.; Nisar, H.; Yap, V.V. Recognition of Useful Music for Emotion Enhancement Based on Dimensional Model. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on BioSignal Analysis, Processing and Systems (ICBAPS), Kuching, Malaysia, 24–26 July 2018; pp. 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Zheng, W.; Lu, C.; Zong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Z. MPED: A multi-modal physiological emotion database for discrete emotion recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12177–12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrantonakis, P.C.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Emotion recognition from EEG using higher order crossings. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 14, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrantonakis, P.C.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Emotion recognition from brain signals using hybrid adaptive filtering and higher order crossings analysis. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2010, 1, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrantonakis, P.C.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. A novel emotion elicitation index using frontal brain asymmetry for enhanced EEG-based emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 15, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, N.; Viga, R.; Dogangün, A.; Grabmaier, A. Measurement and Analysis of Local Pulse Transit Time for Emotion Recognition. IEEE Sensors J. 2019, 19, 7683–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yin, R.; Shu, L.; Xu, X. Emotion recognition using frontal eeg in vr affective scenes. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Nanjing, China, 6–8 May 2019; Volume 1, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.; Maeng, J.; Kim, D.H. Inner Emotion Recognition using Multi Bio-Signals. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), JeJu, Korea, 24–26 June 2018; pp. 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Chamola, V.; Vineet, A.; Nayyar, A.; Hossain, E. Brain-Computer Interface-Based Humanoid Control: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.; Seeja, K. Subject independent emotion recognition from EEG using VMD and deep learning. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Ki, M.; Hong, K.; Byun, H. Subject-Independent EEG-based Emotion Recognition using Adversarial Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwon, Korea, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Perusquía-Hernández, M.; Hirokawa, M.; Suzuki, K. A wearable device for fast and subtle spontaneous smile recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 8, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, E.M.; Milone, D.H. Emotion recognition in never-seen languages using a novel ensemble method with emotion profiles. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 8, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, L.N.; Yang, H.J.; Nguyen, H.D.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, G.S.; Na, I.S. Deep neural network-based fusion model for emotion recognition using visual data. J. Supercomput. 2021, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov, D.; Patkin, M. Real-time emotion recognition on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; p. 787. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, H.; Lee, J.; Choi, J. Emotion Recognition in Gamers Wearing Head-mounted Display. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (VR), Osaka, Japan, 23–27 March 2019; pp. 1251–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Katsimerou, C.; Heynderickx, I.; Redi, J.A. Predicting mood from punctual emotion annotations on videos. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2015, 6, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Dai, F.; Huang, L.; Xiong, J.; Gui, G. HERO: Human emotions recognition for realizing intelligent Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 24321–24332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cheong, Y.G. A Multi-modal Approach for Emotion Recognition of TV Drama Characters Using Image and Text. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), Busan, Korea, 19–22 February 2020; pp. 420–424. [Google Scholar]
- Pathar, R.; Adivarekar, A.; Mishra, A.; Deshmukh, A. Human Emotion Recognition using Convolutional Neural Network in Real Time. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st International Conference on Innovations in Information and Communication Technology (ICIICT), Chennai, India, 25–26 April 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Joesph, C.; Rajeswari, A.; Premalatha, B.; Balapriya, C. Implementation of physiological signal based emotion recognition algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 36th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Dallas, TX, USA, 20–24 April 2020; pp. 2075–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, A.; Konar, A.; Chakraborty, U.K.; Chatterjee, A. Emotion recognition from facial expressions and its control using fuzzy logic. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2009, 39, 726–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G. An emotion recognition system for mobile applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołakowska, A.; Landowska, A.; Szwoch, M.; Szwoch, W.; Wrobel, M.R. Emotion recognition and its applications. In Human-Computer Systems Interaction: Backgrounds and Applications 3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sadka, O.; Antle, A. Interactive Technologies for Emotion-regulation Training: Opportunities and Challenges. In Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- JavaScript API for Face Detection. Available online: https://github.com/justadudewhohacks/face-api.js/ (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Quazi, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Suryadevara, N.; Huang, Y.M. Towards the smart sensors based human emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012; pp. 2365–2370. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.W. Speech emotion recognition: Two decades in a nutshell, benchmarks, and ongoing trends. Commun. ACM 2018, 61, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Yang, S.; Lai, Y.; Sui, C. High-Speed Optical 3D Measurement Sensor for Industrial Application. IEEE Sensors J. 2021, 21, 11253–11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelaarporn, P.; Wachiraphan, P.; Kaewlee, T.; Udsa, T.; Chaisaen, R.; Choksatchawathi, T.; Laosirirat, R.; Lakhan, P.; Natnithikarat, P.; Thanontip, K.; et al. Sensor-Driven Achieving of Smart Living: A Review. IEEE Sensors J. 2021, 21, 10369–10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Hitchens, M.; Varadharajan, V. Access control for Internet of Things—enabled assistive technologies: An architecture, challenges and requirements. In Assistive Technology for the Elderly; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Andalibi, N.; Buss, J. The Human in Emotion Recognition on Social Media: Attitudes, Outcomes, Risks. In Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 April 2020; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.H.; Rust, R.T. A strategic framework for artificial intelligence in marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2021, 49, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Khanna, A.; Gupta, D. Emotion recognition and detection methods: A comprehensive survey. J. Artif. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 53–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J. Suspect AI: Vibraimage, Emotion Recognition Technology, and Algorithmic Opacity. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.00502. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo-Reyes, J.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A.; Bustamante-Bello, M.R.; Pons-Rovira, J.L.; Gonzalez-Vargas, J.E. Emotion recognition for semi-autonomous vehicles framework. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2018, 12, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordorintelligence. The Emotion Detection and Recognition Market. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/emotion-detection-and-recognition-edr-market (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Wu, D.; Hossain, M.S.; Ghoneim, A.; Chen, M. Emotion-aware multimedia systems security. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 21, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ling, W. Joint Motion Information Extraction and Human Behavior Recognition in Video Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 11919–11926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.C.; Wang, K.Y.; Fahier, N.; Ho, Y.L.; Huang, Y.D. Development and validation of an EEG-based real-time emotion recognition system using edge AI computing platform with convolutional neural network system-on-chip design. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2019, 9, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagendorff, T.; Wezel, K. 15 challenges for AI: Or what AI (currently) can’t do. AI Soc. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Hitchens, M.; Varadharajan, V.; Rabehaja, T. Policy-based access control for constrained healthcare resources. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 19th International Symposium on A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM), Chania, Greece, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 588–599. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Hitchens, M.; Varadharajan, V. On the design of security mechanisms for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 Eleventh International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 4–6 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaneh, I.A.; Sankoh, I.; Koroma, D.K. A survey on security issues and wearable sensors in wireless body area network for healthcare system. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing (ICCWAMTIP), Chengdu, China, 15–17 December 2017; pp. 304–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, S.A.; Yahya, K.; Al-Turjman, F.; Yang, M.H. A secure and reliable device access control scheme for IoT based sensor cloud systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 139244–139254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Hitchens, M.; Varadharajan, V. Towards a secure access control architecture for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 42nd Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), Singapore, 9–12 October 2017; pp. 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Rabehaja, T.; Hill, A.; Hitchens, M.; Varadharajan, V. On the integration of blockchain to the internet of things for enabling access right delegation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 7, 2630–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Hitchens, M.; Rabehaja, T.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Security requirements for the internet of things: A systematic approach. Sensors 2020, 20, 5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, V.; Singh, R.; Reddy, R.; Churi, P. Privacy Issues in Wearable Technology: An Intrinsic Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Computing & Communications (ICICC), Delhi, India, 6 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Poonia, A.S.; Banerjee, C.; Banerjee, A.; Sharma, S. Security Issues in Internet of Things (IoT)-Enabled Systems: Problem and Prospects. In Soft Computing: Theories and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1419–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S.; Hitchens, M.; Varadharajan, V. Modeling identity for the internet of things: Survey, classification and trends. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Limerick, Ireland, 4–6 December 2018; pp. 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rabehaja, T.; Pal, S.; Hitchens, M. Design and implementation of a secure and flexible access-right delegation for resource constrained environments. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 99, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S. Wind energy—An innovative solution to global warming? In Proceedings of the 2009 1st International Conference on the Developements in Renewable Energy Technology (ICDRET), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–19 December 2009; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, S. Evaluating the impact of network loads and message size on mobile opportunistic networks in challenged environments. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 81, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S. Extending Mobile Cloud Platforms Using Opportunistic Networks: Survey, Classification and Open Issues. J. UCS 2015, 21, 1594–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, K.; Rehman, M.H.U.; Nizamuddin, N.; Al-Fuqaha, A. Blockchain for AI: Review and open research challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 10127–10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. A Review on the Use of Blockchain for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32979–33001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Establishment of Music Emotion Model Based on Blockchain Network Environment. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 8870886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.S.; Jena, D. Decentralizing AI Using Blockchain Technology for Secure Decision Making. In Advances in Machine Learning and Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 687–694. [Google Scholar]

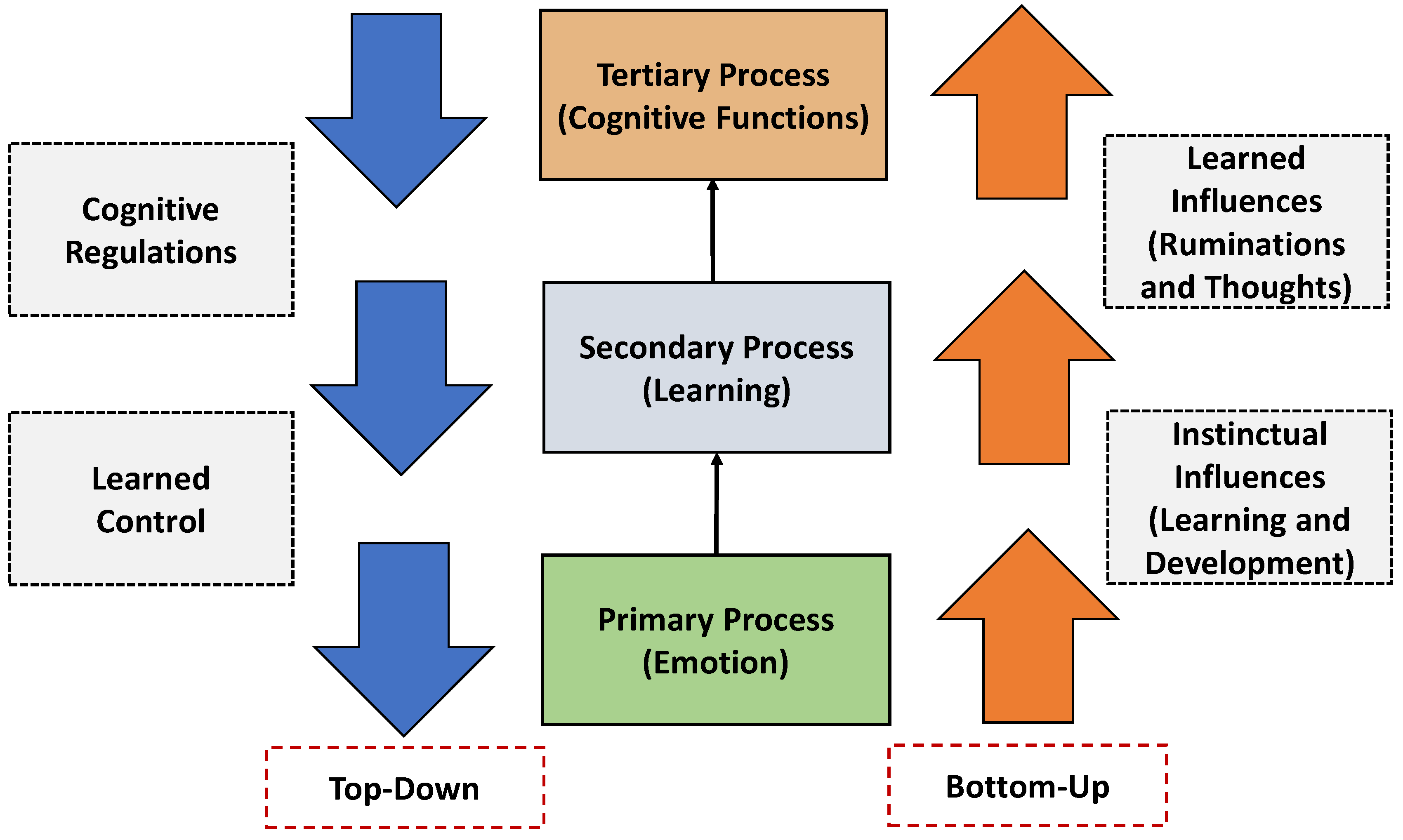



| Method | Activity Monitoring | Approach (References) |
|---|---|---|
| SKT | Skin temperature | [89] |
| PPG | Heart rate monitoring | [89] |
| EEG | Electrophysiological signals (from brain) | [93,94,95] |
| EMG | Nerve’s stimulation of the muscle | [120] |
| ECG | Electrical signal from heart | [117] |
| EOG | Signals from outer retina | [120] |
| GSR | Signals from sweat gland activity | [113] |
| Measurements Depending on Electrical Constraints | Measurements Depending on Non-Electrical Constraints | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct contact with sensors | Modulated sensors | Contact | Non-contact |
| EEG, EMG, ECG, EOG | GSR | PPG, RR, SKT | PPG |
| Less intrusive | More intrusive | ||
| More usability | Less usability | ||
| Interface for user is less | Interface for user is more | ||
| Integrate new components | Moderate integration of components | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pal, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Suryadevara, N. Development and Progress in Sensors and Technologies for Human Emotion Recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 5554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165554
Pal S, Mukhopadhyay S, Suryadevara N. Development and Progress in Sensors and Technologies for Human Emotion Recognition. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165554
Chicago/Turabian StylePal, Shantanu, Subhas Mukhopadhyay, and Nagender Suryadevara. 2021. "Development and Progress in Sensors and Technologies for Human Emotion Recognition" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165554
APA StylePal, S., Mukhopadhyay, S., & Suryadevara, N. (2021). Development and Progress in Sensors and Technologies for Human Emotion Recognition. Sensors, 21(16), 5554. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165554








