Tissue Oximeter with Selectable Measurement Depth Using Spatially Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Analysis
2.2. Spatially Resolved Oximeter
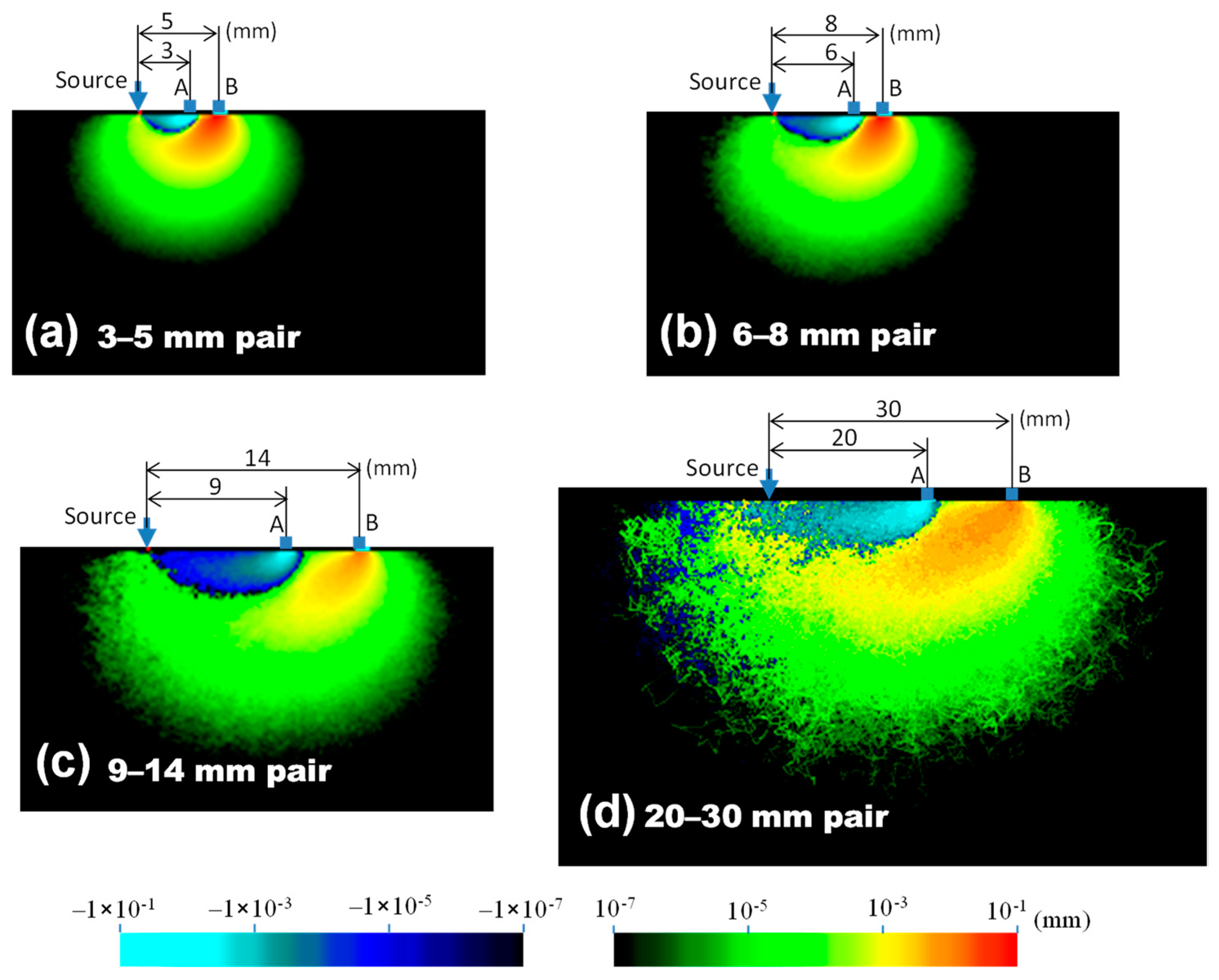
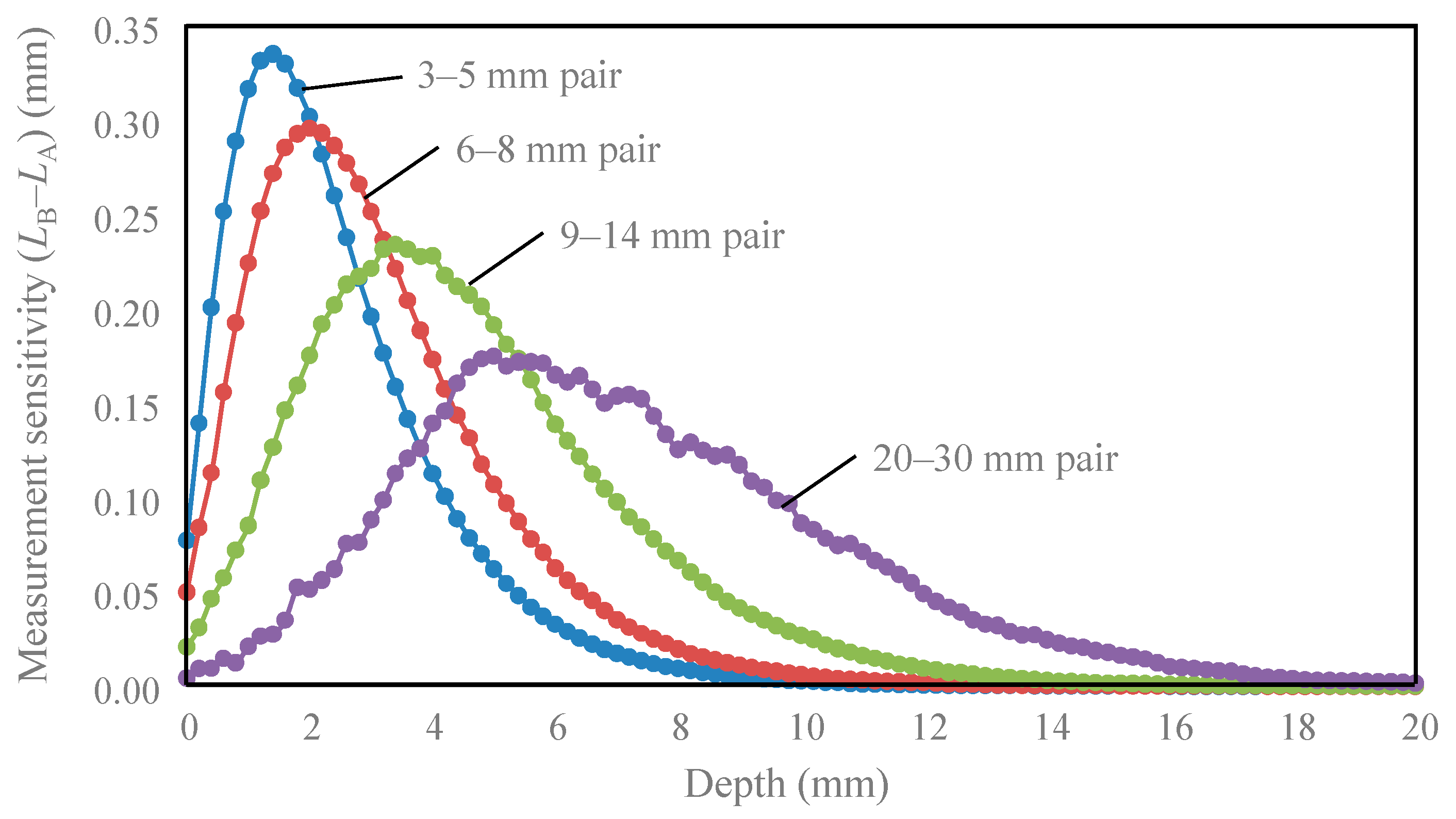
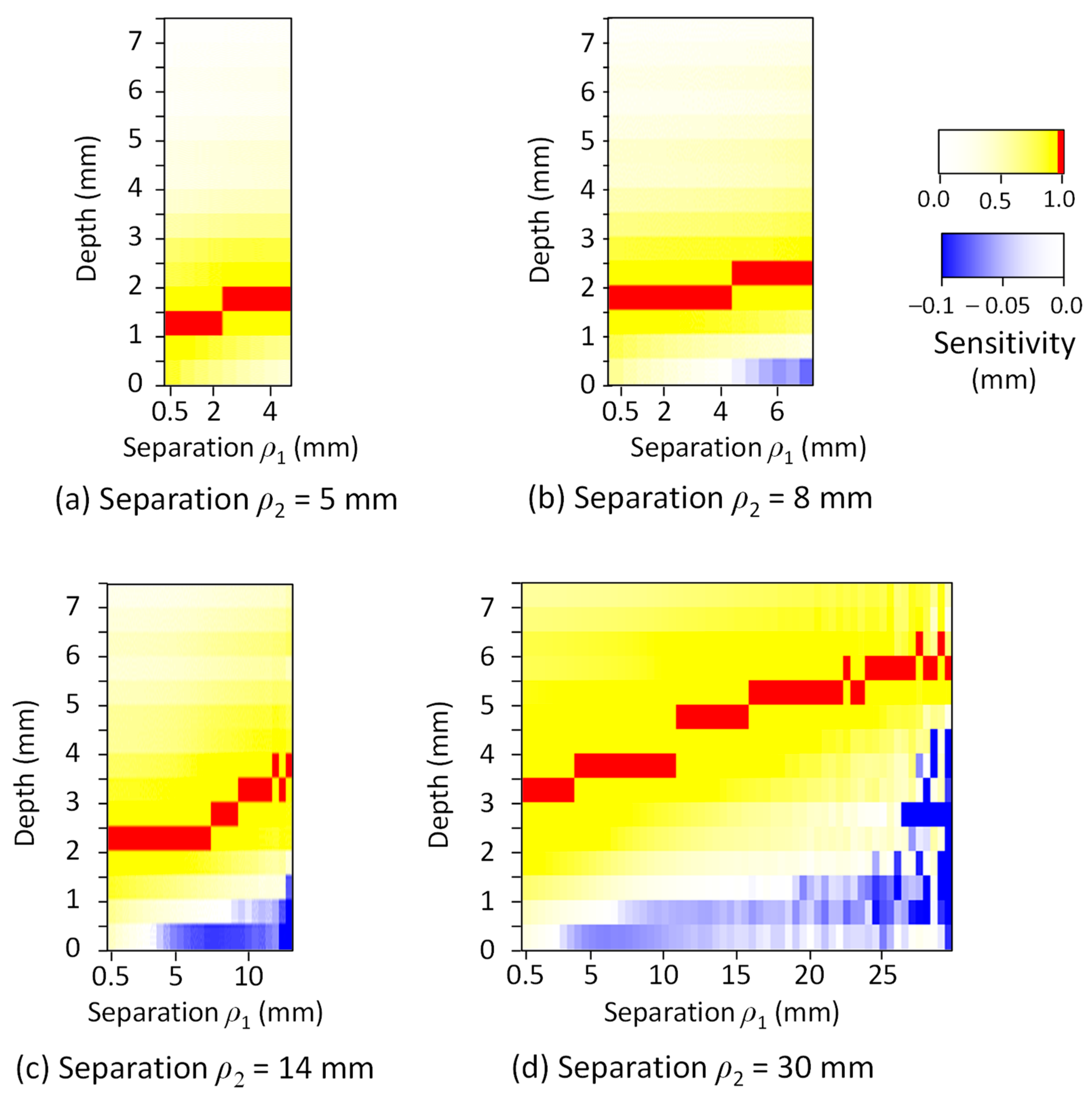
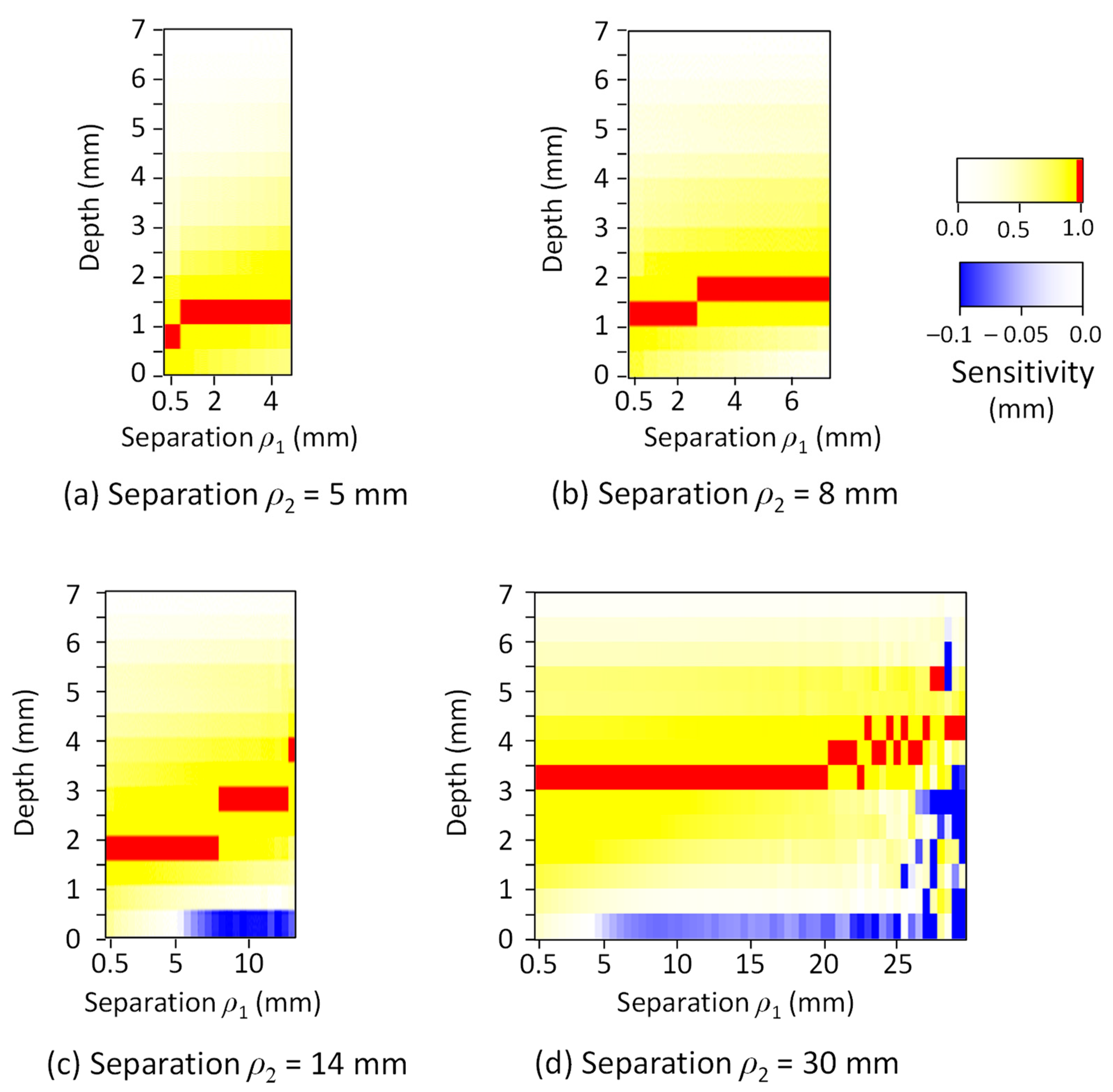
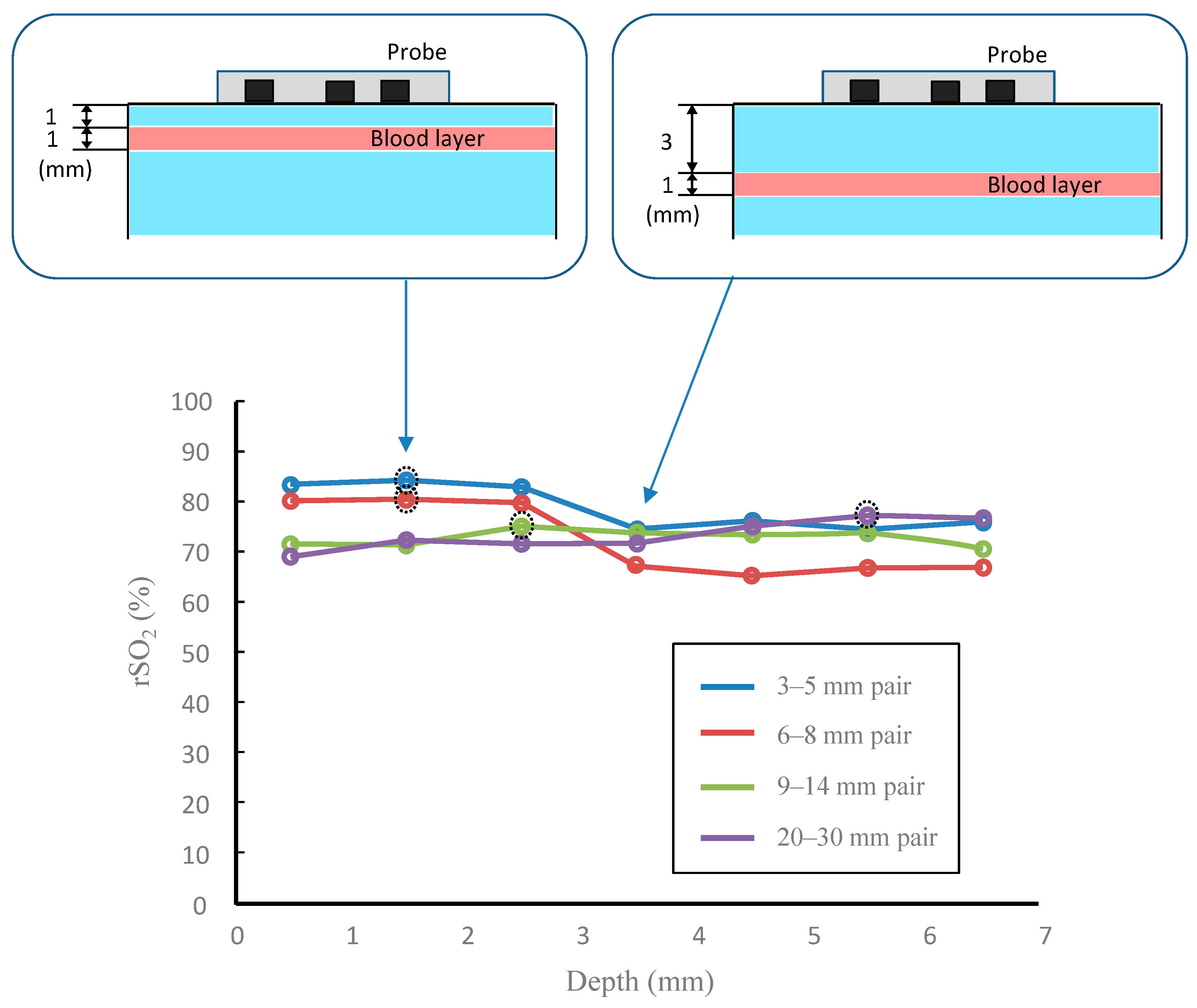
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barberio, M.; Felli, E.; Pop, R.; Pizzicannella, M.; Geny, B.; Lindner, V.; Baiocchini, A.; Jansen-Winkeln, B.; Moulla, Y.; Agnus, V.; et al. A novel technique to improve anastomotic perfusion prior to esophageal surgery: Hybrid ischemic preconditioning of the stomach. preclinical effcacy proof in a porcine survival model. Cancers 2020, 12, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilli, P.; Mari, G.M.; Crippa, J.; Miranda, A.; Santurro, L.; Riggio, V.; Gerosa, M.; Ascheri, P.; Cordaro, G.; Costanzi, A.T.M.; et al. 4K ultra HD technology reduces operative time and intraoperative blood loss in colorectal laparoscopic surgery. F1000Research 2020, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, T. Pulse oximetry: Its invention, theory, and future. J. Anesth. 2003, 17, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, C.V.; Ippen, E.P.; Bersohn, R. Time-resolved spectroscopy of hemoglobin and its complexes with subpicosecond optical pulses. Science 1976, 193, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, B.; Cope, M.; Gratton, E.; Ramanujam, N.; Tromberg, B. Phase measurement of light absorption and scatter in human tissue. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1998, 69, 3457–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrell, T.J.; Patterson, M.S.; Wilson, B. A diffusion theory model of spatially resolved, steady-state diffuse reflectance for the noninvasive determination of tissue optical properties in vivo. Med. Phys. 1992, 19, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienle, A.; Lilge, L.; Patterson, M.S.; Hibst, R.; Steiner, R.; Wilson, B.C. Spatially resolved absolute diffuse reflectance measurements for noninvasive determination of the optical scattering and absorption coefficients of biological tissue. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matcher, S.J.; Kirkpatrick, P.; Nahid, K.; Cope, M.; Delpy, D.T. Absolute quantification methods in tissue near infrared spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the Optical Tomography, Photon Migration, and Spectroscopy of Tissue and Model Media: Theory, Human Studies, and Instrumentation, San Jose, CA, USA, 1–28 February 1995; Volume 2359, pp. 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, F.M.; Berchem, J.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Alcantara, J.M.A.; Ortiz-Alvarez, L.; Hamaoka, T.; Ruiz, J.R. Near-infrared spatially resolved spectroscopy as an indirect technique to assess brown adipose tissue in young women. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanayama, N.; Niwayama, M. Examiner’s finger-mounted fetal tissue oximetry. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 67008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwayama, M. Voxel-based measurement sensitivity of spatially resolved near-infrared spectroscopy in layered tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 030503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yata, T.; Sano, M.; Kayama, T.; Naruse, E.; Yamamoto, N.; Inuzuka, K.; Saito, T.; Katahashi, K.; Yamanaka, Y.; Uchida, T.; et al. Utility of a finger-mounted tissue oximeter with near-infrared spectroscopy to evaluate limb ischemia in patients with peripheral arterial disease. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2019, 12, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujita, T. Method for evaluating gastrointestinal blood flow and reducing suture failure in esophageal cancer: Blood flow evaluation using regional SO2 (%) and total hemoglobin index (Japanese). In Proceedings of the 81st Annual Congress of Japan Surgical Association, Kochi, Japan, 15 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuge, I.; Enoshiri, T.; Saito, S.; Suzuki, S. A quick evaluation of TRAM flap viability using fingerstall-type tissue oximetry. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 5, e1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, M.; Setayeshi, S.; Ardehali, S.H.; Arabalibeik, H. Modeling of diffuse reflectance of light in heterogeneous biological tissue to analysis of the effects of multiple scattering on reflectance pulse oximetry. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehrabi, M.; Setayeshi, S.; Ghannadi Maragheh, M.; Ardehali, S.H.; Arabalibeik, H. Design of a new reflectance pulse oximeter by obtaining the optimal source-detector space. Optik 2018, 168, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.C.; Adam, G. A Monte Carlo model for the absorption and flux distributions of light in tissue. Med. Phys. 1983, 10, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jacques, S.L.; Zheng, L. MCML-Monte Carlo modeling of light transport in multi-layered tissues. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 1995, 47, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaegen, D. Radiative transfer in statistically heterogeneous mixtures. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1986, 36, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasouri, B.; Murphy, T.E.; Berberoglu, H. Simulation of laser propagation through a three-layer human skin model in the spectral range from 1000 to 1900 nm. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 075003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Salo, D.; Kim, D.M.; Komarov, S.; Tai, Y.-C.; Berezin, M.Y. Penetration depth of photons in biological tissues from hyperspectral imaging in shortwave infrared in transmission and reflection geometries. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 126006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douven, L.F.A.; Lucassen, G.W. Retrieval of optical properties of skin from measurement and modeling the diffuse reflectance. In Proceedings of the Laser-Tissue Interaction XI: Photochemical, Photothermal, and Photomechanical, San Jose, CA, USA, 22–28 January 2000; Volume 3914, pp. 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Anderson, R.R.; Parrish, J.A. Analytical modeling for the optical properties of the skin with in vitro and in vivo applications. Photochem. Photobiol. 1981, 34, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkatov, A.N.; Genina, E.A.; Kochubey, V.I.; Tuchin, V.V. Optical properties of human skin, subcutaneous and mucous tissues in the wavelength range from 400 to 2000 nm. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.R.; Kohl, M.; Essenpreis, M.; Cope, M. Near-infrared optical properties of ex vivo human skin and subcutaneous tissues measured using the Monte Carlo inversion technique. Phys. Med. Biol. 1998, 43, 2465–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.K.; Sorg, B.; Protsenko, D.; O’Neil, M.; Motamedi, M.; Welch, A.J. Effects of compression on soft tissue optical properties. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 1996, 2, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitic, G.; Kolzer, J.; Otto, J.; Plies, E.; Solkner, G.; Zinth, W. Time-gated transillumination of biological tissues and tissuelike phantoms. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 6699–6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaccanti, G.; Taddeucci, A.; Barilli, M.; Bruscaglioni, P.; Martelli, F. Optical properties of biological tissues. In Proceedings of the Optical Tomography, Photon Migration, and Spectroscopy of Tissue and Model Media: Theory, Human Studies, and Instrumentation, San Jose, CA, USA, 1–28 February 1995; Volume 2359, pp. 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraev, K.M.; Ashurbekov, N.A.; Lakhina, M.A. Optical absorption and scattering spectra of pathological stomach tissues. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 78, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpy, D.T.; Arridge, S.R.; Cope, M.; Edwards, D.; Reynolds, E.O.R.; Richardson, C.E.; Wray, S.; Wyatt, J.; van der Zee, P. Quantitation of pathlength in optical spectroscopy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1989, 248, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matcher, S.J.; Elwell, C.E.; Cooper, C.E.; Cope, M.; Delpy, D.T. Performance comparison of several published tissue near-infrared spectroscopy algorithms. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 227, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aernouts, B.; Van Beers, R.; Watté, R.; Lammertyn, J.; Saeys, W. Dependent scattering in Intralipid® phantoms in the 600–1850 nm range. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkruysse, W.; Lucassen, G.W.; de Boer, J.F.; Smithies, D.J.; Nelson, J.S.; van Gemert, M.J. Modelling light distributions of homogeneous versus discrete absorbers in light irradiated turbid media. Phys. Med. Biol. 1997, 42, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niedorf, F.; Jungmann, H.; Kietzmann, M. Noninvasive reflection spectra provide quantitative information about the spatial distribution of skin chromophores. Med. Phys. 2005, 32, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Tissue Type | Thickness (mm) | Scattering Coefficient (mm−1) 770 nm and 830 nm | Absorption Coefficient (mm−1) (770 and 830 nm) | Anisotropic Factor (770 and 830 nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin | 1.5 | 26 | 23 | 0.020 | 0.95 |
| Fat | 2.5 | 24 | 22 | 0.003 | 0.95 |
| Muscle | 20.0 | 14 | 13 | 0.025 | 0.95 |
| Gastric tissue | 7.0 | 15 | 14 | 0.030 | 0.92 |
| Detector Pair | Peak Depth (mm) | Depth Range of 50% of Peak (mm) | Depth Reduced to 10% of Peak (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3–5 mm | 1.4 | 0.3–3.3 | 6.0 |
| 6–8 mm | 2.0 | 0.5–4.5 | 7.3 |
| 9–14 mm | 3.4 | 1.3–6.5 | 10.3 |
| 20–30 mm | 5.0 | 3.0–9.8 | 15.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niwayama, M.; Unno, N. Tissue Oximeter with Selectable Measurement Depth Using Spatially Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors 2021, 21, 5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165573
Niwayama M, Unno N. Tissue Oximeter with Selectable Measurement Depth Using Spatially Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165573
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiwayama, Masatsugu, and Naoki Unno. 2021. "Tissue Oximeter with Selectable Measurement Depth Using Spatially Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165573
APA StyleNiwayama, M., & Unno, N. (2021). Tissue Oximeter with Selectable Measurement Depth Using Spatially Resolved Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Sensors, 21(16), 5573. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165573






