Comparing Class-Aware and Pairwise Loss Functions for Deep Metric Learning in Wildlife Re-Identification †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- highlight the need for increased research into loss functions and neural network architecture specifically for wildlife re-identification;
- improve on the state-of-the-art results in numerous animal re-identification tasks;
- contribute two new benchmark datasets with results;
- provide minor support for a choice of triplet loss with a VGG-11 backbone as an initial architecture and loss.
2. Related Work
2.1. Animal Biometrics and Computer Vision
- Universality: all the individuals in the population must have such a feature;
- Uniqueness: two or more individuals should have a different form of the same feature.
2.2. Classification vs. Similarity Learning
2.3. Similarity Learning
2.4. Sampling Techniques for Pairwise Training
2.4.1. Hard Negative Mining
2.4.2. Semi-Hard Negative Mining
2.5. Challenges in Deep Metric Learning
2.6. Animal Biometrics Using Image Features
2.7. Loss Functions
2.7.1. Pairwise Loss
2.7.2. Class Distribution Based Loss
2.8. Motivation
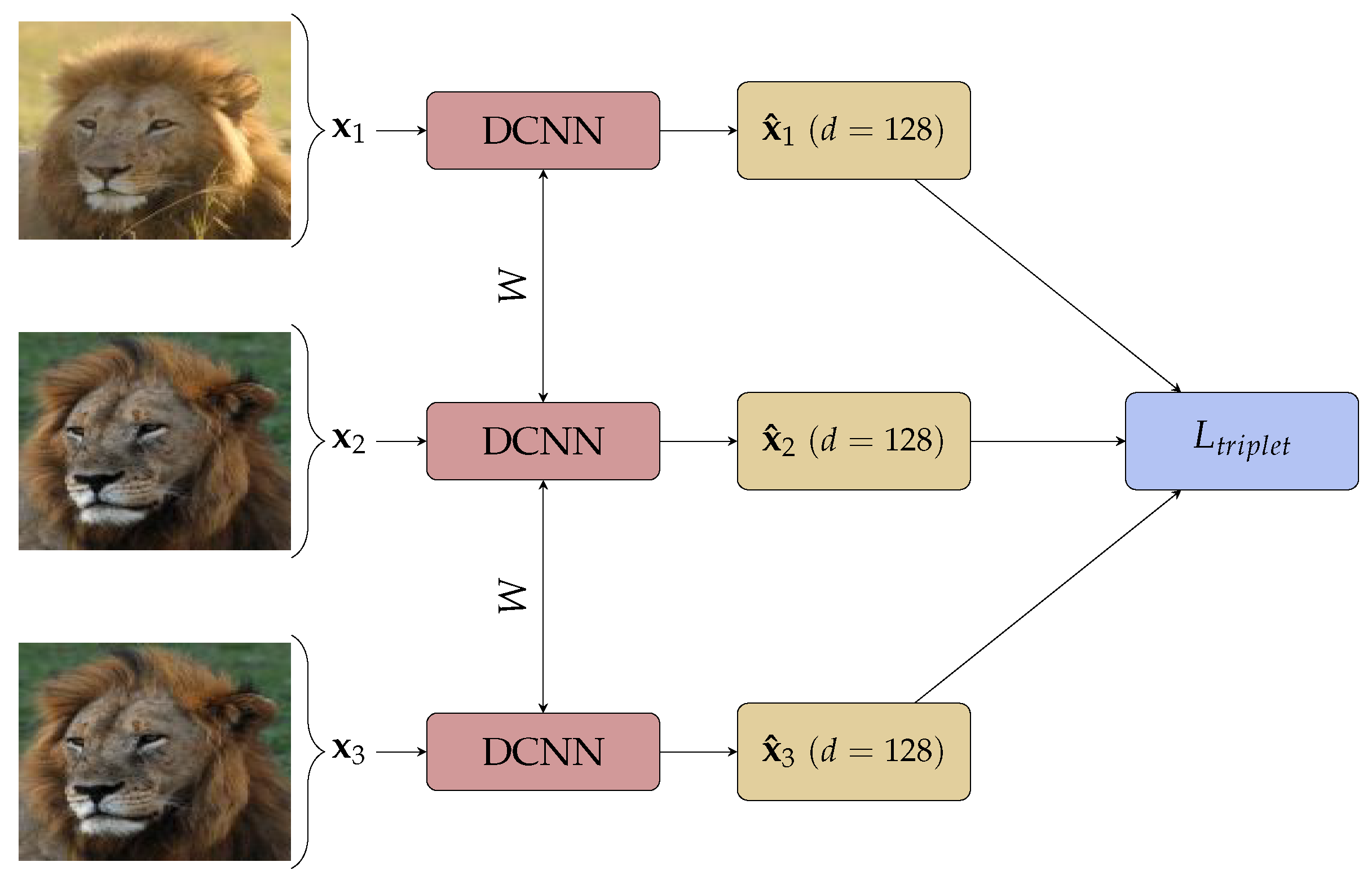
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Neural Network Architectures
3.3. Training
3.4. Metrics Measured
3.5. Embedding Dimension Size
4. Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Class Aware vs. Pairwise Loss
5.2. Backbone Architectures
5.3. Flanks vs. Faces
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Network |
| P-NCA | Proxy Neighbourhood Component Analysis |
| Proxy-NCA | Proxy Neighbourhood Component Analysis |
| MAP | Mean Average Precision |
References
- Borchers, D.L.; Zucchini, W.; Fewster, R.M. Mark-recapture models for line transect surveys. Biometrics 1998, 54, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariff, M.; Ismail, I. Livestock information system using Android Smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Systems, Process & Control (ICSPC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–15 December 2013; pp. 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Schacter, C.R.; Jones, I.L. Effects of geolocation tracking devices on behavior, reproductive success, and return rate of Aethia auklets: An evaluation of tag mass guidelines. Wilson J. Ornithol. 2017, 129, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.W.; Stien, L.H.; Dempster, T.; Oppedal, F. Differential effects of internal tagging depending on depth treatment in Atlantic salmon: A cautionary tale for aquatic animal tag use. Curr. Zool. 2019, 65, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A.I. From classical methods to animal biometrics: A review on cattle identification and tracking. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Maclagan, S.J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, T.; Flemons, P.; Andrews, K.; Ritchie, E.G.; Phung, D. Animal recognition and identification with deep convolutional neural networks for automated wildlife monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Tokyo, Japan, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Han, T.X.; He, Z.; Kays, R.; Forrester, T. Deep convolutional neural network based species recognition for wild animal monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 858–862. [Google Scholar]
- van Zyl, T.L.; Woolway, M.; Engelbrecht, B. Unique Animal Identification using Deep Transfer Learning For Data Fusion in Siamese Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION 2020), Rustenburg, South Africa, 6–9 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, G.K.; Gupta, P. Wild animal detection using deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Computer Vision & Image Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 327–338. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.; van Zyl, T.L. Automated Music Recommendations Using Similarity Learning. In Proceedings of the SACAIR 2020, Muldersdrift, Africa, 22–26 February 2021; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Manack, H.; Van Zyl, T.L. Deep Similarity Learning for Soccer Team Ranking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Rustenburg, South Africa, 6–9 July 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, M.; Bilge, H.Ş. Deep metric learning: A survey. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musgrave, K.; Belongie, S.; Lim, S.N. A metric learning reality check. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Glasgow, UK, 2020; pp. 681–699. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.K.; Flynn, P.; Ross, A.A. Handbook of Biometrics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Korschens, M.; Denzler, J. Elpephants: A fine-grained dataset for elephant re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kühl, H.S.; Burghardt, T. Animal biometrics: Quantifying and detecting phenotypic appearance. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, R. Human identification in information systems. Inf. Technol. People 1994, 7, 6–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowcliffe, J.M.; Field, J.; Turvey, S.T.; Carbone, C. Estimating animal density using camera traps without the need for individual recognition. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhou, Y. Deep discriminative representation learning with attention map for scene classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face representation by joint identification-verification. In Proceedings of the 27 International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montereal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 1988–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, B.J.; Drummond, T. The importance of metric learning for robotic vision: Open set recognition and active learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 2924–2931. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.; van Zyl, T.L. Comparative Analysis of Catastrophic Forgetting in Metric Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Soft Computing & Machine Intelligence (ISCMI), Stockholm, Sweden, 14–15 November 2020; pp. 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger, K.Q.; Saul, L.K. Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 207–244. [Google Scholar]
- El-Naqa, I.; Yang, Y.; Galatsanos, N.P.; Nishikawa, R.M.; Wernick, M.N. A similarity learning approach to content-based image retrieval: Application to digital mammography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromley, J.; Guyon, I.; LeCun, Y.; Säckinger, E.; Shah, R. Signature verification using a “siamese” time delay neural network. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 29 November–2 December 1994; pp. 737–744. [Google Scholar]
- Dlamini, N.; van Zyl, T.L. Author Identification from Handwritten Characters using Siamese CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Multidisciplinary Information Technology and Engineering Conference (IMITEC), Vanderbijlpark, South Africa, 21–22 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, S.; Hadsell, R.; LeCun, Y. Learning a similarity metric discriminatively, with application to face verification. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Liu, T.; Gong, M.; Ding, C.; Tao, D. Correcting the triplet selection bias for triplet loss. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Charoenphakdee, N.; Sato, I.; Sugiyama, M. Classification from Triplet Comparison Data. Neural Comput. 2020, 32, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xuan, H.; Stylianou, A.; Pless, R. Improved embeddings with easy positive triplet mining. In Proceedings of the The IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 2474–2482. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.; Taylor, G.W.; Kremer, S.C. Similarity learning networks for animal individual re-identification-beyond the capabilities of a human observer. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Snowmass, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, K.; Milbich, T.; Sinha, S.; Gupta, P.; Ommer, B.; Cohen, J.P. Revisiting training strategies and generalization performance in deep metric learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Vienna, Austria, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 8242–8252. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, T.; Gong, M.; Zafeiriou, S. Sub-center arcface: Boosting face recognition by large-scale noisy web faces. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Glasgow, UK, 2020; pp. 741–757. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Roy, P.P.; Jeong, D.M. Efficient facial expression recognition algorithm based on hierarchical deep neural network structure. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 41273–41285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Huang, W.; Dong, D.; Scott, M.R. Multi-similarity loss with general pair weighting for deep metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5022–5030. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.; Taylor, G.W.; Linquist, S.; Kremer, S.C. Past, present and future approaches using computer vision for animal re-identification from camera trap data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Su, D.; Kong, H.; Sukkarieh, S.; Lomax, S.; Clark, C. Individual cattle identification using a deep learning based framework. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; He, Y.; Yang, H.; Connor, T.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Zheng, B.; et al. Identification of animal individuals using deep learning: A case study of giant panda. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 242, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepovinnykh, E.; Eerola, T.; Kalviainen, H. Siamese network based pelage pattern matching for ringed seal re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Snowmass, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burghardt, T.; Calic, J.; Thomas, B.T. Tracking Animals in Wildlife Videos Using Face Detection; EWIMT: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Henschel, P.; Coad, L.; Burton, C.; Chataigner, B.; Dunn, A.; MacDonald, D.; Saidu, Y.; Hunter, L.T. The lion in West Africa is critically endangered. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norouzzadeh, M.S.; Nguyen, A.; Kosmala, M.; Swanson, A.; Palmer, M.S.; Packer, C.; Clune, J. Automatically identifying, counting, and describing wild animals in camera-trap images with deep learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5716–E5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teh, E.W.; DeVries, T.; Taylor, G.W. Proxynca++: Revisiting and revitalizing proxy neighborhood component analysis. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV); Springer: Glasgow, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Isola, P. Understanding contrastive representation learning through alignment and uniformity on the hypersphere. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Cambridge, MA, USA, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 9929–9939. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Li, L. Intriguing Properties of Contrastive Losses. arxiv 2020, arXiv:2011.02803. [Google Scholar]
- Rippel, O.; Paluri, M.; Dollar, P.; Bourdev, L. Metric learning with adaptive density discrimination. arxiv 2015, arXiv:1511.05939. [Google Scholar]
- Movshovitz-Attias, Y.; Toshev, A.; Leung, T.K.; Ioffe, S.; Singh, S. No fuss distance metric learning using proxies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger, J.; Hinton, G.E.; Roweis, S.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Neighbourhood components analysis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2004, 17, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J.; Stark, M.; Deng, J.; Fei-Fei, L. 3D Object Representations for Fine-Grained Categorization. In Proceedings of the 4th International IEEE Workshop on 3D Representation and Recognition (3dRR-13), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2–8 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Luo, P.; Change Loy, C.; Tang, X. A large-scale car dataset for fine-grained categorization and verification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3973–3981. [Google Scholar]
- Wah, C.; Branson, S.; Welinder, P.; Perona, P.; Belongie, S. The Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011 Dataset; Technical Report CNS-TR-2011-001; California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freytag, A.; Rodner, E.; Simon, M.; Loos, A.; Kühl, H.S.; Denzler, J. Chimpanzee faces in the wild: Log-euclidean CNNs for predicting identities and attributes of primates. In German Conference on Pattern Recognition; Springer: Hannover, Germany, 2016; pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiri, M.; Tantipathananandh, C.; Warungu, R.; Rubenstein, D.I.; Berger-Wolf, T.Y. Biometric animal databases from field photographs: Identification of individual zebra in the wild. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Trento, Italy, 18–20 April 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Matkowski, W.M.; Kong, A.W.K.; Su, H.; Chen, P.; Hou, R.; Zhang, Z. Giant panda face recognition using small dataset. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1680–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Qian, R.; Lin, W. ATRW: A benchmark for Amur tiger re-identification in the wild. arxiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05586. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arxiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave, K.; Belongie, S.; Lim, S.N. PyTorch Metric Learning. arxiv 2020, arXiv:2008.09164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Swarup, P.; Matkowski, W.M.; Kong, A.W.K.; Han, S.; Zhang, Z.; Rong, H. A study on giant panda recognition based on images of a large proportion of captive pandas. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Short Biography of Authors
 | Nkosikhona Dlamini is a student at the University of Witwatersrand studying towards a Master of Science in Computer science. Completed honours degree in Computer science at the University of Pretoria. Currently employed at the Tshwane university of Technology. He spent four years working at the CSIR as a research and development technologist focusing on NLP for South African languages. |
 | Terence L. van Zyl holds the Nedbank Research and Innovation Chair at the University of Johannesburg where he is a Professor in the Institute for Intelligent Systems. He is an NRF rated scientist who received his PhD and MSc in Computer Science from the University of Johannesburg for his thesis on agent-based complex adaptive systems. He has over 15 years of experience researching and innovating large scale streaming analytics systems for government and industry. His research interests include data-driven science and engineering, prescriptive analytics, machine learning, meta-heuristic optimisation, complex adaptive systems, high-performance computing, and artificial intelligence. |



| Animal | N | I | Split | N | I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lion | 750 | 98 | 7.7 ± 4.0 | Train Test | 594 156 | 79 19 |
| Nyala | 1934 | 274 | 7.1 ± 5.1 | Train Test | 1213 729 | 179 95 |
| Zebra | 2460 | 45 | 54.7 ± 7.3 | Train Test | 1989 471 | 36 9 |
| Chimp | 5078 | 78 | 65.1 ± 17.0 | Train Test | 3908 1170 | 62 16 |
| Panda | 6462 | 218 | 29.64 ± 8.0 | Train Test | 5546 916 | 174 44 |
| Tiger | 3651 | 182 | 20.1 ± 15.0 | Train Test | 1887 1764 | 107 75 |
| MAP@R% | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dataset | D-64 | D-128 | D-512 |
| Chimp | 8.4 ± 0 | 9.1 ± 1 | 9.1 ± 0 |
| Nyala | 38.0 ± 1 | 38.6 ± 1 | 38.5 ± 1 |
| Zebra | 29.8 ± 2 | 29.6 ± 1 | 30.6 ± 2 |
| Lion | 48.8 ± 2 | 50.6 ± 1 | 50.5 ± 2 |
| Tiger | 21.6 ± 3 | 23.2 ± 2 | 23.0 ± 3 |
| Panda | 27.5 ± 1 | 28.4 ± 2 | 28.1 ± 1 |
| Top-1/Recall@1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faces | Flanks | ||||||
| Architecture | Loss | Lions | Chimps | Pandas | Nyala | Zebra | Tiger |
| VGG-11 | Triplet | 66.5 ± 2 | 79.0 ± 1 | 91.2 ± 1 | 68.7 ± 2 | 94.6 ± 0 | 88.9 ± 1 |
| P-NCA | 68.2 ± 3 | 78.9 ± 1 | 89.3 ± 2 | 68.4 ± 2 | 93.8 ± 2 | 87.0 ± 1 | |
| VGG-19 | Triplet | 70.2 ± 2 | 70.6 ± 0 | 86.3 ± 2 | 72.3 ± 0 | 82.8 ± 1 | 86.3 ± 2 |
| P-NCA | 71.3 ± 3 | 66.3 ± 0 | 90.9 ± 0 | 69.2 ± 3 | 82.7 ± 0 | 84.4 ± 1 | |
| ResNet-18 | Triplet | 67.8 ± 1 | 79.2 ± 2 | 90.0 ± 0 | 64.9 ± 2 | 94.8 ± 1 | 87.1 ± 1 |
| P-NCA | 66.8 ± 3 | 77.9 ± 0 | 90.1 ± 1 | 64.1 ± 0 | 93.6 ± 2 | 84.8 ± 1 | |
| ResNet-152 | Triplet | 63.2 ± 2 | 71.2 ± 1 | 87.6 ± 3 | 61.0 ± 3 | 80.7 ± 0 | 76.5 ± 2 |
| P-NCA | 61.0 ± 1 | 69.5 ± 1 | 83.4 ± 0 | 59.7 ± 0 | 79.1 ± 3 | 75.5 ± 2 | |
| DenseNet-201 | Triplet | 70.1 ± 1 | 79.7 ± 2 | 89.6 ± 1 | 67.1 ± 2 | 89.1 ± 0 | 85.0 ± 1 |
| P-NCA | 69.5 ± 3 | 78.2 ± 2 | 90.7 ± 1 | 66.3 ± 1 | 87.5 ± 0 | 85.6 ± 1 | |
| Prior Research | - | - | 77.5 ± 0 | 92.1 ± – | 72.1 ± 0 | 72.6 ± 0 | 86.3 ± 0 |
| MAP@R | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faces | Flanks | ||||||
| Architecture | Loss | Lions | Chimps | Pandas | Nyala | Zebra | Tiger |
| VGG-11 | Triplet | 16.5 ± 2 | 12.9 ± 2 | 32.0 ± 2 | 11.2 ± 0 | 16.8 ± 1 | 22.8 ± 1 |
| P-NCA | 17.7 ± 1 | 13.8 ± 3 | 31.8 ± 1 | 11.0 ± 1 | 16.5 ± 0 | 22.9 ± 2 | |
| VGG-19 | Triplet | 18.0 ± 2 | 11.7 ± 1 | 25.0 ± 0 | 10.8 ± 1 | 16.7 ± 2 | 21.8 ± 1 |
| P-NCA | 17.7 ± 0 | 12.0 ± 2 | 28.7 ± 0 | 9.7 ± 3 | 16.4 ± 3 | 20.0 ± 1 | |
| ResNet-18 | Triplet | 18.5 ± 0 | 11.2 ± 2 | 26.3 ± 1 | 9.9 ± 2 | 19.0 ± 0 | 24.6 ± 4 |
| P-NCA | 19.0 ± 1 | 11.5 ± 1 | 24.9 ± 0 | 9.5 ± 1 | 18.2 ± 1 | 21.7 ± 2 | |
| ResNet-152 | Triplet | 17.3 ± 2 | 10.1 ± 0 | 26.9 ± 1 | 8.2 ± 0 | 12.1 ± 3 | 12.5 ± 3 |
| P-NCA | 17.1 ± 0 | 9.4 ± 3 | 20.3 ± 1 | 9.0 ± 2 | 11.9 ± 2 | 11.0 ± 1 | |
| DenseNet-201 | Triplet | 20.8 ± 1 | 9.9 ± 2 | 31.1 ± 1 | 11.0 ± 2 | 15.9 ± 2 | 22.3 ± 1 |
| P-NCA | 20.2 ± 2 | 11.6 ± 3 | 28.4 ± 2 | 10.4 ± 1 | 16.0 ± 1 | 23.2 ± 3 | |
| MAP@R | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faces | Flanks | |||||
| Architecture | Lions | Chimps | Panda | Nyala | Zebra | Tiger |
| VGG-11 | 17.7 ± 1 | 13.8 ± 3 | 32.0 ± 2 | 11.2 ± 0 | 16.7 ± 2 | 22.8 ± 1 |
| ResNet-18 | 19.0 ± 1 | 11.2 ± 2 | 26.3 ± 1 | 9.9 ± 2 | 19.0 ± 0 | 24.6 ± 4 |
| DenseNet-201 | 20.8 ± 1 | 11.6 ± 3 | 31.1 ± 1 | 11.0 ± 2 | 16.0 ± 1 | 23.2 ± 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dlamini, N.; van Zyl, T.L. Comparing Class-Aware and Pairwise Loss Functions for Deep Metric Learning in Wildlife Re-Identification. Sensors 2021, 21, 6109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186109
Dlamini N, van Zyl TL. Comparing Class-Aware and Pairwise Loss Functions for Deep Metric Learning in Wildlife Re-Identification. Sensors. 2021; 21(18):6109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186109
Chicago/Turabian StyleDlamini, Nkosikhona, and Terence L. van Zyl. 2021. "Comparing Class-Aware and Pairwise Loss Functions for Deep Metric Learning in Wildlife Re-Identification" Sensors 21, no. 18: 6109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186109
APA StyleDlamini, N., & van Zyl, T. L. (2021). Comparing Class-Aware and Pairwise Loss Functions for Deep Metric Learning in Wildlife Re-Identification. Sensors, 21(18), 6109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186109






