Evaluation of Murrell’s EKF-Based Attitude Estimation Algorithm for Exploiting Multiple Attitude Sensor Configurations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Attitude Determination Hardware and Sensor Models
2.1. Attitude Sensors
2.1.1. Sun Sensor
2.1.2. Magnetometer
2.1.3. Inertial Measurement Unit and Gyro Model
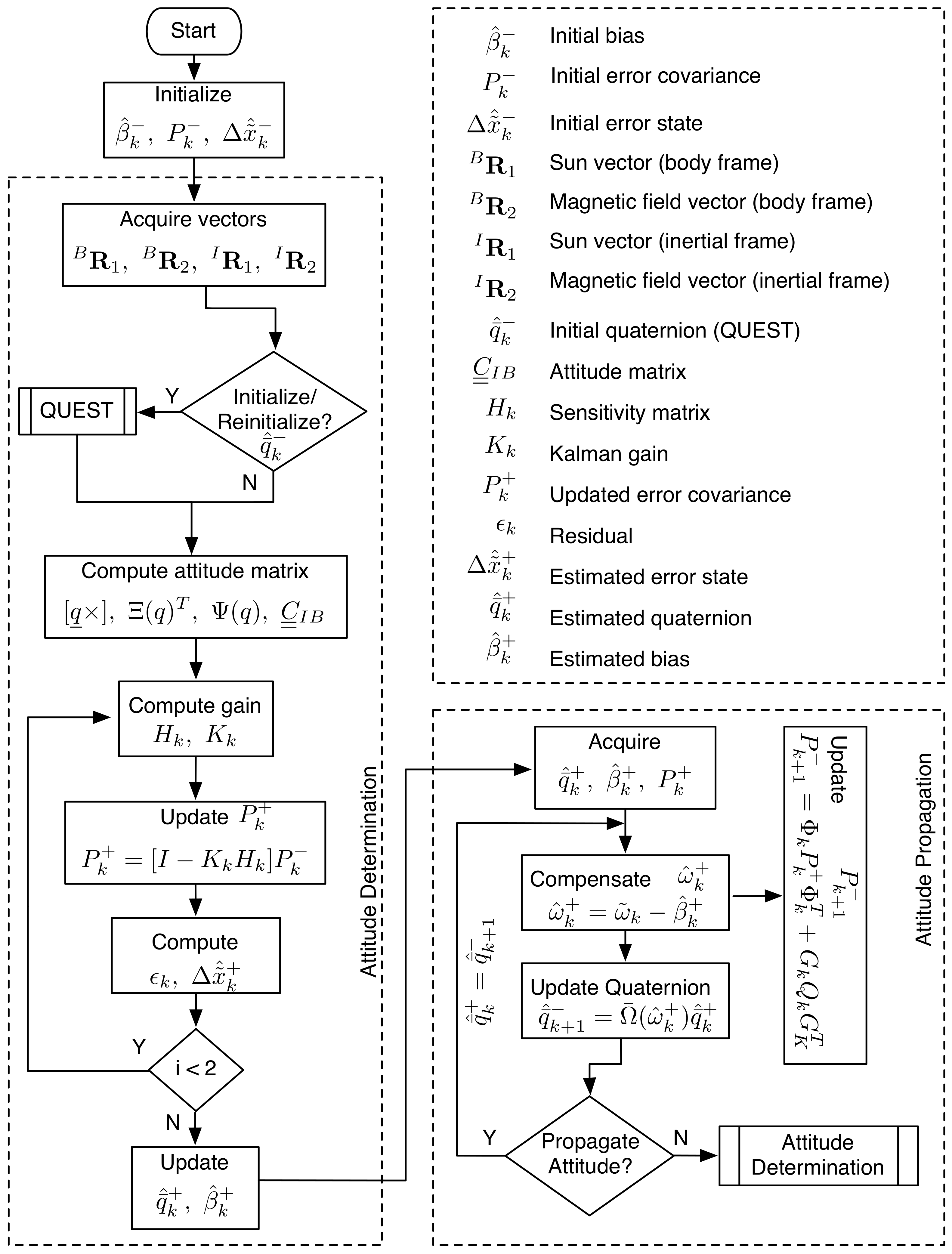
3. Attitude Estimation and Sensor Configurations
3.1. Attitude Estimation Using Sun Sensors and Magnetometer
3.2. Attitude Estimation Using Magnetic Field Vector and Its Time Derivative
3.3. Attitude Estimation Using Magnetic Field Vector
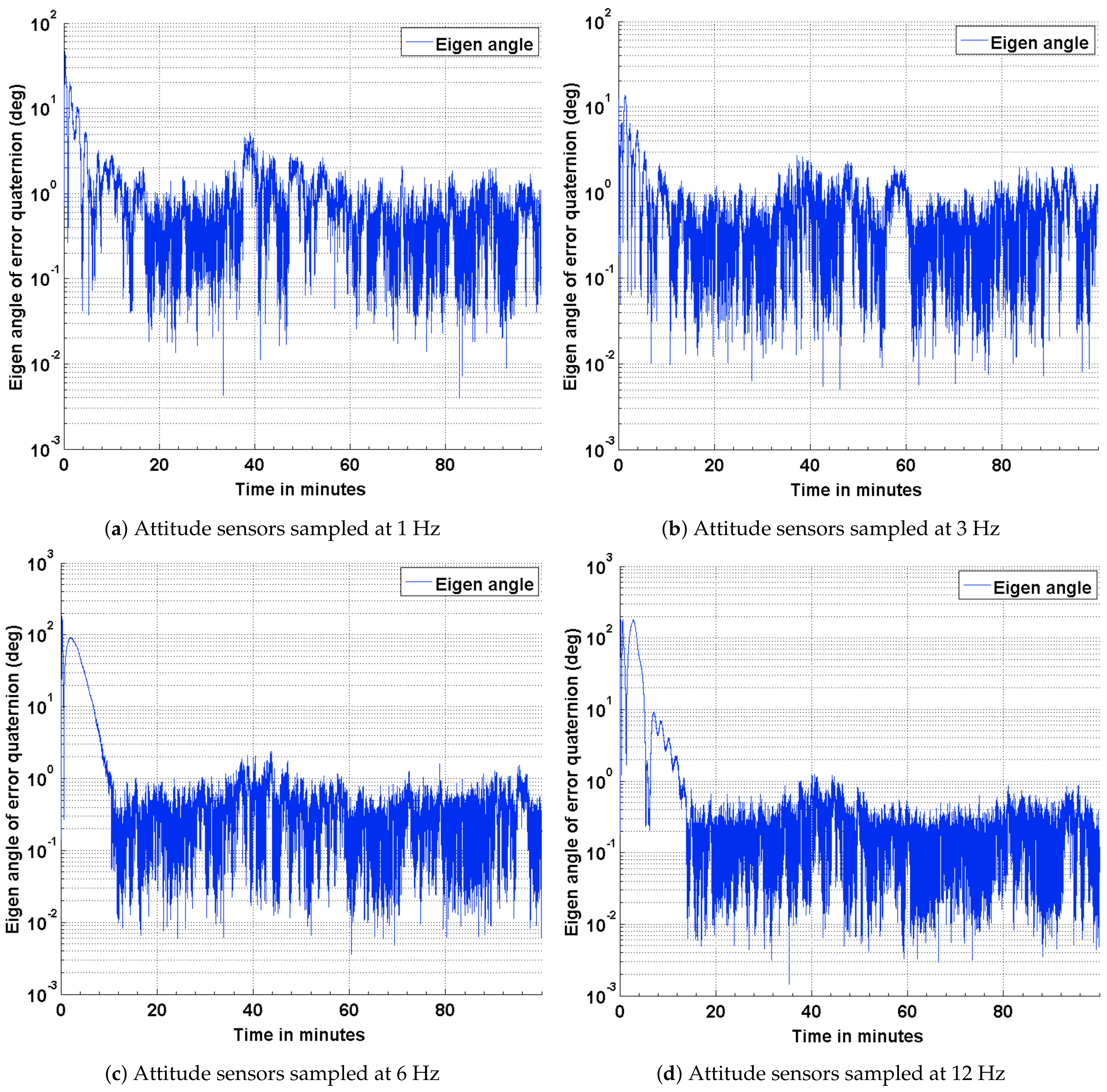
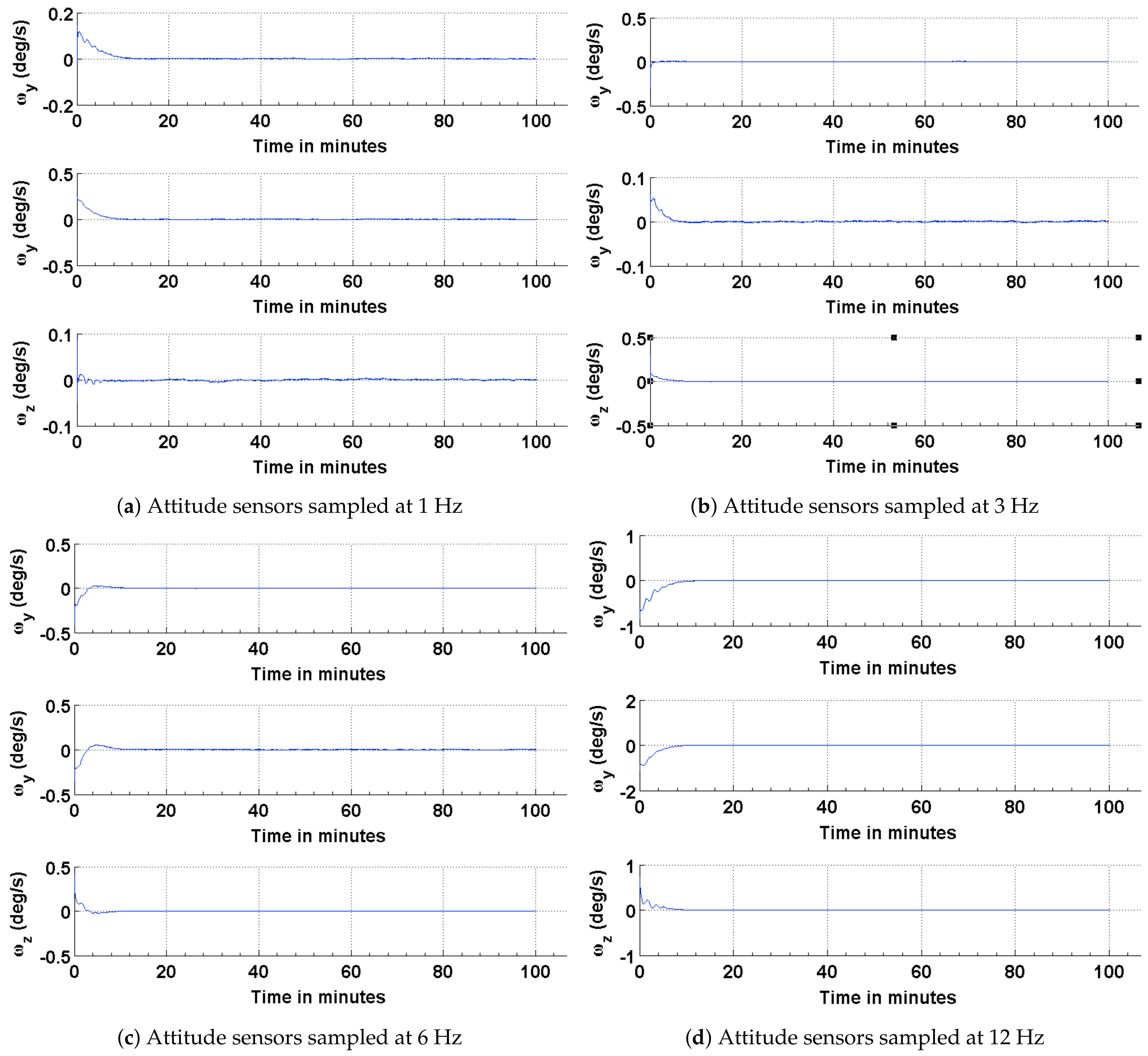
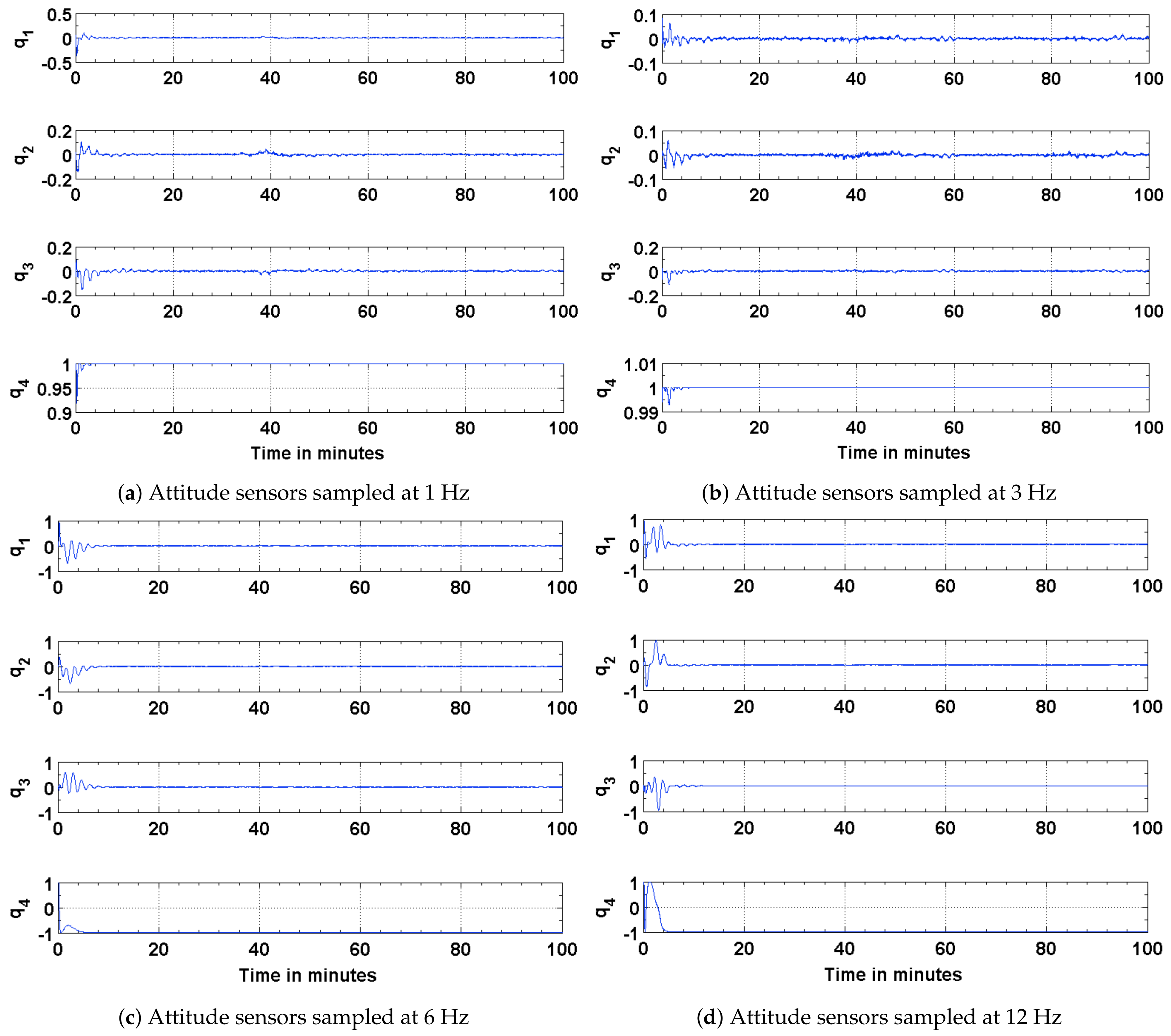
4. Simulation and Results
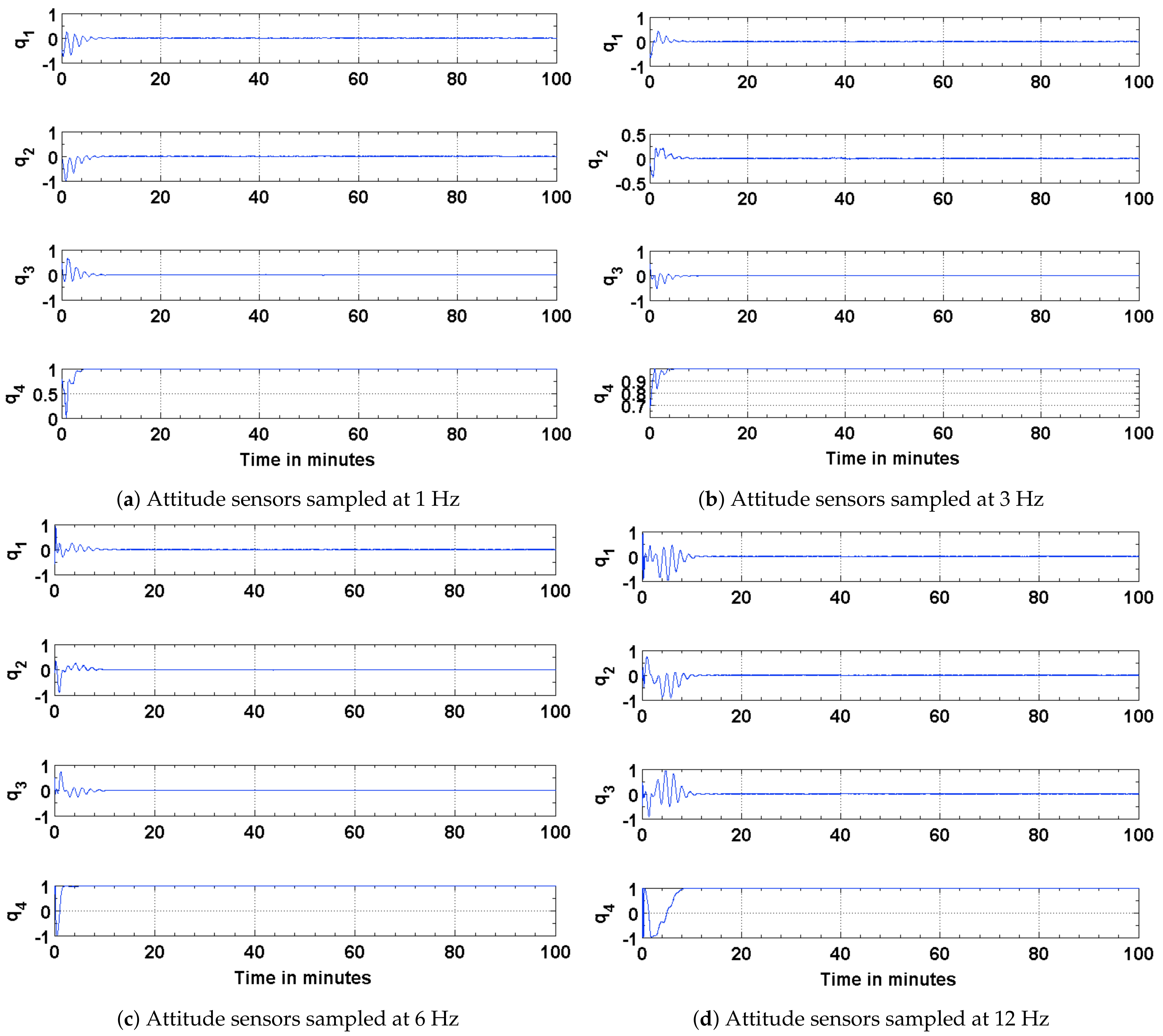
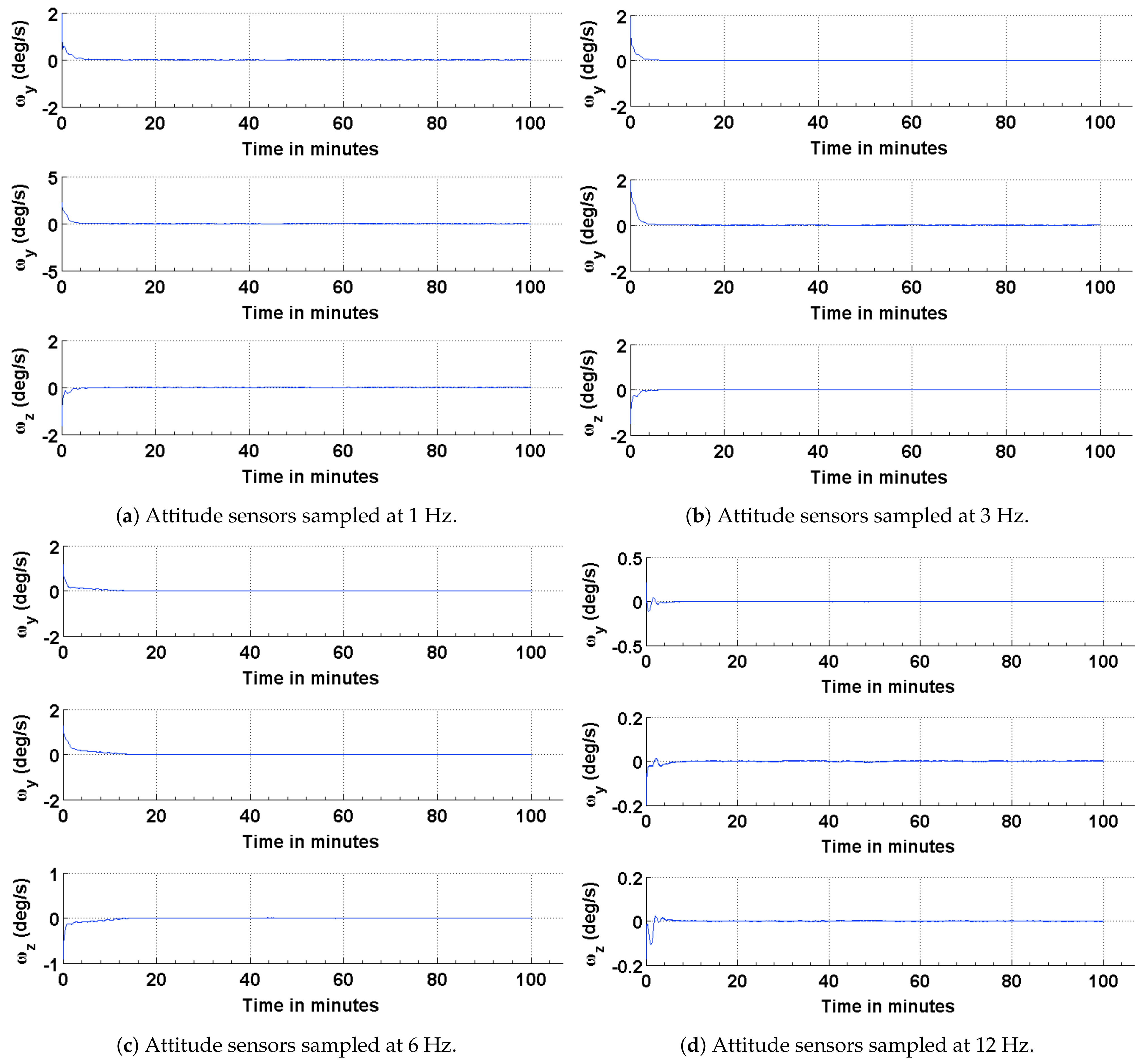
4.1. Estimation Results Using Sun Sensors and Magnetometer
4.2. Estimation Results Using Magnetic Field Vector
4.3. Estimation Results Using Magnetic Field Vector and Its Time Derivative
5. Conclusions
6. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kitts, C.; Hines, J.; Agasid, E.; Ricco, A.; Yost, B.; Ronzano, K.; Puig-Suar, J. The GeneSat-1 Microsatellite Mission: A Challenge in Small Satellite Design. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 14–17 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kitts, C.; Ronzano, K.; Rasay, R.; Mas, I.; Williams, P.; Mahacek, P.; Minelli, G.; Hines, J.; Agasid, E.; Friedericks, C.; et al. Initial Flight Results from the PharmaSat Biological Microsatellite Mission. In Proceedings of the 23th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 10–13 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Minelli, G.; Ricco, A.; Beasley, C.; Hines, J.; Agasid, E.; Yost, B.; Squires, D.; Friedericks, C.; Piccini, M.; Defouw, G.; et al. O/OREOS: A Multi-Payload Technology Demonstration. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 9–12 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bahcivan, H.; Cutler, J.; Buonocore, J.; Bennett, M. Radio Aurora Explorer: Mission Overview and the Science Objectives. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2009, San Francisco, CA USA, 14–18 December 2009; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Woellert, K.; Ehrenfreund, P.; Ricco, A.J.; Hertzfeld, H. Cubesats: Cost-Effective Science and Technology Platforms for Emerging and Developing Nations. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 663–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgeier, S.; Nagabhushan, V.; Leve, F.; Fitz-Coy, N.G. SwampSat - A Technology Demonstrator for Operational Responsive Space. In Proceedings of the 15th CASI (Canadian Aeronautics and Space Institute) Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–19 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Munoz, J.D.; Nagabhushan, V.; Asundi, S.; Fitz-Coy, N.G. High Fidelity Simulation of SwampSat Attitude Determination and Control System. In Spaceflight Mechanics; Univelt, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 140. [Google Scholar]
- Leve, F.; Allgeier, S.; Nagabhushan, V.; Asundi, S.; Buckley, D.; Waldrum, A.; Hiramatsu, T. ASTREC-I Detailed Design Report, FUNSAT IV Design Competition; FUNSAT Design Competition, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Asundi, S.; Mahin, M.; Nagabhushan, V.; Lin, T.; Fitz-Coy, N. Composite and PCB Based Implementations of a Solar Panel Design for SwampSat. In Proceedings of the Utah State University Small Satellite Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 7–12 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Asundi, S.; Fitz-Coy, N. CubeSat Mission Design Based on a Systems Engineering Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Asundi, S.; Fitz-Coy, N. Design of Command, Data and Telemetry Handling System for a Distributed Computing Architecture CubeSat. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Heidt, H.; Puig-Suari, J.; Moore, A.; Nakasuka, S.; Twiggs, R. Cubesat: A new generation of picosatellite for education and industry low-cost space experimentation. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual AIAA/USU Small Satellites Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 21–24 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nugent, R.; Munakata, R.; Chin, A.; Coelho, R.; Puig-Suari, J. The Cubesat: The Picosatellite Standard for Research and Education. In Proceedings of the 2008 AIAA Space Conference and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrparvar, A.; Pignatelli, D.; Carnahan, J.; Munakat, R.; Lan, W.; Toorian, A.; Hutputanasin, A.; Lee, S. Cubesat Design Specification Rev. 13. The CubeSat Program; Cal Poly: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Leve, F. Development of the Spacecraft Orientation Buoyancy Experimental Kiosk. Master’s Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nagabhushan, V. Development of Control Moment Gyroscopes for Attitude Control of Small Satellites. Master’s Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Markley, F.L.; Crassidis, J.L. Fundamentals of Spacecraft Attitude Determination and Control; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Allgeier, S.E.; Mahin, M.; Fitz-Coy, N.G. Design and Analysis of a Coarse Sun Sensor for Pico-Satellites. In Proceedings of the AIAA Infotech@ Aerospace Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Honeywell Magnetometer HMC2003. Available online: https://www.digikey.com/en/products/detail/honeywell-aerospace/HMC2003/334166 (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Honeywell 3-Axis Magnetometer HMC2003 Magnetic Hybrid and HMR2300 Smart Digital Magnetometer. Available online: https://aerospace.honeywell.com/us/en/learn/products/sensors/3-axis-magnetometer (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Crassidis, J.L.; Markley, F.L. Unscented Filtering for Spacecraft Attitude Estimation. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2003, 26, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analog Devices Tri-Axis Inertial Sensor with Magnetometer ADIS16405. Available online: https://www.analog.com/en/products/adis16405.html#product-overview (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Analog Devices Tri-Axis Inertial Sensor with Magnetometer ADIS16495. Available online: https://www.analog.com/en/products/adis16495.html (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Farrenkopf, R.L. Analytic Steady-State Accuracy Solutions for Two Common Spacecraft Attitude Estimators. J. Guid. Control 1978, 1, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.P.; McElroy, T.T. HEAO Attitude Reference Design. In Proceedings of the American Astronautical Society, Annual Rocky Mountain Guidance and Control Conference, Keystone, CO, USA, 10–13 March 1978; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Shuster, M.D.; Oh, S.D. Three-axis Attitude Determination from Vector Observations. J. Guid. Control. 1981, 4, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natanson, G.A.; Challa, M.S.; Deutschmann, J.; Baker, D.F. Magnetometer-only Attitude and Rate Determination for a Gyro-less Spacecraft. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Space Mission Operations and Ground Data Systems, Part 2, Greenbelt, MD, USA, 15–18 November 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Natanson, G.A.; McLaughlin, S.F.; Nicklas, R.C. A Method of Determining Attitude from Magnetometer Data Only. In Proceedings of the Flight Mechanics/Estimation Theory Symposium, Greenbelt, MD, USA, 22–24 May 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Shuster, M.D. SCAD–A Fast Algorithm for Star Camera Attitude Determination. J. Astronaut. Sci. 2004, 52, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGI: Systems Tool Kit (STK). Available online: https://www.agi.com/products/stk (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Crassidis, J.L.; Junkins, J.L. Optimal Estimation of Dynamic Systems; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Markley, F.L. Attitude Estimation or Quaternion Estimation? J. Astronaut. Sci. 2004, 52, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, J.W. Precision Attitude Determination for Multimission Spacecraft. In Proceedings of the Guidance and Control Conference, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 7–9 August 1978; Technical Papers (A78-50159 22-01). American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 70–87. [Google Scholar]
- Crassidis, J.L.; Lai, K.L.; Harman, R.R. Real-time Attitude-independent Three-axis Magnetometer Calibration. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2000, 28, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springmann, J.C. Attitude-Independent Magnetometer Calibration with Time-Varying Bias. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, UT, USA, 8–11 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, R.; Shuster, M.D. Attitude-independent Magnetometer-bias Determination: A Survey. J. Astronaut. Sci. 2002, 50, 453–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre-Egziabher, D.; Elkaim, G.H.; Powell, J.D.; Parkinson, B.W. A Non-linear, Two-step Estimation Algorithm for Calibrating Solid-state Strapdown Magnetometers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems, St. Petersburg, Russia, 24–28 May 2001. [Google Scholar]







| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Semi-major axis (a) | Km |
| Eccentricity (e) | |
| Inclination (i) | deg |
| Argument of perigee () | deg |
| Longitude of ascending node () | deg |
| True anomaly () | deg |
| Quantity | Description |
|---|---|
| 3 × 1 magnetic field vector coordinatized in body frame | |
| 3 × 1 Sun vector coordinatized in body frame | |
| 3 × 1 magnetic field vector coordinatized in ECI frame | |
| 3 × 1 Sun vector coordinatized in ECI frame | |
| 3 × 1 angular velocity vector coordinatized in body frame | |
| 4 × 1 quaternion representing true attitude |
| Parameter/Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Parameter/Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| 175 | |
| Parameter/Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Magnetometer & Sun Sensors | 1 Magnetic Field Vector | 2 Magnetic Field Vectors | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attitude accuracy (@ 12 Hz) | <1.5 deg | <1.5 deg | <8 deg |
| Attitude accuracy (@ 1 Hz) | <5 deg | <3 deg | ∼ 20 deg |
| Converging Time (minutes) | ∼5 | ∼10 | ∼8 |
| Computational iterations | Two | One | Two |
| Equations (9)–(13) | |||
| Eclipse time estimation | Not possible | Possible | Possible |
| Sensor power consumption (mW) | 300 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asundi, S.; Fitz-Coy, N.; Latchman, H. Evaluation of Murrell’s EKF-Based Attitude Estimation Algorithm for Exploiting Multiple Attitude Sensor Configurations. Sensors 2021, 21, 6450. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196450
Asundi S, Fitz-Coy N, Latchman H. Evaluation of Murrell’s EKF-Based Attitude Estimation Algorithm for Exploiting Multiple Attitude Sensor Configurations. Sensors. 2021; 21(19):6450. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196450
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsundi, Sharanabasaweshwara, Norman Fitz-Coy, and Haniph Latchman. 2021. "Evaluation of Murrell’s EKF-Based Attitude Estimation Algorithm for Exploiting Multiple Attitude Sensor Configurations" Sensors 21, no. 19: 6450. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196450
APA StyleAsundi, S., Fitz-Coy, N., & Latchman, H. (2021). Evaluation of Murrell’s EKF-Based Attitude Estimation Algorithm for Exploiting Multiple Attitude Sensor Configurations. Sensors, 21(19), 6450. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196450






