LoRa-Based Traffic Flow Detection for Smart-Road
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Deployment (Materials and Methods)
2.1. Hardware Description
2.2. Short LoRa Network Topology
2.3. Short Lora Network Protocol
2.4. Short Lora Network for Traffic Flow Detection
- The coordinator node sends a multicast synchronous service frame each 250 ms because the data transmission package is 6 bytes with a time on air of 36.10 ms, then a time slot of 50 ms is given to each node for its own communication avoiding collisions in this process. The system has a cycle frequency of 4 Hz. The beacon is the signal indicator to start the vehicle detection process.
- When EDs receive the multicast synchronous service frame signal, the Node #1 time slot of 50 ms is opened. Node #1 sends a broadcast of 2 bytes and saves the RSSI given by the node coordinator, Node #2, Node #3 and Node #4. Afterwards, to save all the RSSI information, it is sent to the network coordinator in order to be processed when the detection cycle finished.
- Next, Node #2 transmits in their time slot. First, it sends a multicast synchronous service frame, and after save the RSSI information and sends it to the coordinator node. This process is repeated for all End-Devices.
2.5. Testbed
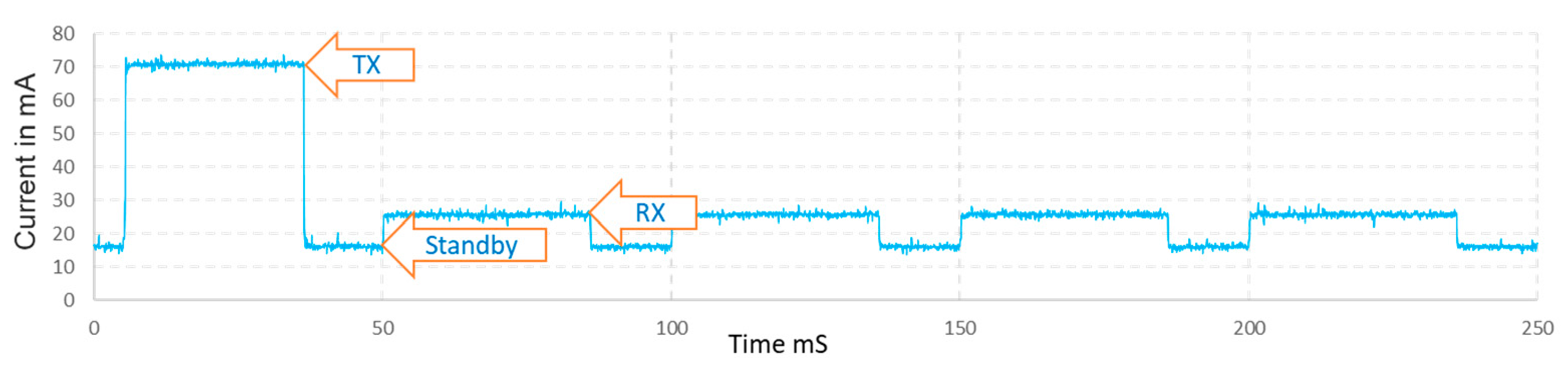
2.6. Power Consumption Analysis
3. Data Analysis and Results
3.1. Derivative Data Analysis Method for Vehicule Detection
3.2. Link Budget Compensated Data Analysis Method for Vehicule Detection
3.3. Results
3.4. Dicussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadowski, S.; Spachos, P. RSSI-Based Indoor Localization with the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 30149–30161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, M.; Roedig, U. LoRa Transmission Parameter Selection. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS), Ottawa, ON, USA, 5–7 June 2017; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bor, M.; Vidler, J.E.; Roedig, U. LoRa for the Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Embedded Wireless Systems and Networks, Graz, Austria, 15–17 February 2016; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Petajajarvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Roivainen, A.; Hanninen, T.; Pettissalo, M. On the coverage of LPWANs: Range evaluation and channel attenuation model for LoRa technology. In Proceedings of the 2015 14th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications (ITST), Copenhagen, Denmark, 2–4 December 2015; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Iova, O.; Murphy, A.L.; Picco, G.P.; Ghiro, L.; Molteni, D.; Ossi, F.; Cagnacci, F. LoRa from the City to the Mountains: Exploration of Hardware and Environmental Factors. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Embedded Wireless Systems and Networks, Uppsala, Sweden, 20–22 February 2017; pp. 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, J.-W.; Yu, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Hu, W.-F. Automatic traffic surveillance system for vehicle tracking and classification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2006, 7, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, J.; Chen, X. Vehicle recognition and classification method based on laser scanning point cloud data. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Wuhan, China, 25–28 June 2015; pp. 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.; Mary, L.; Riyas, K.S. Vehicle detection and classification from acoustic signal using ANN and KNN. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Control Communication and Computing (ICCC), Thiruvananthapuram, India, 13–15 December 2013; pp. 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Taghvaeeyan, S.; Rajamani, R. Portable Roadside Sensors for Vehicle Counting, Classification, and Speed Measurement. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xing, D.; McKee, A.; Bajwa, R.; Flores, C.; Fuller, B.; Varaiya, P. A Wireless Accelerometer-Based Automatic Vehicle Classification Prototype System. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.; Patwari, N. Radio Tomographic Imaging with Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2010, 9, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumrosen, G.; Luttwak, A. Human Body Parts Tracking and Kinematic Features Assessment Based on RSSI and Inertial Sensor Measurements. Sensors 2013, 13, 11289–11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Hamzin, A.; Degbelo, A. A Low-Cost Open Hardware System for Collecting Traffic Data Using Wi-Fi Signal Strength. Sensors 2018, 18, 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Husseiny, A.; Youssef, M. RF-Based Traffic Detection and Identification. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Fall), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 3–6 September 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kassem, N.; Kosba, A.E.; Youssef, M. RF-Based Vehicle Detection and Speed Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 75th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Yokohama, Japan, 6–9 May 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, R.; Maurya, A.; Raman, B.; Mehta, R.; Kalyanaraman, R.; Singh, A. Road-RFSense: A Practical RF Sensing–Based Road Traffic Estimation System for Developing Regions. Acm Trans. Sen. Netw. 2014, 11, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, M.; Boano, C.A.; Römer, K. An Experimental Evaluation of the Reliability of LoRa Long-Range Low-Power Wireless Communication. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldoni, E.; Prando, L.; Vizziello, A.; Savazzi, P.; Gamba, P. Experimental data set analysis of RSSI-based indoor and outdoor localization in LoRa networks. Internet Technol. Lett. 2019, 2, e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poursafar, N.; Alahi, M.E.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Long-range wireless technologies for IoT applications: A review. In Proceedings of the 2017 Eleventh International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 4–6 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- LoRaWAN® Specification v1.0.3|LoRa AllianceTM. Available online: https://lora-alliance.org/resource-hub/lorawanr-specification-v103 (accessed on 5 November 2019).
- ERC Recommendation 70-03. Available online: https://docdb.cept.org/download/25c41779-cd6e/Rec7003e.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- LoRaWAN® Regional Parameters v1.1rB|LoRa AllianceTM. Available online: https://lora-alliance.org/resource-hub/lorawanr-regional-parameters-v11rb (accessed on 5 November 2019).
- LoRaWAN® Back-End Interfaces v1.0|LoRa AllianceTM. Available online: https://lora-alliance.org/resource-hub/lorawanr-back-end-interfaces-v10 (accessed on 5 November 2019).
- Final Draft ETSI EN 300 220-2 V3.2.1. 33. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_en/300200_300299/30022002/03.02.01_30/en_30022002v030201v.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- AN1200.22 LoRaTM Modulation Basics 2015. Available online: https://semtech.my.salesforce.com/sfc/p/#E0000000JelG/a/2R0000001OJk/yDEcfAkD9qEz6oG3PJryoHKas3UMsMDa3TFqz1UQOkM (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- SX1276/77/78/79—137 MHz to 1020 MHz Low Power Long Range Transceiver Datasheet 2020. Available online: https://semtech.my.salesforce.com/sfc/p/#E0000000JelG/a/2R0000001Rbr/6EfVZUorrpoKFfvaF_Fkpgp5kzjiNyiAbqcpqh9qSjE (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Casals, L.; Mir, B.; Vidal, R.; Gomez, C. Modeling the Energy Performance of LoRaWAN. Sensors 2017, 17, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagaraj, V.; Kiran, V.; Padmaja, K.V. 6LoWPAN based intelligent transport system for surveillance—A model of ubiquitous computing technology. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eighth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Vienna, Austria, 5–8 July 2016; pp. 801–803. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, F.; Pau, G.; Severino, A. A Review on IEEE 802.11p for Intelligent Transportation Systems. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2020, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Attribute | LTE-M | NB-IoT | Sigfox | LoRa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | 700–900 MHz | 700–900 MHz | 868, 902 MHz | Sub-GHz ISM |
| Data Rate | 375 kbps | 25–65 kbps | 0.1 kbps | 0.3–37.5 kbps |
| Bandwidth | 1.08 MHz | 200 kHz | 100 Hz | <500 kHz |
| Range | <15 km | <35 km | Rural: 30–50 km Urban: 3‒10 km | Rural: 10–15 km Urban: 3‒5 km |
| Band Number | Frequency (MHz) | Duty Cycle | Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| g0 | 865.0–868.0 | 1% or LBT + AFA 1 | 25 mW = 14 dBm |
| g1 | 868.0–868.6 | 1% or LBT + AFA | 25 mW = 14 dBm |
| g2 | 868.7–869.2 | 0.1% or LBT + AFA | 25 mW = 14 dBm |
| g3 | 869.4–869.65 | 10% or LBT + AFA | 500 mW = 27 dBm |
| g4 | 869.7–870.0 | 1% or LBT + AFA | 25 mW (no duty-cycle requirement if power < 5 mW/7 dBm) |
| Frequency [MHz] | Power [mW] | Modulation [kHz] | Spreading Factor | Time on Air [ms] | Duty Cycle [%] | Cycle Scan Network [s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 868.3 | 25 | 250 | SF7 | 18.05 | 1 | 1.805 |
| 869.525 | 25 | 125 | SF9 | 123.90 | 10 | 1.239 |
| 869.525 | 500 | 125 | SF7 | 36.1 | 1 | 3.61 |
| 868.8 | 25 | 125 | FSK | 3.871 | 1 | 0.386 |
| 869.850 | 5 | 125 | SF7 | 36.1 | 100 1 | 0.1805 |
| Standard LoRa MType Value | Short LoRa MType Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 000 | Not Available | Join Request |
| 001 | Not Available | Join Accept |
| 010 | 00 | Unconfirmed Data Up |
| 011 | 01 | Unconfirmed Data Down |
| 100 | 10 | Confirmed Data Up |
| 101 | 11 | Confirmed Data Down |
| 110 | Not Available | RFU |
| 111 | Not Available | Proprietary |
| Number of Bytes | Time on Air [ms] |
|---|---|
| 2 | 30.98 |
| 6 | 36.10 |
| 16 | 51.46 |
| Connection | Max. Signal (dB) | Min. Signal (dB) | Mean Signal (dB) | RMS Signal (dB) | RMS Noise (dB) | RMS SNR 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gates Distance 20 m | ||||||
| Gate1(#1–#2) | 27.00 | 8.00 | 16.54 | 16.96 | 0.46 | 16.50 |
| Gate1(#2–#1) | 27.00 | 7.00 | 15.46 | 16.13 | 0.51 | 15.62 |
| Gate1(#3–#4) | 27.00 | 10.00 | 16.21 | 16.65 | 0.94 | 15.71 |
| Gate1(#4–#3) | 26.00 | 8.00 | 15.95 | 16.50 | 1.00 | 15.50 |
| Mean Gates | 26.75 | 8.25 | 16.04 | 16.56 | 0.73 | 15.83 |
| Crosses1(#1–#4) | 19.00 | 6.00 | 8.83 | 9.44 | 0.35 | 9.09 |
| Crosses1(#4–#1) | 16.00 | 6.00 | 8.96 | 9.42 | 0.85 | 8.57 |
| Crosses2(#2–#3) | 12.00 | 6.00 | 7.14 | 7.34 | 0.73 | 6.60 |
| Crosses2(#3–#4) | 20.00 | 6.00 | 7.63 | 8.30 | 1.21 | 7.09 |
| Mean Crosses | 16.75 | 6.00 | 8.14 | 8.62 | 0.79 | 7.84 |
| Gates Distance 10 m | ||||||
| Gate1(#1–#2) | 29.00 | 14.00 | 19.68 | 19.89 | 0.20 | 19.69 |
| Gate1(#2–#1) | 29.00 | 13.00 | 19.71 | 20.11 | 0.50 | 19.61 |
| Gate1(#3–#4) | 33.00 | 9.00 | 18.00 | 19.01 | 0.97 | 18.03 |
| Gate1(#4–#3) | 28.00 | 10.00 | 16.95 | 17.61 | 0.53 | 17.08 |
| Mean Gates | 29.75 | 11.50 | 18.58 | 19.15 | 0.55 | 18.60 |
| Crosses1(#1–#4) | 22.00 | 7.00 | 12.34 | 13.01 | 0.40 | 12.61 |
| Crosses1(#4–#1) | 24.00 | 8.00 | 12.03 | 12.62 | 0.31 | 12.31 |
| Crosses2(#2–#3) | 24.00 | 7.00 | 11.64 | 12.63 | 0.42 | 12.21 |
| Crosses2(#3–#4) | 19.00 | 6.00 | 9.92 | 10.43 | 0.63 | 9.80 |
| Mean Crosses | 22.25 | 7.00 | 11.48 | 12.17 | 0.44 | 11.73 |
| Laser Measurements | ShortLoRa Network Measurements (Derivative Method) | ShortLoRa Network Measurements (Link Budget Compensated Method) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car Velocity (Km/h) | Differential Gates Time (s) | Velocity (km/h) | Differential Gates Time (s) | Velocity (km/h) | Differential Gates Time (s) | Velocity (km/h) |
| Gates Distance 20 m | ||||||
| 10 | 6.77 | 10.63 | 6.8 | 10.58 | 6.8 | 10.58 |
| 10 | −6.78 | −10.61 | −6.5 | −11.07 | −6.7 | −10.74 |
| 20 | 3.54 | 20.32 | 3.8 | 18.94 | 3.5 | 20.57 |
| 20 | −3.78 | −19.04 | −3.7 | −19.45 | −3.7 | −19.45 |
| 30 | 2.59 | 27.71 | 2.8 | 25.71 | 2.5 | 28.8 |
| 30 | −2.54 | −28.27 | −2.5 | −28.8 | −2.2 | −32.72 |
| 40 | 1.92 | 37.42 | 2 | 36 | 2 | 36 |
| 40 | −1.87 | −38.35 | −1.7 | −42.35 | −1.8 | −40 |
| 50 | 1.51 | 47.58 | 1.5 | 48 | 1.5 | 48 |
| 50 | −1.51 | −47.65 | −1.5 | −48 | −1.3 | −55.38 |
| Gates Distance 10 m | ||||||
| 10 | 3.69 | 9.92 | 3.5 | 10.28 | 3.7 | 9.72 |
| 10 | −2.92 | −12.32 | −2.8 | −12.85 | −2.7 | −13.33 |
| 20 | 1.92 | 18.73 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 18 |
| 20 | −1.93 | −18.65 | −1.7 | −21.17 | −1.7 | −21.17 |
| 30 | 1.27 | 28.27 | 1.3 | 27.69 | 1.5 | 24 |
| 30 | −1.21 | −29.72 | −1.3 | −27.69 | −1 | −36 |
| 40 | 0.93 | 38.37 | 1 | 36 | 1 | 36 |
| 40 | −0.93 | −38.66 | −0.7 | −51.42 | −0.8 | −45 |
| 50 | 0.72 | 50.06 | 0.8 | 45 | 0.7 | 51.42 |
| 50 | −0.75 | −48 | −0.8 | −45 | −0.6 | −60 |
| Derivative Method | Link Budget Compensated Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car Velocity (Km/h) | Absolute Error | Relative Error | Absolute Error | Relative Error |
| Gates Distance 20 m | ||||
| 10 | 0.05 | 0.004 | 0.05 | 0.004 |
| 10 | 0.46 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.01 |
| 20 | 1.38 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.01 |
| 20 | 0.42 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 0.02 |
| 30 | 2.00 | 0.07 | 1.09 | 0.04 |
| 30 | 0.52 | 0.02 | 4.45 | 0.16 |
| 40 | 1.42 | 0.04 | 1.42 | 0.04 |
| 40 | 3.99 | 0.10 | 1.64 | 0.04 |
| 50 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.01 |
| 50 | 0.35 | 0.01 | 7.73 | 0.16 |
| Gates Distance 10 m | ||||
| 10 | 0.37 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| 10 | 0.53 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.08 |
| 20 | 0.73 | 0.04 | 1.38 | 0.04 |
| 20 | 2.52 | 0.14 | 0.42 | 0.14 |
| 30 | 0.59 | 0.02 | 2.00 | 0.15 |
| 30 | 2.04 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 0.21 |
| 40 | 2.38 | 0.06 | 1.42 | 0.06 |
| 40 | 12.76 | 0.33 | 3.99 | 0.16 |
| 50 | 5.07 | 0.10 | 0.41 | 0.03 |
| 50 | 3.00 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.25 |
| Classification | Low Power Wireless Personal Area Network (LWPAN) | Wireless Access Spaces for Vehicular Environment (WAVE/DSRC) | Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | IEEE 802.15.4 | IEEE 802.11p | LoRa |
| OS | No | Yes | No |
| Range | 10–100 m | 100–1000 m | 1000–10,000 m |
| Power | Low | Medium | Low |
| High Layers | ZigBee, 6LoWPAN | IPv6, WSMP (WAVE Short Message Protocol) | LoraWAN |
| Modulation Type | BPSK, OQPKS | BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM | LoRa, FSK |
| Bit Rate (Mbps) | 0.020 to 0.25 | 3 to 27 | 0.003 to 0.050 |
| Frequency Bands of Operation | 868 MHz, 915 MHz and 2.4 GHz | 5.9 GHz | 433 MHz, 868 MHz and 915 MHz |
| Network Architecture | Peer-to-peer or star networks | Peer-to-peer ad hoc network in topology and location based | Star-of-stars topology in which gateways |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asiain, D.; Antolín, D. LoRa-Based Traffic Flow Detection for Smart-Road. Sensors 2021, 21, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020338
Asiain D, Antolín D. LoRa-Based Traffic Flow Detection for Smart-Road. Sensors. 2021; 21(2):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020338
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsiain, David, and Diego Antolín. 2021. "LoRa-Based Traffic Flow Detection for Smart-Road" Sensors 21, no. 2: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020338
APA StyleAsiain, D., & Antolín, D. (2021). LoRa-Based Traffic Flow Detection for Smart-Road. Sensors, 21(2), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020338







