Design and Application of Mixed Natural Gas Monitoring System Using Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Design for Mixed Natural Gas Monitoring
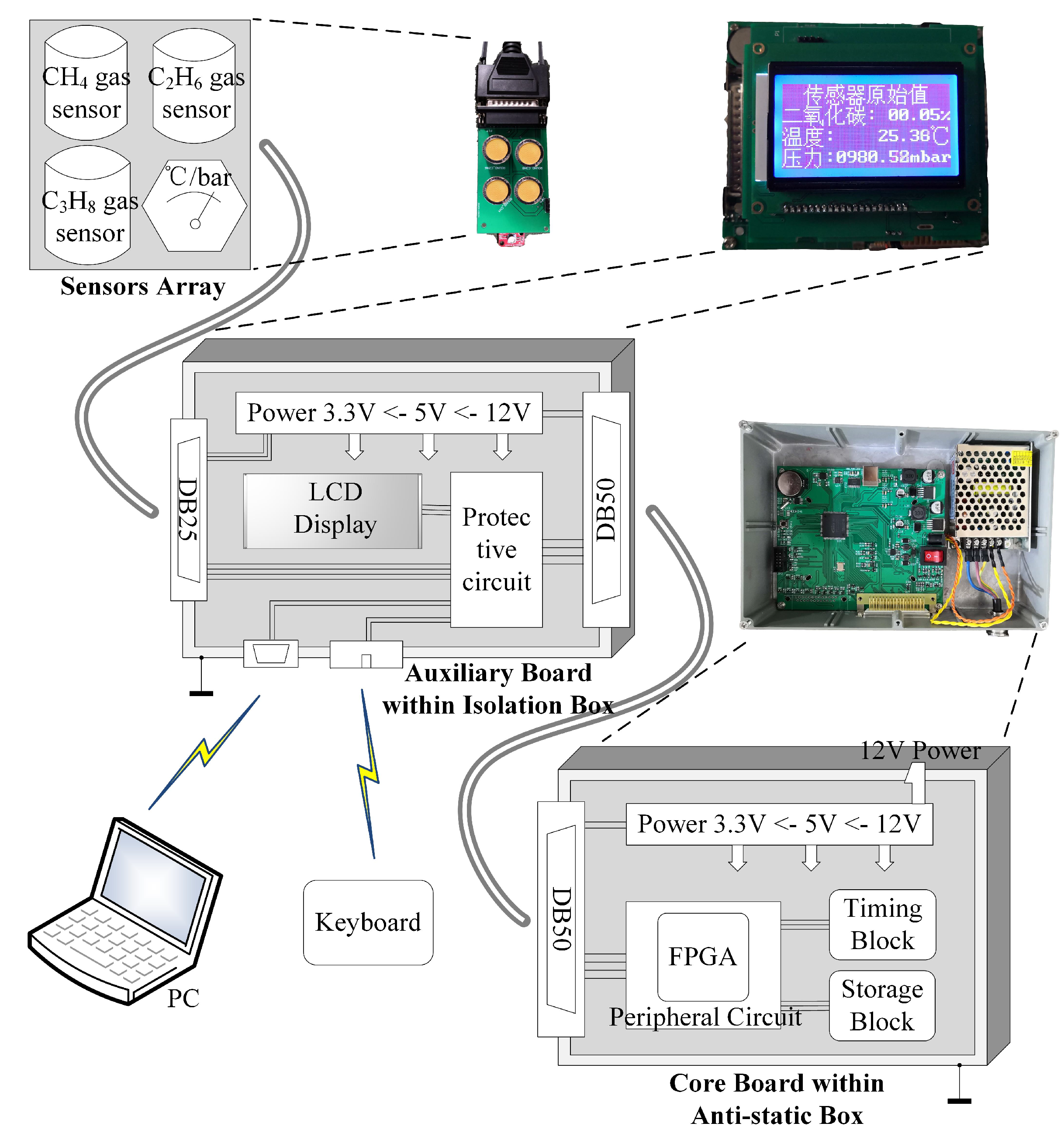
2.1. Sensor Array and Isolation Box
2.2. Core Circuit and Anti-Static Box
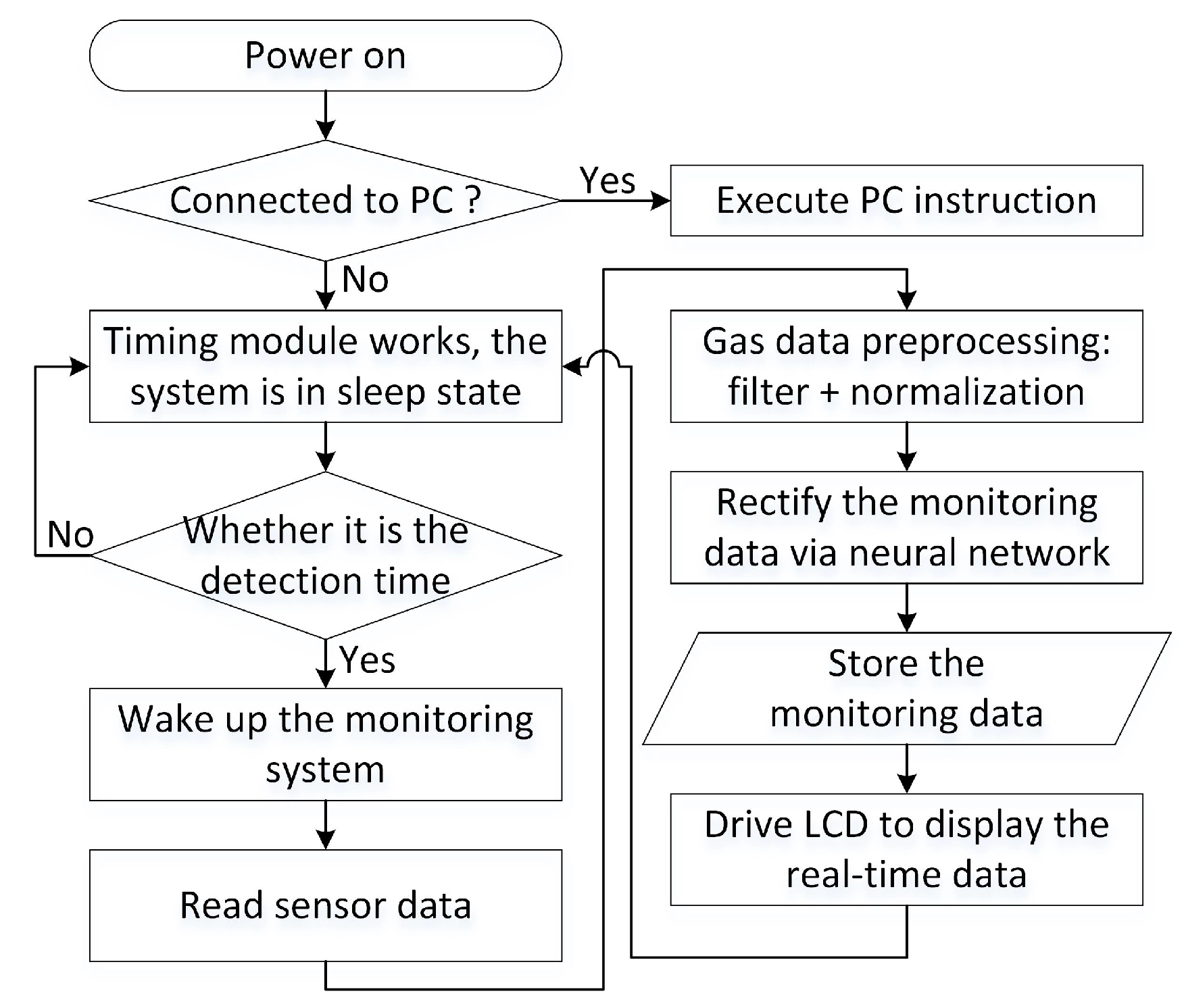
2.3. Cooperation between Hardware and Software
3. Data Processing on FPGA
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Artificial Neural Network Tailored for Gas Monitoring
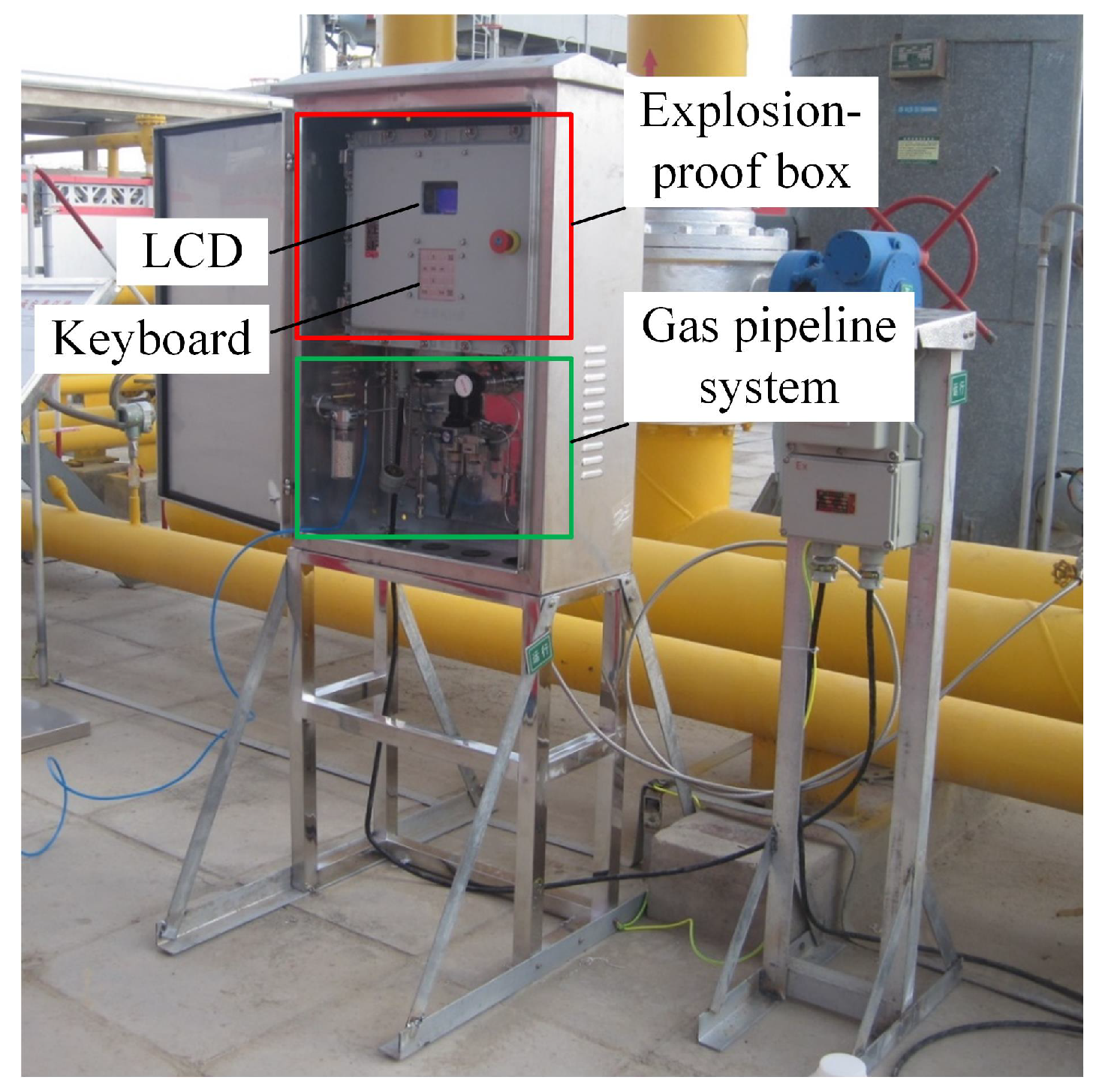
4. Field Work of the Mixed Natural Gas Monitoring System and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, J.; Zhang, X. China’s natural-gas supply security and its suggestions. Nat. Gas Technol. Econ. 2020, 14, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mac Kinnon, M.A.; Brouwer, J.; Samuelsen, S. The role of natural gas and its infrastructure in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, improving regional air quality, and renewable resource integration. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 64, 62–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, K.M.; Kuczynski, S.; Barbacki, J.; Wlodek, T.; Smulski, R.; Nagy, S. Downhole measurements and determination of natural gas composition using Raman spectroscopy. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 65, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaczykowski, M.; Sund, F.; Zarodkiewicz, P.; Hope, S.M. Gas composition tracking in transient pipeline flow. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 55, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, H.; Koturbash, T.; Kutcherov, V. Review of impacts of gas qualities with regard to quality determination and energy metering of natural gas. Meas. Ence Technol. 2019, 30, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.S.; Milton, M.J.T.; Cowper, C.J.; Squire, G.D.; Bremser, W.; Branch, R.W. Analysis of natural gas by gas chromatography reduction of correlated uncertainties by normalisation. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1040, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.J.; Brenna, J.T. Curve Fitting for Restoration of Accuracy for Overlapping Peaks in Gas Chromatography/Combustion Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1994, 64, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airiau, C.Y.; Brereton, R.G.; Dunkerley, S. Quantitative resolution of overlapping tailing peaks obtained by diode-array detector high performance liquid chromatography in the absence of pure standards using simple chemical knowledge. Analyst 2000, 125, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Lu, P. Correction method for quantitative area determination of overlapping chromatographic peaks based on the exponentially modified Gaussian (EMG) model. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 10, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Dondi, F.; Bassi, A.; Cavazzini, A.; Pietrogrande, M.C. A Quantitative Theory of the Statistical Degree of Peak Overlapping in Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P. Composition Analysis of Natural Gas by Multi-Dimensional Gas Chromatography. Xinjiang Oil Gas 2014, 10, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Paczkowski, S.; Jaeger, D.; Pelz, S. Semi-conductor metal oxide gas sensors for online monitoring of oak wood VOC emissions during drying. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, A.; Redon, N.; Coddeville, P.; Hanoune, B. Identification of indoor air quality events using a K-means clustering analysis of gas sensors data. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, C.; Glockler, J.; El Azizi, O.; Gonzalez, O.; Padilla, M.; Mitrovics, J.; Mizaikoff, B. An Innovative Modular eNose System Based on a Unique Combination of Analog and Digital Metal Oxide Sensors. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.F.; Li, W.J.; Yang, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, D.W.; Fan, C.Y.; Yang, A.J.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, X.H.; Rong, M.Z. Quantitative Detection of Mixed Gases by Sensor Array Using C-Means Clustering and Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON), Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.L.; Tylczak, J.; Yu, Y.; Panagakos, G.; Ohodnicki, P. Multi-component optical sensing of high temperature gas streams using functional oxide integrated silica based optical fiber sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Guo, T.; Wang, X. Mixed Natural Gas Online Recognition Device Based on a Neural Network Algorithm Implemented by an FPGA. Sensors 2019, 19, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sui, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z. Design and Application of Toxic and Harmful Gas Monitoring System in Fire Fighting. Sensors 2019, 19, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xibilia, M.G.; Latino, M.; Marinkovic, Z.; Atanaskovic, A.; Donato, N. Soft Sensors Based on Deep Neural Networks for Applications in Security and Safety. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 7869–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Choi, J.H.; Rana, A.H.S.; Kim, H.S. Least Squares Neural Network-Based Wireless E-Nose System Using an SnO2 Sensor Array. Sensors 2018, 18, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benrekia, F.; Attari, M.; Bouhedda, M. Gas Sensors Characterization and Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) Hardware Implementation for Gas Identification Using a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). Sensors 2013, 13, 2967–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Rajput, N.S. A novel modular ANN architecture for efficient monitoring of gases/odours in real-time. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 045904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, A.H.; Jilani, M.T. Application of IoT and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) for Monitoring of Underground Coal Mines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Science and Communication Technology (ICISCT), Karachi, Pakistan, 8–9 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, F.; Hong, F. Distribution characteristics of giant gas fields in the world and its enlightenment. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 860–865. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, S.; Kamde, K.; Jana, A.; Korde, S.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Sankar, R.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Pandey, R.A. Calibration transfer between electronic nose systems for rapid In situ measurement of pulp and paper industry emissions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 841, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, Y. Electrostatic hazard and protection in the electronic industry. Electron. World 2014, 14, 349–350. [Google Scholar]
- Dynament Infrared Gas Sensors. (Model: MSHia-P/HCP/NC/5/V/P/XTR/F). Available online: https://www.dynament.com/_webedit/uploaded-files/All%20Files/Data/tds0123.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Dynament Infrared Gas Sensors. (Model: MSHia-P/HHCP/NC/5/V/P/XTR/F). Available online: https://www.dynament.com/_webedit/uploaded-files/All%20Files/Data/tds0143_1.7_Platinum%20High%20Range%20Non-Certified%20Hydrocarbon%20Sensor%20Data%20Sheet.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Measurement Specialties Inc. (Model: MS5803-14BA). Available online: https://www.te.com/commerce/DocumentDelivery/DDEController?Action=showdoc&DocId=Data+Sheet%7FDS_MS5803-14BA%7FA6%7Fpdf%7FEnglish%7FENG_DS_DS_MS5803-14BA_A6.pdf%7FMS580314BA01-50 (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Roberts, S.W. Control Chart Tests Based on Geometric Moving Averages. Technometrics 2000, 42, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridy, S.; Shamsuzzaman, M.; Alsyouf, I.; Mukherjee, A. An improved design of exponentially weighted moving average scheme for monitoring attributes. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshavskiy, I.E.; Krasnova, A.I.; Polivanov, V.V. Efficiency Estimation of the Noise Digital Filtering Algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), St. Petersburg, Russia, 28–31 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nugrahani, T.A.; Adi, K.; Suseno, J.E. Information System Prediction With Weighted Moving Average (WMA) Method And Optimization Distribution Using Vehicles Routing Problem (VRP) Model for Batik Product. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Energy, Environmental and Information System (ICENIS 2018), Semarang, Indonesia, 14–15 August 2018. [Google Scholar]




| Type | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Company(Sensor Model) | Dynament(MSHia-P/HCP(HHCP)/NC/5/V/P/XTR/F) | |
| Resolution | 0.1% | |
| Alkane sensor | Detection limit | 0–200% |
| Selectivity | has cross-sensitivity to alkane | |
| Response time | 30 s | |
| Company(Sensor Model) | MEAS(MS5803-14BA) | |
| Pressure Range | 0–14 bar | |
| Pressure Resolution | 0.2 mbar | |
| Temperature | Pressure Accuracy | −40–+40 mbar at −40 C to +85 C, 0 to 6 bar |
| -pressure sensor | Temperature Range | −40–+85 C |
| Temperature Resolution | <0.01 C | |
| Temperature Accuracy | −0.8–+0.8 C |
| Instruction | Function |
|---|---|
| 0x8003e011 | Set time |
| 0x81002610 | Set sampling period |
| 0x82f70001 | Set display mode |
| 0x4f000001 | Read historical data (raw data) |
| 0x4e000000 | Read historical data (rectified data) |
| 0x4d07f010 | Update the parameters of neural network |
| 0x20000000 | Manually start monitoring |
| 0x21000000 | Force to stop monitoring |
| 0xff000000 | Soft reset of the system |
| 0xff00ff00 | Stop the current task, start receiving host commands |
| …… | …… |
| Parameter | Illustration |
|---|---|
| input concentration of each gas | |
| gas sensor output | |
| CH sensor output | |
| CH sensor output | |
| CH sensor output | |
| output of the monitoring system |
| 0 | 6.1 | 3.3 | 90.6 | 0 | 12.3 | 10.1 | 0 | 6.2 | 6.8 | 0.3 | 5.96 | 3.55 | 0.3 | 0.14 | 0.25 |
| 9.3 | 5.3 | 2.8 | 82.6 | 8.3 | 18.0 | 16.2 | 1.0 | 12.7 | 13.4 | 9.42 | 5.46 | 2.68 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
| 20.6 | 5.1 | 6.7 | 67.6 | 28.6 | 32.2 | 29.9 | 8 | 27.1 | 23.2 | 20.37 | 4.73 | 6.26 | 0.23 | 0.37 | 0.44 |
| 30.2 | 8.6 | 5.1 | 56.1 | 41.1 | 31.0 | 28.1 | 10.9 | 22.4 | 23.0 | 30.78 | 9.75 | 6.28 | 0.58 | 1.15 | 1.18 |
| 40.4 | 3.5 | 5 | 51.1 | 51.8 | 33.4 | 30.9 | 11.4 | 29.9 | 25.9 | 40.23 | 3.2 | 4.9 | 0.17 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| 50 | 9.5 | 4.4 | 36.1 | 61.7 | 78.6 | 80.1 | 11.7 | 69.1 | 75.7 | 50.3 | 9.76 | 4.07 | 0.3 | 0.26 | 0.33 |
| 60.1 | 9.6 | 2.1 | 28.2 | 71.3 | 79.8 | 81.3 | 11.2 | 70.2 | 79.2 | 60.21 | 9.87 | 1.87 | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.23 |
| 69.5 | 5.2 | 3.1 | 22.2 | 77.4 | 52.7 | 52.5 | 7.9 | 47.5 | 49.4 | 69.4 | 4.97 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 0.23 | 0.2 |
| 80.2 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 10 | 83.2 | 67.1 | 68.6 | 3 | 62.2 | 63.7 | 80 | 5.27 | 5.58 | 0.2 | 0.37 | 0.68 |
| 90 | 3.4 | 4.9 | 1.7 | 91.5 | 66.5 | 66.4 | 1.5 | 63.1 | 61.5 | 90.14 | 3.26 | 4.6 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.3 |
| 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.9 | 20.9 | 20.7 | 0.9 | 20.9 | 20.7 | 99.6 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.4 | 0.19 | 0.31 |
| Item | Chromatography | Spectrograph | Single Gas Sensor | Our System |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | high | high | low | high |
| Online | no | no | yes | yes |
| Response time | very slow | very slow | fast | fast |
| Maintainability | low | low | high | high |
| Require human operation | yes | yes | no | no |
| Required gas volume | large | large | small | small |
| Cost | high | very high | very low | low |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Li, B.; Lei, B.; Ma, P.; Lian, S.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Lei, S. Design and Application of Mixed Natural Gas Monitoring System Using Artificial Neural Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020351
Wang J, Li B, Lei B, Ma P, Lian S, Wang N, Li X, Lei S. Design and Application of Mixed Natural Gas Monitoring System Using Artificial Neural Networks. Sensors. 2021; 21(2):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020351
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jinlei, Bing Li, Bingjie Lei, Peiyuan Ma, Sai Lian, Ning Wang, Xin Li, and Shaochong Lei. 2021. "Design and Application of Mixed Natural Gas Monitoring System Using Artificial Neural Networks" Sensors 21, no. 2: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020351
APA StyleWang, J., Li, B., Lei, B., Ma, P., Lian, S., Wang, N., Li, X., & Lei, S. (2021). Design and Application of Mixed Natural Gas Monitoring System Using Artificial Neural Networks. Sensors, 21(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020351





