Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Differential Code Biases (DCBs) Using a Multi-Spacing Software Receiver
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Correlator Spacing Influence on Pseudorange Measurements
2.2. GNSS Observation and Pre-Processing
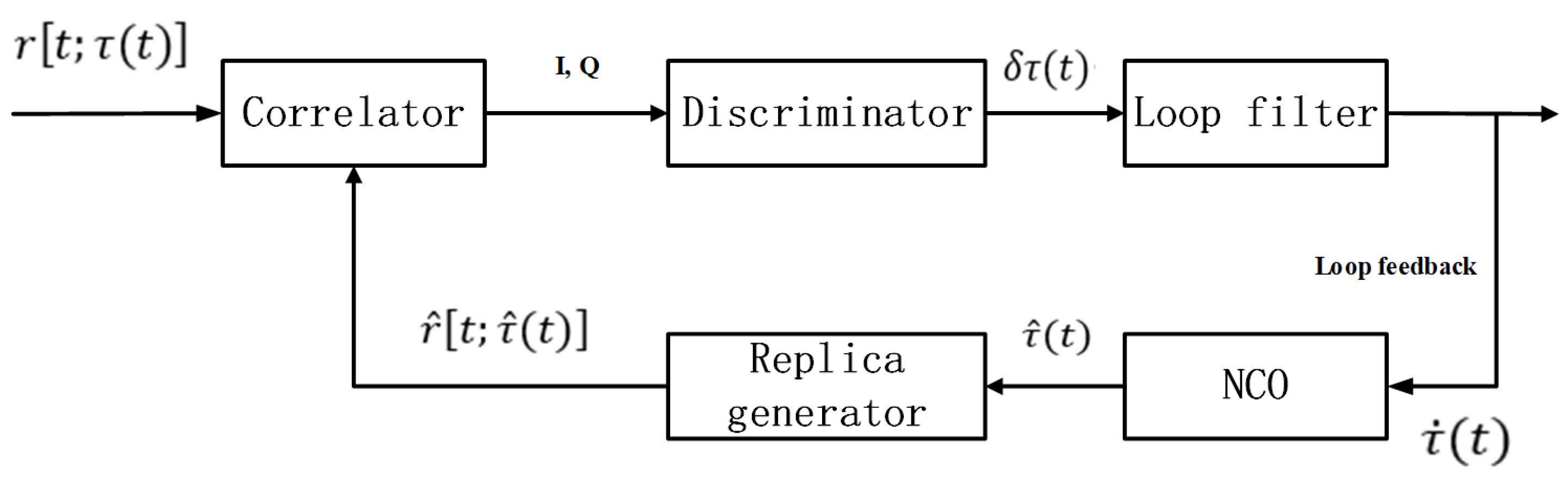
2.3. Satellite DCB Estimation by a Correlator Spacing Flexible Receiver
- a bias priori fixed receiver;
- the imposition of a satellite DCBs zero-mean condition;
- zero references selection from DCB relatively stable satellites.
- data collection and processing, collect IONEX files, MGEX sp3 files, and receiver coordinates;
- collect IF data with dual-frequency front-end;
- using a spacing flexible software receiver to get observations of different spacing;
- local ionospheric TEC modeding;
- DCB estimation by Least Squate estimation method.

3. Experiment, Result Comparison, and Analysis
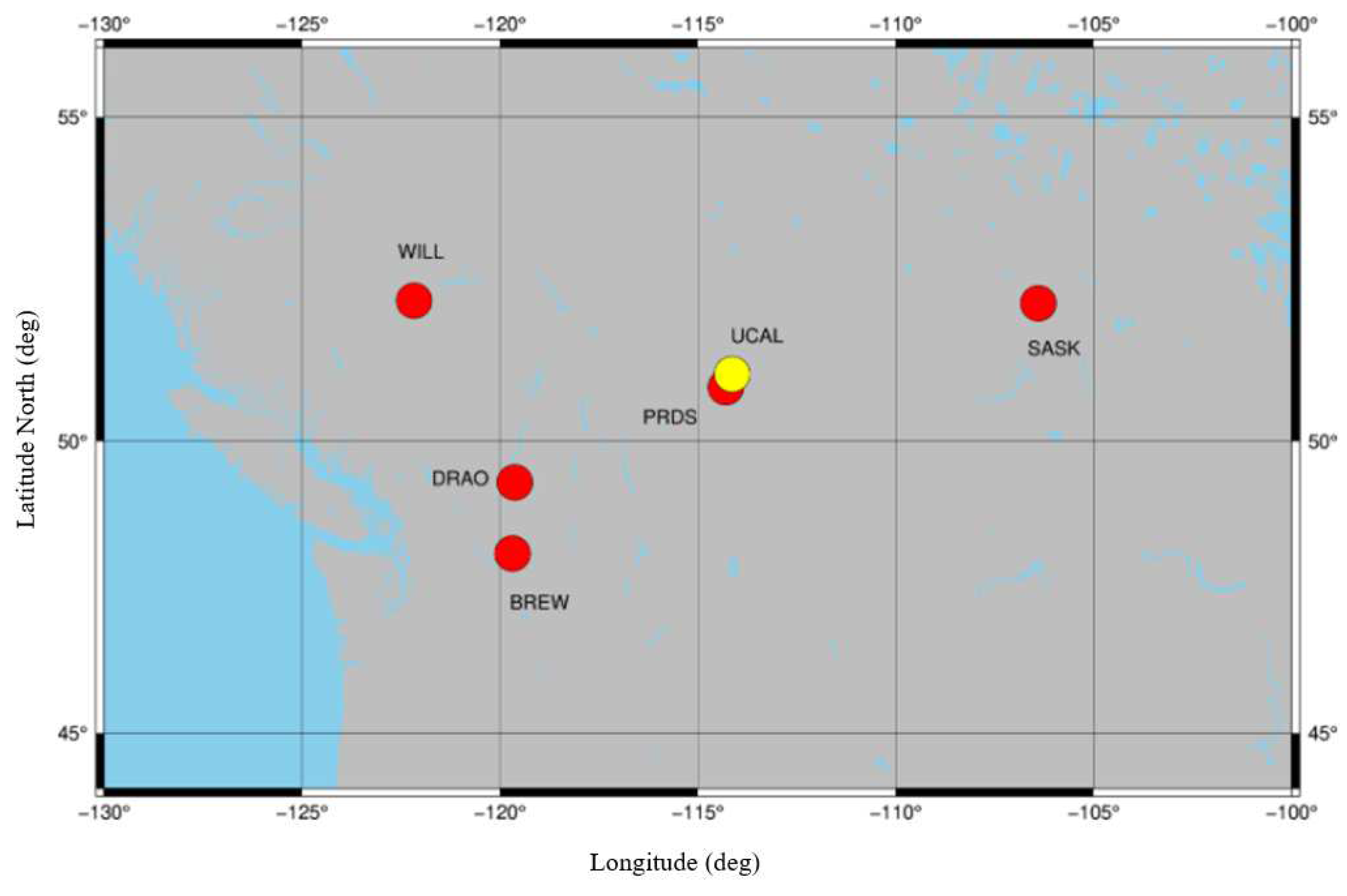
3.1. Experimental Outline
3.2. Stability of 15 Min Estimated DCBs
3.3. Correlator Spacing Influence on the Multi-Station Estimated DCBs
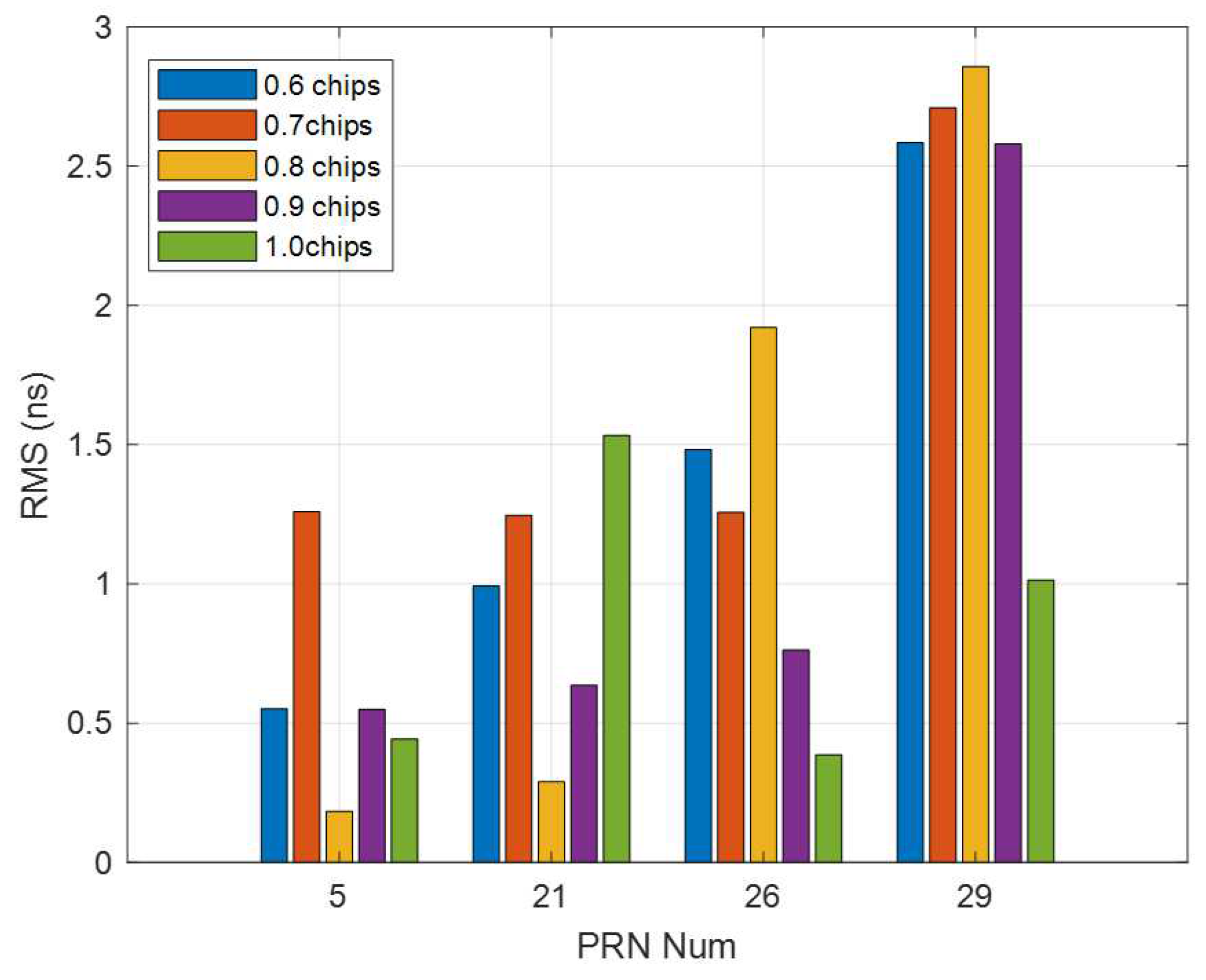
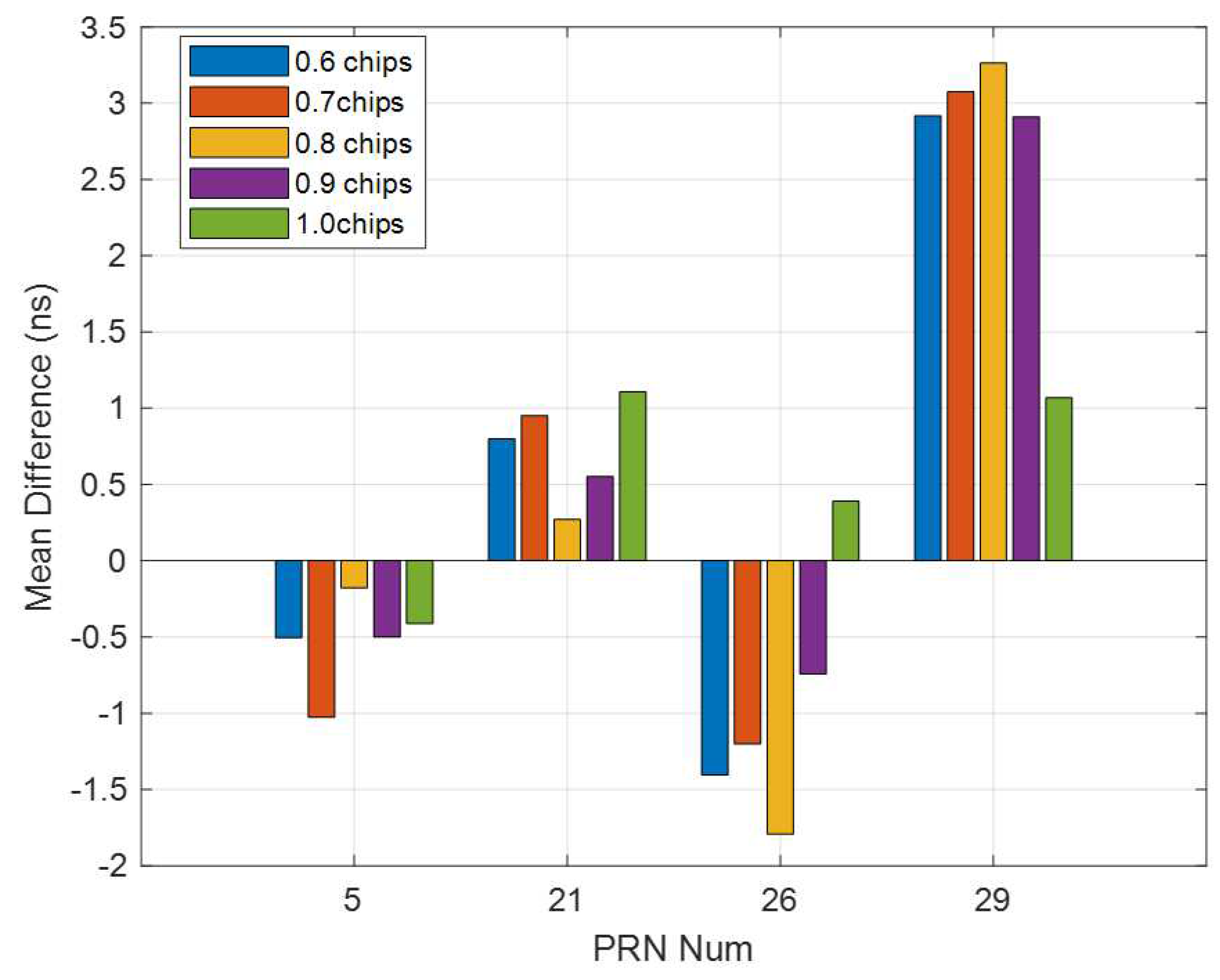
3.4. Correlator Spacing Flexible Receiver-Based Single-Station Multi-Spacing Estimated DCBs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Håkansson, M.; Jensen, A.B.; Horemuz, M.; Hedling, G. Review of code and phase biases in multi-GNSS positioning. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Jin, S.; Feng, G. M_DCB: Matlab code for estimating GNSS satellite and receiver differential code biases. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, W. Investigation and Validation of the Time-Varying Characteristic for the GPS Differential Code Bias. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, J.F.; Azpilicueta, F.; Brunini, C. Accuracy assessment of the GPS-TEC calibration constants by means of a simulation technique. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardon, E.; Rius, A.; Zarraoa, N. Estimation of the transmitter and receiver differential biases and the ionospheric total electron content from Global Positioning System observations. Radio Sci. 1994, 29, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Montenbruck, O.; Tan, B. Determination of differential code biases with multi-GNSS observations. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhou, F.; Sun, B.; Wang, S.; Shi, B. The impact of satellite time group delay and inter-frequency differential code bias corrections on multi-GNSS combined positioning. Sensors 2017, 17, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Q. Global ionosphere mapping and differential code bias estimation during low and high solar activity periods with GIMAS software. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Jin, S.; Hoque, M. Estimation of GPS Differential Code Biases Based on Independent Reference Station and Recursive Filter. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, L.; Huo, X.; Hsu, H. Determination of the differential code bias for current BDS satellites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 3968–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P. Differential code bias estimation using multi-GNSS observations and global ionosphere maps. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2014, 61, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Kuang, C. An approach to speed up single-frequency PPP convergence with quad-constellation GNSS and GIM. Sensors 2017, 17, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Gao, Y. An Enhanced Mapping Function with Ionospheric Varying Height. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, M.; Shi, C.; Fang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, X.; Yang, G.; Bai, W. GPS and BeiDou differential code bias estimation using Fengyun-3C satellite onboard GNSS observations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.; Hegarty, C. Understanding GPS: Principles and Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mitelman, A.M.; Phelts, R.E.; Akos, D.M.; Pullen, S.P.; Enge, P.K. Signal deformations on nominally healthy GPS satellites. In Proceedings of the National Technical Meeting of the ION, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–28 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, G.; Phelts, R.E.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Characterization of signal deformations for GPS and WAAS satellites. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2010), Portland, OR, USA, 21–24 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, G.; Phelts, R.E.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. Alternative characterization of analog signal deformation for GNSS-GPS satellites. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–26 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O.; Thölert, S.; Erker, S.; Meurer, M.; Ashjaee, J. A multi-technique approach for characterizing the SVN49 signal anomaly, part 1: Receiver tracking and IQ constellation. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoelert, S.; Meurer, M.; Erker, S.; Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Fenton, P. A multi-technique approach for characterizing the SVN49 signal anomaly, part 2: Chip shape analysis. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. A study on the dependency of GNSS pseudorange biases on correlator spacing. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.; Montenbruck, O. Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, J. A Guide to Using International GNSS Service (IGS) Products. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jan_Kouba/publication/228663800_A_guide_to_using_International_GNSS_Service_IGS_products/links/54fcc30c0cf270426d102cd3.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2009).
- CODE. IGS Analysis Center. Available online: https://www.aiub.unibe.ch/research/code___analysis_center/differential_code_biases_dcb/index_eng.html (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Roman, R.C.; Precup, R.E.; Petriu, E.M. Hybrid data-driven fuzzy active disturbance rejection control for tower crane systems. Eur. J. Control 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Improving Low-Cost GNSS Receiver Carrier Phase Tracking for High Precision Applications. 2017. Available online: https://prism.ucalgary.ca/handle/11023/4242 (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Zhu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, C. Event-triggered adaptive fuzzy control for stochastic nonlinear systems with unmeasured states and unknown backlash-like hysteresis. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, S.; Gao, Y. Research on dependency of carrier phase biases on correlator spacing. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2018), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ciraolo, L.; Azpilicueta, F.; Brunini, C.; Meza, A.; Radicella, S. Calibration errors on experimental slant total electron content (TEC) determined with GPS. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Ou, J.; Huo, X. Two-step method for the determination of the differential code biases of COMPASS satellites. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, S. helvétique des sciences naturelles. In Mapping and Predicting the Earth’s Ionosphere Using the Global Positioning System; Commission Géodésique, Technische Hochschule Zürich, Institut für Geodäsie und Photogrammetrie, Eds.; Technische Hochschule Zürich: Zürich, Switzerland, 1999; Volume 59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. GAMP: An open-source software of multi-GNSS precise point positioning using undifferenced and uncombined observations. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, M. The Theory and Method of Wide Area Differential GPS; Surveying and Mapping Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Collins, J. Global Positioning System: Theory and Practice; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, P.; Han, W.; Ge, M.; Shi, C. Eliminating negative VTEC in global ionosphere maps using inequality-constrained least squares. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, S.; Gurtner, W.; Feltens, J. IONEX: The ionosphere map exchange format version 1. In Proceedings of the IGS AC Workshop, Darmstadt, Germany, 9–11 February 1998; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Dach, R.; Hugentobler, U.; Fridez, P.; Meindl, M. Bernese GPS Software Version 5.0; Astronomical Institute, University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Y. Determination and analysis of front-end and correlator spacing induced biases for code and carrier phase observations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 115011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Prades, C.; Arribas, J.; Closas, P.; Aviles, C.; Esteve, L. GNSS-SDR: An open source tool for researchers and developers. In Proceedings of the 24th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2011), Portland, OR, USA, 19–23 September 2011; pp. 780–794. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Kubo, N. GNSS-SDRLIB: An open-source and real-time GNSS software defined radio library. In Proceedings of the 27th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2014), Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 September 2014; pp. 1364–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner, W.; Estey, L. Rinex-the Receiver Independent Exchange Format-Version 3.00; Astronomical Institute, University of Bern and Unavco: Bolulder, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y. Estimation and analysis of the short-term variations of multi-GNSS receiver differential code biases using global ionosphere maps. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


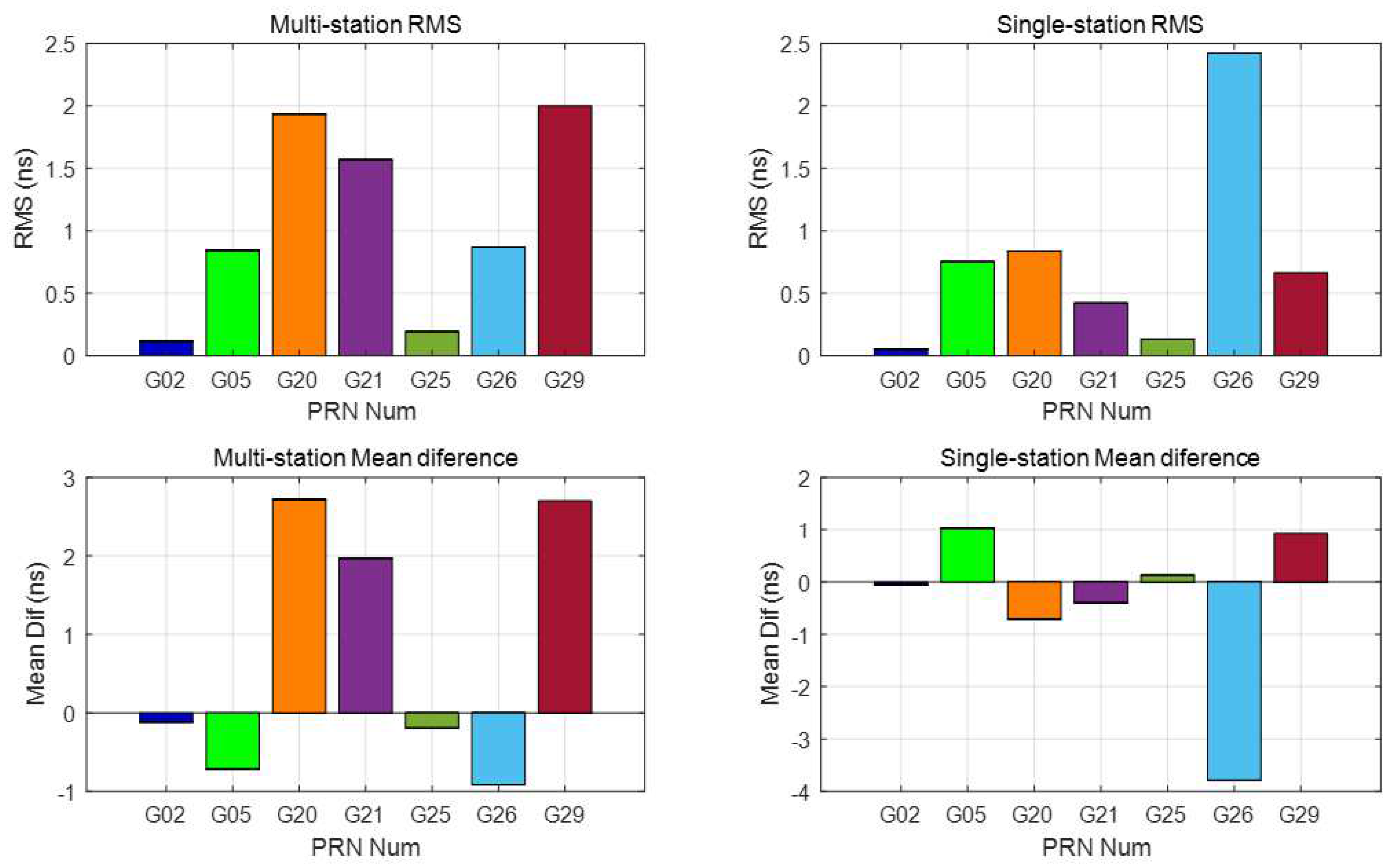

| PRN | M-RMS (ns) | M-Mean (ns) | S-RMS (ns) | S-Mean (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05 | 0.8426 | −0.3588 | 0.7519 | 0.5125 |
| 25 | 0.1916 | −0.0970 | 0.4204 | −0.2970 |
| 26 | 0.8696 | −0.4573 | 2.4240 | −1.8955 |
| 29 | 2.9393 | 2.1005 | 0.6646 | 0.4640 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Y. Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Differential Code Biases (DCBs) Using a Multi-Spacing Software Receiver. Sensors 2021, 21, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020443
Wang Y, Zhao L, Gao Y. Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Differential Code Biases (DCBs) Using a Multi-Spacing Software Receiver. Sensors. 2021; 21(2):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020443
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ye, Lin Zhao, and Yang Gao. 2021. "Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Differential Code Biases (DCBs) Using a Multi-Spacing Software Receiver" Sensors 21, no. 2: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020443
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhao, L., & Gao, Y. (2021). Estimation and Analysis of GNSS Differential Code Biases (DCBs) Using a Multi-Spacing Software Receiver. Sensors, 21(2), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21020443






