Automated ELISA On-Chip for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Traditional ELISA on a Microplate
2.3. Assay’s Methodology and Experimental Setup of the Automated ELISA On-Chip
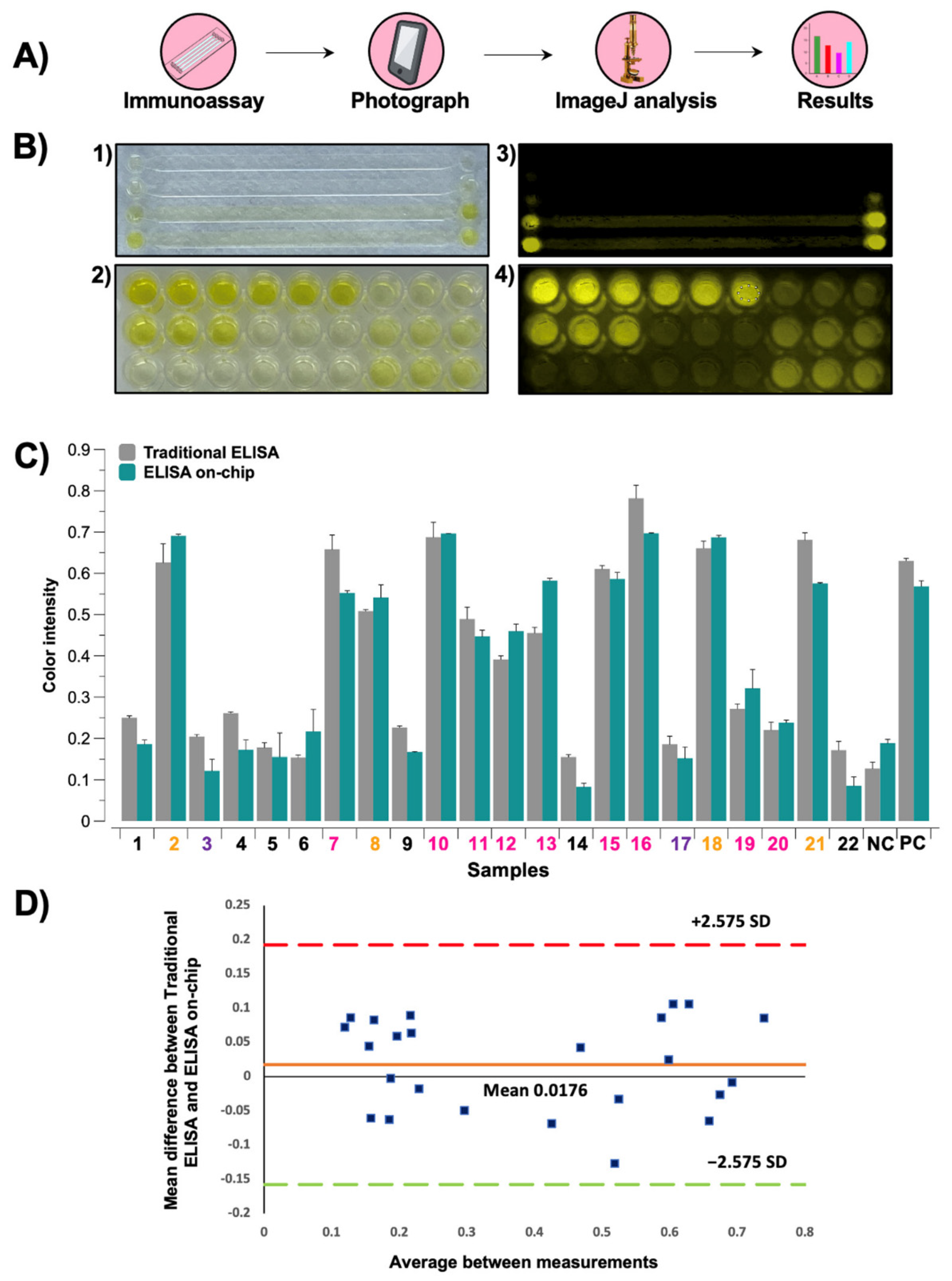
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Immunoassays’ Comparison
3.2. Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Post-Infection
3.3. Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Post-Vaccine
3.4. Image Analysis of Colorimetric Reactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Kirby, T. New variant of SARS-CoV-2 in UK causes surge of COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, e20–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Filipe, A.; Shepherd, J.G.; Williams, T.; Hughes, J.; Aranday-Cortes, E.; Asamaphan, P.; Ashraf, S.; Balcazar, C.; Brunker, K.; Campbell, A.; et al. Genomic epidemiology reveals multiple introductions of SARS-CoV-2 from mainland Europe into Scotland. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogels, C.B.F.; Brito, A.F.; Wyllie, A.L.; Fauver, J.R.; Ott, I.M.; Kalinich, C.C.; Petrone, M.E.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Muenker, M.C.; Moore, A.J.; et al. Analytical sensitivity and efficiency comparisons of SARS-CoV-2 RT–qPCR primer–probe sets. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMullan, M.A.; Ibrayeva, A.; Trettner, K.; Deming, L.; Das, S.; Tran, F.; Moreno, J.R.; Casian, J.G.; Chellamuthu, P.; Kraft, J.; et al. ELISA detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in saliva. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Li, M.; Song, H.; Chen, J.; Ren, W.; Feng, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Song, J.; Peng, Y.; Su, B.; et al. Early Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Antibodies as a Serologic Marker of Infection in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Elslande, J.; Decru, B.; Jonckheere, S.; Van Wijngaerden, E.; Houben, E.; Vandecandelaere, P.; Indevuyst, C.; Depypere, M.; Desmet, S.; André, E.; et al. Antibody response against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and nucleoprotein evaluated by four automated immunoassays and three ELISAs. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1557.e1–1557.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isho, B.; Abe, K.T.; Zuo, M.; Jamal, A.J.; Rathod, B.; Wang, J.H.; Li, Z.; Chao, G.; Rojas, O.L.; Bang, Y.M.; et al. Persistence of serum and saliva antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 spike antigens in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.S.; Jones, F.K.; Nodoushani, A.; Kelly, M.; Becker, M.; Slater, D.; Mills, R.; Teng, E.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; et al. Persistence and decay of human antibody responses to the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe0367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widge, A.T.; Rouphael, N.G.; Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; et al. Durability of Responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewer, K.J.; Barrett, J.R.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Sharpe, H.; Makinson, R.; Morter, R.; Flaxman, A.; Wright, D.; Bellamy, D.; Bittaye, M.; et al. T cell and antibody responses induced by a single dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine in a phase 1/2 clinical trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, B.; Lester, S.; Mills, L.; Rasheed, M.A.U.; Moye, S.; Abiona, O.; Hutchinson, G.; Morales-Betoulle, M.; Krapinunaya, I.; Gibbons, A.; et al. Validation of a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein ELISA for use in contact investigations and sero-surveillance. bioRxiv Prepr. Serv. Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Márquez-Ipiña, A.R.; González-González, E.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Lara-Mayorga, I.M.; Mejía-Manzano, L.A.; Sánchez-Salazar, M.G.; González-Valdez, J.G.; Ortiz-López, R.; Rojas-Martínez, A.; Santiago, G.T.; et al. Serological Test to Determine Exposure to SARS-CoV-2: ELISA Based on the Receptor-Binding Domain of the Spike Protein (S-RBDN318-V510) Expressed in Escherichia coli. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tozetto-Mendoza, T.R.; Kanunfre, K.A.; Vilas-Boas, L.S.; Sanchez Espinoza, E.P.; Paião, H.G.O.; Rocha, M.C.; de Paula, A.V.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Zampelli, D.B.; Vieira, J.M.; et al. Nucleoprotein-based ELISA for detection of SARS-COV-2 IgG antibodies: Could an old assay be suitable for serodiagnosis of the new coronavirus? J. Virol. Methods 2021, 290, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Moncayo, R.; Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Guevara-Pantoja, P.E.; Chavez-Pineda, O.G.; Hernandez-Ortiz, J.A.; Amador-Hernandez, J.U.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Sanchez-Muñoz, F.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Patino-Lopez, L.D.; et al. A high-throughput multiplexed microfluidic device for COVID-19 serology assays. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Agrawal, A. Blood Plasma Microfluidic Device: Aiming for the Detection of COVID-19 Antibodies Using an On-Chip ELISA Platform. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2020, 5, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Wen, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Kong, J. Microfluidic Immunoassays for Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of IgG/IgM/Antigen of SARS-CoV-2 within 15 min. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9454–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Yin, J.; Lv, S.; Wang, B.; Mu, Y. Advanced “lab-on-a-chip” to detect viruses—Current challenges and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, Y.; Kunduru, V.; Bothara, M.; Muthukumar, S. Lab-on-a-chip. In Handbook of Physics in Medicine and Biology; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 9781420075250. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.A.; Kim, S. Microfluidics: Basic issues, applications, and challenges. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, D.J.; Mensing, G.A.; Walker, G.M. Physics and Applications of Microfluidics in Biology. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 4, 261–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassy, J.; Lacoux, C.; Leroy, S.; Noussair, L.; Hubac, S.; Degoutte, A.; Vassaux, G.; Leclercq, V.; Rouquié, D.; Marquette, C.-H.; et al. Versatile and flexible microfluidic qPCR test for high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 and cellular response detection in nasopharyngeal swab samples. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0243333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swank, Z.; Michielin, G.; Yip, H.M.; Cohen, P.; Andrey, D.O.; Vuilleumier, N.; Kaiser, L.; Eckerle, I.; Meyer, B.; Maerkl, S.J. A high-throughput microfluidic nanoimmunoassay for detecting anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in serum or ultralow-volume blood samples. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025289118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.-C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, P.-H.; Zhang, F.; Richardus, J.H. Disappearance of Antibodies to SARS-Associated Coronavirus after Recovery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1162–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, D.C.; Iblan, I.; Rha, B.; Alqasrawi, S.; Haddadin, A.; Al Nsour, M.; Alsanouri, T.; Ali, S.S.; Harcourt, J.; Miao, C.; et al. Persistence of Antibodies against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1824–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labriola, L.; Scohy, A.; Seghers, F.; Perlot, Q.; De Greef, J.; Desmet, C.; Romain, C.; Morelle, J.; Yombi, J.C.; Kabamba, B.; et al. A longitudinal, 3-month serologic assessment of sars-cov-2 infections in a belgian hemodialysis facility. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 613–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhi, H.; Dahmane, D.; Attias, P.; Kofman, T.; Bouvier, M.; Lapidus, N.; Fourati, S.; El Karoui, K.; Mondor NephroCov Study Group. Kinetics of Anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies in Hemodialysis Patients Six Months after Infection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnberg, A.; Amanat, F.; Firpo, A.; Altman, D.R.; Bailey, M.J.; Mansour, M.; McMahon, M.; Meade, P.; Mendu, D.R.; Muellers, K.; et al. Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection persist for months. Science 2020, 370, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalkanen, P.; Kolehmainen, P.; Häkkinen, H.K.; Huttunen, M.; Tähtinen, P.A.; Lundberg, R.; Maljanen, S.; Reinholm, A.; Tauriainen, S.; Pakkanen, S.H.; et al. COVID-19 mRNA vaccine induced antibody responses against three SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earle, K.A.; Ambrosino, D.M.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Goldblatt, D.; Gilbert, P.B.; Siber, G.R.; Dull, P.; Plotkin, S.A. Evidence for antibody as a protective correlate for COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4423–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, K.E.; Le Gars, M.; Sadoff, J.; de Groot, A.M.; Heerwegh, D.; Truyers, C.; Atyeo, C.; Loos, C.; Chandrashekar, A.; McMahan, K.; et al. Immunogenicity of the Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine for COVID-19. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauk, M.G.; Song, J.; Bau, H.H.; Liu, C. Point-of-Care Molecular Test for Zika Infection. Clin. Lab. Int. 2017, 41, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrberg, C.D.; Manz, A.; Neužil, P. Palm-Sized Device for Point-of-Care Ebola Detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4803–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Y.C.; Shen, C.F.; Cheng, C.M. Point-of-Care RNA-Based Diagnostic Device for COVID-19. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Zapatero-Rodríguez, J.; Estrela, P.; O’Kennedy, R.J. Point-of-Care Diagnostics in Low Resource Settings: Present Status and Future Role of Microfluidics. Biosensors 2015, 5, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
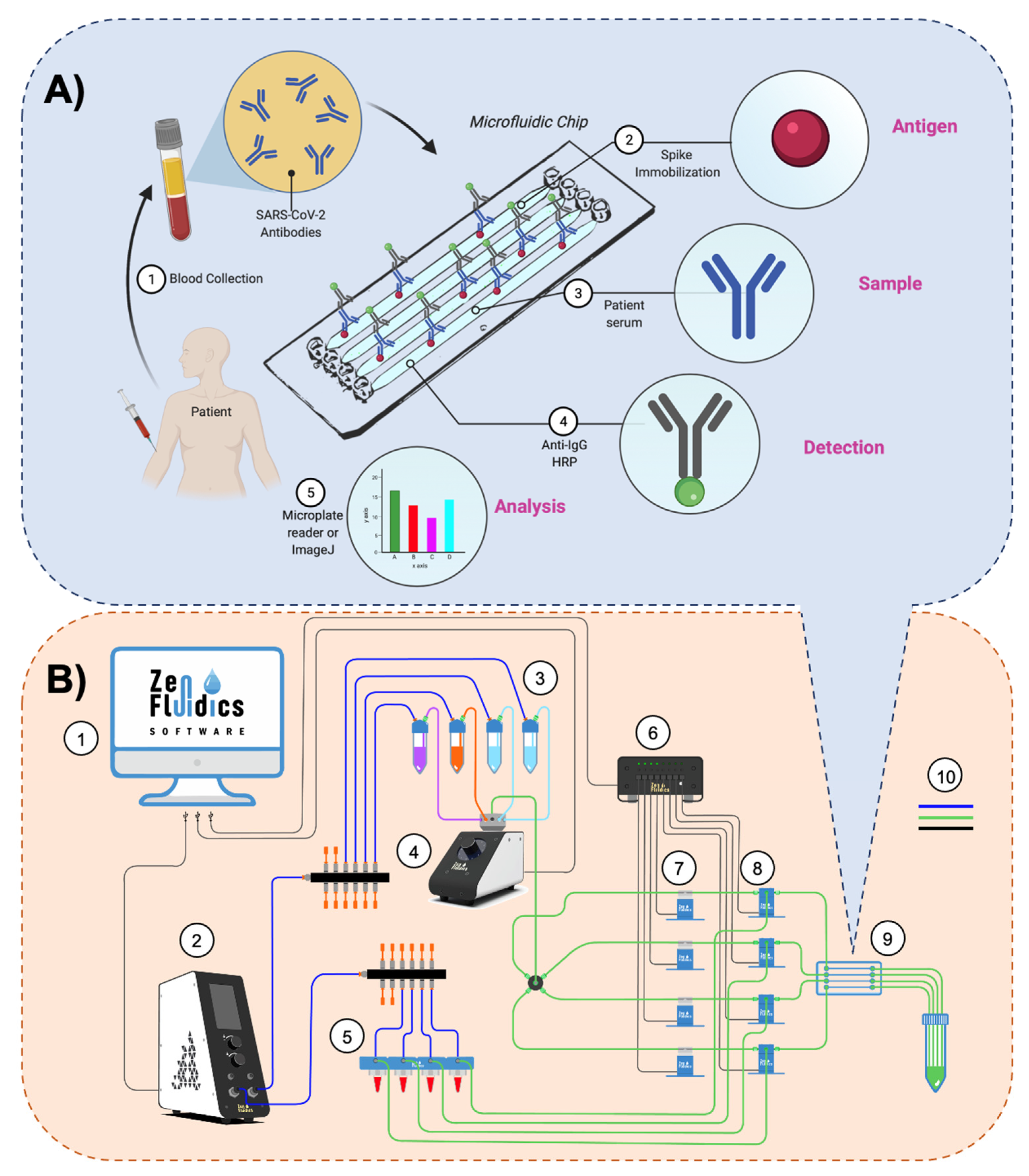


| Step | Reagent | On-Chip Flow Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Antigen immobilization | 1 μg/mL spike protein in PBS | 500 μL/min (30 s)–incubation (1 h/RT) |
| 2. Wash | 0.05% Tween-20TM in PBS | 500 μL/min (30 s) |
| 3. Blocking | 5% skim milk in PBS | 500 μL/min (1 min)–incubation (30 min/RT) |
| 4. Wash | 0.05% Tween-20TM in PBS | 500 μL/min (1 min)–3 times |
| 5. Pumping of samples | Serum (diluted in PBS 1:100) | 500 μL/min (1 min)–incubation (50 min/RT) |
| 6. Wash | 0.05% Tween-20TM in PBS | 500 μL/min (1 min)–3 times |
| 7. Anti-IgG-HRP binding | Anti-IgG-HRP (diluted in PBS 1:15,000) | 500 μL/min (30 s)–incubation (50 min/RT) |
| 8. Wash | 0.05% Tween-20TM in PBS | 500 μL/min (1 min)–3 times |
| 9. HRP reaction | TMB-ELISA | 50 μL–incubation (3 min/RT) |
| 10. Reaction halt | 1 M H2SO4 | 50 μL (final reaction) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-González, E.; Garcia-Ramirez, R.; Díaz-Armas, G.G.; Esparza, M.; Aguilar-Avelar, C.; Flores-Contreras, E.A.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.P.; Delgado-Balderas, J.R.; Soto-García, B.; Aráiz-Hernández, D.; et al. Automated ELISA On-Chip for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Sensors 2021, 21, 6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21206785
González-González E, Garcia-Ramirez R, Díaz-Armas GG, Esparza M, Aguilar-Avelar C, Flores-Contreras EA, Rodríguez-Sánchez IP, Delgado-Balderas JR, Soto-García B, Aráiz-Hernández D, et al. Automated ELISA On-Chip for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Sensors. 2021; 21(20):6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21206785
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-González, Everardo, Ricardo Garcia-Ramirez, Gladys Guadalupe Díaz-Armas, Miguel Esparza, Carlos Aguilar-Avelar, Elda A. Flores-Contreras, Irám Pablo Rodríguez-Sánchez, Jesus Rolando Delgado-Balderas, Brenda Soto-García, Diana Aráiz-Hernández, and et al. 2021. "Automated ELISA On-Chip for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies" Sensors 21, no. 20: 6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21206785
APA StyleGonzález-González, E., Garcia-Ramirez, R., Díaz-Armas, G. G., Esparza, M., Aguilar-Avelar, C., Flores-Contreras, E. A., Rodríguez-Sánchez, I. P., Delgado-Balderas, J. R., Soto-García, B., Aráiz-Hernández, D., Abarca-Blanco, M., Yee-de León, J. R., Velarde-Calvillo, L. P., Abarca-Blanco, A., & Yee-de León, J. F. (2021). Automated ELISA On-Chip for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. Sensors, 21(20), 6785. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21206785







