On–Off Scheduling for Electric Vehicle Charging in Two-Links Charging Stations Using Binary Optimization Approaches
Abstract
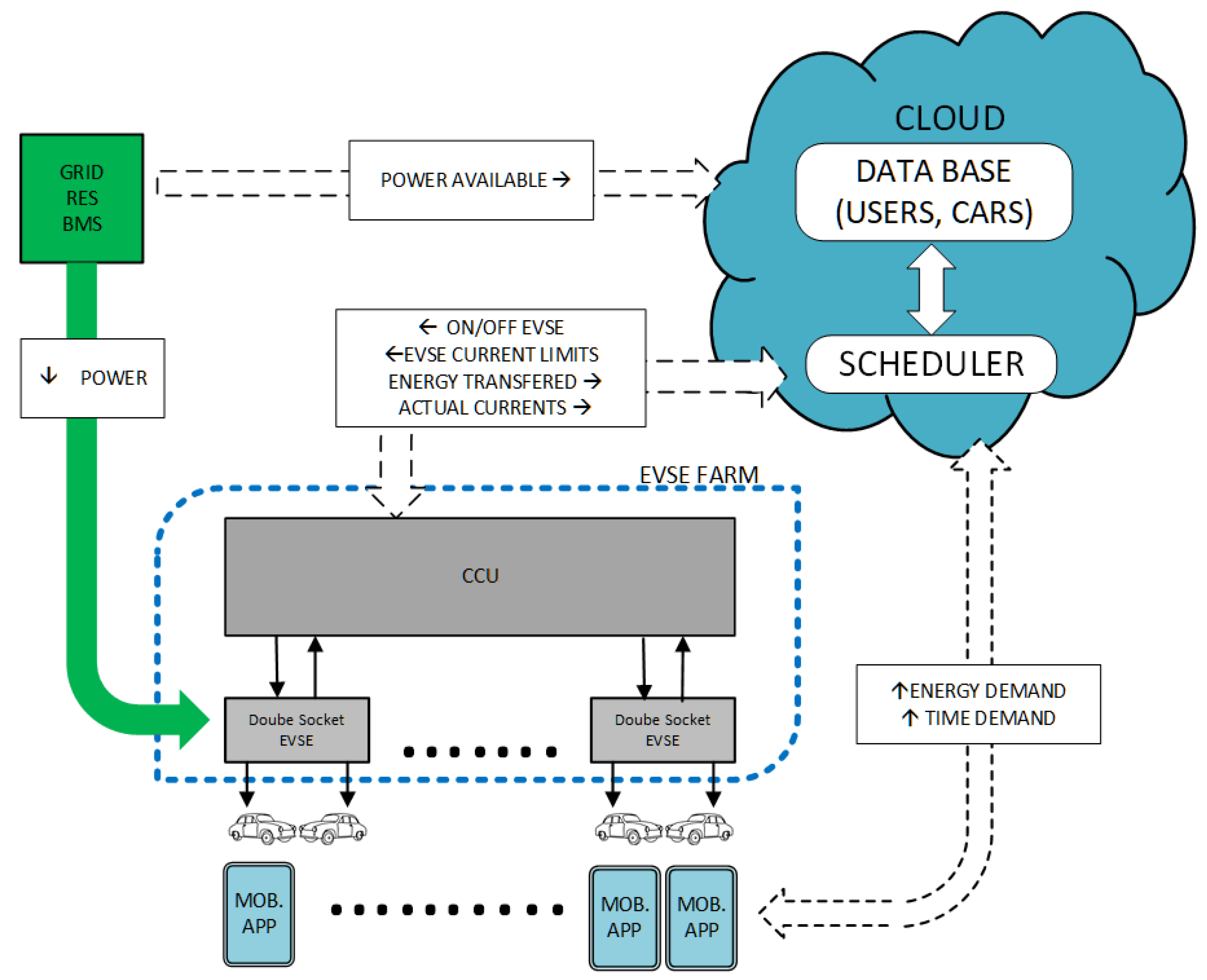
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Scheduling Problem
3.1. Problem Formulation
- Linear: Motivated by the concept of the objective weighting, given in [38], we formulate the weighted linear function:where , where . The parameters and were experimentally set to and . Vector w represents a piecewise linear function. The first entries are equal to one, whereas the others linearly increase from one to . Such weighting aims to penalize decision variables in later time slots, which should enforce charging as early as possible. Minimization of a linear function can be performed using any BLP solver. This approach is computationally efficient; however, it is not flexible owing to the limited possibility of using multiple penalties.
- Quadratic I: In this model, we assume charging of all EVs with a possibly maximum power, which leads to the following objective function:where for , and . Matrix has a task similar to that of the linear function.
- Quadratic II: Another possibility is to reinforce the SoC level bilanse with additional weighting of time slots. This task can be achieved using the following objective function:
- Penalized quadratic with smoothness constraints: None of the above-mentioned objective functions assures a smooth solution, indicating that the number of switching on/off charging stations is not controlled within the area of feasibility bounded by the constraints. However, the number of switching operations can be minimized by introducing a trade-off between the model fitting and the local smoothness measure. Taking into account the objective functions (12) and (13), the degradation of model fitting by adding a regularization or penalty term is not a problematic issue because the model constraints are explicitly added to the optimization problem and guarantee feasibility.The local smoothness of the charging profile for each EV can be measured according to the following function:Let L be the first-order differential operator defined as:The function can be equivalently rewritten using matrix L in the form . Consequently, the objective function (13) with the additive smoothness penalty term is given bywhere is a penalty term.
- Quadratic I:
- Quadratic II:
- Penalized quadratic form with smoothness constraints:
3.2. Algorithmic Approach
3.2.1. Frank—Wolfe Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: FW Algorithm |
 |
3.2.2. Successive Linear Approximations
4. Numerical Simulations
4.1. Setup
- BLP: Binary linear programming (BLP) with objective function in (24);
- FA-FS: First-arrive-first-serve (FA-FS) approach.
4.2. Results
4.3. Discussion
4.4. Engineering Aspects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Karmaker, A.K.; Hossain, M.A.; Manoj Kumar, N.; Jagadeesan, V.; Jayakumar, A.; Ray, B. Analysis of Using Biogas Resources for Electric Vehicle Charging in Bangladesh: A Techno-Economic-Environmental Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samadi, M.; Fattahi, J.; Schriemer, H.; Erol-Kantarci, M. Demand Management for Optimized Energy Usage and Consumer Comfort Using Sequential Optimization. Sensors 2021, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, K.N.; Alhudhaif, A.; Jeon, G. Electric-vehicle energy management and charging scheduling system in sustainable cities and society. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Wolfe, P. An algorithm for quadratic programming. Nav. Res. Logist. Q. 1956, 3, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telli, M.; Bentobache, M.; Mokhtari, A. A successive linear approximation algorithm for the global minimization of a concave quadratic program. Comp. Appl. Math. 2020, 39, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ogaili, A.S.; Hashim, T.J.T.; Rahmat, N.A.; Ramasamy, A.; Marsadek, M.; Faisal, M.; Hannan, M. Review on Scheduling, Clustering, and Forecasting Strategies for Controlling Electric Vehicle Charging: Challenges and Recommendations. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128353–128371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Tareen, W.U.K.; Usman, M.; Ali, H.; Bari, I.; Horan, B.; Mekhilef, S.; Asif, M.; Ahmed, S.; Mahmood, A. A Review of Optimal Charging Strategy for Electric Vehicles under Dynamic Pricing Schemes in the Distribution Charging Network. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Vasant, P.M.; Singh, B.S.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Adnan, N. Review of recent trends in optimization techniques for plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicle charging infrastructures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Vasant, P.; Singh, B.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M. Novel metaheuristic optimization strategies for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles: A holistic review. Intell. Decis. Technol. 2016, 10, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Topcu, U.; Low, S.H. Optimal decentralized protocol for electric vehicle charging. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, L.; Topcu, U.; Low, S.H. Stochastic distributed protocol for electric vehicle charging with discrete charging rate. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.J.; Gupta, V.; Topcu, U. On distributed charging control of electric vehicles with power network capacity constraints. In Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 June 2014; pp. 4306–4311. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Feng, D.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Jing, L.; Wang, J. Ant-Based Swarm Algorithm for Charging Coordination of Electric Vehicles. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2013, 9, 268942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karfopoulos, E.; Hatziargyriou, N. Distributed coordination of electric vehicles for conforming to an energy schedule. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 151, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakanian, O.; Keshav, S.; Rosenberg, C. Real-Time Distributed Control for Smart Electric Vehicle Chargers: From a Static to a Dynamic Study. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; An, D.; Yu, W.; Tan, Z.; Yang, X. Towards Stochastic Optimization-Based Electric Vehicle Penetration in a Novel Archipelago Microgrid. Sensors 2016, 16, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Callaway, D.S.; Hiskens, I.A. Decentralized Charging Control of Large Populations of Plug-in Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, W.; Han, Z.; Cao, Z. Charging Scheduling of Electric Vehicles With Local Renewable Energy Under Uncertain Electric Vehicle Arrival and Grid Power Price. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 2600–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Tan, C.W.; Quek, T.Q.S. Electric Vehicle Charging in Smart Grid: Optimality and Valley-Filling Algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2014, 8, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Mu, B.; Wang, L.Y.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Morais, H. Decentralized Electric Vehicle Charging Strategies for Reduced Load Variation and Guaranteed Charge Completion in Regional Distribution Grids. Energies 2017, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.U.; Mehmood, K.K.; Haider, Z.M.; Rafique, M.K.; Khan, M.O.; Kim, C.H. Coordination of Multiple Electric Vehicle Aggregators for Peak Shaving and Valley Filling in Distribution Feeders. Energies 2021, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.; Flynn, D.; Keane, A. Optimal Charging of Electric Vehicles in Low-Voltage Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Venkatesh, B.; Guan, L. Optimal Scheduling for Charging and Discharging of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoog, J.; Alpcan, T.; Brazil, M.; Thomas, D.A.; Mareels, I. Optimal Charging of Electric Vehicles Taking Distribution Network Constraints Into Account. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, Z. High efficient valley-filling strategy for centralized coordinated charging of large-scale electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2017, 186, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.M.; Caramanis, M.C. Optimal Power Market Participation of Plug-In Electric Vehicles Pooled by Distribution Feeder. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundstom, O.; Binding, C. Optimization Methods to Plan the Charging of Electric Vehicle Fleets. ACEEE Int. J. Commun. 2010, 1, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Rautiainen, J.; Dahlhaus, D.; Lakshman, A.; Toebermann, J.C.; Braun, M. Online Optimal Charging Strategy for Electric Vehicles. Energy Procedia 2015, 73, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Arauzo, A.; Puente, J.; Varela, R.; Sedano, J. Electric vehicle charging under power and balance constraints as dynamic scheduling. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 85, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clement, K.; Haesen, E.; Driesen, J. Coordinated charging of multiple plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in residential distribution grids. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, Seattle, WA, USA, 15–18 March 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Khaki, B.; Chung, Y.W.; Chu, C.; Gadh, R. Hierarchical Distributed EV Charging Scheduling in Distribution Grids. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Power Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sundstrom, O.; Binding, C. Flexible Charging Optimization for Electric Vehicles Considering Distribution Grid Constraints. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binetti, G.; Davoudi, A.; Naso, D.; Turchiano, B.; Lewis, F.L. Scalable Real-Time Electric Vehicles Charging with Discrete Charging Rates. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Kim, D.; Oh, S.; Jun, J. A queuing model with random interruptions for electric vehicle charging systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2011; pp. 679–680. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.; Dusparic, I.; Galván-López, E.; Marinescu, A.; Cahill, V.; Clarke, S. Set point control for charging of electric vehicles on the distribution network. In Proceedings of the ISGT 2014, Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.L.; Tran-Quoc, T.; Bacha, S.; Nguyen, B. Charging strategies to minimize the peak load for an electric vehicle fleet. In Proceedings of the IECON 2014—40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Dallas, TX, USA, 29 October–1 November 2014; pp. 3522–3528. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, X.; Rebelo, J.; Gouveia, J.; Maia, R.; Silva, N.B. On-off scheduling schemes for power-constrained electric vehicle charging. Q. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 15, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, B.; Huang, Z.; Tan, X.; Tsang, D.H.K. Optimal Scheduling for Electric Vehicle Charging With Discrete Charging Levels in Distribution Grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, M.; Qureshi, M.B.; Ali, S.M.; Shabbir, N.; Khan, M.U.S.; Aloraini, A.; Nawaz, R. A Cost-Effective Electric Vehicle Intelligent Charge Scheduling Method for Commercial Smart Parking Lots Using a Simplified Convex Relaxation Technique. Sensors 2020, 20, 4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashash, S.; Moura, S.J.; Forman, J.C.; Fathy, H.K. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle charge pattern optimization for energy cost and battery longevity. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.B.; Apt, J.; Whitacre, J. Lithium-ion battery cell degradation resulting from realistic vehicle and vehicle-to-grid utilization. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trippe, A.E.; Arunachala, R.; Massier, T.; Jossen, A.; Hamacher, T. Charging optimization of battery electric vehicles including cycle battery aging. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–15 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- De Vroey, L.; Jahn, R.; Omar, N.; Van Mierlo, J. Impact of smart charging on the EV battery ageing—Discussion from a 3 years real life experience. World Electr. Veh. J. 2015, 7, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Kooten Niekerk, M.E.; Van den Akker, J.M.; Hoogeveen, J.A. Scheduling electric vehicles. Public Transp. 2017, 9, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetani, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Morita, H. A linear programming based heuristic algorithm for charge and discharge scheduling of electric vehicles in a building energy management system. Omega 2017, 67, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, G.B.; Ang, S.G. A study of electric vehicle battery charging demand in the context of Singapore. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Power Engineering Conference (IPEC 2007), Singapore, 3–6 December 2007; pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sassi, O.; Oulamara, A. Electric vehicle scheduling and optimal charging problem: Complexity, exact and heuristic approaches. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.F.; Rider, M.J.; Romero, R. An MILP model for the plug-in electric vehicle charging coordination problem in electrical distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting|Conference Exposition, National Harbor, MD, USA, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nizami, M.S.H.; Hossain, M.J.; Mahmud, K. A Coordinated Electric Vehicle Management System for Grid-Support Services in Residential Networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 2066–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y. Two-stage battery recharge scheduling and vehicle-charger assignment policy for dynamic electric dial-a-ride services. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Álvarez, J.; González, M.A.; Vela, C.R. A Genetic Algorithm for Scheduling Electric Vehicle Charging. In Proceedings of the GECCO ’15: Proceedings of the 2015 Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, Madrid, Spain, 11–15 July 2015; pp. 393–400. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Pang, G.K.H.; Choy, K.L.; Lam, H.Y. Dynamic resource allocation for parking lot electric vehicle recharging using heuristic fuzzy particle swarm optimization algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 71, 538–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Ming, Z.; Wen, T. Scheduling strategy of electric vehicle charging considering different requirements of grid and users. Energy 2021, 232, 121118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, N.B.; Franco, J.F.; Lavorato, M.; Romero, R. Metaheuristic optimization algorithms for the optimal coordination of plug-in electric vehicle charging in distribution systems with distributed generation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 142, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Álvarez, J.; González, M.A.; Vela, C.R. Metaheuristics for solving a real-world electric vehicle charging scheduling problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 65, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Álvarez, J.; González, M.Á.; Rodríguez Vela, C.; Varela, R. Electric Vehicle Charging Scheduling by an Enhanced Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Energies 2018, 11, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usman, M.; Tareen, W.U.K.; Amin, A.; Ali, H.; Bari, I.; Sajid, M.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Stojcevski, A.; Mahmood, A.; Mekhilef, S. A Coordinated Charging Scheduling of Electric Vehicles Considering Optimal Charging Time for Network Power Loss Minimization. Energies 2021, 14, 5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Amaris, H.; Germain, J.G.; Galan, J.M. Optimal Charging Scheduling of Electric Vehicles in Smart Grids by Heuristic Algorithms. Energies 2014, 7, 2449–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, A.G.; Jacobsen, R.H. Agent-based charging scheduling of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Online Conference on Green Communications (OnlineGreenComm), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 14–17 November 2016; pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xydas, E.; Marmaras, C.; Cipcigan, L.M. A multi-agent based scheduling algorithm for adaptive electric vehicles charging. Appl. Energy 2016, 177, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, F.; Tang, B.; Fan, W. Effective Charging Planning Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Xiong, X. An Orderly EV Charging Scheduling Method Based on Deep Learning in Cloud-Edge Collaborative Environment. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6690610. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Coutiño, M.; Giannakis, G.B.; Leus, G. A Momentum-Guided Frank-Wolfe Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 3597–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, O.P.; Sosa, W.S. On the Frank–Wolfe algorithm for non-compact constrained optimization problems. Optimization 2021, 1–15, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, F.; Yang, G.; Træholt, C.; Larsen, E.; Rasmussen, C.; You, S. Demand Profile Study of Battery Electric Vehicle under Different Charging Options. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Hynan, P.; von Jouanne, A.; Yokochi, A. Current Li-Ion Battery Technologies in Electric Vehicles and Opportunities for Advancements. Energies 2019, 12, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | |
| 3 | 6 | 12 | 25 | 50 |
| Algorithm | Mean () | Median () | [%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLP | 0.088 | 187.7 (37.7) | 107 | 76 | 4 | 96.7 | |
| Q1-FW | 1.09 | 191.7 (72) | 105 | 85 | 4 | 76.7 | |
| SmQ2-FW | 3.07 | 3.61 | 82.27 (38.8) | 39 | 71 | 5 | 43.3 |
| SmQ2-NG-FW | 2.54 | 71.33 (28.58) | 41 | 72 | 5 | 51 | |
| SmSLA | 100.38 (60.57) | 92 | 81 | 4 | 100 | ||
| FA-FS | 0 | 0 | 31.13 (1.45) | 15 | 53 | 8 | 100 |
| Algorithm | Mean () | Median () | [%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLP | 3505 (238) | 1909 | 84 | 50 | 100 | ||
| Q1-FW | 4259 (416) | 2152 | 94 | 50 | 100 | ||
| SmQ2-FW | 924.6 (27.68) | 644 | 87 | 50 | 100 | ||
| SmQ2-NG-FW | 772.9 (18.44) | 515 | 93 | 50 | 100 | ||
| SmSLA | 892.6 (22.66) | 621 | 90 | 50 | 100 | ||
| FA-FS | 0 | 0 | 502.3 (3.57) | 242 | 66 | 123 | 100 |
| Algorithm | Mean () | Median () | [%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLP | 2.97 | 2.92 | 848.4 (240.6) | 395 | 65 | 78 | 0 |
| Q1-FW | 0.141 | 1322 (178) | 745 | 94 | 61 | 90 | |
| SmQ2-FW | 2.61 | 2.65 | 614 (34.17) | 304 | 65 | 70 | 0 |
| SmQ2-NG-FW | 2.48 | 2.44 | 557 (25.4) | 268 | 65 | 72 | 0 |
| SmSLA | 454.5 (38.1) | 335 | 92 | 62 | 100 | ||
| FA-FS | 0 | 0 | 394.6 (12.15) | 188 | 65 | 105 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdunek, R.; Grobelny, A.; Witkowski, J.; Gnot, R.I. On–Off Scheduling for Electric Vehicle Charging in Two-Links Charging Stations Using Binary Optimization Approaches. Sensors 2021, 21, 7149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217149
Zdunek R, Grobelny A, Witkowski J, Gnot RI. On–Off Scheduling for Electric Vehicle Charging in Two-Links Charging Stations Using Binary Optimization Approaches. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217149
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdunek, Rafał, Andrzej Grobelny, Jerzy Witkowski, and Radosław Igor Gnot. 2021. "On–Off Scheduling for Electric Vehicle Charging in Two-Links Charging Stations Using Binary Optimization Approaches" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217149
APA StyleZdunek, R., Grobelny, A., Witkowski, J., & Gnot, R. I. (2021). On–Off Scheduling for Electric Vehicle Charging in Two-Links Charging Stations Using Binary Optimization Approaches. Sensors, 21(21), 7149. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217149







