Cough Sounds Recorded via Smart Devices as Useful Non-Invasive Digital Biomarkers of Aspiration Risk: A Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case 1
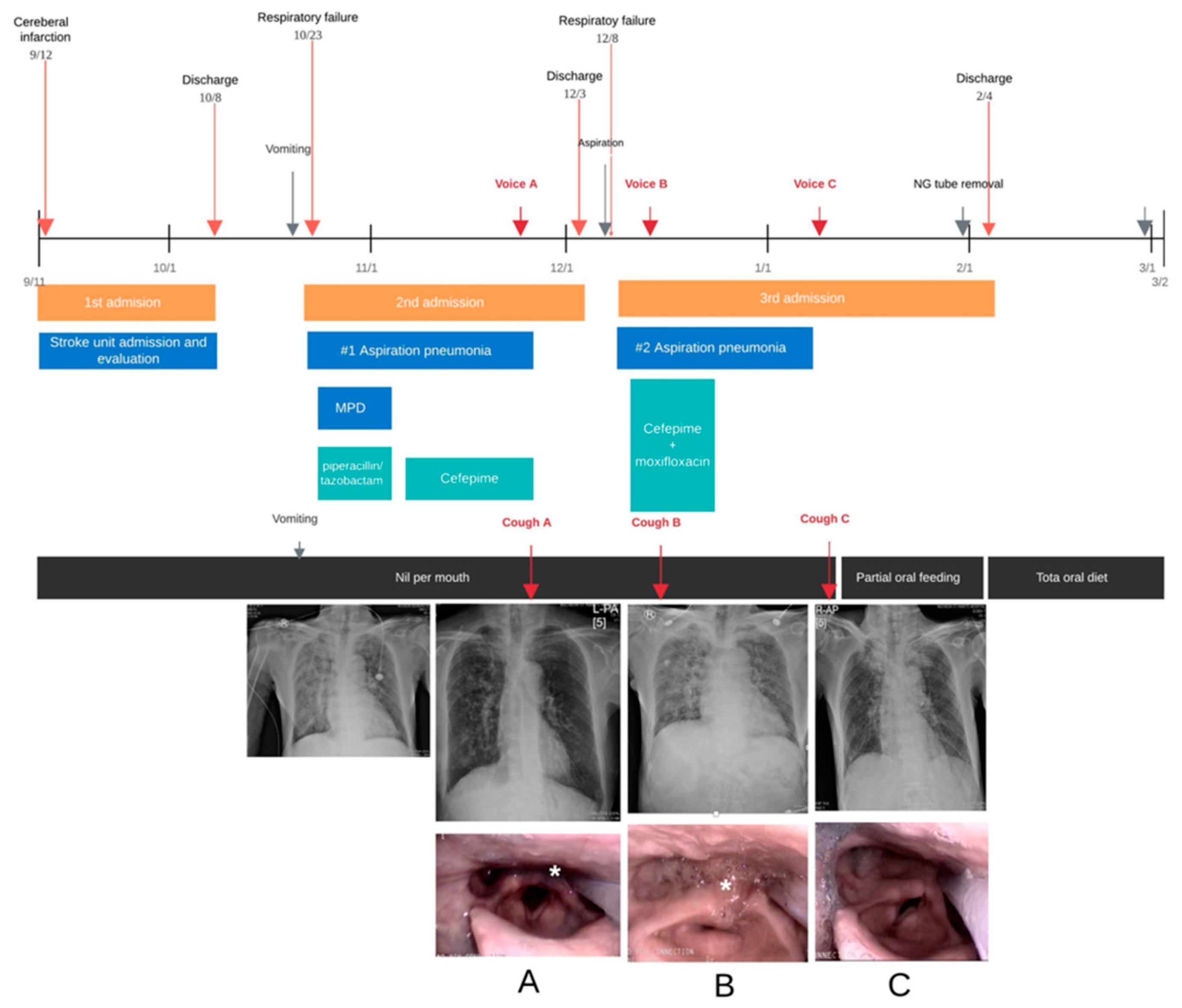
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Technical Aspects of Recording
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Porter, P.; Brisbane, J.M.; Abeyratne, U.; Wood, J.; Peltonen, V.; Bear, N.; Smith, C.; Della, P.; Claxton, S. Diagnosing Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Diagnostic accuracy study of a cough-centred algorithm for use in primary and acute-care consultations. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 71, e258–e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, S.; Fukuchi, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Sato, K.; Sekizawa, K.; Matsuse, T.; Japanese Study Group on Aspiration Pulmonary, D. High incidence of aspiration pneumonia in community- and hospital-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients: A multicenter, prospective study in Japan. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umayahara, Y.; Soh, Z.; Sekikawa, K.; Kawae, T.; Otsuka, A.; Tsuji, T. Clinical Significance of Cough Peak Flow and Its Non-Contact Measurement via Cough Sounds: A Narrative Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laguarta, J.; Hueto, F.; Subirana, B. COVID-19 Artificial Intelligence Diagnosis Using Only Cough Recordings. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2020, 1, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudraraju, G.; Palreddy, S.; Mamidgi, B.; Sripada, N.R.; Sai, Y.P.; Vodnala, N.K.; Haranath, S.P. Cough sound analysis and objective correlation with spirometry and clinical diagnosis. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2020, 19, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouawad, P.; Dubnov, T.; Dubnov, S. Robust Detection of COVID-19 in Cough Sounds: Using Recurrence Dynamics and Variable Markov Model. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohmetra, H.; Raghunath, N.; Narang, P.; Chamola, V.; Guizani, M.; Lakkaniga, N.R. AI-enabled remote monitoring of vital signs for COVID-19: Methods, prospects and challenges. Computing 2021, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, A.H.; Fontana, G.A.; Belvisi, M.G.; Birring, S.S.; Chung, K.F.; Dicpinigaitis, P.V.; Kastelik, J.A.; McGarvey, L.P.; Smith, J.A.; Tatar, M.; et al. ERS guidelines on the assessment of cough. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 1256–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.J.; Jang, Y.J.; Park, G.Y.; Joo, Y.H.; Im, S. Role of injection laryngoplasty in preventing post-stroke aspiration pneumonia, case series report. Medicine 2020, 99, e19220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, G.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, Y.W.; Jo, K.W.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Im, S. Decreased diaphragm excursion in stroke patients with dysphagia as assessed by M-mode sonography. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umayahara, Y.; Soh, Z.; Sekikawa, K.; Kawae, T.; Otsuka, A.; Tsuji, T. A Mobile Cough Strength Evaluation Device Using Cough Sounds. Sensors 2018, 18, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crary, M.A.; Mann, G.D.; Groher, M.E. Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.O.; Comina, G.; Hernandez-Cordova, G.; Naik, N.; Gayoso, O.; Ticona, E.; Coronel, J.; Evans, C.A.; Zimic, M.; Paz-Soldan, V.A.; et al. Cough dynamics in adults receiving tuberculosis treatment. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, R.S.; Singh, V.P.; Mittal, V.K. Discriminant Feature Vectors for Characterizing Ailment Cough vs. Simulated Cough. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Singapore, 22–25 November 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Xu, W. Theory and Application of Audio-Based Assessment of Cough. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, C.; Baiardi, P.; Khirani, S.; Cantarella, G. Cough peak flow as a predictor of pulmonary morbidity in patients with dysphagia. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, D.; Park, G.Y.; Koo, H.; Jang, Y.; Han, Y.; Im, S. Determining Peak Cough Flow Cutoff Values to Predict Aspiration Pneumonia Among Patients with Dysphagia Using the Citric Acid Reflexive Cough Test. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 2532–2539.e2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Ohira, M.; Yokokawa, Y. Cough Strength Is an Indicator of Aspiration Risk When Restarting Food Intake in Elderly Subjects with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Respir. Care 2020, 65, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laciuga, H.; Brandimore, A.E.; Troche, M.S.; Hegland, K.W. Analysis of Clinicians’ Perceptual Cough Evaluation. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnecke, T.; Im, S.; Kaiser, C.; Hamacher, C.; Oelenberg, S.; Dziewas, R. Aspiration and dysphagia screening in acute stroke—The Gugging Swallowing Screen revisited. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnecke, T.; Dziewas, R.; Oelenberg, S.; Ritter, M.; Dittrich, R.; Schabitz, W.R.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Nabavi, D.G. Serial fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing in patients with acute stroke and dysphagia: Case report and general considerations. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2006, 15, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, R.V.; Abeyratne, U.R.; Swarnkar, V.R.; Claxton, S.; Hukins, C.; Porter, P. Predicting spirometry readings using cough sound features and regression. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterling, M.; Rhee, H.; Bocko, M. Automated Cough Assessment on a Mobile Platform. J. Med. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jeon, J.; Han, Y.J.; Joo, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Im, S. Convolutional Neural Network Classifies Pathological Voice Change in Laryngeal Cancer with High Accuracy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyratne, U.R.; Swarnkar, V.; Setyati, A.; Triasih, R. Cough sound analysis can rapidly diagnose childhood pneumonia. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 2448–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metheny, N.A. Risk Factors for Aspiration. J. Parent. Enter. Nutr. 2002, 26, S26–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.-S.; Lee, E.-G.; Kim, C.-K.; Jung, A.; Song, C.; Im, S. Cough Sounds Recorded via Smart Devices as Useful Non-Invasive Digital Biomarkers of Aspiration Risk: A Case Report. Sensors 2021, 21, 8056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238056
Kang H-S, Lee E-G, Kim C-K, Jung A, Song C, Im S. Cough Sounds Recorded via Smart Devices as Useful Non-Invasive Digital Biomarkers of Aspiration Risk: A Case Report. Sensors. 2021; 21(23):8056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238056
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Hye-Seon, Eung-Gu Lee, Cheol-Ki Kim, Andy Jung, Catherine Song, and Sun Im. 2021. "Cough Sounds Recorded via Smart Devices as Useful Non-Invasive Digital Biomarkers of Aspiration Risk: A Case Report" Sensors 21, no. 23: 8056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238056
APA StyleKang, H.-S., Lee, E.-G., Kim, C.-K., Jung, A., Song, C., & Im, S. (2021). Cough Sounds Recorded via Smart Devices as Useful Non-Invasive Digital Biomarkers of Aspiration Risk: A Case Report. Sensors, 21(23), 8056. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238056





