A Dual Approach of an Oil–Membrane Composite and Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode to Mitigate Biofluid Interferences
Abstract
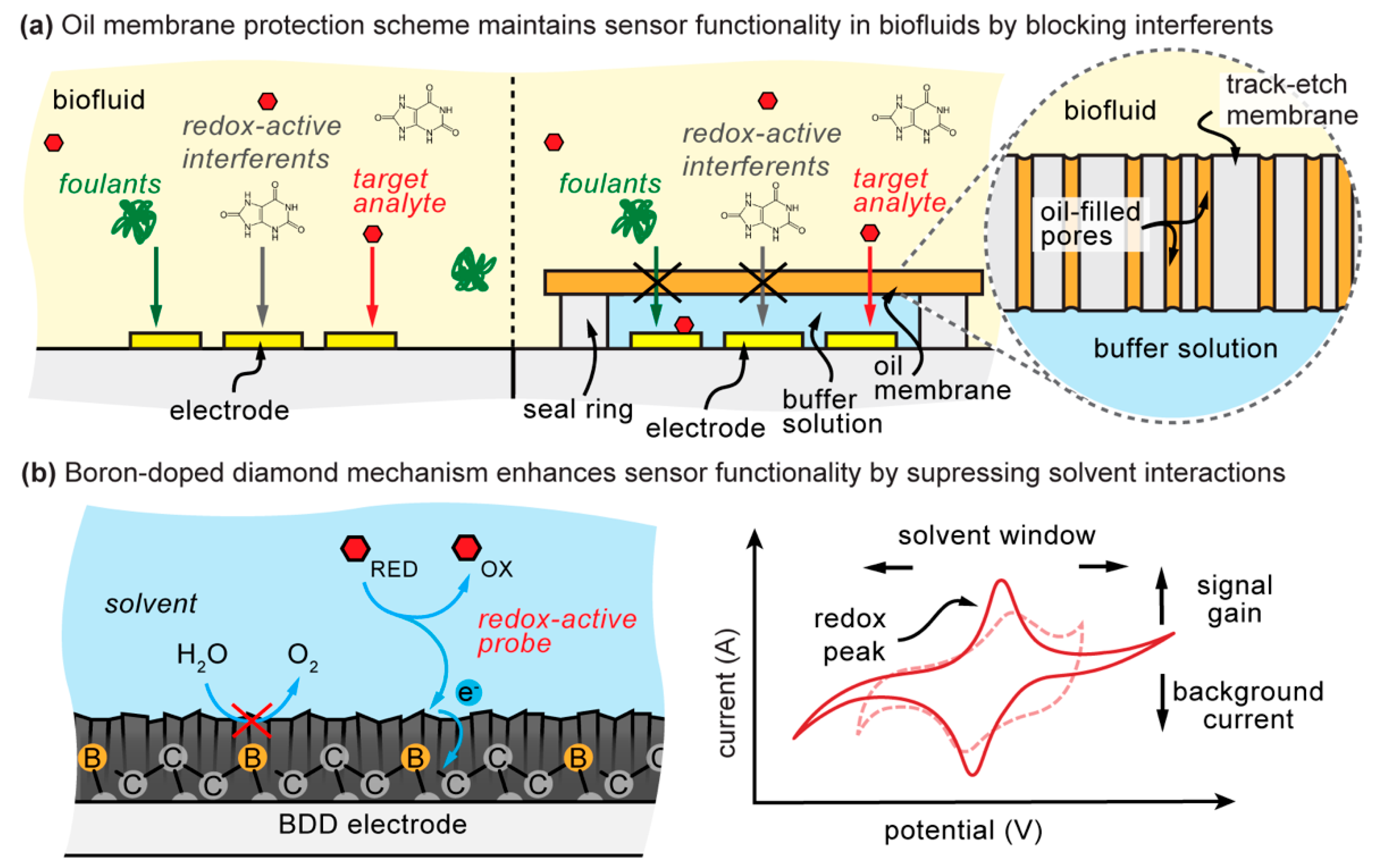
:1. Introduction
2. Background and Limitations of Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Electrode Storage and Preparation
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3.5. Oil–Membrane Composite Protection
3.6. Analysis of Titration Data
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Boron-Doped Diamond Displays Wide Potential Window
4.2. Boron-Doped Diamond Outperforms Gold in Buffer
4.3. Boron-Doped Diamond Performance Significantly Reduced in Biofluid
4.4. Oil–Membrane Protection Maintains Boron-Doped Diamond Performance in Biofluids
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Gamella, M.; Serafín, V.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Beyond sensitive and selective electrochemical biosensors: Towards continuous, real-time, antibiofouling and calibration-free devices. Sensors 2020, 20, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikenfeld, J.; Jajack, A.; Feldman, B.; Granger, S.W.; Gaitonde, S.; Begtrup, G.; Katchman, B.A. Accessing analytes in biofluids for peripheral biochemical monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, S.O. What Are Clinically Relevant Levels of Cellular and Biomolecular Analytes? ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, M.C.; Debrosse, M.; Grigsby, C.C.; Naik, R.R.; Hussain, S.M.; Heikenfeld, J.; Kim, S.S. Achievements and Challenges for Real-Time Sensing of Analytes in Sweat within Wearable Platforms. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo-Currás, N.; Dauphin-Ducharme, P.; Scida, K.; Chávez, J.L. From the beaker to the body: Translational challenges for electrochemical, aptamer-based sensors. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1288–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchitta, G.; Spanu, A.; Babudieri, S.; Latte, G.; Madeddu, G.; Galleri, G.; Nuvoli, S.; Bagella, P.; Demartis, M.I.; Fiore, V.; et al. Enzyme biosensors for biomedical applications: Strategies for safeguarding analytical performances in biological fluids. Sensors 2016, 16, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masson, J.F. Consideration of Sample Matrix Effects and “biological” Noise in Optimizing the Limit of Detection of Biosensors. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3290–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.; Gutknecht, J. Permeability of small nonelectrolytes through lipid bilayer membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 1986, 90, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannesschlaeger, C.; Horner, A.; Pohl, P. Intrinsic Membrane Permeability to Small Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5922–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berben, P.; Bauer-Brandl, A.; Brandl, M.; Faller, B.; Flaten, G.E.; Jacobsen, A.C.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P. Drug permeability profiling using cell-free permeation tools: Overview and applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 119, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical biosensors—Sensor principles and architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, F.; Magner, E. Biosensors—Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Sensors 2020, 20, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.S.; Gifford, R. Biosensors for real-time in vivo measurements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2388–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotanen, C.N.; Moussy, F.G.; Carrara, S.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Implantable enzyme amperometric biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, J.V. A practical guide to using boron doped diamond in electrochemical research. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 2935–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einaga, Y. Diamond electrodes for electrochemical analysis. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, S.J.; Ayres, Z.J.; Macpherson, J.V. Boron Doped Diamond: A Designer Electrode Material for the Twenty-First Century. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 11, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Einaga, Y. Effect of sp2 species in a boron-doped diamond electrode on the electrochemical reduction of CO2. Electrochem. Commun. 2020, 115, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, T.L.; Cobb, S.J.; Macpherson, J.V. An sp2 Patterned Boron Doped Diamond Electrode for the Simultaneous Detection of Dissolved Oxygen and pH. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yokota, Y.; Wong, R.A.; Kim, Y.; Einaga, Y. Unusual Electrochemical Properties of Low-Doped Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes Containing sp2 Carbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, M.C.; Xu, J.; Strojek, J.W.; Swain, G.M. Polycrystalline diamond electrodes: Basic properties and applications as amperometric detectors in flow injection analysis and liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 397, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.S.; de Moraes, M.C.; Rocha-Filho, R.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O.; Cass, Q.B. A multidimensional high performance liquid chromatography method coupled with amperometric detection using a boron-doped diamond electrode for the simultaneous determination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in bovine milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 654, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouillon, R.; O’Hare, D. Comparison of glassy carbon and boron doped diamond electrodes: Resistance to biofouling. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6586–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trouillon, R.; O’Hare, D.; Einaga, Y. Effect of the doping level on the biological stability of hydrogenated boron doped diamond electrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5422–5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, J.; Wei, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhou, K.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, S.; Zhu, R.; Yang, W.; Lin, C.-T.; et al. Antifouling nanoporous diamond membrane for enhanced detection of dopamine in human serum. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Connal, L.A. Antibiofouling polymer interfaces: Poly(ethylene glycol) and other promising candidates. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Antifouling (Bio)materials for electrochemical (bio)sensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svítková, J.; Ignat, T.; Švorc, Ľ.; Labuda, J.; Barek, J. Chemical Modification of Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes for Applications to Biosensors and Biosensing. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 46, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, T.; Ujie, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Einaga, Y.; Daidoji, T.; Nakaya, T.; Sato, T. Avian Influenza Virus Detection by Optimized Peptide Termination on a Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeser, J.; Alting, N.F.A.; Permentier, H.P.; Bruins, A.P.; Bischoff, R. Boron-doped diamond electrodes for the electrochemical oxidation and cleavage of peptides. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6626–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.D.; Nugent, P.F. The electrochemistry of gold: I. The redox behaviour of the metal in aqueous media. Gold Bull. 1997, 30, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burke, L.D.; Nugent, P.F. The electrochemistry of gold: II The electrocatalytic behaviour of the metal in aqueous media. Gold Bull. 1998, 31, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Makaraviciute, A.; Pettersson, J.; Zhang, S.L.; Nyholm, L.; Zhang, Z. Revisiting the factors influencing gold electrodes prepared using cyclic voltammetry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandford, C.; Edwards, M.A.; Klunder, K.J.; Hickey, D.P.; Li, M.; Barman, K.; Sigman, M.S.; White, H.S.; Minteer, S.D. A synthetic chemist’s guide to electroanalytical tools for studying reaction mechanisms. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6404–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Debrosse, M.; Brothers, M.; Kim, S.; Sereda, A.; Ivanov, N.; Hussain, S.; Heikenfeld, J. Oil-Membrane Protection of Electrochemical Sensors for Fouling- and pH-Insensitive Detection of Lipophilic Analytes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 53553–53563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Environment | Electrode | Sensitivity (ΔC/mM) | LOD (μM) | LOD Fold Reduction (High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1× PBS | BDD | 22.7 ± 2.6 | 1.03 ± 0.43 | 142 (365) |
| Gold | 50.8 ± 0.6 | 116 ± 63 | ||
| Serum | BDD | 0.97 ± 0.53 | 83 ± 47 | --- |
| Gold | 36.0 ± 1.5 | 15.4 ± 3.8 |
| Membrane | Sensitivity (ΔC/mM) | LOD (μM) | LOD Fold Reduction (High) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Castor Oil | 7.8 ± 2.8 | 1.8 ± 1.3 | 84 (247) |
| No Oil | 1.19 ± 0.45 | 82 ± 43 |
| Electrode | Sensitivity (ΔC/mM) | LOD (μM) | LOD Fold Reduction (High) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDD | 62.9 ± 3.2 | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 185 (303) |
| Gold | 52.6 ± 3.9 | 155 ± 20 |
| Membrane | Sensitivity (ΔC/mM) | LOD (μM) | LOD Fold Reduction (High) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Castor Oil | 61.5 ± 6.0 | 7.3 ± 4.2 | 13 (34) |
| None | 48.9 ± 4.6 | 6.7 ± 3.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeBrosse, M.; Yuan, Y.; Brothers, M.; Karajic, A.; van Duren, J.; Kim, S.; Hussain, S.; Heikenfeld, J. A Dual Approach of an Oil–Membrane Composite and Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode to Mitigate Biofluid Interferences. Sensors 2021, 21, 8063. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238063
DeBrosse M, Yuan Y, Brothers M, Karajic A, van Duren J, Kim S, Hussain S, Heikenfeld J. A Dual Approach of an Oil–Membrane Composite and Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode to Mitigate Biofluid Interferences. Sensors. 2021; 21(23):8063. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238063
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeBrosse, Madeleine, Yuchan Yuan, Michael Brothers, Aleksandar Karajic, Jeroen van Duren, Steve Kim, Saber Hussain, and Jason Heikenfeld. 2021. "A Dual Approach of an Oil–Membrane Composite and Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode to Mitigate Biofluid Interferences" Sensors 21, no. 23: 8063. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238063
APA StyleDeBrosse, M., Yuan, Y., Brothers, M., Karajic, A., van Duren, J., Kim, S., Hussain, S., & Heikenfeld, J. (2021). A Dual Approach of an Oil–Membrane Composite and Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode to Mitigate Biofluid Interferences. Sensors, 21(23), 8063. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21238063






