Evaluation of Solid Particle Number Sensors for Periodic Technical Inspection of Passenger Cars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Procedure
2.2. PTI Sensors
2.2.1. Sampling and Measurement Technologies
2.2.2. Calibration Values
2.3. Vehicles
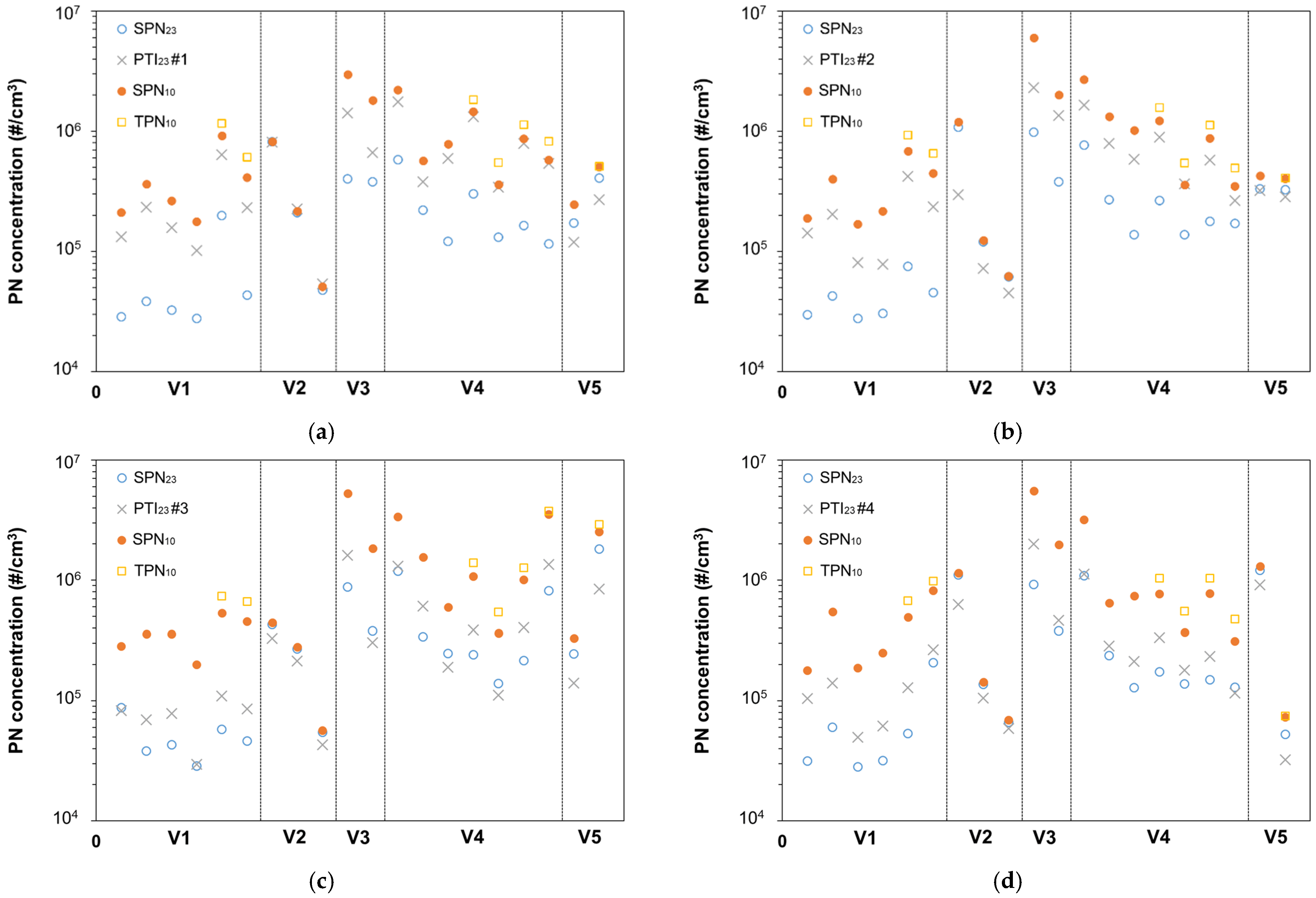
3. Results
3.1. Vehicles without Particulate Filter
3.2. Malfunctioning DPF
3.3. After DPF Regeneration
3.4. High Sub-23 nm Fraction
3.5. Total Particles
3.6. Summary of Results
4. Discussion
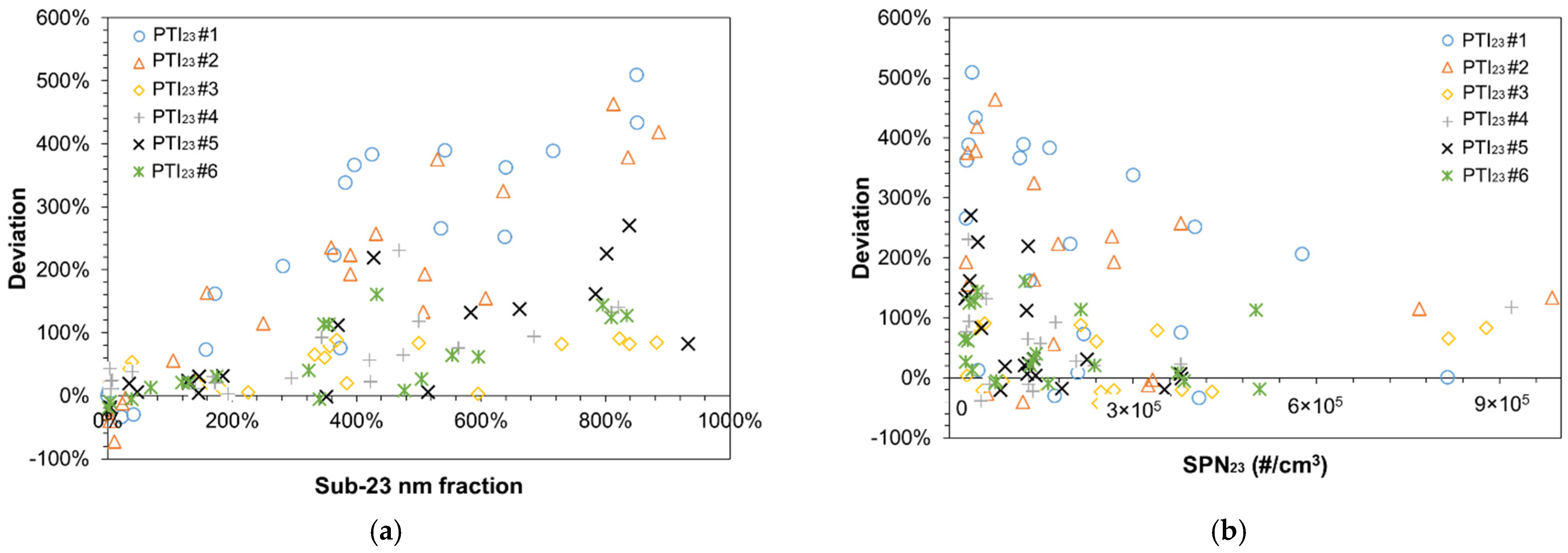
4.1. The Role of Sub-23 nm Particles in the PTI Sensors Deviation
4.2. Sub-23 nm Particles at Idling
4.3. The Importance of PTI Sensors Efficiency in the Sub-23 nm Size Region
4.4. Gasoline Vehicles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, J.M.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung Cancer, Cardiopulmonary Mortality, and Long-Term Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Maricq, M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dardiotis, C.; Wang, X.; Axmann, H.; Bergmann, A.; Schindler, W. Review of Motor Vehicle Particulate Emissions Sampling and Measurement: From Smoke and Filter Mass to Particle Number. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 67, 719–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Joshi, A.; Ntziachristos, L.; Dilara, P. European Regulatory Framework and Particulate Matter Emissions of Gasoline Light-Duty Vehicles: A Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, A.; Matter, U.; Scheidegger, G.; Czerwinski, J.; Wyser, M.; Kieser, D.; Weidhofer, J. Particulate Traps for Retro-Fitting Construction Site Engines VERT: Final Measurement and Implementation. SAE Tech. Pap. 1999, 90092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.; Olfert, J.; Wong, K.; Kunert, S.; Richter, J.M. Effect of Engine-out Soot Emissions and the Frequency of Regeneration on Gasoline Particulate Filter Efficiency. SAE Tech. Pap. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, T.; Glasson, T.; Rose, D.; Ingram-Ogunwumi, R.; Wu, H. Next Generation Gasoline Particulate Filters for Uncatalyzed Applications and Lowest Particulate Emissions. SAE Tech. Pap. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, A.; Guiseppin, L.; Blangiardo, M.; Ghersi, V.; Fuller, G.W. A Tale of Two Cities: Is Air Pollution Improving in Paris and London? Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murzyn, F.; Sioutas, C.; Cavellin, L.D.; Joly, F.; Baudic, A.; Mehel, A.; Cuvelier, P.; Varea, E.; Rouland, B.P. Assessment of Air Quality in Car Cabin in and around Paris from On-Board Measurements and Comparison with 2007 Data. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 158, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstandopoulos, A.G.; Kostoglou, M.; Skaperdas, E.; Papaioannou, E.; Zarvalis, D.; Kladopoulou, E. Fundamental Studies of Diesel Particulate Filters: Transient Loading, Regeneration and Aging. SAE Tech. Pap. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B. Particle Number Emissions of a Diesel Vehicle during and between Regeneration Events. Catalysts 2020, 10, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H. Improving Methodology of Particulate Measurement in Periodic Technical Inspection with High-Sensitivity Techniques: Laser Light Scattering Photometry and Particle Number Method. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2019, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, G.A.; Cutler, W.A.; Warren, C.J. Thermal Durability of Wall-Flow Ceramic Diesel Particulate Filters. SAE Tech. Pap. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, N.; Nickel, K.G.; Engel, C.; Mattern, A. Mechanisms and Orientation Dependence of the Corrosion of Single Crystal Cordierite by Model Diesel Particulate Ashes. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Fox, J.T.; Hunsicker, R. Characterizing Diesel Particulate Filter Failure during Commercial Fleet Use Due to Pinholes, Melting, Cracking, and Fouling. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- UN ECE. Tampering of Emissions Control Systems. Available online: https://unece.org/DAM/trans/doc/2019/wp29grpe/GRPE-78-04e.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Boveroux, F.; Cassiers, S.; Buekenhoudt, P.; Chavatte, L.; De Meyer, P.; Jeanmart, H.; Verhelst, S.; Contino, F. Feasibility Study of a New Test Procedure to Identify High Emitters of Particulate Matter during Periodical Technical Inspection. SAE Tech. Pap. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H.; Lutz, T.; Mayer, A. A New Periodic Technical Inspection for Particle Emissions of Vehicles. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2019, 5, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, C.; Victor, V.M.; Pierre, B.; Carsten, G.; Jelica, P.; Dario, M.; Robert, L.; Barouch, G.; Massimo, C.; Marcos, O.G.; et al. Joint Research Centre 2019 Light-Duty Vehicles Emissions Testing, JRC122035; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Posada, F.; Bandivadekar, A. Global Overview of On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) Systems for Heavy-Duty Vehicles. Available online: https://theicct.org/sites/default/files/publications/ICCT_Overview_OBD-HDVs_20150209.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, P.; He, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; He, W.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, Q.; et al. On-Board Monitoring (OBM) for Heavy-Duty Vehicle Emissions in China: Regulations, Early-Stage Evaluation and Policy Recommendations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.; Rhys-Tyler, G. New Insights from Comprehensive On-Road Measurements of NOx, NO2 and NH3 from Vehicle Emission Remote Sensing in London, UK. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruening, C.; Bonnel, P.; Clairotte, M.; Giechaskiel, B.; Valverdre, V.; Zardini, A.; Carriero, M. Potential of Remote Sensing Devices (RSDs) to Screen Vehicle Emissions; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/9f6af994-fa26-11e9-8c1f-01aa75ed71a1/language-en (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Ropkins, K.; DeFries, T.H.; Pope, F.; Green, D.C.; Kemper, J.; Kishan, S.; Fuller, G.W.; Li, H.; Sidebottom, J.; Crilley, L.R.; et al. Evaluation of EDAR Vehicle Emissions Remote Sensing Technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadijk, G.; Elstgeest, M.; Ligterink, N.E.; Van der Mark, P.J. Investigation into a Periodic Technical Inspection (PTI) Test Method to Check for Presence and Proper Functioning of Diesel Particulate Filters in Light-Duty Diesel Vehicles–Part 2; TNO: Hague, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Valverdre, V.; Clairotte, M. Comparisons of Laboratory and On-Road Type-Approval Cycles with Idling Emissions. Implications for Periodical Technical Inspection (PTI) Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Clairotte, M.; Grigoratos, T.; Zardini, A.; Perujo, A.; Martini, G. Particle Number Measurements in the European Legislation and Future JRC Activities. Combust. Engines 2018, 174, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Valverdre, V.; Kontses, A.; Melas, A.; Martini, G.; Balazs, A.; Andersson, J.; Samaras, Z.; Dilara, P. Particle Number Emissions of a Euro 6d-Temp Gasoline Vehicle under Extreme Temperatures and Driving Conditions. Catalysts 2021, 11, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Lutz, T.; Spielvogel, J.; Franken, O.; Heuser, M. PTI by Particle Count PN at Low Idle; TA-024/21; VERT Association: Niederweningen, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kupper, M.; Kraft, M.; Boies, A.; Bergmann, A. High-Temperature Condensation Particle Counter Using a Systematically Selected Dedicated Working Fluid for Automotive Applications. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Wang, X.; Horn, H.G.; Spielvogel, J.; Gerhart, C.; Southgate, J.; Jing, L.; Kasper, M.; Drossinos, Y.; Krasebrink, A. Calibration of Condensation Particle Counters for Legislated Vehicle Number Emission Measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierz, M.; Meier, D.; Steigmeier, P.; Burtscher, H. Aerosol Measurement by Induced Currents. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schriefl, M.A.; Bergmann, A. Design Principles for Diffusion Chargers Sensing Particle Number Concentration. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Sensors, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rüggeberg, T.; Fierz, M.; Burtscher, H.; Melas, A.D.; Deloglou, D.; Papaioannou, E.; Konstandopoulos, A.G. Application of DC-Sensors to Measure Ultrafine Particles from Combustion Engines. In Proceedings of the 23rd Transport and Air Pollution Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece, 15–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Drossinos, Y. Theoretical Investigation of Volatile Removal Efficiency of Particle Number Measurement Systems. SAE Int. J. Engines 2010, 3, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H.; Baltensperger, U.; Bukowiecki, N.; Cohn, P.; Hüglin, C.; Mohr, M.; Matter, U.; Nyeki, S.; Schmatloch, V.; Streit, N.; et al. Separation of Volatile and Non-Volatile Aerosol Fractions by Thermodesorption: Instrumental Development and Applications. J. Aerosol Sci. 2001, 32, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalek, I.S.; Kittelson, D.B. Real Time Measurement of Volatile and Solid Exhaust Particles Using a Catalytic Stripper. In Proceedings of the International Congress & Exposition, Detroit, MI, USA, 27 February–2 March 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Katsaounis, D.; Samaras, Z.; Bergmann, A. Evaluation of an Oxidation Catalyst (‘Catalytic Stripper’) in Eliminating Volatile Material from Combustion Aerosol. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 57, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melas, A.D.; Koidi, V.; Deloglou, D.; Daskalos, E.; Zarvalis, D.; Papaioannou, E.; Konstandopoulos, A.G. Development and Evaluation of a Catalytic Stripper for the Measurement of Solid Ultrafine Particle Emissions from Internal Combustion Engines. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Melas, A.D.; Lähde, T.; Martini, G. Non-Volatile Particle Number Emission Measurements with Catalytic Strippers: A Review. Vehicles 2020, 2, 342–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Melas, A.D.; Valverdre, V.; Clairotte, M. Uncertainty of Laboratory and Portable Solid Particle Number Systems for Regulatory Measurements of Vehicle Emissions. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Funato, K.; Sakurai, H. Application of the PMP Methodology to the Measurement of Sub-23 Nm Solid Particles: Calibration Procedures, Experimental Uncertainties, and DATA Correction Methods. J. Aerosol Sci. 2015, 88, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Mamakos, A.; Andersson, J.; Dilara, P.; Martini, G.; Schindler, W.; Bergmann, A. Measurement of Automotive Nonvolatile Particle Number Emissions within the European Legislative Framework: A Review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 719–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Schwelberger, M.; Kleinbach, T.; Roske, H.; Teti, E.; van den Bos, T.; Neils, P.; Delacroix, C.; Jakobsson, T.; et al. Particle Number Measurements Directly from the Tailpipe for Type Approval of Heavy-Duty Engines. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terres, A.; Giechaskiel, B.; Nowak, A.; Ebert, V. Calibration Uncertainty of 23nm Engine Exhaust Condensation Particle Counters with Soot Generators: A European Automotive Laboratory Comparison. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, S.; Maricq, M.M.; Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. Application of the Dual Pegasor Particle Sensor to Real-Time Measurement of Motor Vehicle Exhaust PM. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 103, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; McNeill, V.F.; Collins, D.R.; Flagan, R.C. Fast Mixing Condensation Nucleus Counter: Application to Rapid Scanning Differential Mobility Analyzer Measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainschab, M.; Schriefl, M.A.; Bergmann, A. Particle Number Measurements within Periodic Technical Inspections: A First Quantitative Assessment of the Influence of Size Distributions and the Fleet Emission Reduction. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 8, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosinski, W.; Wisniowski, P. Verifying the Efficiency of a Diesel Particulate Filter Using Particle Counters with Two Different Measurements in Periodic Technical Inspection of Vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Lähde, T.; Giechaskiel, B. Verification of NPTI-Instruments for Diesel and Petrol Vehicles—First Results. Presented at the ETH Conference on Nanoparticles, Zurich, Switzerland, 21 June 2018; Available online: https://www.nanoparticles.ch/archive/2018_Suarez_PR.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Schriefl, M.A.; Bergmann, A.; Fierz, M. Design Principles for Sensing Particle Number Concentration and Mean Particle Size with Unipolar Diffusion Charging. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, H. Physical Characterization of Particulate Emissions from Diesel Engines: A Review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 896–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Bergmann, A.; Samaras, Z. Impact of Selective Catalytic Reduction on Exhaust Particle Formation over Excess Ammonia Events. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11527–11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamakos, A.; Schwelberger, M.; Fierz, M.; Giechaskiel, B. Effect of Selective Catalytic Reduction on Exhaust Nonvolatile Particle Emissions of Euro VI Heavy-Duty Compression Ignition Vehicles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Filippo, A.; Maricq, M.M. Diesel Nucleation Mode Particles: Semivolatile or Solid? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7957–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Lähde, T.; Drossinos, Y. Regulating Particle Number Measurements from the Tailpipe of Light-Duty Vehicles: The next Step? Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
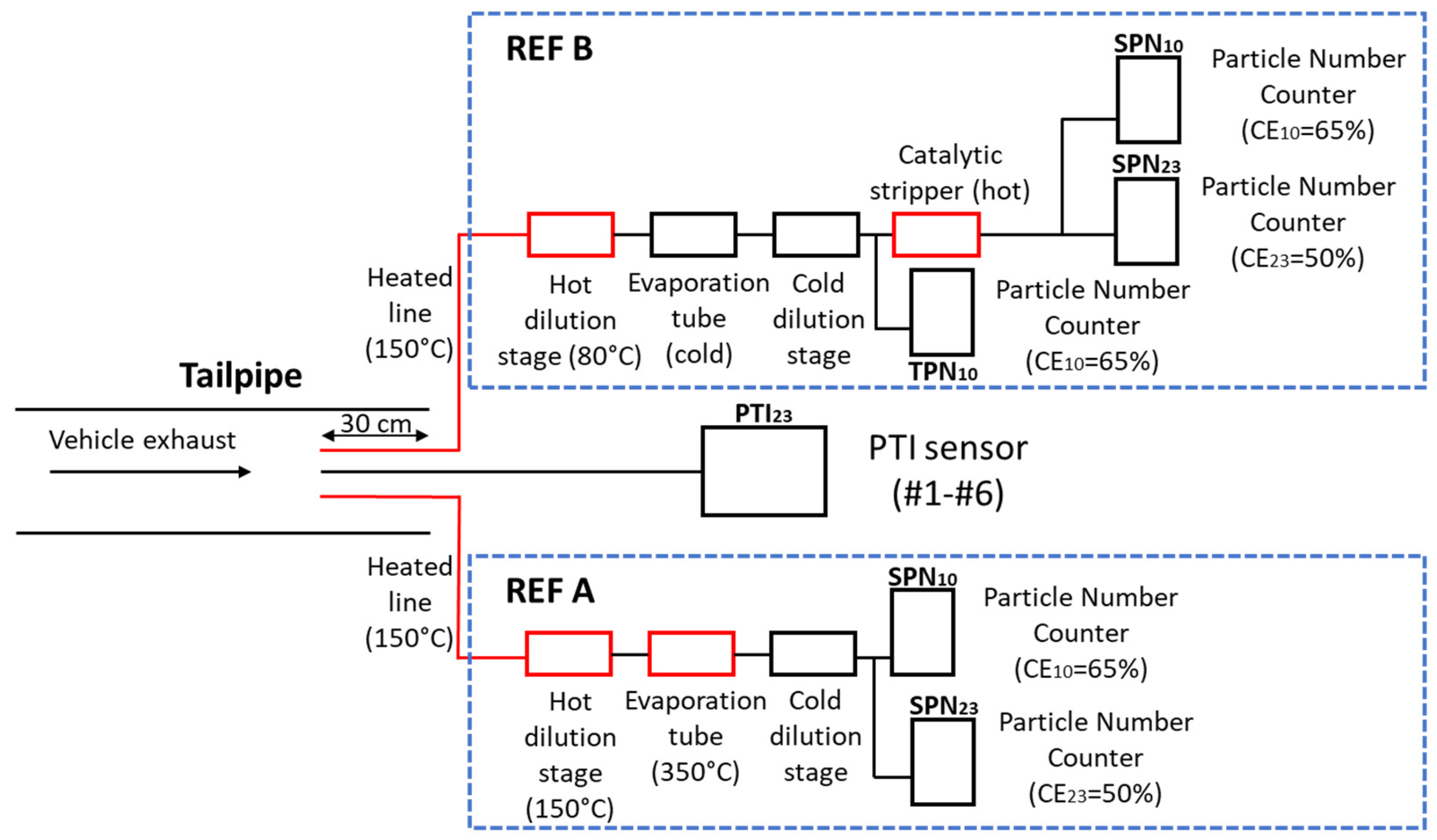
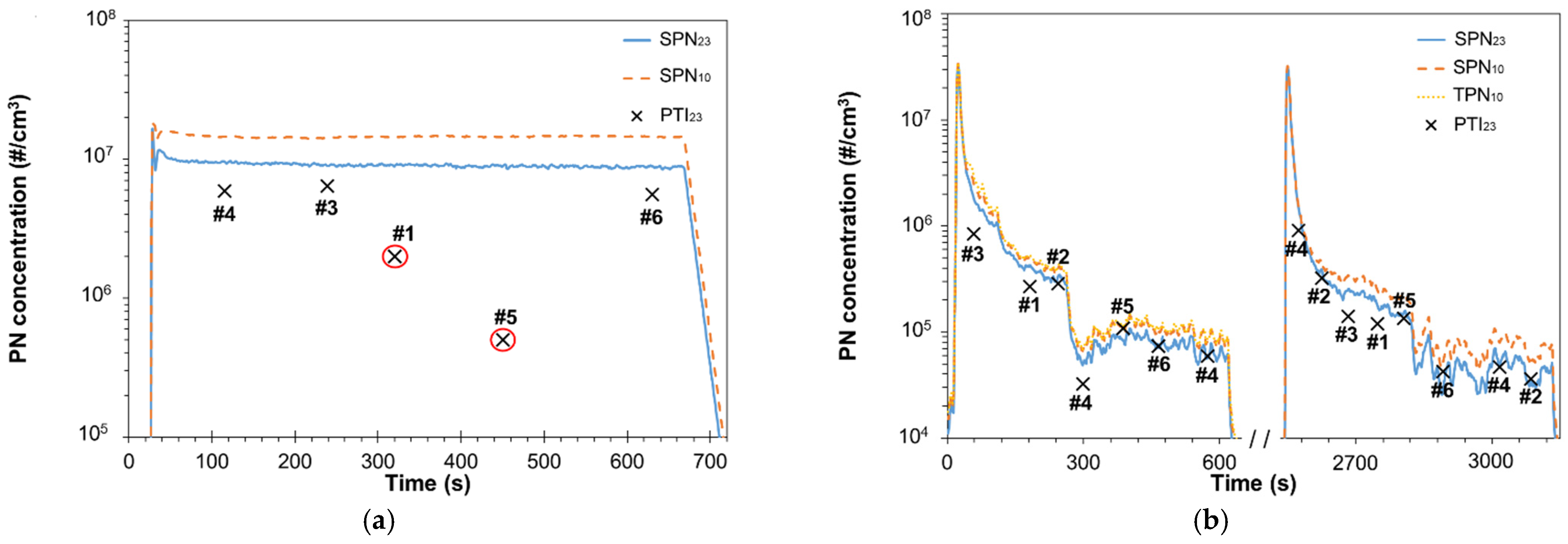
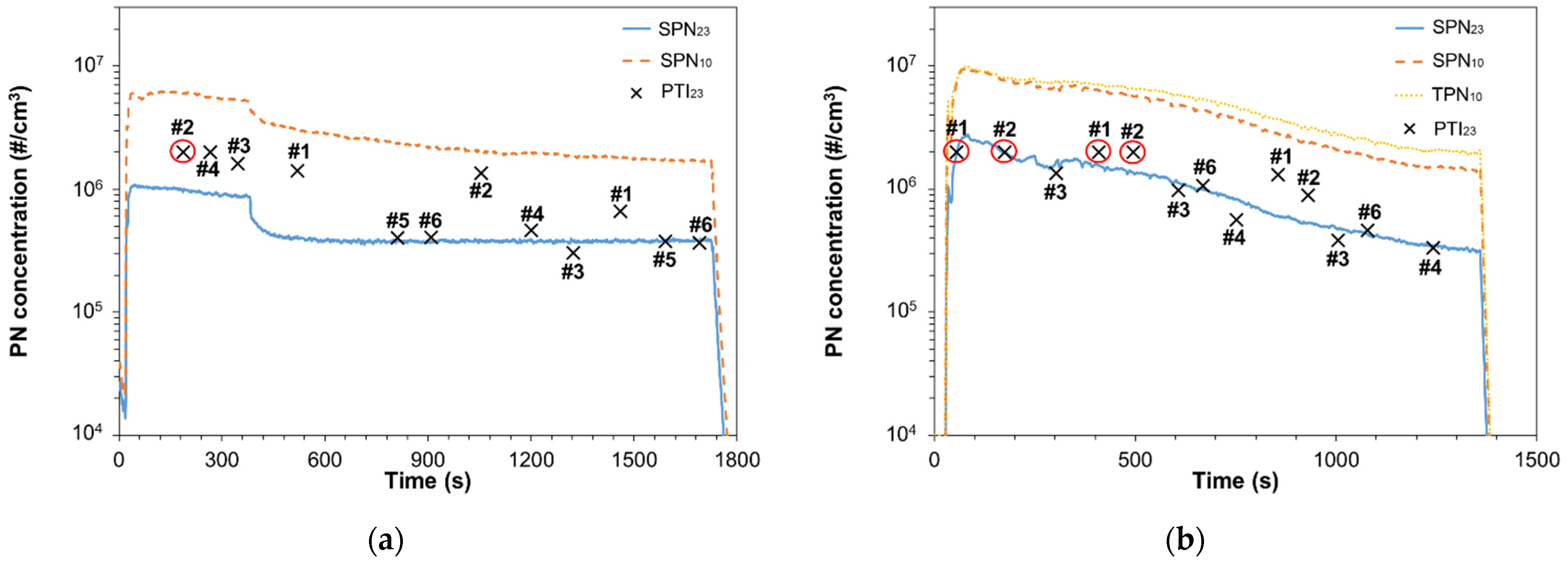
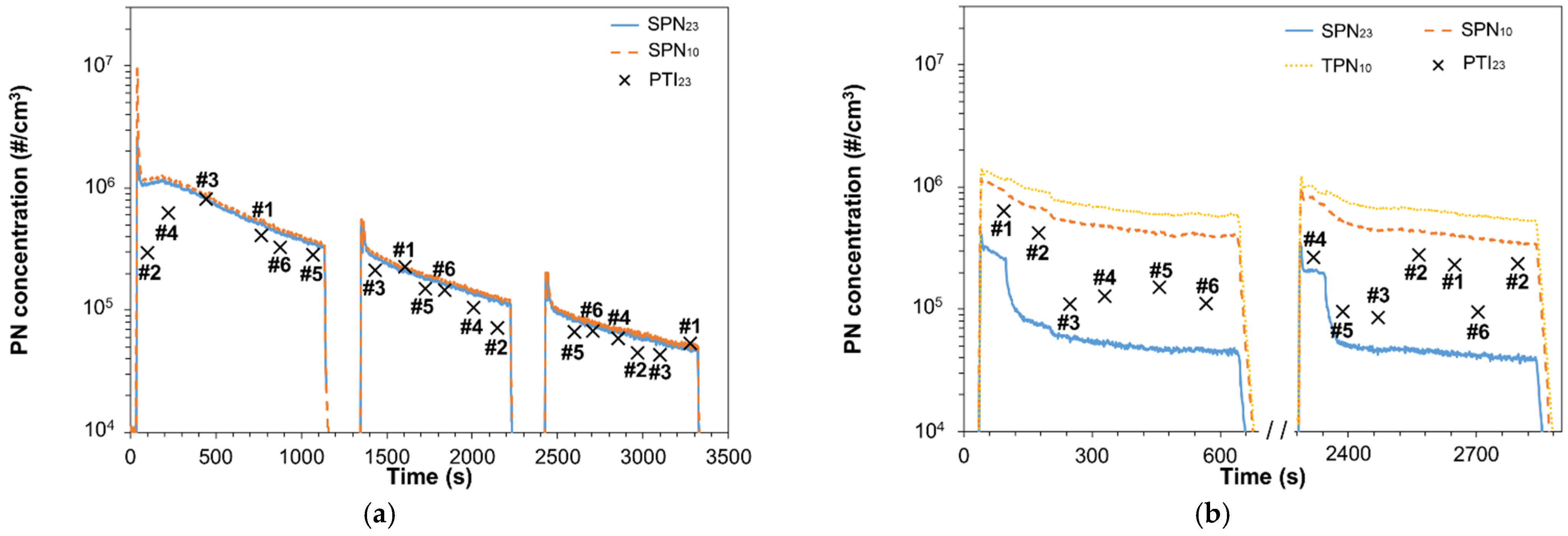

| PTI | Sampling Line | Dilution (Temp.) | Volatile Particle Remover | Particle Detector | Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Heated (75 °C) | No | Thermal denuder (150 °C) | DC | NL |
| #2 | Heated (90 °C) | Venturi (150 °C) | Evaporation tube (200 °C) | DC | NL |
| #3 | Heated (60 °C) | No | Evaporation tube (300 °C) | DC | N/A |
| #4 | Heated (70 °C) | 200:1 (ambient) | Evaporation tube (250 °C) | CPC | NL |
| #5 | Not heated | 20:1 (ambient) | Catalytic stripper (350 °C) | CPC | N/A |
| #6 | Not heated | 10:1 (ambient) | Catalytic stripper (350 °C) | CPC | CH |
| Counting Efficiency | Linearity (80 nm) | VRE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 nm | 50 nm | 80 nm | 200 nm | Polydisperse | 30 nm Tetracontane | |
| CH | <0.50 | * | 0.70–1.30 | <1.30 | >90% (<105 #/cm3) | |
| NL | 0.20–0.60 | 0.60–1.30 | 0.70–1.30 | - | 0.75–1.25 | >95% (<105 #/cm3) |
| VERT | 0.20–0.60 | 0.60–1.30 | 0.70–1.30 | <2.00 | 0.75–1.25 | >95% (<105 #/cm3) |
| #1 | 0.34 | 0.75 | 1.00 | - | 1.03 (80 nm) | >95% (104 #/cm3) |
| #2 | 0.47 | 0.86 | 1.12 | - | 0.99 (76 nm) | >95% (105 #/cm3) |
| #3 | 0.43 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 1.67 | 0.99 (37–56 nm) | 100% (>104 #/cm3) |
| #4 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.998 (poly) | 99.9% (3.5 × 104 #/cm3) |
| #5 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 1.02 (70 nm) | 1.04 | N/A | N/A |
| #6 | 0.33 | 0.55 (41 nm) | - | - | 1.04 (no size info) | >99% |
| Code | Euro | Fuel | Year | Mileage (km) | Engine Displacement (cm3) | Power (kW) | Particulate Filter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | 6b | Diesel | 2017 | 23,540 | 1.560 | 88 | Yes |
| V2 | 6d | Diesel | 2019 | 4.100 | 1.999 | 132 | Yes |
| V3 | 4 | Diesel | 2009 | 209,000 | 1.997 | 100 | Yes |
| V4 | 6d | Diesel | 2020 | 4.200 | 1.968 | 110 | Yes 1 |
| V5 | 5b | Gasoline DI | 2012 | 151,831 | 1.197 | 77 | No |
| V6 | 3 | Diesel | 2004 | 286,000 | 2.993 | 150 | No |
| Vehicle | Comment | SPN23 (#/cm3) | SPN10 (#/cm3) | Sub-23 nm Fraction | TPN10 (#/cm3) | Volatiles Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | DPF (high sub-23) | 4.0 × 104 | 3.5 × 105 | 775% | 4.5 × 105 | 47% |
| V2 | DPF (after regen.) | 4.8 × 104 | 5.0 × 104 | 5% | - | |
| V3 | DPF (old) | 3.8 × 105 | 1.7 × 106 | 346% | - | |
| V4 | DPF (bypass) | 2.7 × 105 | 7.0 × 105 | 158% | 1.1 × 106 | 57% |
| V5 | G-DI (no filter) | 7.6 × 104 | 1.0 × 105 | 35% | 1.1 × 105 | 6% |
| V6 | No DPF | 8.9 × 106 | 1.4 × 107 | 63% | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melas, A.; Selleri, T.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Giechaskiel, B. Evaluation of Solid Particle Number Sensors for Periodic Technical Inspection of Passenger Cars. Sensors 2021, 21, 8325. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248325
Melas A, Selleri T, Suarez-Bertoa R, Giechaskiel B. Evaluation of Solid Particle Number Sensors for Periodic Technical Inspection of Passenger Cars. Sensors. 2021; 21(24):8325. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248325
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelas, Anastasios, Tommaso Selleri, Ricardo Suarez-Bertoa, and Barouch Giechaskiel. 2021. "Evaluation of Solid Particle Number Sensors for Periodic Technical Inspection of Passenger Cars" Sensors 21, no. 24: 8325. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248325
APA StyleMelas, A., Selleri, T., Suarez-Bertoa, R., & Giechaskiel, B. (2021). Evaluation of Solid Particle Number Sensors for Periodic Technical Inspection of Passenger Cars. Sensors, 21(24), 8325. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248325







