Enhancing EEG-Based Mental Stress State Recognition Using an Improved Hybrid Feature Selection Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Develop an experimental protocol to induce stress on participants while solving mental arithmetic tasks under time pressure and negative feedback.
- Extract multi-domain features from multi-EEG channels and fuse them to form a large pool of feature vectors.
- Propose a novel EEG feature selection method called mRMR-PSO-SVM to improve the search of local optimal and fit for binary feature selection.
- Validate the proposed method by utilizing our dataset with another three public datasets of EEG on mental stress state and compare its performance with several metaheuristic algorithms.
2. Experiment and Materials
2.1. Participants
2.2. Stress Inducement Method
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Description of Public Datasets
2.4.1. DEAP Dataset
2.4.2. SEED Dataset
2.4.3. EDPMSC Dataset
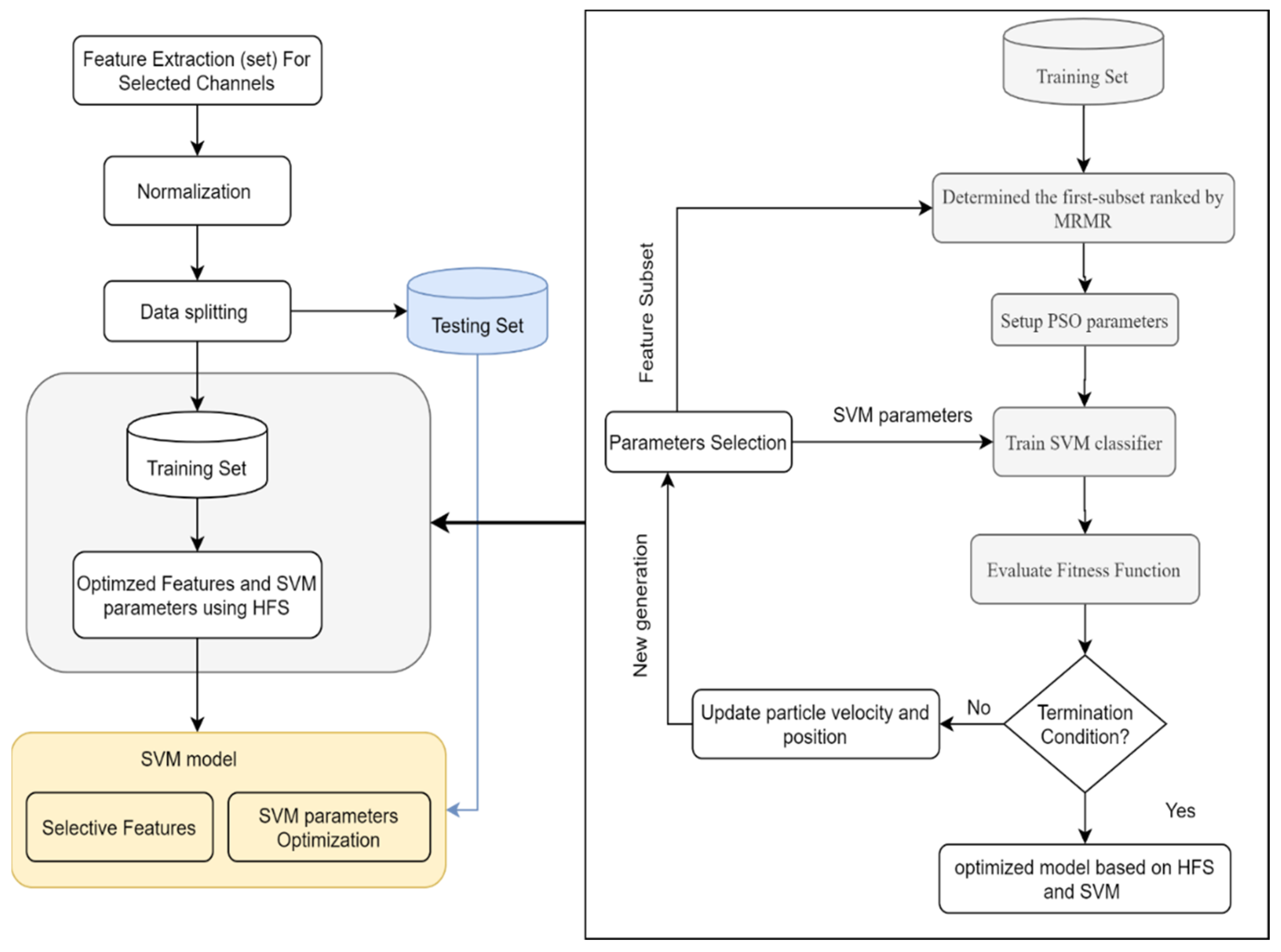
3. Methodology
- Dataset preprocessing
- Multi-domain features are extracted from multi-EEG channels and combined to form a large feature vector.
- Feature selection based on the proposed mRMR-PSO method identifies discriminative features.
- Classification parameters of SVM were optimized using PSO.
- The proposed model was validated with three different public datasets.
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.3. Feature Selection Using mRMR-PSO
3.3.1. Minimum-Redundancy Maximum Relevance (mRMR)
3.3.2. PSO Algorithm
3.3.3. Proposed Hybrid Method: mRMR-PSO-SVM
4. Result
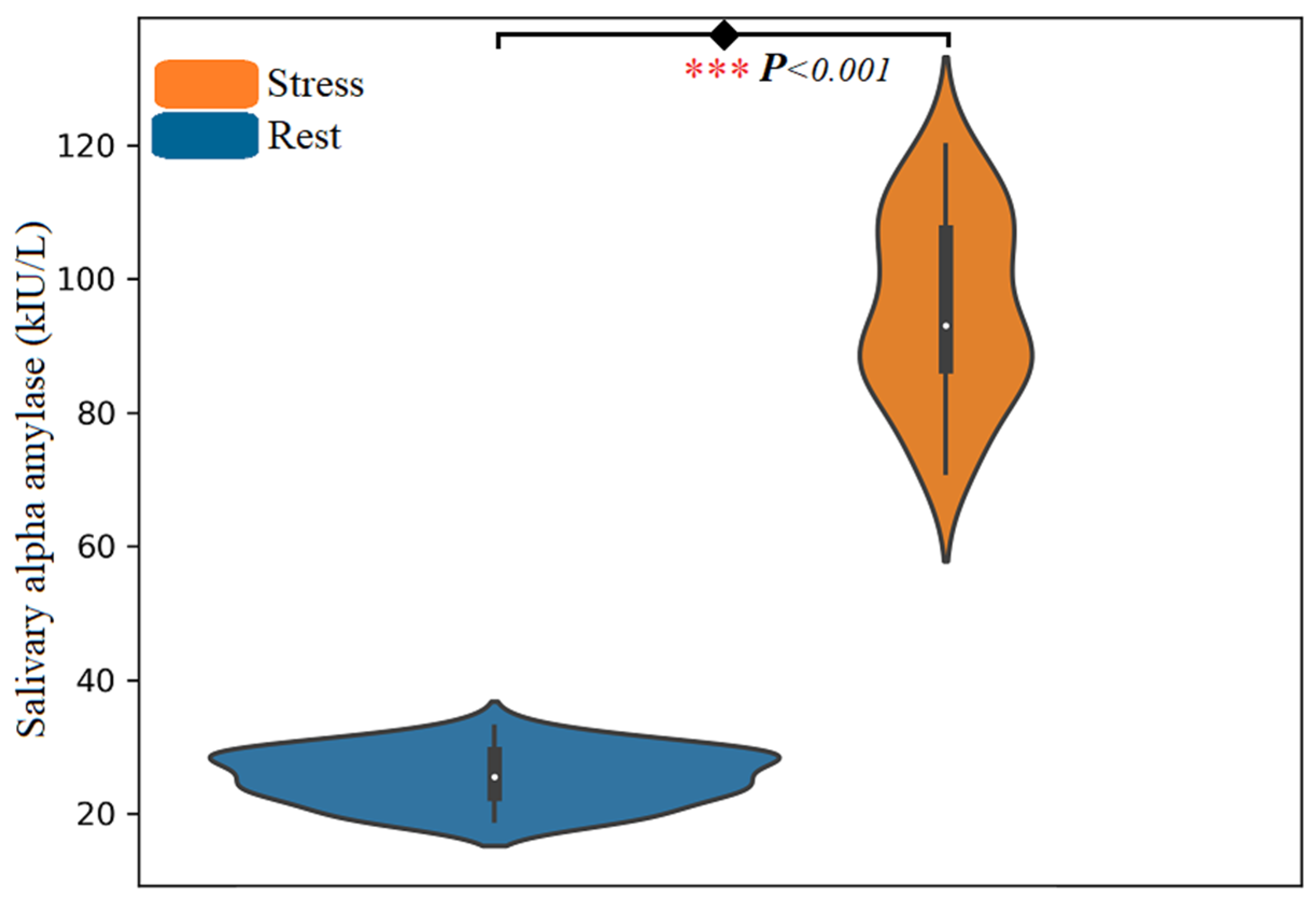
4.1. Statistical Analysis
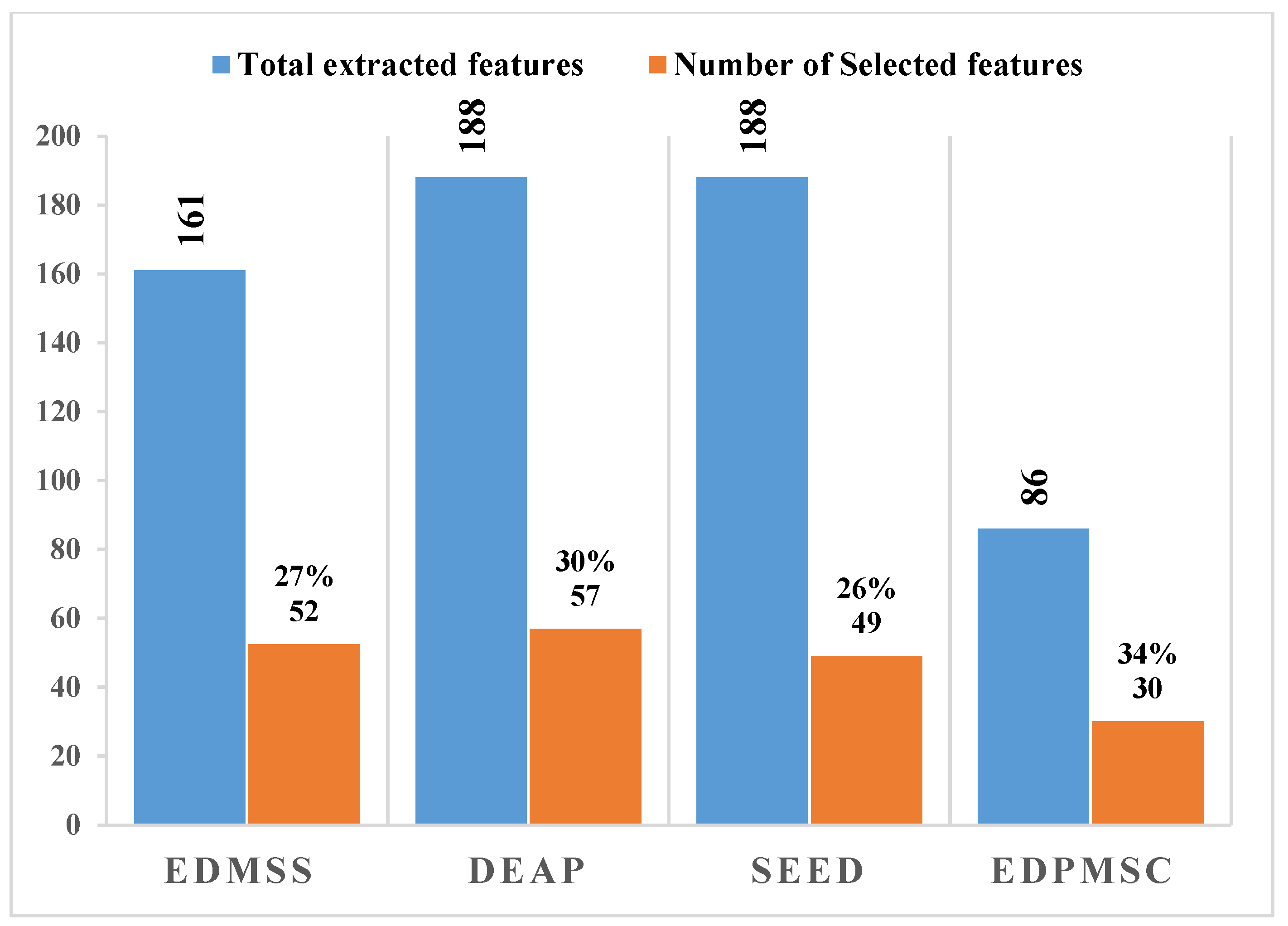
4.2. Performance Analysis of Feature Selection and Multi-Domain Features
5. Discussion
| #Ref. | Dataset | FS-Classifier | Total Feature Vector/ Selected Features | No. Channels | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [50] | DEAP | GA- KNN | 673/not mentioned | 32 | 71.76% |
| [24] | DEAP | Boruta-KNN | 608/288 | 32 | 73.38% |
| [25] | EDPMSC | Wrapper FS- (MLP, SVM) | 90/18 | 4 | 89.30% MLP, 67.85% SVM for pre-active phase |
| [23] | DEAP | 2-D AlexNet-CNN 3-D AlexNet-CNN | 5 PSD bands converted to image | 32 | 84.77%, 86.12% |
| [70] | SEED, DEAP | DWT-BODF (SVM, KNN) | 225 × 30 SEED 576 × 40 DEAP | 62 SEED 32 DEAP | 93.8% SVM (SEED) 77.4% SVM (DEAP) |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katmah, R.; Al-Shargie, F.; Tariq, U.; Babiloni, F.; Al-Mughairbi, F.; Al-Nashash, H. A Review on Mental Stress Assessment Methods Using EEG Signals. Sensors 2021, 21, 5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussien, A.G.; Oliva, D.; Houssein, E.H.; Juan, A.A.; Yu, X. Binary whale optimization algorithm for dimensionality reduction. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Berahmand, K.; Nasiri, E.; Forouzandeh, S. Review of swarm intelligence-based feature selection methods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 100, 104210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Handayani, D.O.D.; Chong, P.P.; Acharya, U.R. Profiling of pornography addiction among children using EEG signals: A systematic literature review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 125, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Z.; Wang, H.; Bezerianos, A.; Li, J. EEG-Based Multiclass Workload Identification Using Feature Fusion and Selection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, T.; Dogan, S.; Subasi, A. EEG-based driving fatigue detection using multilevel feature extraction and iterative hybrid feature selection. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angga Yuwono, H.; Kusuma Wijaya, S.; Prajitno, P. Feature selection with Lasso for classification of ischemic strokes based on EEG signals. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1528, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, M.K.I.; Al Shiam, A.; Islam, M.R.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, T. Discriminative Feature Selection-Based Motor Imagery Classification Using EEG Signal. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 98255–98265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimourta, K.D.; Astrakas, L.G.; Gianni, A.M.; Tzallas, A.T.; Giannakeas, N.; Paliokas, I.; Tsalikakis, D.G.; Tsipouras, M.G. Evaluation of window size in classification of epileptic short-term EEG signals using a Brain Computer Interface software. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2018, 8, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, Z.; Duan, F.; Liu, Y. A Novel Multimodal Approach for Hybrid Brain–Computer Interface. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 89909–89918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, R.A.; Jahromi, G.P.; Shahyad, S.; Meftahi, G.H. A major depressive disorder classification framework based on EEG signals using statistical, spectral, wavelet, functional connectivity, and nonlinear analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 358, 109209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X. EEG emotion recognition using fusion model of graph convolutional neural networks and LSTM. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, Z.; Rehan, M. On identification of driving-induced stress using electroencephalogram signals: A framework based on wearable safety-critical scheme and machine learning. Inf. Fusion 2020, 53, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hag, A.; Handayani, D.; Pillai, T.; Mantoro, T.; Kit, M.H.; Al-Shargie, F. EEG Mental Stress Assessment Using Hybrid Multi-Domain Feature Sets of Functional Connectivity Network and Time-Frequency Features. Sensors 2021, 21, 6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhani, A.R.; Mumtaz, W.; Saad, M.N.B.M.; Kamel, N.; Malik, A.S. Machine Learning Framework for the Detection of Mental Stress at Multiple Levels. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 13545–13556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Badruddin, N.; Kiguchi, M. Towards multilevel mental stress assessment using SVM with ECOC: An EEG approach. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A.; Khalilzadeh, M.A.; Naghibi-Sistani, M.B.; Homam, S.M. Emotional stress recognition using a new fusion link between electroencephalogram and peripheral signals. Iran. J. Neurol. 2015, 14, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, A.; Majid, M.; Anwar, S.M. Human stress classification using EEG signals in response to music tracks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 107, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, P.; Schächinger, H.; Naumann, E.; Schilling, T.M.; Zhang, X.; Larra, M.F. Emotional stress regulation: The role of relative frontal alpha asymmetry in shaping the stress response. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 138, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, A.; Singh, M. Psychological stress detection using phonocardiography signal: An empirical mode decomposition approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 49, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillon, J.; Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Pelayo, F. Stress Assessment by Prefrontal Relative Gamma. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gedam, S.; Paul, S. A Review on Mental Stress Detection Using Wearable Sensors and Machine Learning Techniques. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 84045–84066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodrigo, A.; García-Martínez, B.; Huerta, Á.; Alcaraz, R. Detection of Negative Stress through Spectral Features of Electroencephalographic Recordings and a Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.J.; Kim, J.M. A Hybrid Feature Pool-Based Emotional Stress State Detection Algorithm Using EEG Signals. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arsalan, A.; Majid, M.; Butt, A.R.; Anwar, S.M. Classification of Perceived Mental Stress Using A Commercially Available EEG Headband. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inform. 2019, 23, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Stress Assessment Based on Decision Fusion of EEG and fNIRS Signals. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19889–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, D.; Übeyli, E.D.; Cosic, I. Wavelet transform feature extraction from human PPG, ECG, and EEG signal responses to ELF PEMF exposures: A pilot study. Digit. Signal Process. A Rev. J. 2008, 18, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyakitanont, P.; Lek-uthai, A.; Chomtho, K.; Songsiri, J. A review of feature extraction and performance evaluation in epileptic seizure detection using EEG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 57, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toradmalle, D.; Muthukuru, J.; Sathyanarayana, B. Hybrid Feature Selection Method based on Particle Swarm Optimization and Adaptive local Search Method. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2019, 9, 3228–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafarja, M.M.; Mirjalili, S. Hybrid Whale Optimization Algorithm with simulated annealing for feature selection. Neurocomputing 2017, 260, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, W.A.H.M.; Jantan, A. Novel multi-objective artificial bee colony optimization for wrapper based feature selection in intruction detectoin. Int. J. Adv. Soft Comput. Appl. 2016, 8, 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Browne, W.N. Particle Swarm Optimization for Feature Selection in Classification: A Multi-Objective Approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 1656–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, B.; Anuradha, J. A review of Feature Selection and its methods. Cybern. Inf. Technol. 2019, 19, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Jiao, L. A two-stage hybrid ant colony optimization for high-dimensional feature selection. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 116, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garro, B.A.; Salazar-Varas, R.; Vazquez, R.A. EEG Channel Selection using Fractal Dimension and Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Bangalore, India, 18–21 November 2018; pp. 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 89, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangir, P.; Parmar, S.A.; Trivedi, I.N.; Bhesdadiya, R.H. A novel hybrid Particle Swarm Optimizer with multi verse optimizer for global numerical optimization and Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch problem. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghian, Z.; Akbari, E.; Nematzadeh, H. A hybrid feature selection method based on information theory and binary butterfly optimization algorithm. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 97, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bablani, A.; Edla, D.R.; Tripathi, D.; Dodia, S.; Chintala, S. A Synergistic Concealed Information Test with Novel Approach for EEG Channel Selection and SVM Parameter Optimization. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 3057–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naserbegi, A.; Aghaie, M.; Zolfaghari, A. Implementation of Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO) algorithm to multi-objective loading pattern optimization of a PWR reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 148, 107703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Qi, D.; Alshemmary, E.N. Effective hybrid method for the detection and rejection of electrooculogram (EOG) and power line noise artefacts from electroencephalogram (EEG) mixtures. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 202919–202932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Abutarboush, H.F.; Ganesh, T.; Mohamed, A.W. Metaheuristic algorithms on feature selection: A survey of one decade of research (2009–2019). IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26766–26791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Lu, X.; Sun, G.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Xiao, Y. Bio-Inspired Feature Selection: An Improved Binary Particle Swarm Optimization Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85989–86002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Badruddin, N.; Kiguchi, M. Simultaneous measurement of EEG-fNIRS in classifying and localizing brain activation to mental stress. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2015 International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications ICSIPA, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 October 2015; 2016; pp. 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Assessment of mental stress effects on prefrontal cortical activities using canonical correlation analysis: An fNIRS-EEG study. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Kiguchi, M.; Badruddin, N.; Dass, S.C.; Hani, A.F.M.; Tang, T.B. Mental stress assessment using simultaneous measurement of EEG and fNIRS. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis; Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özerdem, M.S.; Polat, H. Emotion recognition based on EEG features in movie clips with channel selection. Brain Inform. 2017, 4, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zoubi, O.; Awad, M.; Kasabov, N.K. Anytime multipurpose emotion recognition from EEG data using a Liquid State Machine based framework. Artif. Intell. Med. 2018, 86, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, D.; Im, K.; Park, J.H.; Lim, D.S.; Jang, B.; Kim, J.M. Emotional Stress State Detection Using Genetic Algorithm-Based Feature Selection on EEG Signals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, B.L. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from eeg. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019, 10, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tariq, U.; Alex, M.; Mir, H.; Al-Nashash, H. Emotion Recognition Based on Fusion of Local Cortical Activations and Dynamic Functional Networks Connectivity: An EEG Study. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 143550–143562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, R.; Echauz, J.; Tcheng, T.; Litt, B.; Pless, B. Line length: An efficient feature for seizure onset detection. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. 2001, 2, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alimardani, F.; Cho, J.H.; Boostani, R.; Hwang, H.J. Classification of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia using steady-state visual evoked potential based features. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 40379–40388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalan, A.; Majid, M. Human stress classification during public speaking using physiological signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, B.; Zheng, X.; Li, X. EEG-Based Mild Depressive Detection Using Differential Evolution. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 7814–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Direito, B.; Duarte, J.; Teixeira, C.; Schelter, B.; Le Van Quyen, M.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Sales, F.; Dourado, A. Feature selection in high dimensional EEG features spaces for epileptic seizure prediction. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2011, 44, 6206–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Anand, R.; Wang, M. Maximum Relevance and Minimum Redundancy Feature Selection Methods for a Marketing Machine Learning Platform. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Washington, DC, USA, 5–8 October 2019; pp. 442–452. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, R.M.; Lee, H.J. Emotion recognition from EEG brain signals based on particle swarm optimization and genetic search. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Liu, Y.T.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chuang, C.H.; Lin, C.T. Fuzzy Integral with Particle Swarm Optimization for a Motor-Imagery-Based Brain-Computer Interface. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 25, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.T.; Der Lee, J.; Chang, T.C.; Huang, C.H.; Wang, J.J.; Hsu, W.C.; Chan, H.L.; Wai, Y.Y.; Li, K.Y. Discrimination between Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment using SOM and PSO-SVM. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Chen, J. A novel wrapper method for feature selection and its applications. Neurocomputing 2015, 159, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, B.; Sun, S.; Cai, H. EEG-based mild depressive detection using feature selection methods and classifiers. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 136, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.W.; Ying, K.C.; Chen, S.C.; Lee, Z.J. Particle swarm optimization for parameter determination and feature selection of support vector machines. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 35, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurma, R.A.; Aljarah, I.; Sharieh, A.; Mirjalili, S. EvoloPy-FS: An Open-Source Nature-Inspired Optimization Framework in Python for Feature Selection. In Evolutionary Machine Learning Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 131–173. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, L.; Zhao, J.; Fu, W. Emotion Recognition and Channel Selection Based on EEG Signal. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, ICICTA, Changsha, China, 22–23 September 2018; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicska, G.; Kiss, A. Comparing Swarm Intelligence Algorithms for Dimension Reduction in Machine Learning. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2021, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Song, H.; Cheng, Z.; Chang, T.; Bi, Y.; Sun, K. Improvement and Application of Hybrid Firefly Algorithm. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 165458–165477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.A.; Khan, M.J.; Fawad; Amin, Y.; Rizwan, M.; Rahman, M.; Badnava, S.; Mirjavadi, S.S. EEG-based multi-modal emotion recognition using bag of deep features: An optimal feature selection approach. Sensors 2019, 19, 5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

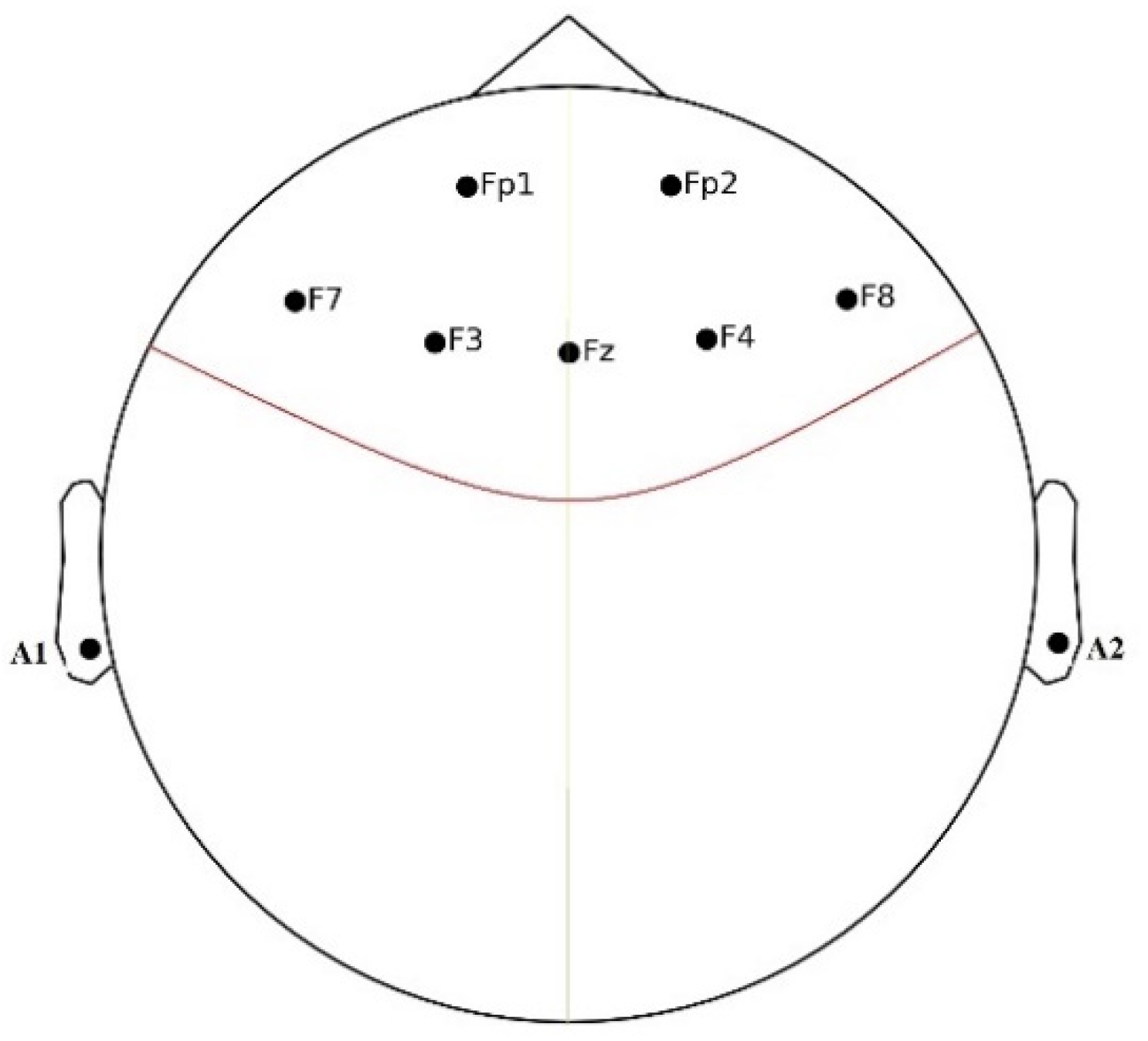

| Dataset | Stimuli (Stressor) | Stress Labelling | Total EEG Channels | Selected Channels | No. Participants/ Total Experiments | Frequency Rate (Hz) | Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEAP | Music video | SAM | 32 | AF3’, ‘FC5’, ‘F8’, ‘Fp1’, ‘AF4’, ‘P7’, ‘Fp2’, ‘F7 | 32/32 | 128 | Stress/ calm |
| SEED | Emotional video | Questionnaire | 62 | ‘AF3’, ‘FC5’, ‘F8’, ‘Fp1’, ‘AF4’, ‘P7’, ‘Fp2’, ‘F7’ | 15/45 | 200 | Negative/positive |
| EDPMSC | History | PSS | 4 | ‘TP9’, ‘AF7’, ‘AF8’,’TP10’ | 28/84 | 256 | Stress/ not stress |
| Our | MA, negative feedback and time pressure | Saliva cortisol | 7 | ‘Fp1’, ‘Fp2’, ‘F7’, ‘F3’, ‘Fz’, ‘F4’, ‘F8’ | 22/22 | 256 | Stress/ rest |
| Domain | Feature Name | Description | No. Features | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Phase Locking Value [52] | It is a proportion of phase difference between signals over different trials above or below the 0 degree | ||
| Time | Hjorth parameters of activity mobility, and complexity [28] | Activity is the variance of the signal on-time. | 1 | |
| Mobility represents the proportion of standard deviation of the window signal in the time domain. | 1 | |||
| Complexity represents how the shape of a signal is similar to a pure sine wave. | 1 | |||
| Peak to peak amplitude | Represents the peak time of EEG signal between the various windows. | 1 | ||
| Line length [28,53] | Named a curve length, which indicates the total vertical length of the signal. | 1 | ||
| Kurtosis [54,55] | Shows the sharpness of EEG signals’ peaks. | 1 | ||
| Skewness [17] | Represents the asymmetry of an EEG signal. | 1 | ||
| Frequency | Relative powers of [18]: Theta (4–8 Hz) Alpha (8–12 Hz) Sigma (12–15 Hz) Low beta (15–20 Hz)A high beta (20–30 Hz). | Relative power represents the average absolute power of the given band intervals. | 5 | |
| Time-Frequency | Spectral entropy (PSD, Welch) [12,56] | Measures the distribution of signal power over frequency. | 1 | |
| Katz fractal dimension [35] | Represents the maximum distance between the first point and any other point of the signal’s time window. | 1 |
| Algorithm | Execution Time | Accuracy | #No Selected Features | Execution Time | Accuracy | #No Selected Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDMSS DATASET | EDPMSC DATASET | |||||
| BAT | 4.315 | 67.624 | 75 | 15.378 | 87.703 | 44 |
| FFA | 19.615 | 65.172 | 79 | 19.285 | 87.935 | 36 |
| GWO | 9.234 | 67.664 | 74 | 15.001 | 87.703 | 55 |
| MFO | 4.336 | 67.267 | 85 | 16.586 | 88.167 | 55 |
| MVO | 4.135 | 67.631 | 80 | 14.620 | 88.863 | 45 |
| PSO | 5.530 | 65.289 | 108 | 15.923 | 84.919 | 55 |
| WOA | 5.773 | 64.224 | 72 | 15.195 | 89.327 | 36 |
| Proposed | 11.719 | 77.222 | 52 | 60.700 | 88.301 | 30 |
| DEAP DATASET | SEED DATASET | |||||
| BAT | 10.328 | 88.229 | 80 | 2.946 | 68.889 | 86 |
| FFA | 41.391 | 88.079 | 87 | 14.852 | 74.815 | 90 |
| GWO | 21.013 | 87.515 | 83 | 6.939 | 71.111 | 84 |
| MFO | 46.348 | 88.182 | 97 | 2.865 | 70.370 | 85 |
| MVO | 10.695 | 88.877 | 86 | 2.869 | 70.370 | 85 |
| PSO | 13.682 | 88.276 | 121 | 4.027 | 66.667 | 122 |
| WOA | 14.482 | 88.697 | 79 | 4.236 | 68.148 | 79 |
| Proposed | 53.768 | 93.878 | 57 | 9.346 | 84.167 | 49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hag, A.; Handayani, D.; Altalhi, M.; Pillai, T.; Mantoro, T.; Kit, M.H.; Al-Shargie, F. Enhancing EEG-Based Mental Stress State Recognition Using an Improved Hybrid Feature Selection Algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21, 8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248370
Hag A, Handayani D, Altalhi M, Pillai T, Mantoro T, Kit MH, Al-Shargie F. Enhancing EEG-Based Mental Stress State Recognition Using an Improved Hybrid Feature Selection Algorithm. Sensors. 2021; 21(24):8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248370
Chicago/Turabian StyleHag, Ala, Dini Handayani, Maryam Altalhi, Thulasyammal Pillai, Teddy Mantoro, Mun Hou Kit, and Fares Al-Shargie. 2021. "Enhancing EEG-Based Mental Stress State Recognition Using an Improved Hybrid Feature Selection Algorithm" Sensors 21, no. 24: 8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248370
APA StyleHag, A., Handayani, D., Altalhi, M., Pillai, T., Mantoro, T., Kit, M. H., & Al-Shargie, F. (2021). Enhancing EEG-Based Mental Stress State Recognition Using an Improved Hybrid Feature Selection Algorithm. Sensors, 21(24), 8370. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248370








