Radiometric Identification of Signals by Matched Whitening Transform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Framework for Radiometric Identification
2.1. The Whitening Transform
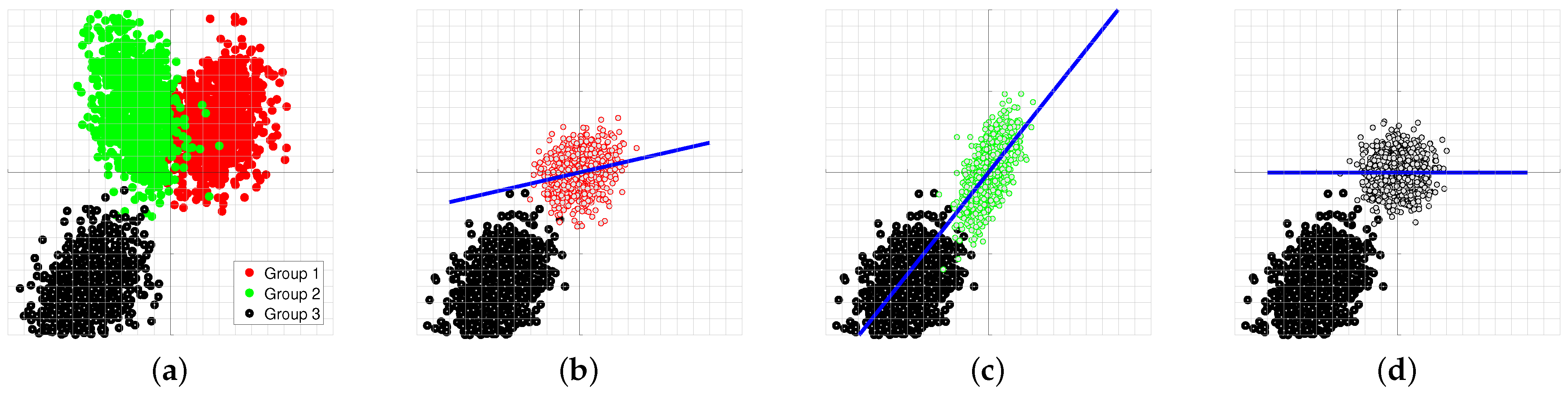
2.2. Classification by Matched Whitening
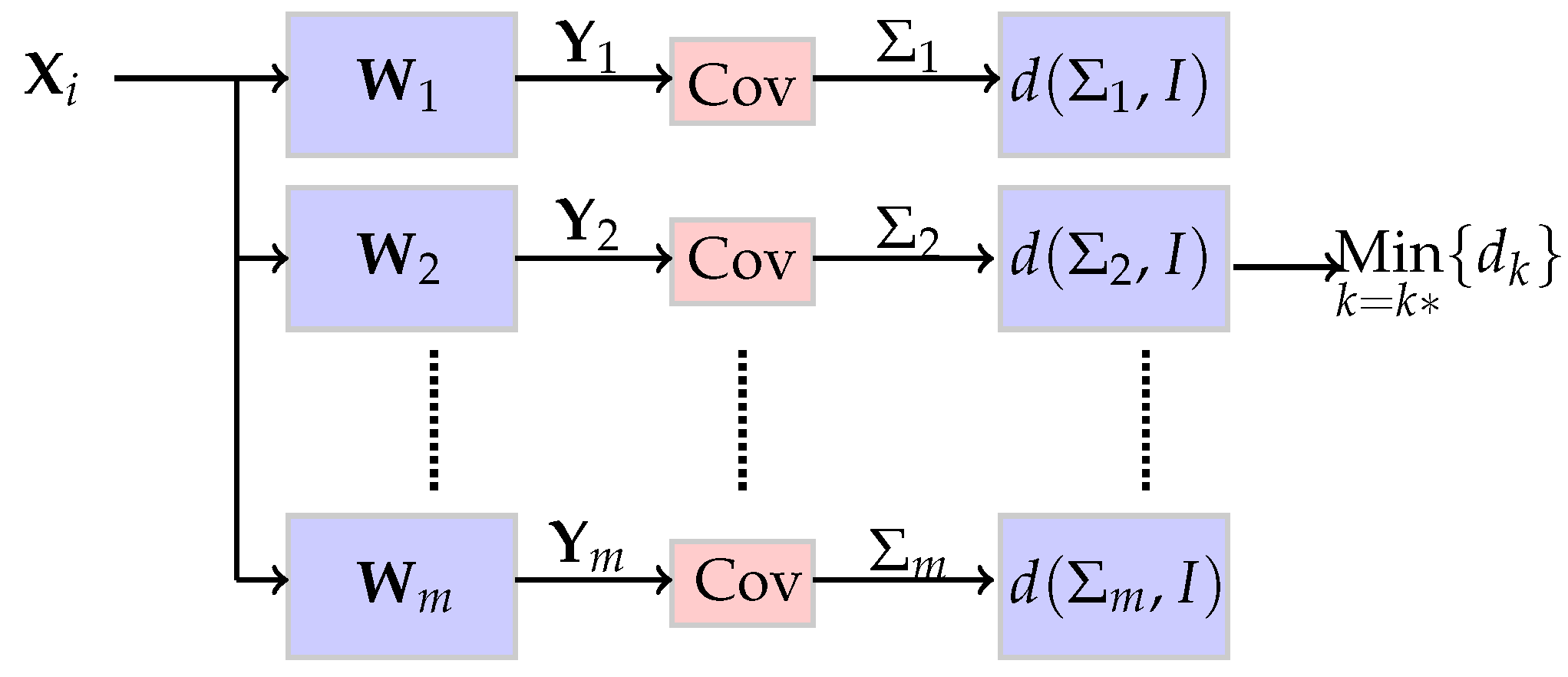
2.3. Development of a Whitening Measure
3. Reversing Phase and Frequency Offsets
3.1. Background
3.2. Signal Model
4. Results
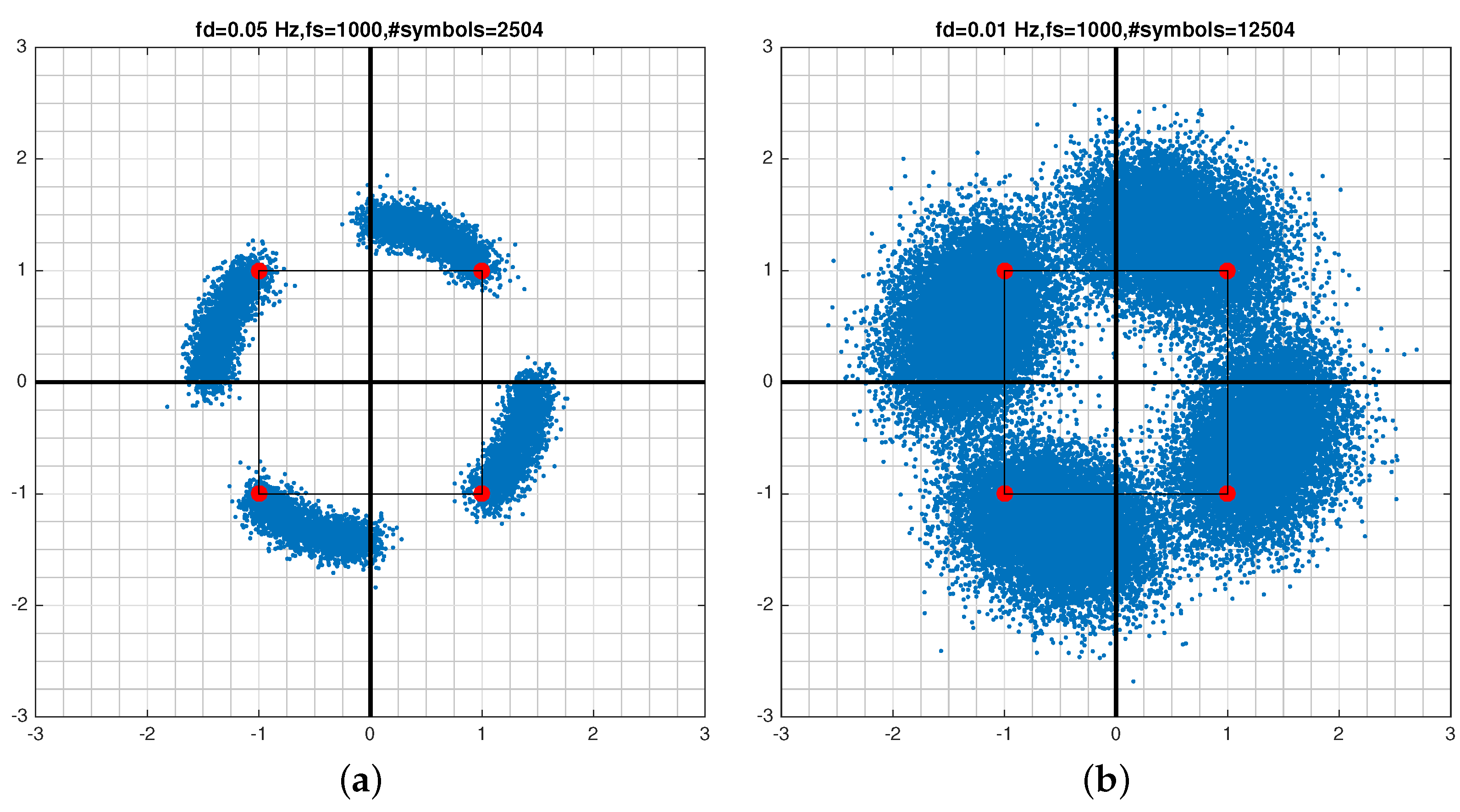
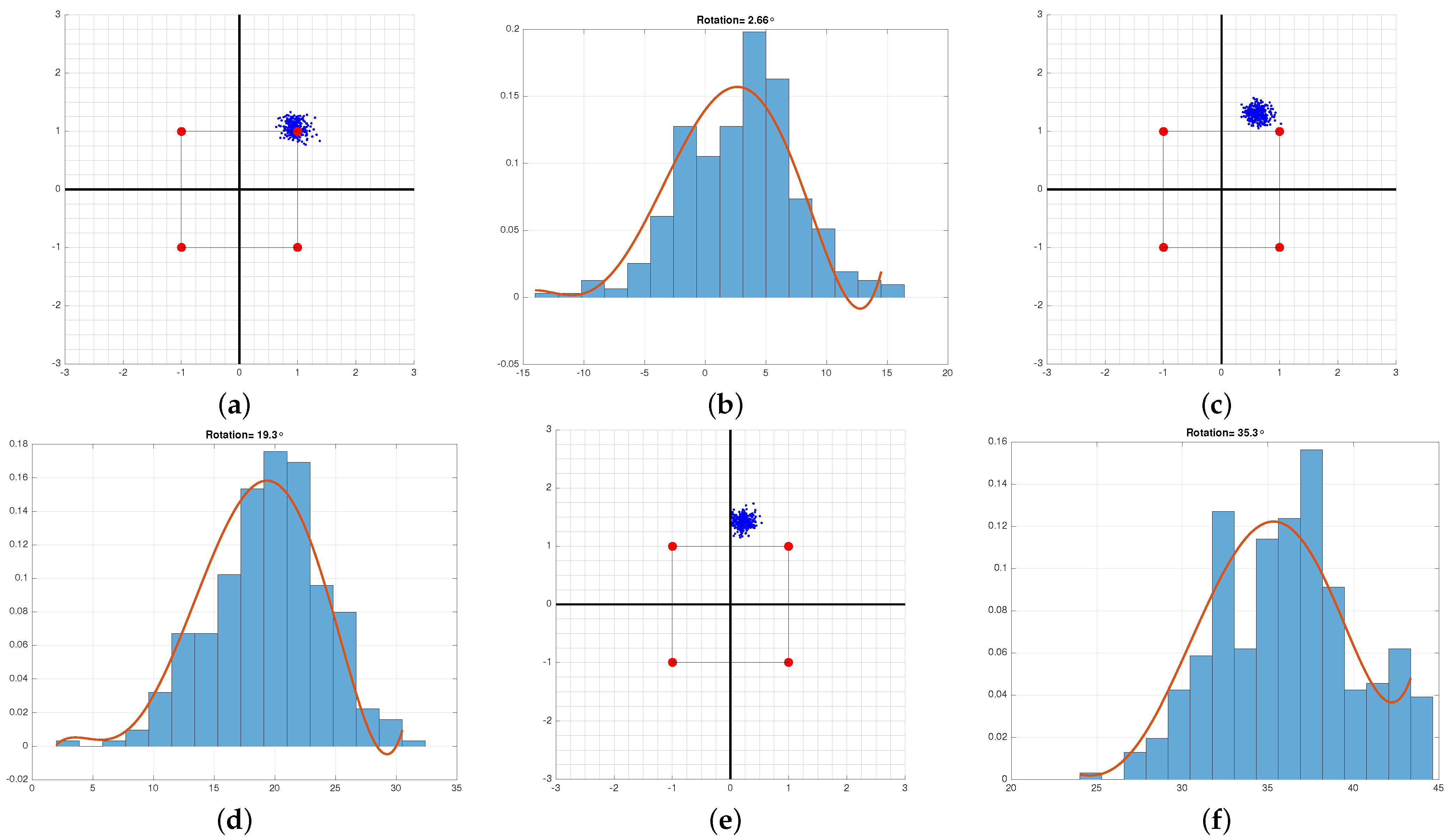
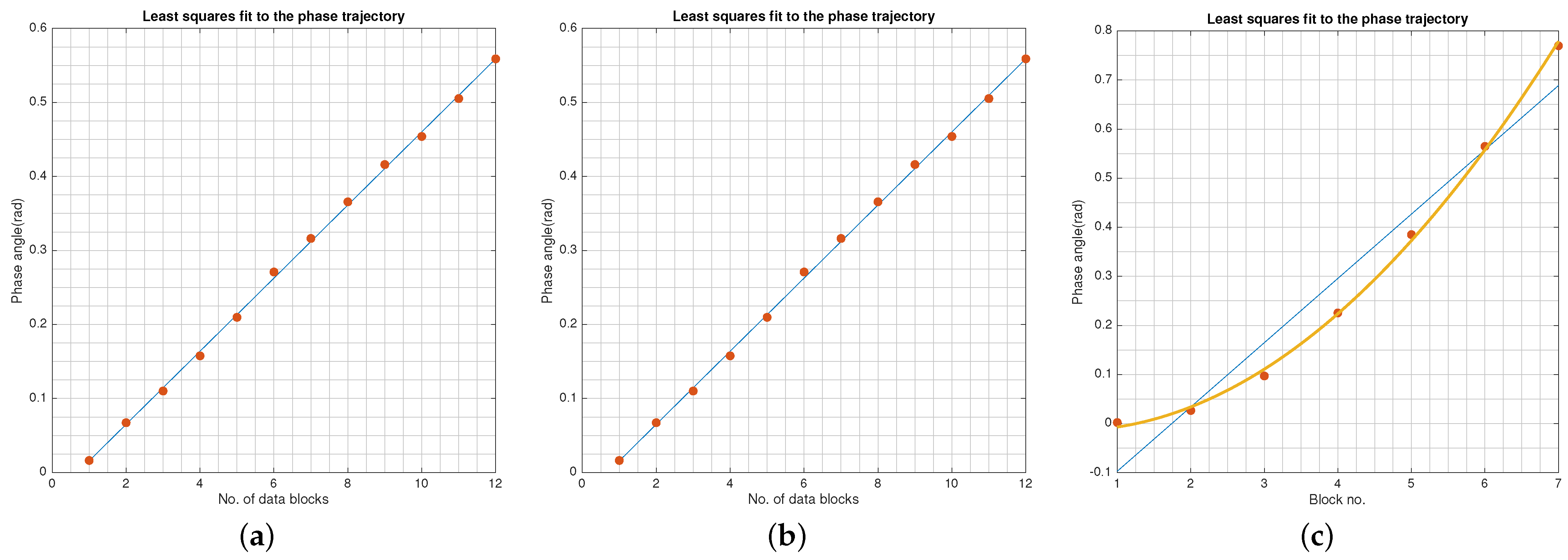
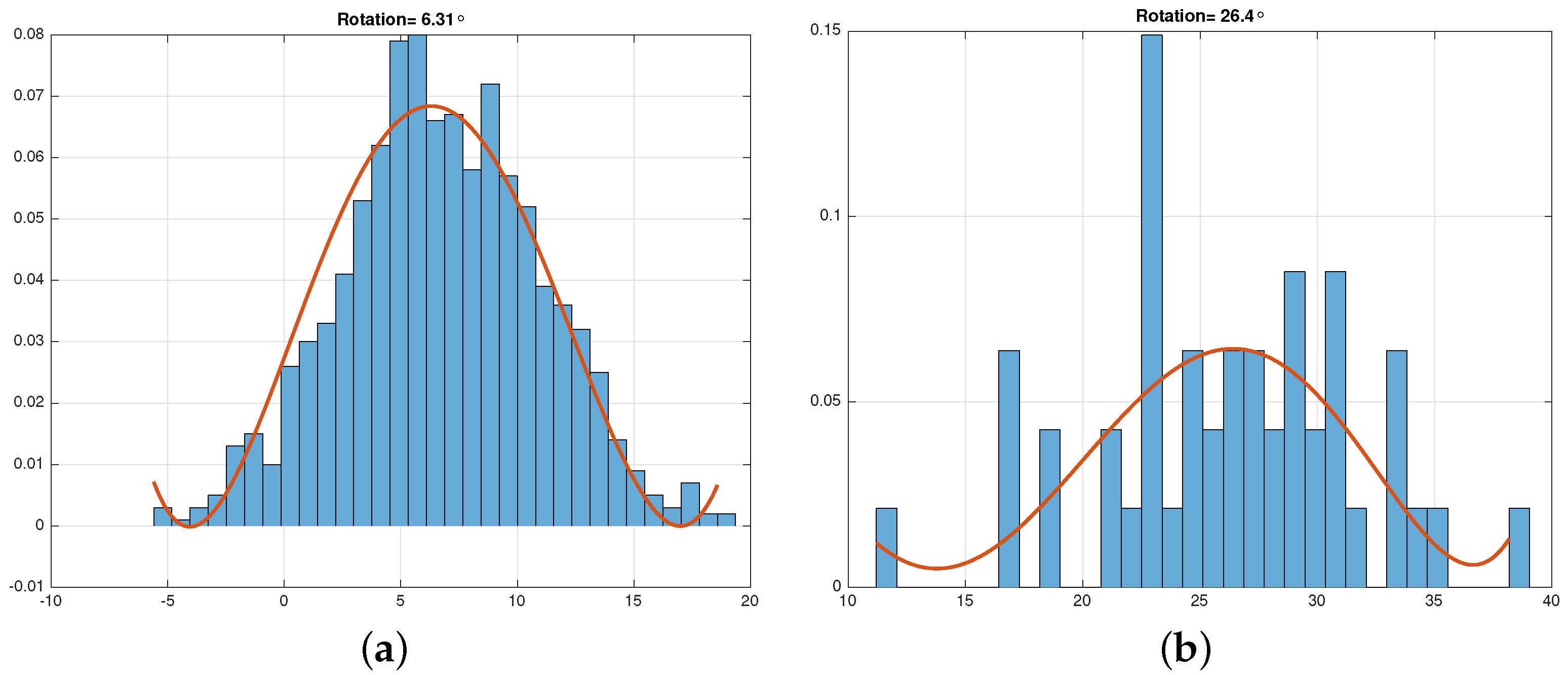
4.1. Signal Phase and Offset Frequency Correction
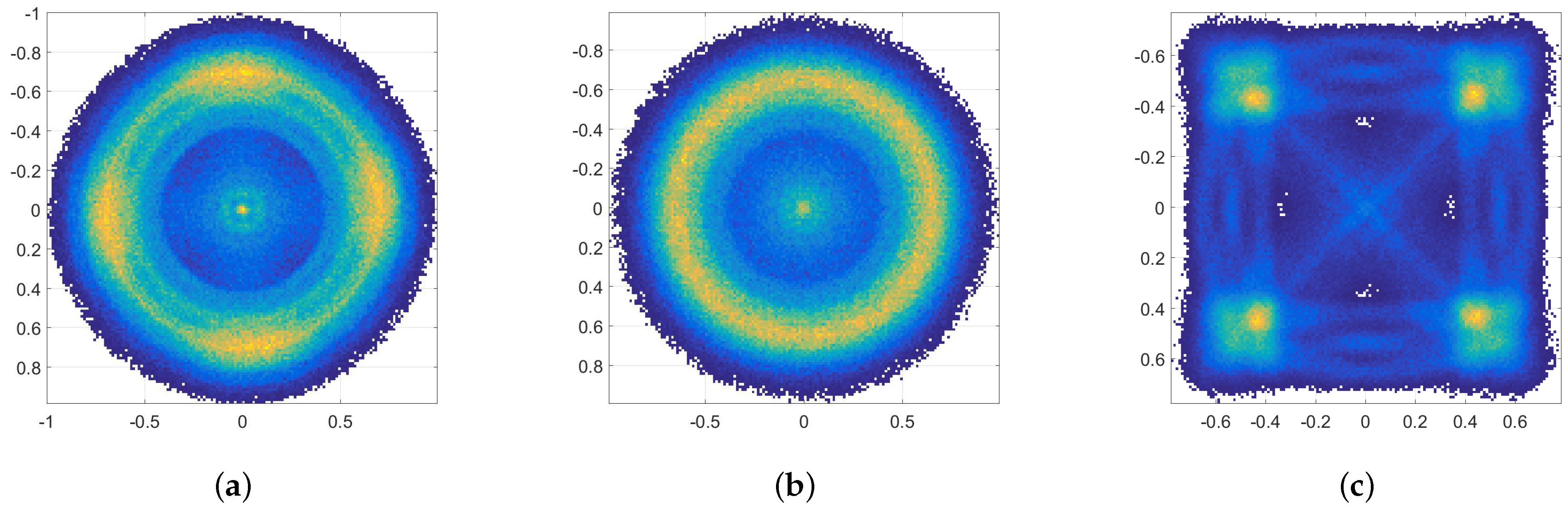
4.2. Radiometric Identification
4.3. Class Confusion Matrices
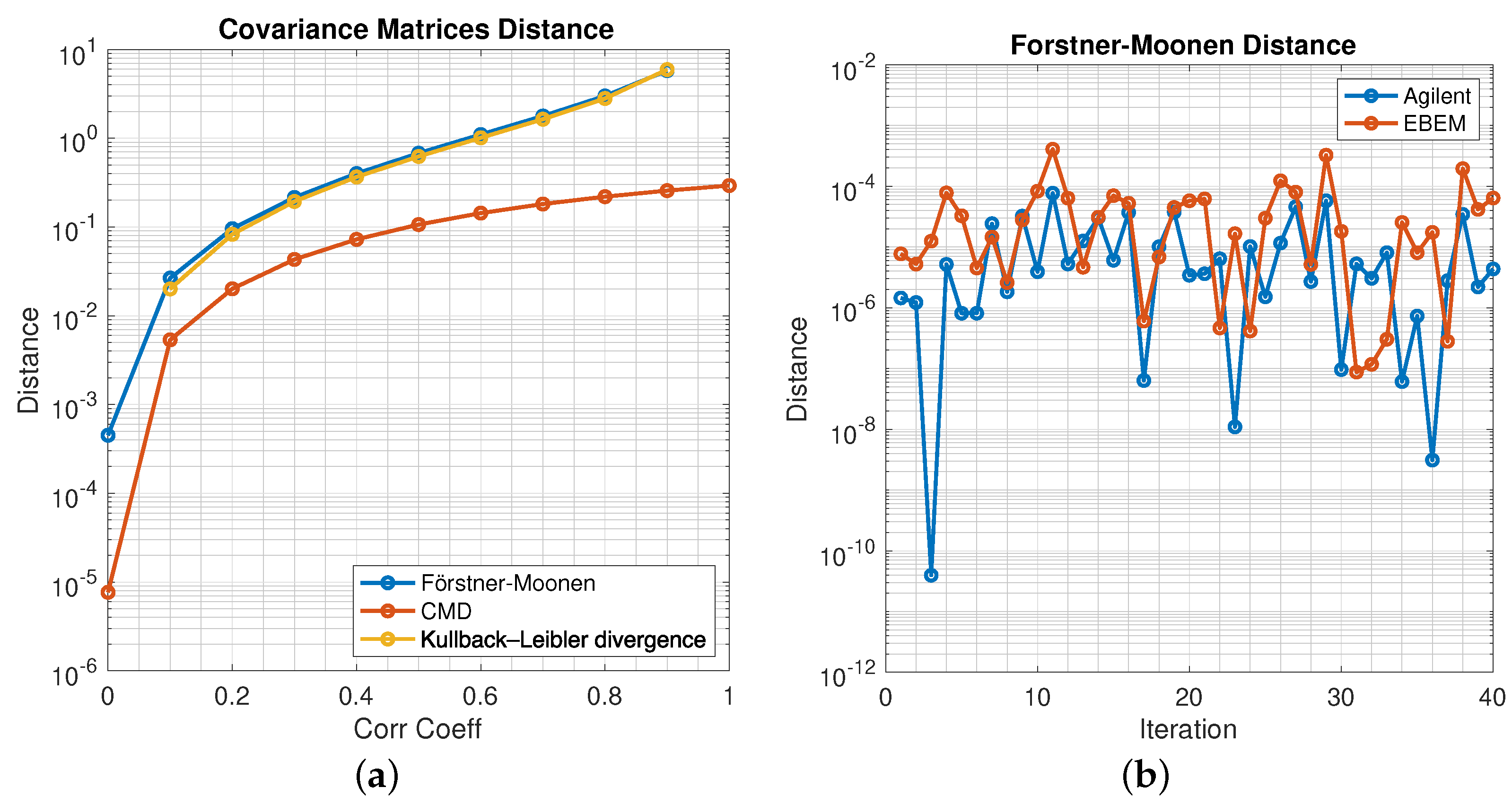
4.4. Comparisons
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nandi, A.K.; Azzouz, E.E. Algorithms for automatic modulation recognition of communication signals. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1998, 46, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, G.J.; Bora, P.K. Parameter estimation for blind classification of digital modulations. IET Signal Process. 2016, 10, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata’a, A.W.; Abdullah, S.N. Deinterleaving of radar signals and PRF identification algorithms. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2007, 1, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, G.; Alp, Y.K.; Arikan, O. A New Method for Specific Emitter Identification With Results on Real Radar Measurements. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 3335–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, K.; Lang, D.; Wang, C.; Bai, Y. Specific Emitter Identification Techniques for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, W. A Game Theory Based Collaborative Security Detection Method for Internet of Things Systems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1432–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, J.; Padilla, P.; Valenzuela-Valdés, J.; Ramírez, J.; Górriz, J. RF fingerprint measurements for the identification of devices in wireless communication networks based on feature reduction and subspace transformation. Measurement 2014, 58, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihl, T.J.; Bauer, K.W.; Temple, M.A. Feature Selection for RF Fingerprinting with Multiple Discriminant Analysis and Using ZigBee Device Emissions. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Huang, B.; Xu, L.; Xu, Z. Radio Transmitter Classification using a New Method of Stray Features Analysis Combined with PCA. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2007-IEEE Military Communications Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 29–31 October 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Ma, J.; Gan, L. Combined Optimization of Feature Reduction and Classification for Radiometric Identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danev, B.; Capkun, S. Transient-based identification of wireless sensor nodes. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–16 April 2009; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, I.O.; Scanlon, P.; Mullany, F.J.; Buddhikot, M.M.; Nolan, K.E.; Rondeau, T.W. Radio Transmitter Fingerprinting: A Steady State Frequency Domain Approach. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 68th Vehicular Technology Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.; Bouchard, L.; Haigh, K.; Silovsky, J.; Thapa, B.; Valk, C.V. Machine Learning Approach to RF Transmitter Identification. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2018, 2, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafari, H.; Omotere, O.; Adesina, D.; Wu, H.; Qian, L. IoT Devices Fingerprinting Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2018—2018 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 29–31 October 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, K.; Revay, S.; Stantchev, G.; Nousain, B. Deep Learning for RF Device Fingerprinting in Cognitive Communication Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Meert, W.; Giustiniano, D.; Lenders, V.; Pollin, S. Deep learning models for wireless signal classification with distributed low-cost spectrum sensors. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W. Specific Emitter Identification via Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 2591–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.; Rai, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Doja, M.N.; Ahmad, M. Detecting distraction of drivers using convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 139, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, S.; Peng, H.; Li, T.; Wang, W. Specific Emitter Identification Based on Deep Residual Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54425–54434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Qi, J.; Kuai, X.; Han, G.; Sun, H.; Hong, S. Specific Emitter Identification Based on Multi-Level Sparse Representation in Automatic Identification System. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 2872–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; He, X.; Cai, X.; Bi, D. Balanced Neural Architecture Search and Its Application in Specific Emitter Identification. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 5051–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z. Specific Emitter Identification Based on Nonlinear Dynamical Characteristics. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2016, 39, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z. Specific emitter identification for communications transmitter using multi-measurements. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 94, 1523–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, Z.T.; Wu, H.; Wang, X. Specific emitter identification based on Hilbert-Huang transform-based time-frequency-energy distribution features. IET Commun. 2014, 8, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, P.; Padilla, J.; Valenzuela-Valdes, J. Radiofrequency identification of wireless devices based on RF fingerprinting. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 1409–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A. Preamble-based detection of Wi-Fi transmitter RF fingerprints. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Candore, A.; Kocabas, O.; Koushanfar, F. Robust stable radiometric fingerprinting for wireless devices. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27–29 July 2009; pp. 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Dudczyk, J.; Kawalec, A. Fast-decision identification algorithm of emission source pattern in database. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci.-Tech. Sci. 2015, 63, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawalec, A.; Rapacki, T.; Wnuczek, S.; Dudczyk, J.; Owczarek, R. Mixed Method Based on Intrapulse Data and Radiated Emission to Emitter Sources Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Microwaves, Radar Wireless Communications, Krakow, Poland, 22–24 May 2006; pp. 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, F.; St-Hilaire, M. Radiometric identification of LTE transmitters. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–13 December 2013; pp. 4116–4121. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Yan, W.; Zhang, L.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Y. Specific Emitter Identification Based on Software-Defined Radio and Decision Fusion. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 86217–86229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Kasera, S.K. On fast and accurate detection of unauthorized wireless access points using clock skews. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2009, 9, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conning, M.; Potgieter, F. Analysis of measured radar data for specific emitter identification. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 May 2010; pp. 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Polak, A.C.; Goeckel, D.L. Wireless device identification based on RF oscillator imperfections. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, A.C.; Goeckel, D.L. RF fingerprinting of users who actively mask their identities with artificial distortion. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference Record of the Forty Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 6–9 November 2011; pp. 270–274. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.W.; Doherty, J.F. Specific emitter identification using nonlinear device estimation. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Sarnoff Symposium, Princeton, NJ, USA, 28–30 April 2008; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Srivastava, G.; Liu, S. Wireless transmitter identification based on device imperfections. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 59305–59314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolatshahi, S.; Polak, A.; Goeckel, D.L. Identification of wireless users via power amplifier imperfections. In Proceedings of the 2010 Conference Record of the Forty Fourth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 7–10 November 2010; pp. 1553–1557. [Google Scholar]
- D’Agostino, S.; Foglia, G.; Pistoia, D. Specific emitter identification: Analysis on real radar signal data. In Proceedings of the 2009 European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Rome, Italy, 30 September–2 October 2009; pp. 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; White, R.E.; Low, M. A comparison study of radar emitter identification based on signal transients. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, K.I.; Duley, P.R.; Hyatt, M.H. Specific emitter identification and verification. Technol. Rev. 2003, 113, 113–133. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I. Orthogonal Subspace Projection (OSP) revisited: A comprehensive study and analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvick, P.A.; Lind, M.A.; Mackey, P.S.; Nuffer, L.L.; Foote, H.P. 3D-FFT for Signature Detection in LWIR Images; Technical Report; Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, R.; Bucholtz, F.; Scribner, D. Object detection by using whitening/dewhitening to transform target signatures in multitemporal hyperspectral and multispectral imagery. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 2003, 41, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessy, A.; Lewin, A.; Strimmer, K. Optimal Whitening and Decorrelation. Am. Stat. 2018, 72, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.J.; Sejnowski, T.J. The “independent components” of natural scenes are edge filters. Vis. Res. 1997, 37, 3327–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Förstner, W.; Moonen, B. A metric for covariance matrices. In Geodesy—The Challenge of the 3rd Millennium; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Kulis, B.; Sustik, M.A.; Dhillon, I.S. Low-Rank Kernel Learning with Bregman Matrix Divergences. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 341–376. [Google Scholar]
- Herdin, M.; Czink, N.; Ozcelik, H.; Bonek, E. Correlation Matrix Distance, a Meaningful Measure for Evaluation of Non-Stationary MIMO Channels. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE 61st Vehicular Technology Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 30 May–1 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncheva, L.I. A theoretical study on six classifier fusion strategies. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proakis, J.G.; Salehi, M. Digital Communications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Agilent Vector Signal Generator. 2021. Available online: https://www.keysight.com/us/en/assets/7018-01039/data-sheets/5988-4039.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Viasat Enhanced Bandwidth Efficient SATCOM Modem. 2021. Available online: https://www.viasat.com/products/modems/md-1366-ebem/ (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Teledyn Paradise Datacom. 2021. Available online: https://www.teledynedefenseelectronics.com/paradisedatacom/Pages/Satellite%20Modems.aspx (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Kratos RTSIM. 2021. Available online: https://www.kratosdefense.com/products/space/signals/test-and-simulation (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Ettus USRP. 2021. Available online: https://www.ettus.com/products/ (accessed on 26 November 2021).
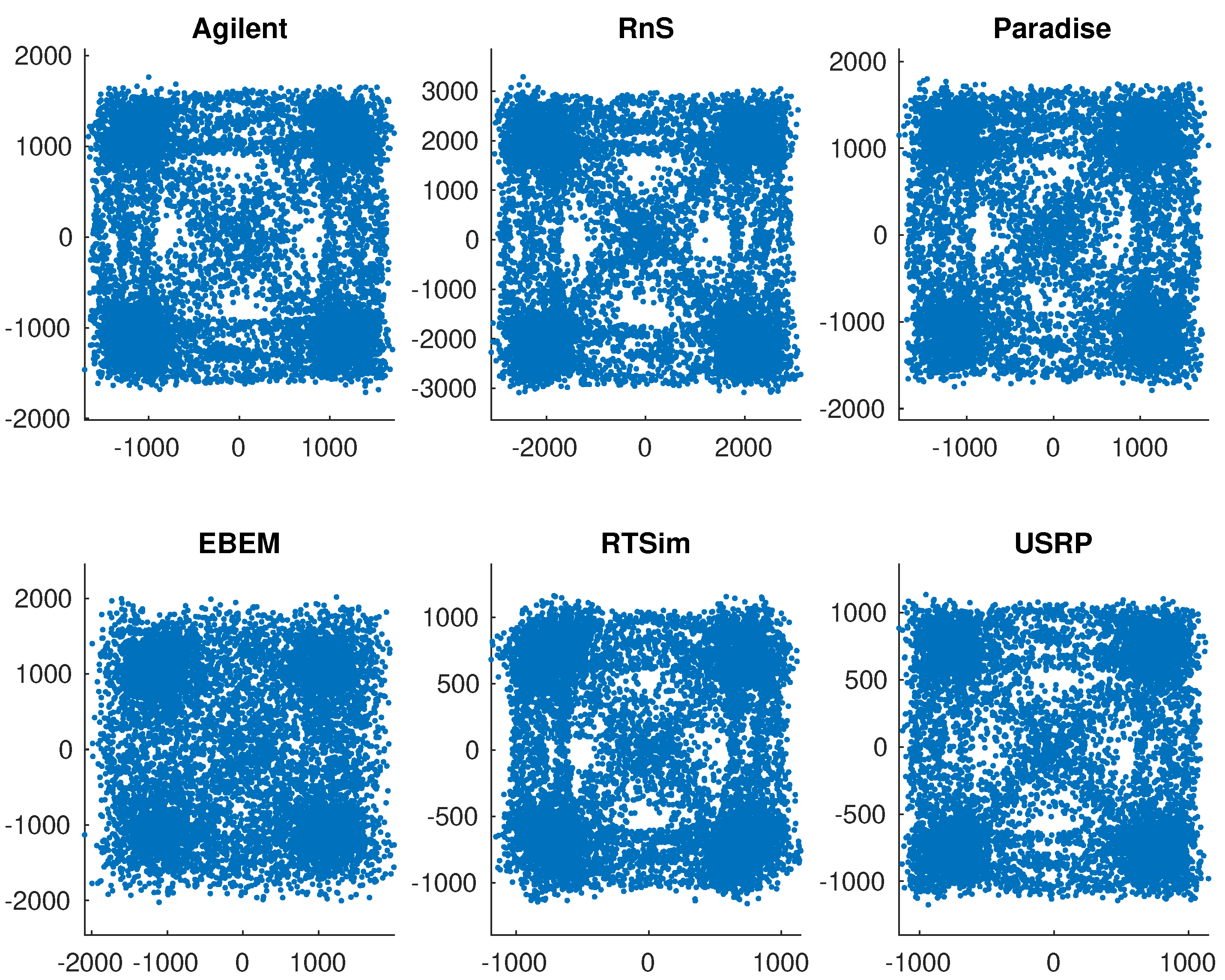
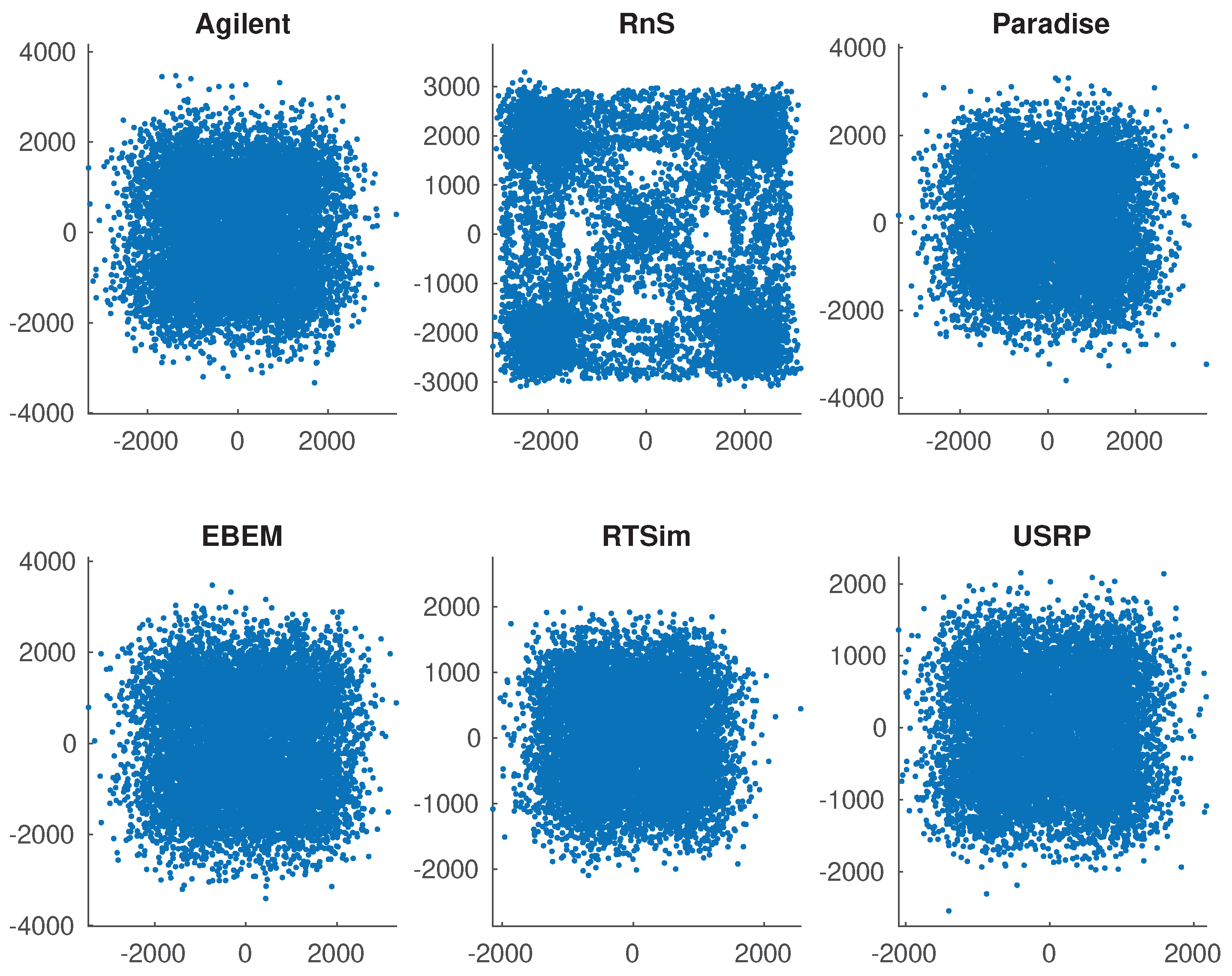
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Modulation | QPSK |
| Symbol rate | 1000/s |
| Block length | 0.312 s |
| Symbols/block | 3120 |
| No. of blocks | 8 |
| Segment length | 2.5 s |
| Total no. of symbols | 2504 |
| Max. rotation per block | 5.62° |
| Total rotation per segment | 45° |
| Offset frequency () | 0.05 Hz |
| SNR | 20 dB |
| Agilent | Viasat EBEM | Paradise | RTSim | USRP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agilent | 91.4 | 0 | 0 | 8.6 | 0 |
| EBEM | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Teledyne Paradise | 0 | 0 | 77.1 | 0 | 22.9 |
| KRATOS RTSim | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| USRP | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Agilent | EBEM | Paradise | RTSim | USRP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agilent | 30.0 | 22.5 | 12.5 | 0.0 | 22.5 |
| Viasat EBEM | 15.0 | 85.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Teledyne Paradise | 5.0 | 2.5 | 77.5 | 2.5 | 12.5 |
| KRATOS RTSim | 2.5 | 12.5 | 22.5 | 20.0 | 15.0 |
| USRP | 22.5 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 0.0 | 57.5 |
| Agilent | EBEM | Paradise | RTSim | USRP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agilent | 22.5 | 20.0 | 7.5 | 15.0 | 17.5 |
| Viasat EBEM | 10.0 | 80.0 | 2.5 | 0 | 5.0 |
| Teledyne Paradise | 15.0 | 0 | 52.5 | 12.5 | 10.0 |
| KRATOS RTsim | 12.5 | 20.0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 15.0 |
| USRP | 35.0 | 2.5 | 20.0 | 2.5 | 37.5 |
| Agilent | EBEM | Paradise | RTSim | USRP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agilent | 17.5 | 27.5 | 17.5 | 5.0 | 10.0 |
| Viasat EBEM | 20.0 | 60.0 | 5.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Teledyne Paradise | 15.0 | 5.0 | 27.5 | 17.5 | 15.0 |
| KRATOS RTsim | 7.5 | 22.5 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 12.5 |
| USRP | 20.0 | 12.5 | 17.5 | 2.5 | 17.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mobasseri, B.G.; Lulu, A. Radiometric Identification of Signals by Matched Whitening Transform. Sensors 2021, 21, 8398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248398
Mobasseri BG, Lulu A. Radiometric Identification of Signals by Matched Whitening Transform. Sensors. 2021; 21(24):8398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248398
Chicago/Turabian StyleMobasseri, Bijan G., and Amro Lulu. 2021. "Radiometric Identification of Signals by Matched Whitening Transform" Sensors 21, no. 24: 8398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248398
APA StyleMobasseri, B. G., & Lulu, A. (2021). Radiometric Identification of Signals by Matched Whitening Transform. Sensors, 21(24), 8398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21248398






