Structural Design and Physical Mechanism of Axial and Radial Sandwich Resonators with Piezoelectric Ceramics: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
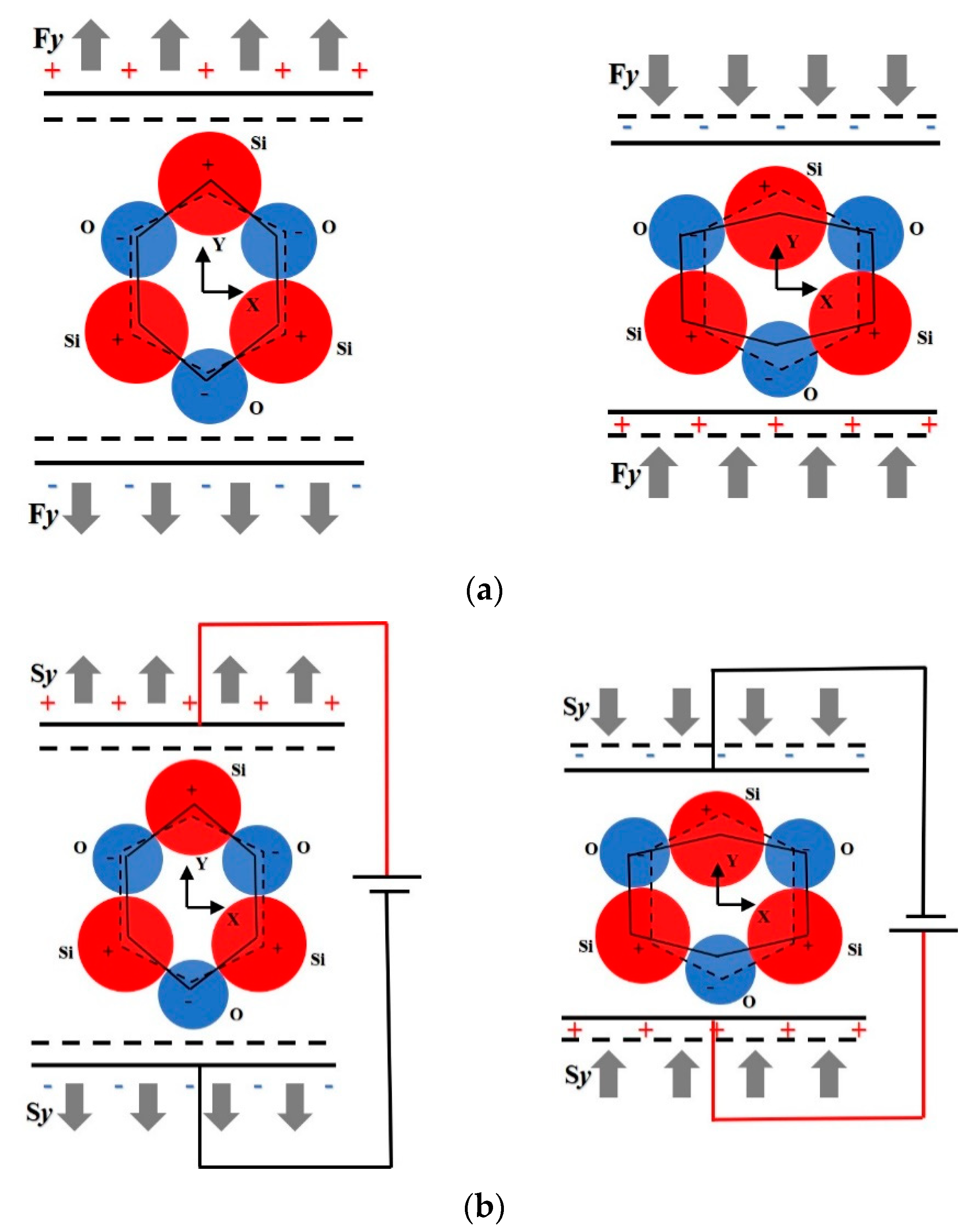
2. Physical Mechanism and Application of Piezoelectric Effect
3. Theoretical Mechanism of Numerical Simulation
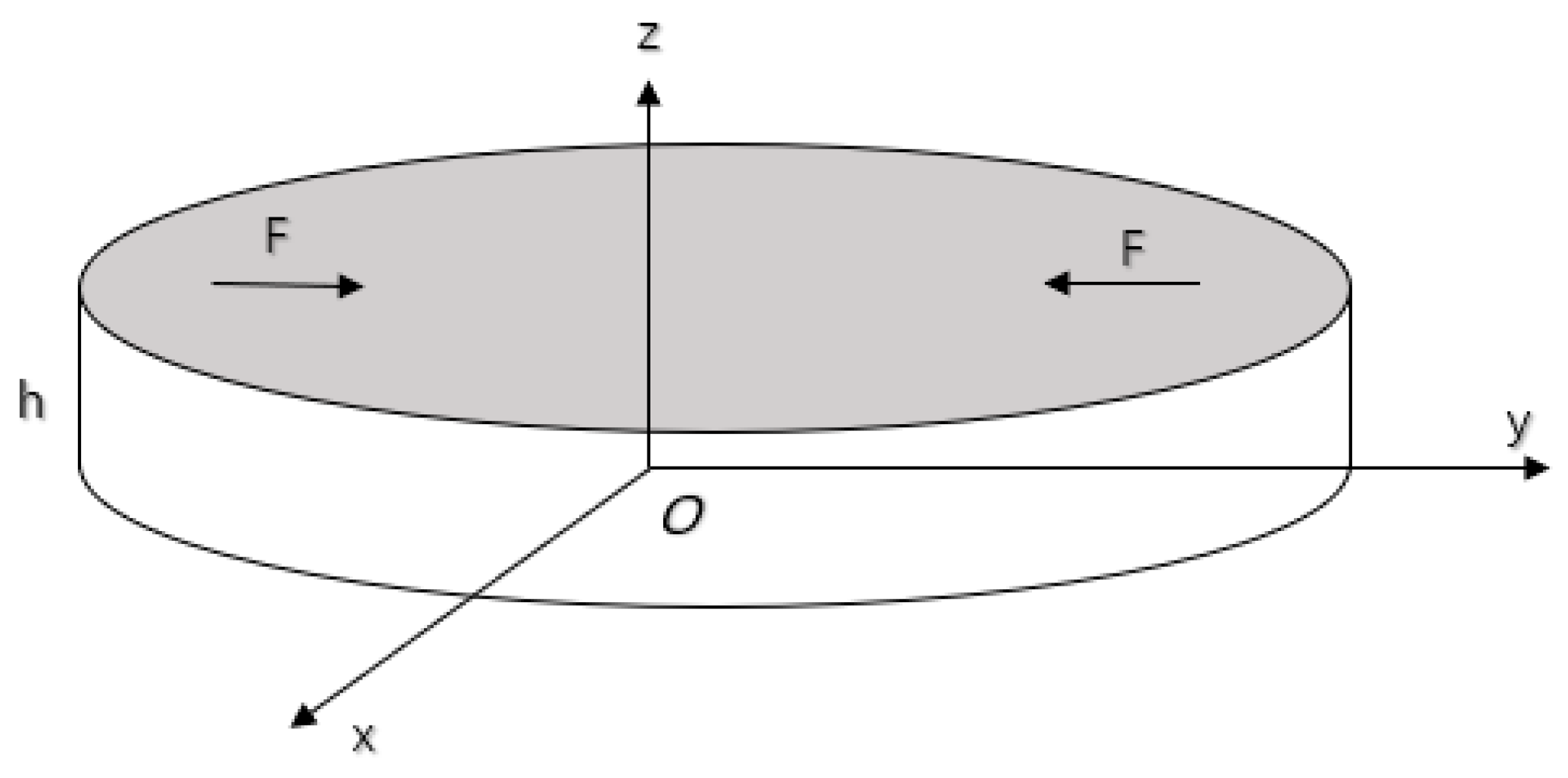
3.1. Piezoelectric Ceramic Sheet
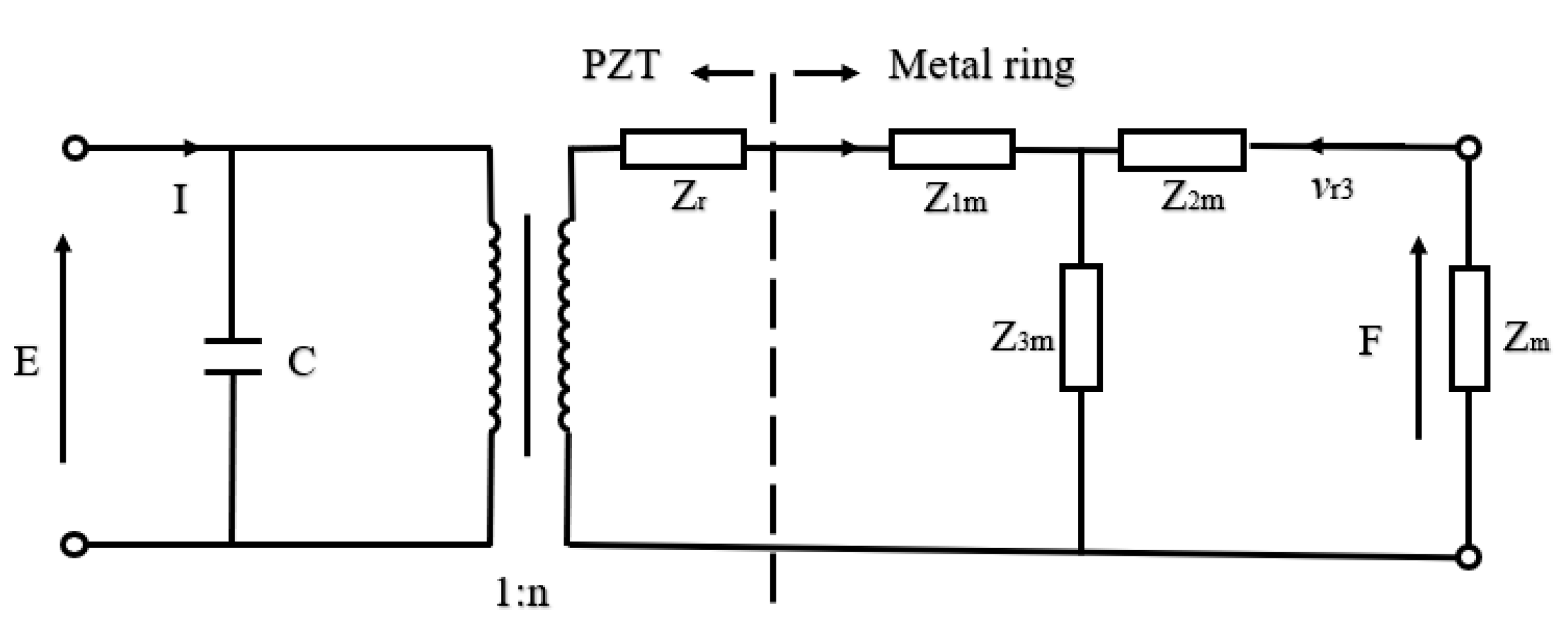
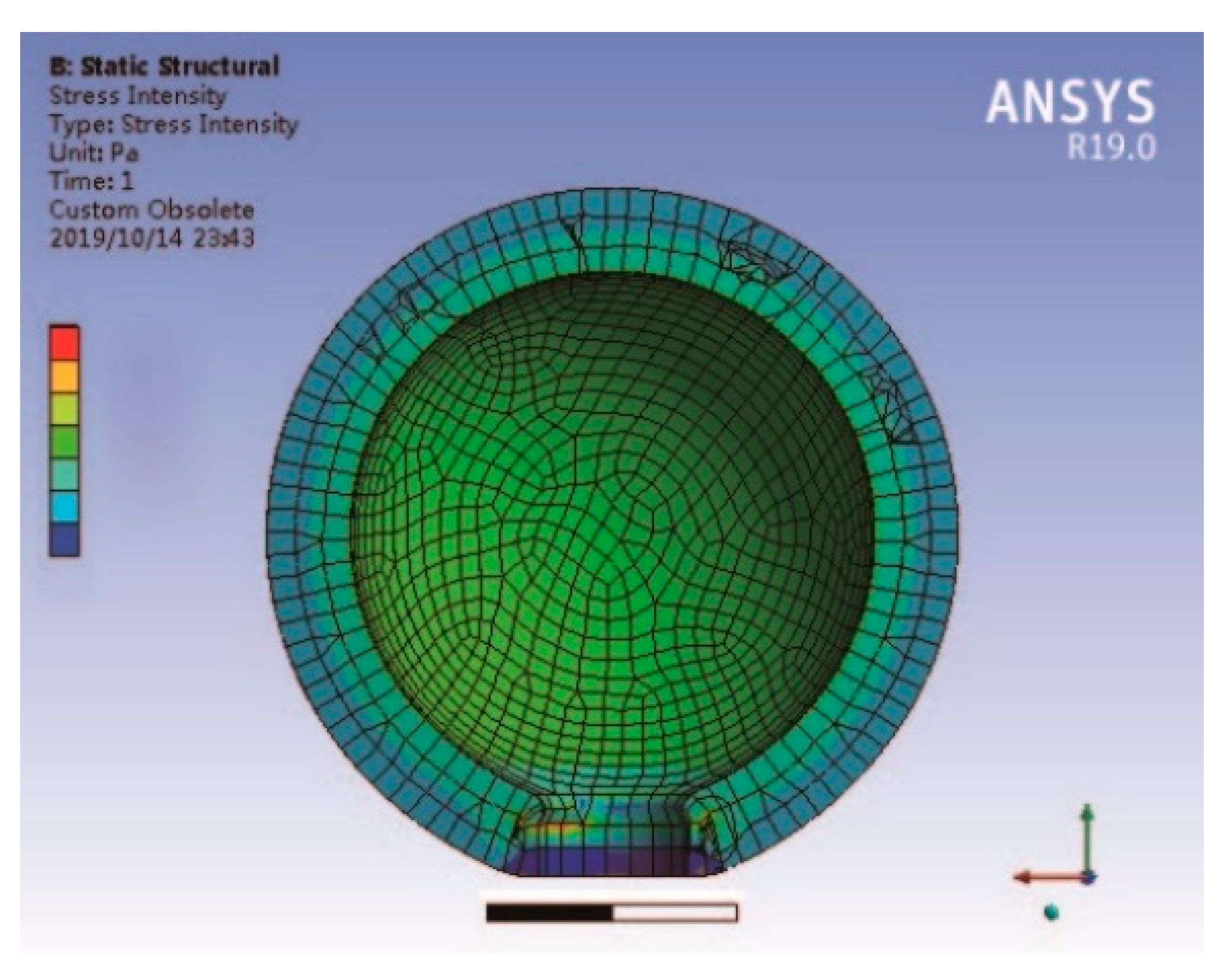
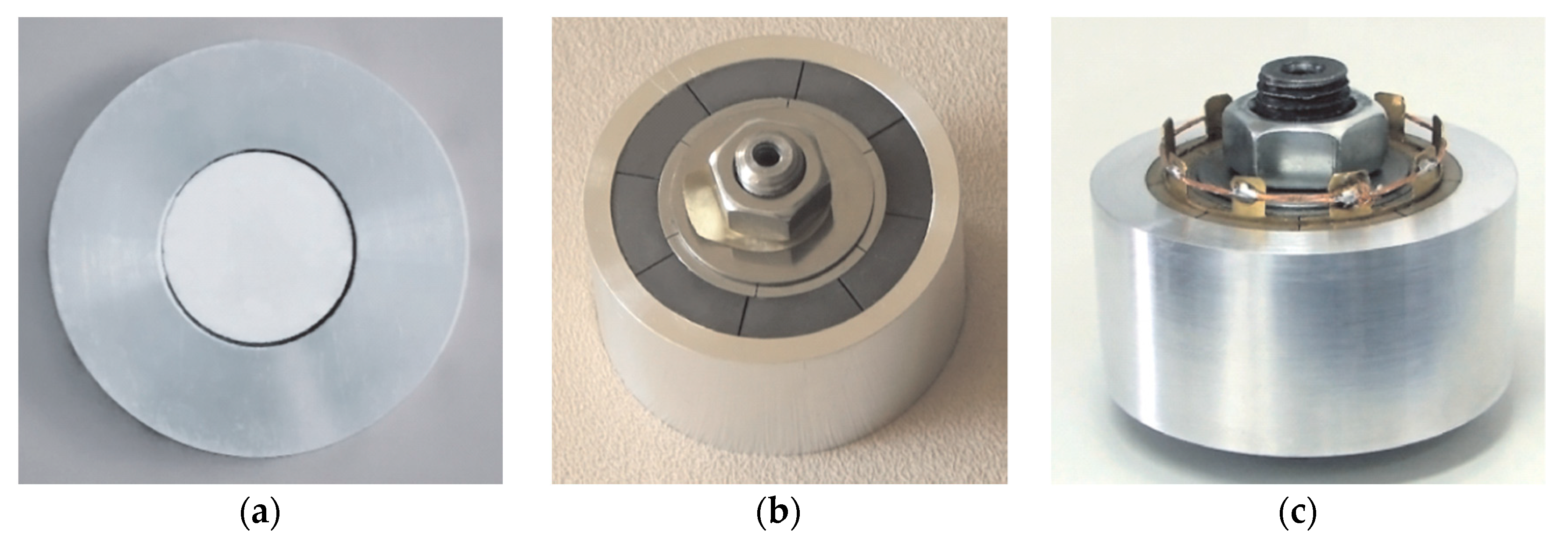
3.2. Piezoelectric Ceramic Disc with a Metal Ring
3.3. Piezoelectric Ceramic Ring with a Metal Ring
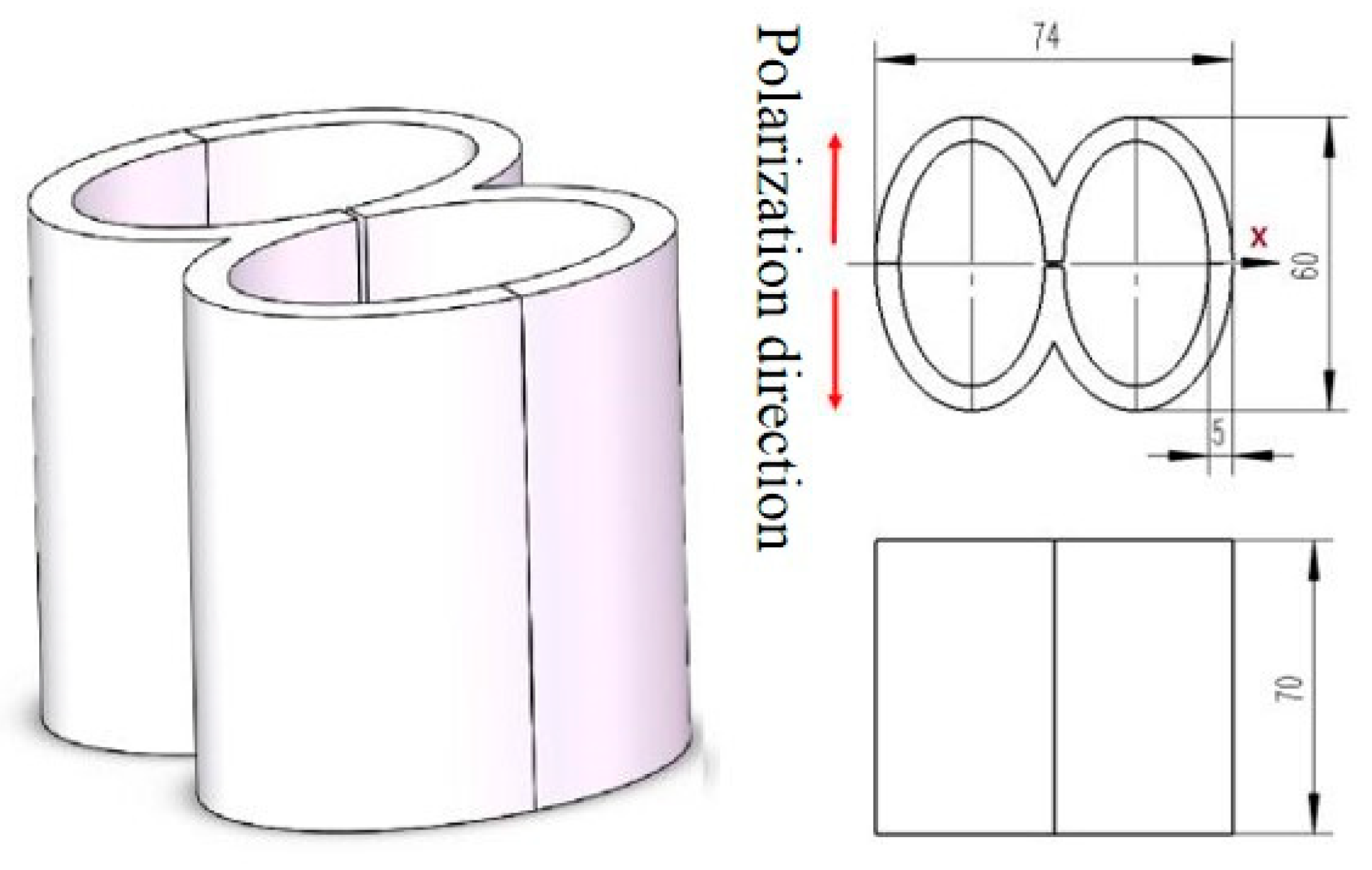
3.4. Cascaded Piezoelectric Transducer
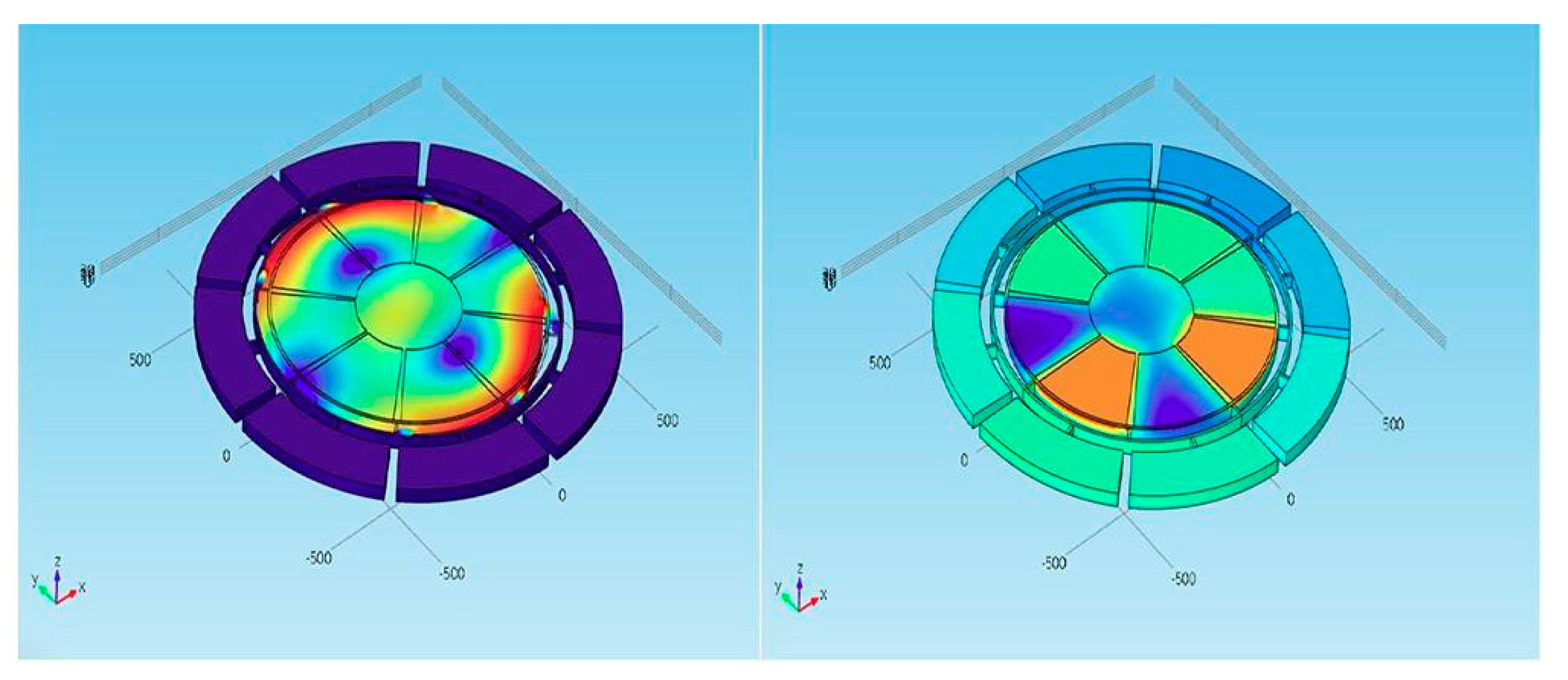
4. Different Sandwich Structures of Piezoelectric Resonator
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, C.; Czanderna, A.W. The Applications of Piezoelectric Quartz Crystal Microbalances. Anal. Chim. Acta 1984, 199, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunde, R.L.; Jarvi, E.J.; Rosentreter, J.J. Piezoelectric quartz crystal biosensors. Talanta 1998, 46, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’sullivan, C.K.; Guilbault, G.G. Commercial quartz crystal microbalances–theory and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1999, 14, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Minamoto, H.; Sakai, G.; Yamazoe, N. New-type calorimetric gas sensor using temperature characteristics of piezoelectric quartz crystal fitted with noble metal catalyst film. Sens. Actuat. B. Chem. 1991, 5, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, B.; Cook, W.R.; Jaffe, H.L.C. Gelcasting of Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 Based Piezoelectric Ceramics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb, C.V.; Flinn, I. Improving the linearity of piezoelectric ceramic actuators. Electron. Lett. 2007, 18, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curie, J.; Curie, P. On electric polarization in hemihedral crystals with inclined faces. Comptes Rendus 1880, 91, 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- Curie, J.; Curie, P. Development, via compression, of electric polarization in hemihedral crystals with inclined faces. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 1880, 3, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Curie, J.; Curie, P. Contractions and expansions produced by voltages in hemihedral crystals with inclined faces. Comptes Rendus 1881, 93, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Woldemar, V. Lehrbuch der Kristallphysik; Vieweg Teubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, P. Process and Apparatus for the Production of Directed Submarine Signals and for the Location of Submarine Objects. French Patent 502913, 26 May 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, P. Procédé et appareil d’emission et de réception des ondes elastiques sous-marines à l’aide des propriétés piézoélectriques du quartz. French Patent 505 703, 17 September 1918. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, P.; Ishimoto, M.J. Utilisation des phénoménes piézo-électriques pour la mesure de l’intensité des sons en valeur absolue. Physique et Radium 1923, 4, 539. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, P. Procédés et appareils pour le sondage et la localisation en distance d’obstacles sous-marins, au moyen d’échos ultra-sonores. French Patent 575435, 27 December 1923. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, P. Procédé et appareils permettant la mesure directe ou l’enregistrement des profondeurs ou des distances en mer par la méthode de l’écho ultra-sonore. French Patent 576281, 11 January 1924. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, P. Procédé et dispositions améliorant l’efficacité des projecteurs ultrasonores piézo-électriques. French Patent 622035, 11 February 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Valasek, J. Piezoelectric and Allied Phenomena in Rochelle Salt. Phys. Rev. 1921, 17, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valasek, J. Piezoelectric activity of Rochelle salt under various conditions. Phys. Rev. 1922, 19, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valasek, J. Properties of Rochelle salt related to the piezo-electric effect. Phys. Rev. 1922, 20, 639–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valasek, J. Dielectric anomalies in Rochelle salt crystals. Phys. Rev. 1924, 24, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haertling, G.H. Ferroelectric Ceramics: History and Technology. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 797–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywang, W.; Lubitz, K.; Wersing, W. Piezoelectricity—Evolution and Future of a Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-68680-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Advances in Lead-Free Piezoelectric Materials; Spinger: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-981-10-8997-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Ramachndra, R. Preparation and dielectric study of high-quality PLZT ferroelectric ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 71, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.A.; Peixoto, G.; Gomes, M.J. Effect of Nb doping on themicrostructural and electical properties of PZT ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klissurska, R.D.; Brooks, K.G.; Reaney, I.M.; Pawlaczyk, C.; Kosec, M.; Setter, N. Effect of Nb doping on the microstructure of sol-gel derived PZT thin films. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 78, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Choudhary, R.N.P.; Sinha, P.K. Studies on structural, electrical and electromechanical properties of Sb3+-modified PLZT. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Adv. 2004, 1, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Seo, I.T.; Choi, J.H.; Nahm, S.; Lee, H.G. Low-Temperature Sintering and Piezoelectric Properties of (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3 Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, T.; Satou, M.; Nakata, K.; Sakata, K. Piezoelectric properties of Pb(ZnNb)O-KNbO-PZT solid solution. Ferroelectrics 2011, 128, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Nie, R.; Yu, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, D.; Song, H. Influence of sintering temperature on phase structure and electrical properties of 0.55Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.45Pb(Zr0.3Ti0.7)O3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 92, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, K.; Ji, H.; Pang, X.; Luo, J. Effects of Fe2O3 doping on the microstructure and piezoelectric properties of 0.55Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3–0.45Pb(Zr0.3Ti0.7)O3 ceramics. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Kim, H.E. Effect of Lead Content on the Structure and Electrical Properties of Pb((Zn1/3Nb2/3)0.5(Zr0.47Ti0.53)0.5)O3 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, Q.; Wu, H. PSN-PZN-PZT Quaternary Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Inorg. Mater. 2006, 21, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.H.; Lee, Y.W.; Hwang, S.M.; Yoon, H.S.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, J.S.; Yoo, C.S. Piezoelectric properties of PNW-PMN-PZT ceramics for high power piezoelectric transformer. IEEE Int. Symp. Appl. Ferroelectr. 2000, 1, 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.-S.; Yoon, K.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Park, C.-Y. Piezoelectric and dielectric properties of Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3-Pb(Mn1/3Nb2/3)O3-Pb(Zr, Ti)O3 ceramics for piezoelectric transformer. IEEE Int. Symp. Appl. Ferroelectr. 2002, 4, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.L.; Gao, S.H.; Zhang, X.W. Low-Temperature Sintering of Lead-Based Piezoelectric Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 72, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Yu Hai Electric Ceramics Co., Ltd. Products-Piezoeletric Material. Available online: https://www.yhpiezo.com/piezoelectric-material/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Ju De Electric Ceramics Co., Ltd. Technical Parameters. Available online: http://www.judepzt.com/news_920855.html (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Erhart, J. Experiments to demonstrate piezoelectric and pyroelectric effects. Phys. Educ. 2013, 48, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.; Abdolmalaki, R.Y.; Nejad, H.C. Precise Position Tracking Control with an Improved Transient Performance for a Linear Piezoelectric Ceramic Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhou, C.; Jin, J.; Yu, P.; Wang, F. A novel ring-beam piezoelectric actuator for small-size and high-precision manipulator. Ultrasonics 2019, 96, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonny, J.; Jerker, D. Microelectronics mounted on a piezoelectric transducer: Method, simulations, and measurements. Ultrasonic 2006, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, W.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Darvell, B.W.; Chen, Z. Porous Li–Na–K niobate bone-substitute ceramics: Microstructure and piezoelectric properties. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3506–3508. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, H.; Teranishi, K.; Suzuki, S. Observation of light emissions around a piezoelectric transformer in various gases. IEEE Trans. Plasma. Sci. 2002, 30, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, Y.; Nishihara, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Ueda, M.; Miyashita, T. Development of Piezoelectric Thin Film Resonator and Its Impact on Future Wireless Communication Systems. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardaraviius, L.; Kerulis, S.; Kiprijanovi, O.; Imkeviius, E.; Amontas, S. The Barkhausen Method to Investigate Powerful Processes during Action of Piezoelectric Igniters. Mater. Sci. 2020, 26, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, E.; Yang, G.; Han, Y.; Chang, M. Experimental simulation of self-powered overload igniter based on Lead Zirconate Titanate. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2020, 314, 112222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y. High-Speed Driving Power for Piezoelectric Ceramic Actuator. Mod. Electron. Tech. 2009, 32, 180–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Sheng, D.; Peng, H.; Shen, G.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y. A Kind of Antimony Manganese Zirconium Titanate Piezoelectric Ceramics for Igniting and Initiating Device. China Patent CN109665838A, 23 April 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, P.; Verma, K.; Vaish, R. Solar Energy Harvesting Using Pyroelectric Effect Associated with Piezoelectric Buzzer. Phys. Status. Solidi. A 2019, 216, 1900440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Sugisawa, R.; Sakurada, Y.; Aoshima, H.; Hikida, M.; Akaishi, H. Energy Harvesting Devices Utilizing Resonance Vibration of Piezoelectric Buzzer. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 09KD14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.R.; Chen, R.L.; Chuang, C.Y.; Yu, C.S.; Hsieh, H.L. Optimal design of resonant piezoelectric buzzer from a perspective of vibration-absorber theory. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solvay. Products list. Available online: https://www.solvay.com/en/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Steel, G.A.; Smith, B.V.; Gazey, B.K. Tunable sonar transducer. Electron. Lett. 1986, 22, 758–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, L.; Wei, P.; Tang, L. Modeling and analysis of multilayer piezoelectric-elastic spherical transducers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 2437–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-W.; Wang, L.-H. Wide band underwater acoustic transducer for stacked 2-2 piezoelectric composite material tube. Ferroelectrics 2017, 520, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- María, S.; Carlos, L.; Ivan, F.; Juan, M.M.; Miguel, A. Transducer Development and Characterization for Underwater Acoustic Neutrino Detection Calibration. Sensors 2016, 16, 1210. [Google Scholar]
- Savoia, A.S.; Mauti, B.; Caliano, G. A Low Frequency Broadband Flextensional Ultrasonic Transducer Array. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferr. 2015, 63, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.X.; Yang, Q.; Luo, M.; Liu, R. Effect of the physical parameters of longitudinally polarized PZT tubes on PZT sensors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 275501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garroni, S.; Senes, N.; Iacomini, A.; Enzo, S.; Mulas, G.; Pardo, L.; Cuesta-Lopez, S. Advanced Synthesis on Lead-Free KxNa(1−x)NbO3 Piezoceramics for Medical Imaging Applications. Phys. Status Solidi A 2018, 215, 1700896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AAC Technologies. Products List. Available online: https://www.aactechnologies.com/en/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Lee, B.; Paik, S.J.; Kim, B. Orbital Driving and Detection System of Piezoelectric Gyroscopes for Inertia Sensors. J. Semicond. Tech. Sci. 2019, 19, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, X.D.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Y. Modeling and Performance Investigation of a Piezoelectric Vibrating Gyroscope. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Paik, S.J.; Chun, K.; Kim, B. Driving and detection system of vibrating piezoelectric gyroscope at atmospheric pressure for multi-axial inertia sensor. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 4173–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodjat-Shamami, M.; Ayazi, F. Eigenmode operation of piezoelectric resonant gyroscopes. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEDRAT Technologies. Products list. Available online: https://www.cedrat-technologies.com/en/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Asbjoern, K.; Svein, M.; Iversen, N.E. Transducer Arrangement. U.S. Patent US5877996A, 2 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.D.; Wang, C.J.; Wang, J.F. Study on piezoelectric ceramic transducer used in ultrasonic detection of deep-oil-well. J. Func. Mat. Dev. 2002, 4, 418–420. [Google Scholar]
- Kweon, S.-H.; Tani, K.; Kanda, K.; Nahm, S.; Kanno, I. Piezoelectric PZT thin-film transformers with a ring–dot structure. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, SPPD09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Maurya, D.; Carazo, A.V.; Mohan, S.; Priya, S. Tunable High-Power Multilayer Piezoelectric Transformer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 8335–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.T.; Kong, S.H. Design of High Efficiency Controller for Wide Input Range DC-DC Piezoelectric Transformer Converter. IEEE Access 2020, 99, 225650–225662. [Google Scholar]
- Arkema. Products list. Available online: https://www.arkema.com/global/en/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Mide Technology Corporation. Products list. Available online: http://www.mide.com (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- USound. Products list. Available online: http://www.usound.com/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Kyocera. Products list. Available online: https://global.kyocera.com/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Vesper Technologies. Products list. Available online: https://vespermems.com/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Cambridge Touch Technolog. Products list. Available online: http://camtouch3d.com (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Bobrow, L.S. Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering; Oxford University Press: Oxford, MS, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.J.; Jia, S.H.; Yang, J.; Cai, H. Study on Equivalent Circuit Model of Cymbal Transducer. Chin. J. Sens. Actuat. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hu, J.; Fu, Z. Electromechanical characteristics of piezoelectric ceramic transformers in radial vibration composed of concentric piezoelectric ceramic disk and ring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 045018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Radial vibration of the combination of a piezoelectric ceramic disk and a circular ring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Study on the radial vibration of a new type of composite piezoelectric transducer. J. Sound. Vib. 2007, 306, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. The radial composite piezoelectric ceramic transducer. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2008, 141, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. An improved cymbal transducer with combined piezoelectric ceramic ring and metal ring. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2010, 163, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.D.; Lin, S.Y. Analysis on load characteristics of the cascaded piezoelectric transducer. Tech. Acoust. 2019, 38, 232–235. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Lin, S. Analysis of a Cascaded Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Transducer with Three Sets of Piezoelectric Ceramic Stacks. Sensors 2019, 19, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.C.; Dogan, A.; Tressler, J.; Yoshikawa, S.; Newnham, R.E. Ceramic-Metal Composite Actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–11 December 1991; pp. 923–928. [Google Scholar]
- Newnham, R.E.; Dogan, A.; Xu, Q.C.; Onitsuka, K.; Yoshikawa, S. Flextensional Moonie Actuators. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Baltimore, ML, USA, 31 October–3 November 1993; pp. 509–512. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, A.; Yoshikawa, S.; Uchino, K.; Newnham, R.E. The effect of geometry on the characteristics of the moon transducer and reliability issue. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Cannes, France, 1–4 November 1994; pp. 935–939. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, A.; Uchino, K.; Newnham, R.E. Composite piezoelectric transducer with truncated conical endcaps ‘Cymbals’. IEEE Trans. UFFC 1997, 44, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tressler, J.F.; Cao, W.W.; Uchino, K.; Newnham, R.E. Finite element analysis of the Cymbal-Type Flex tensional Transducer. IEEE Trans. UFFC 1998, 45, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tressler, J.F.; Newnham, R.E.; Hughes, W.J. Capped ceramic underwater sound projector. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 101, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newnham, R.E.; Xu, Q.C.; Yoshikawa, S. Transformed Stress Direction-Acoustic Transducer. U.S. Patent 4999819, 12 March 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Sun, F.P.; Rogers, A. Dynamic output characteristics of piezoceramic actuators. In Proceedings of the Smart Structures and Intelligent Systems, SPIE, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1–4 February 1993; pp. 286–298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, M. Testing Technology for Structure Damages Based on Piezoelectric Ceramics Dynamic Information. J. Chongqing Inst. Tech. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2007, 5, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Giurgiutiu, V.; Zagrai, A.N. Embedded self-sensing piezoelectric active sensors for on-line structural identification. J. Vib. Acoust. 2002, 124, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Li, X. A Modified Electro-Mechanical Impedance Model Considering Bonding Layer and Impedance Analytical Expressions. Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 2012, 34, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.F.; Zhou, T.F.; Lan, Y. Research on the low frequency curved hydrophone. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 47, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, F.; He, C.; Luo, H. Displacement amplification and electric characteristics of modified rectangular cymbal transducers using electroactive materials. Solid State Commun. 2007, 143, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, L.C.; Varadan, V.V.; Varadan, V.K. Finite element analysis of flextensional electroacoustic transducers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–11 December 1991; pp. 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.C.; Yoshikawa, S.; Belsick, J.R.; Newnham, R.E. Piezoelectric Composites with High Sensitivity and High Capacitance for Use at High Pressures. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferr. 1991, 38, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, Y. Development of Metal-Ceramic Composite Piezoelectric Actuators and Their Applications. Master’s Thesis, Sophia University, Tokyo, Japan, 1991; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.; Guo, T.; Li, J. A New-Style, Slotted-Cymbal Transducer with Large Displacement and High Energy Transmission. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferr. 2004, 51, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C. Research on the Radial Composite Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Transducers. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk, E.J. Acoustic Cymbal Transducers-Design, Pressure Compensation, and Acoustic Performance. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Manoj, N.; Robert, W.S. Design, fabrication and finite element modeling of a new wagon wheel flextensional transducer. J. Electroceram. 2008, 24, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T. Research on Micro Tube Robot Technology Based on Cymbal Piezoelectric Composite Drive. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hanzhou, China, 2005; pp. 21–62. [Google Scholar]
- Uzgur, E.; Markley, D.C.; Guo, M.; Snyder, B.; Meyer, R.J.; Dogan, A.; Newnham, R.E. Pressure Dependence of Cymbal Transducers. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2007, 32, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jack, H.W.; HladkV-Hcnnion, A.C. Concave cymbal transducers. Mat. Res. Innovat. 1999, 2, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newnham, R.E.; Zhang, J.; Meyer, R., Jr. Cymbal Transducers: A Review. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Symposium on Applications of Ferroelectrics, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21 July–2 August 2000; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hughes, W.J.; Bouchilloux, P.; Meyer, R.J.; Uchino, K.; Newnham, R.E. A miniature class V flextensional cymbal transducer with directional beam patterns: The double -driver. Utrasonics 2001, 39, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T. Cymbal Driver Based on Tangential Deformation and Its Driving Method. China Patent No. 200710030161.5, 7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, C.; Guo, S.; Li, W. A kind of Cymbal Sensor. China Patent No. ZL200420016874.8, 2 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tressler, J.F.; Newnham, R.E. Doubly resonant cymbal-type transducers. IEEE. Trans. Ultrason. Ferr. 1997, 44, 1175–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. New Development of Cymbal Transducer Techniques. Ordnance Ind. Autom. 2014, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa, P.; Villegas, M.; Pons, J.L.; Leidinger, P.; Fernández, J.F. Tunability of Cymbals as Piezocomposite Transducers. J. Electroceram. 2005, 14, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Qin, L.; Wang, T. A Cymbal transducer based low frequency broadband thin panel underwater acoustic projector. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2010, 31, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Wang, T. Design of cymbal-based piezocomposite smart material. J. Funct. Mater. Devices 2010, 16, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.W.; Shi, W.H.; Peter, T.; Yang, M.S. Design and Analysis of Two Piezoelectric Cymbal Transducers with Metal Ring and Add Mass. Sensors 2019, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Peter, T. Low-frequency active noise control of an underwater large-scale structure with distributed giant magnetostrictive actuators. Sens. Actuat. A Phy. 2017, 263, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z. Forecast and Control of the Spring-back of Spherical-cymbal Transducers End-caps in Free-bulging. J. Netshape Form. Eng. 2010, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Pan, Z.M. Research on Displacement Performance of Spherical-Cymbal Transducers. Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 2010, 32, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z. Modeling of the Free-Bulging Process of Spherical-Cymbal Transducer’s End-Caps. Chin. J. Sens. Actuat. 2011, 24, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Pan, Z.M. Finite Element Analysis on Displacement Performance of Spherical-Cymbal Transducers. Chin. J. Sens. Actuat. 2009, 22, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, J.L. Significance Tests on Design Factors Affecting the Frequency Performance of Spherical Cymbal Transducer. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 128–129, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Da, L.L.; Yin, H. Pressure-resistant hydrophone based on piezoelectric ceramic spherical shell. J. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 39, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Xian, X.J.; Li, H.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, L.F.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, D.P. Study on Spherical 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite Ceramic Material. Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 2019, 41, 357–359. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.B.; Qin, L.; Zhong, C.; Wang, L.K. A study of underwater transducers based on piezoelectric composites working at shear vibration modal. J. Vib. Shock 2019, 38, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.J.; Qin, L. Study on flexural transducer based on shear vibration mode. J. Beijing Inf. Sci. Technol. Univ. 2020, 35, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, T.F. Double piezoelectric ceramic elliptical shells transducer and array. Tech. Acoust. 2019, 38, 571–572. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Lin, S.Y. The design thought of a new type of radial transducer using 2-2 type piezoelectric composite material. In Proceedings of the Acoustic Symposium in Western China, Jiuquan, China, 20–24 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, M. Crest Group Products [EB/OL]. Available online: http://www.crest-ultrasonics.com/Push-Pull.htm (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Hielscher. UIP 16000-Industiral Ultrasonic Processor 8000 Watts [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.hielscher.com/i16000_p.htm (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Liu, S.Q.; Lin, S.Y. Radial Vibration Frequency Equation of Composite Disc Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Transducer. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2008, 44, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Yang, X.L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Chen, Z. The radial composite cylindrical piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer. Acta Acustica 2013, 38, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, F.J.; Mühlen, S.S. The resonance frequencies on mechanically pre-stressed ultrasonic piezo transducers. Ultrasonics 2001, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.C. Study on the Prestress of the Longitudinal Piezoelectric Transducer. Ocean Technol. 1996, 15, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Shen, J. The sandwiched radial composite piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer. Acta Acustica 2014, 39, 104–110. [Google Scholar]








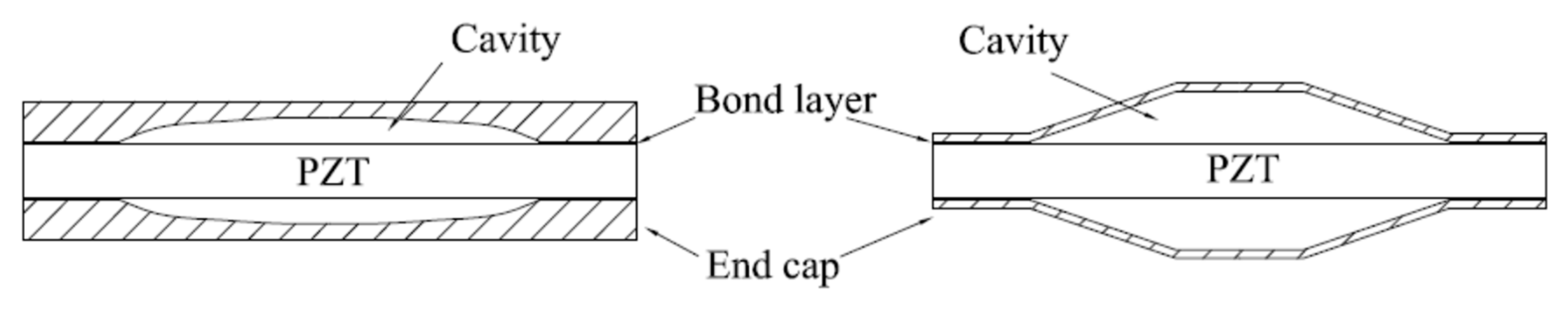

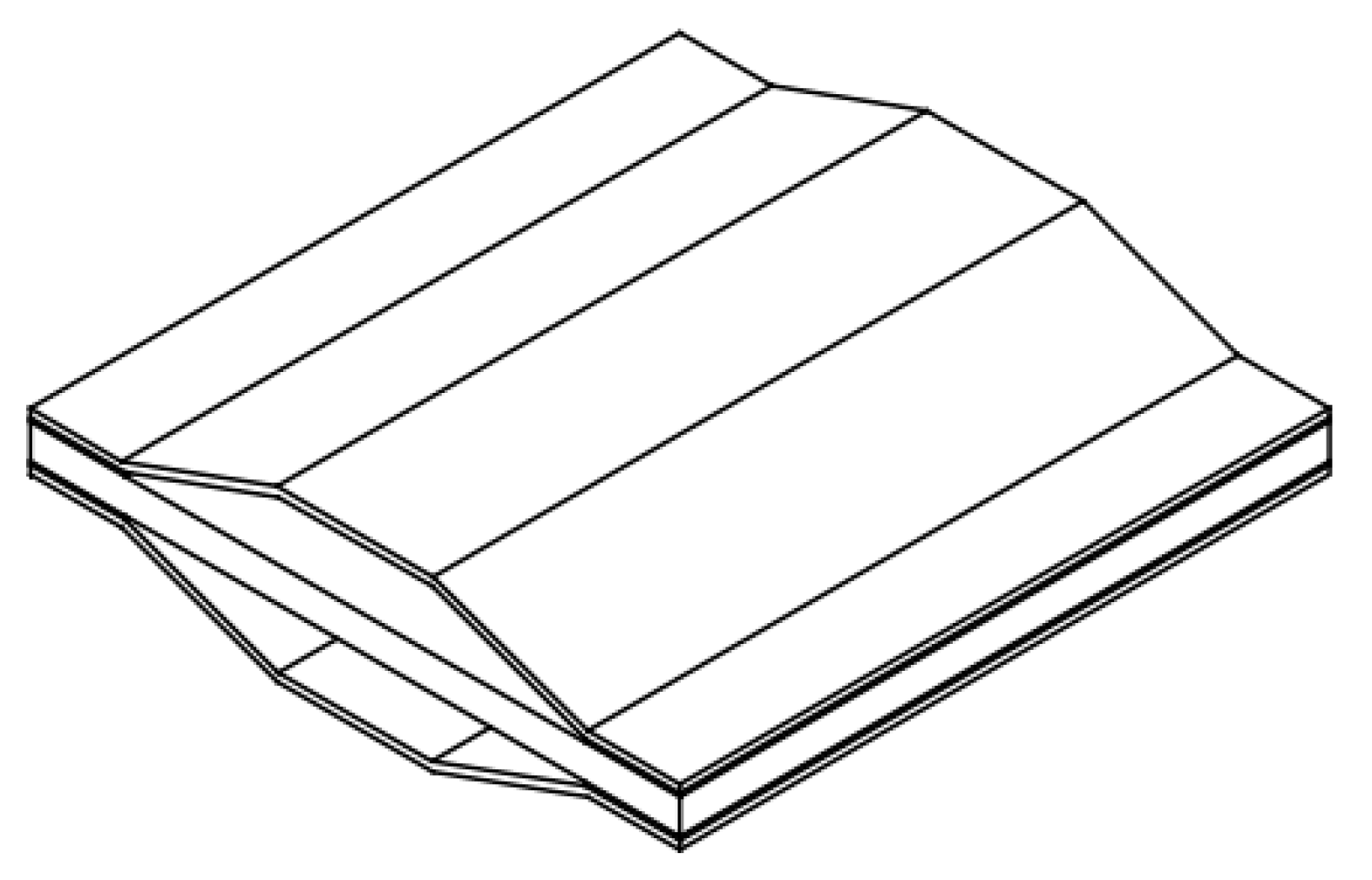



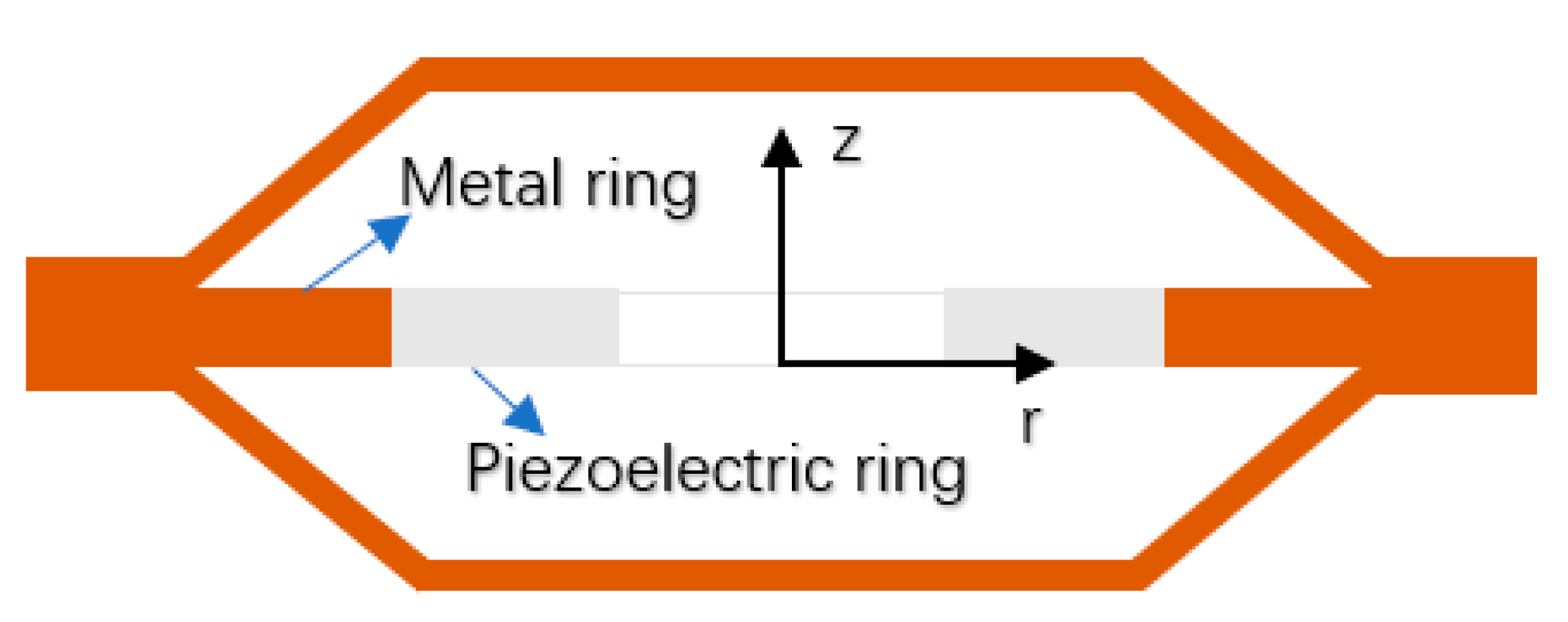



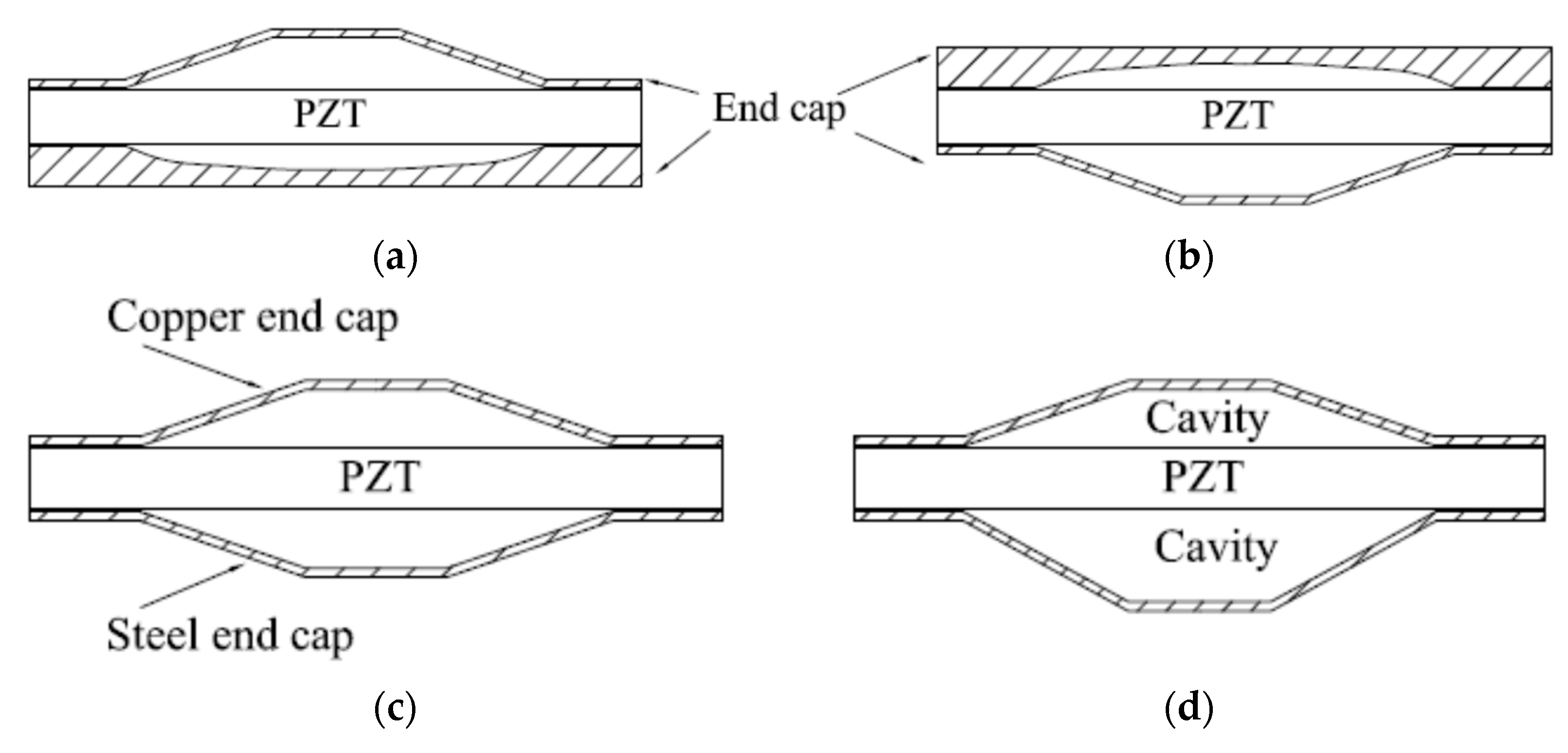






| Ceramic Type | Material Name | Applications | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soft PZT ceramic | PZT-51 | low-power ultrasonic transducers | large piezoelectric constants; high permittivity, large dielectric constants, high dielectric losses, large electromechanical coupling factors, low mechanical quality factors, a low coercive field, poor linearity, easy to depolarize. |
| PZT-52 | low-frequency sound transducers | ||
| PZT-53 | applications with high coefficient | ||
| PZT-5H | microphones, vibration pickups with preamplifier | ||
| PLiS-51 | low-frequency vibration measurements | ||
| PMgN-51 | Hydrophones, transducers in medical diagnostics | ||
| PSnN-5 | Actuators | ||
| Hard PZT ceramic | PZT-41 | small piezoelectric constants, low permittivity, small dielectric constants, low dielectric losses, small electromechanical coupling factors, high mechanical quality factors, high coercive field, good linearity, hard to depolarize. | |
| PZT-42 | High-power acoustic applications | ||
| PZT-43 | Hydroacoustics, sonar technology | ||
| PZT-82 | piezomotor | ||
| PCrN-4 | |||
| PBaS-4 | |||
| Lead free Piezo Ceramic | BaTiO3 | Ultrasonic transducers suitable for low-temperature underwater, for example Ultrasonic Transducer in fishfinder | Low density, low curie temperature, lead free. |
| Material | P-41 | P-51 | P-81 | PbaS-5 | BaTiO3 | PZT-5X | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic compliant constant | S11 (10−12 m2/N) | 12 | 16.7 | 11.1 | 13.5 | 8.4 | 19 |
| Dielectric constant | ε | 1050 | 2200 | 1000 | 1650 | 1550 | 4500 |
| Dielectric loss | tg(%) | <0.3 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 |
| Quality factor | Qm | 1000 | 80 | 800 | 1800 | 1300 | 65 |
| Electromechanical coupling coefficient | kp | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.34 | 0.7 |
| k31 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.3 | 0.34 | 0.196 | 0.4 | |
| k33 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.43 | 0.77 | |
| kt | 0.48 | 0.5 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.32 | 0.53 | |
| Piezoelectric constants | d31 (−10−12 C/N) | 113 | 186 | 90 | 150 | 150 | 300 |
| d33 (10−12 C/N) | 260 | 600 | 220 | 330 | 330 | 750 | |
| g31 (10−3 Vm/N) | 12 | 10 | 11.2 | 10 | 10 | 8 | |
| g33 (10−3 Vm/N) | 28 | 34 | 24.8 | 22 | 22 | 17.5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Thomas, P.J. Structural Design and Physical Mechanism of Axial and Radial Sandwich Resonators with Piezoelectric Ceramics: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041112
Wang W, Jiang Y, Thomas PJ. Structural Design and Physical Mechanism of Axial and Radial Sandwich Resonators with Piezoelectric Ceramics: A Review. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041112
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenjie, Yi Jiang, and Peter J. Thomas. 2021. "Structural Design and Physical Mechanism of Axial and Radial Sandwich Resonators with Piezoelectric Ceramics: A Review" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041112
APA StyleWang, W., Jiang, Y., & Thomas, P. J. (2021). Structural Design and Physical Mechanism of Axial and Radial Sandwich Resonators with Piezoelectric Ceramics: A Review. Sensors, 21(4), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041112







