An Open Dataset for Wearable SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Support
2.2. Participants
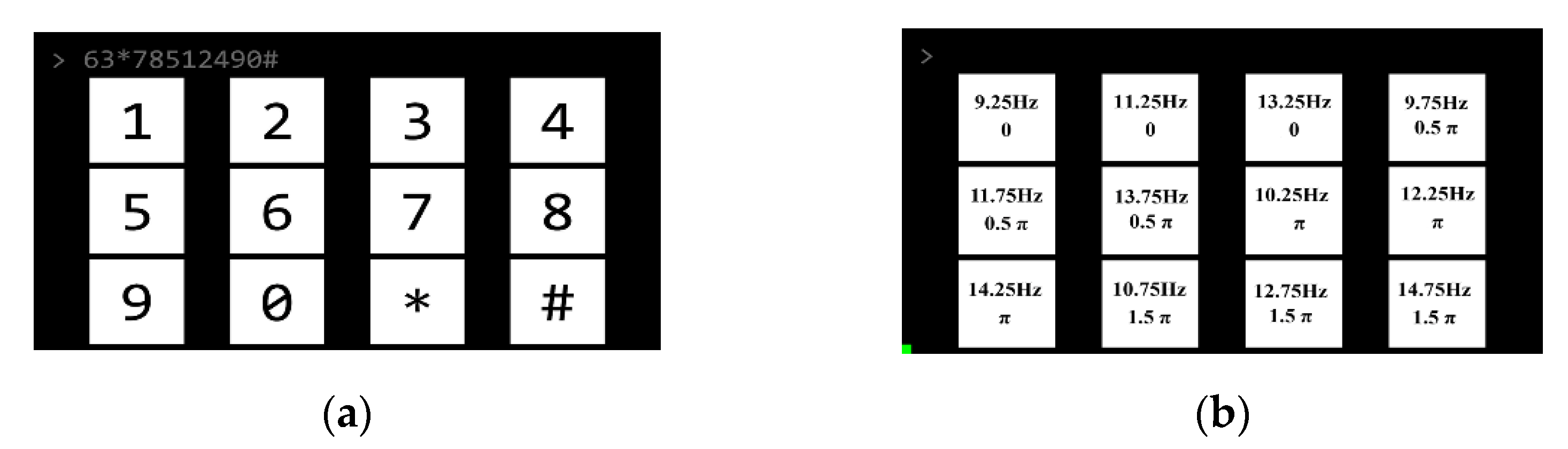
2.3. Stimulus Presentation
2.4. EEG Device and Electrodes
2.5. Experimental Protocol
2.6. Data Acquisition
2.7. Data Preprocessing
2.8. Performance Evaluation
2.9. Data Records
2.9.1. EEG Data
2.9.2. Subject Information and Questionnaires
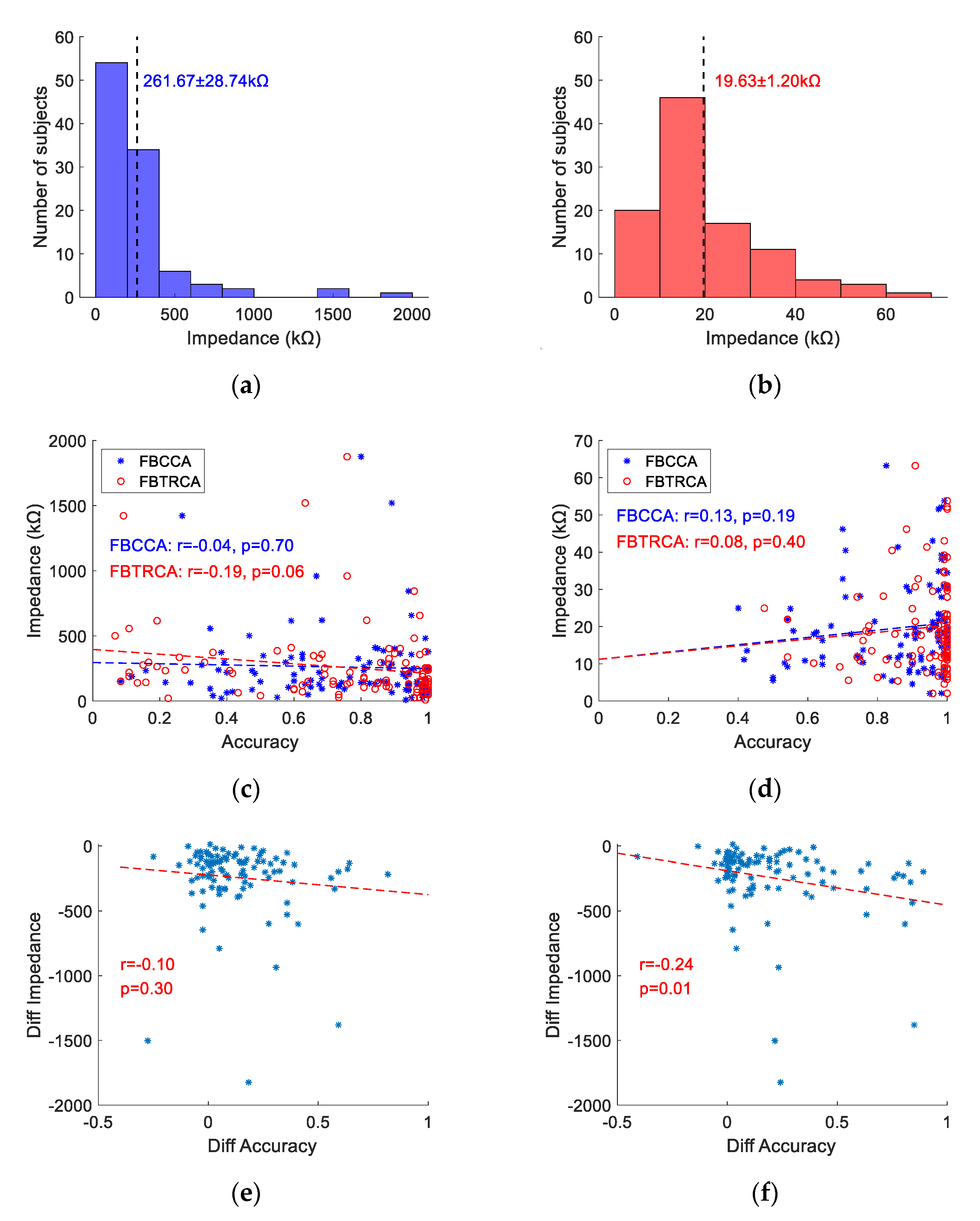
2.9.3. Impedance Information
3. Results
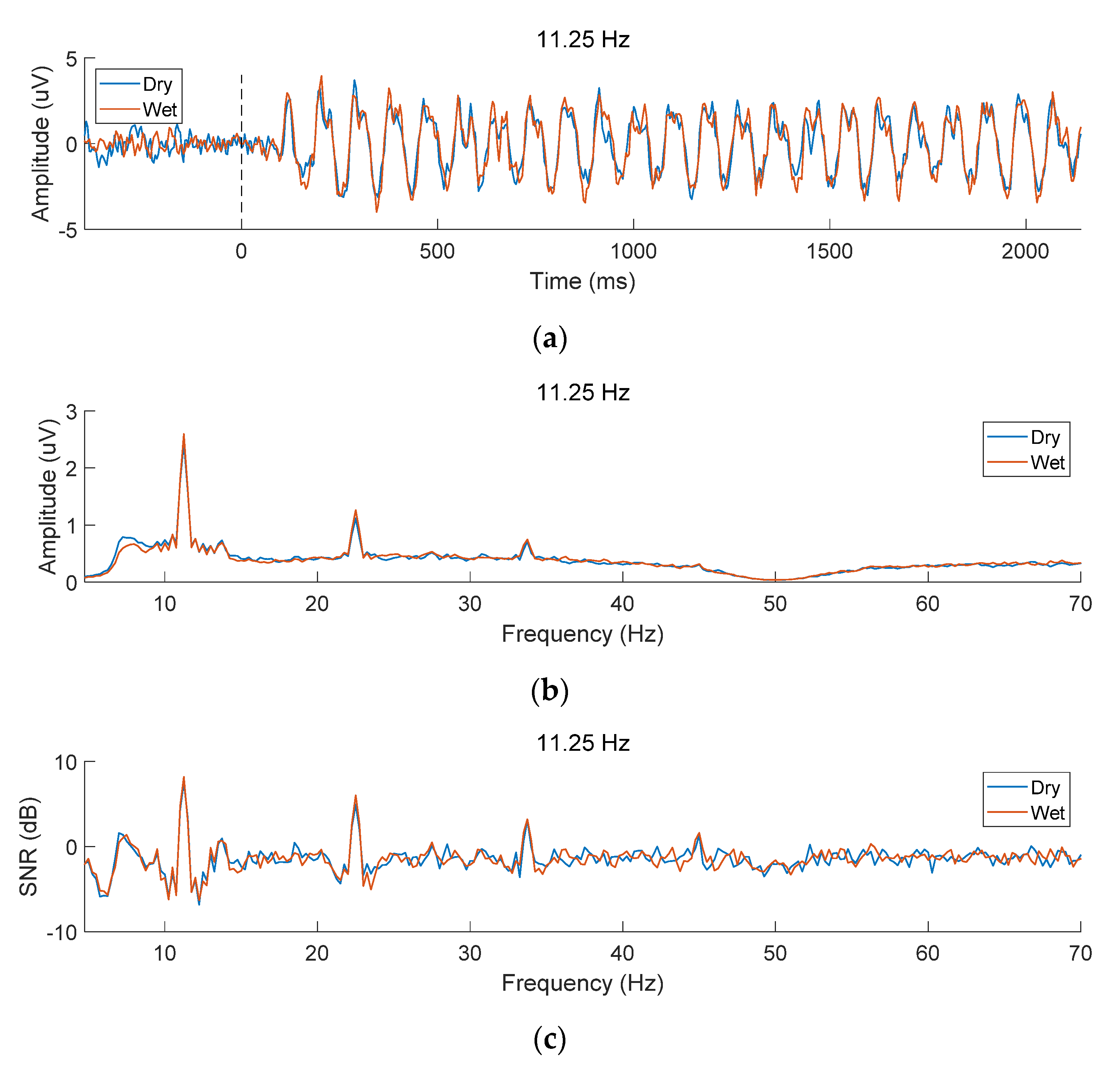
3.1. EEG Characteristics of SSVEPs
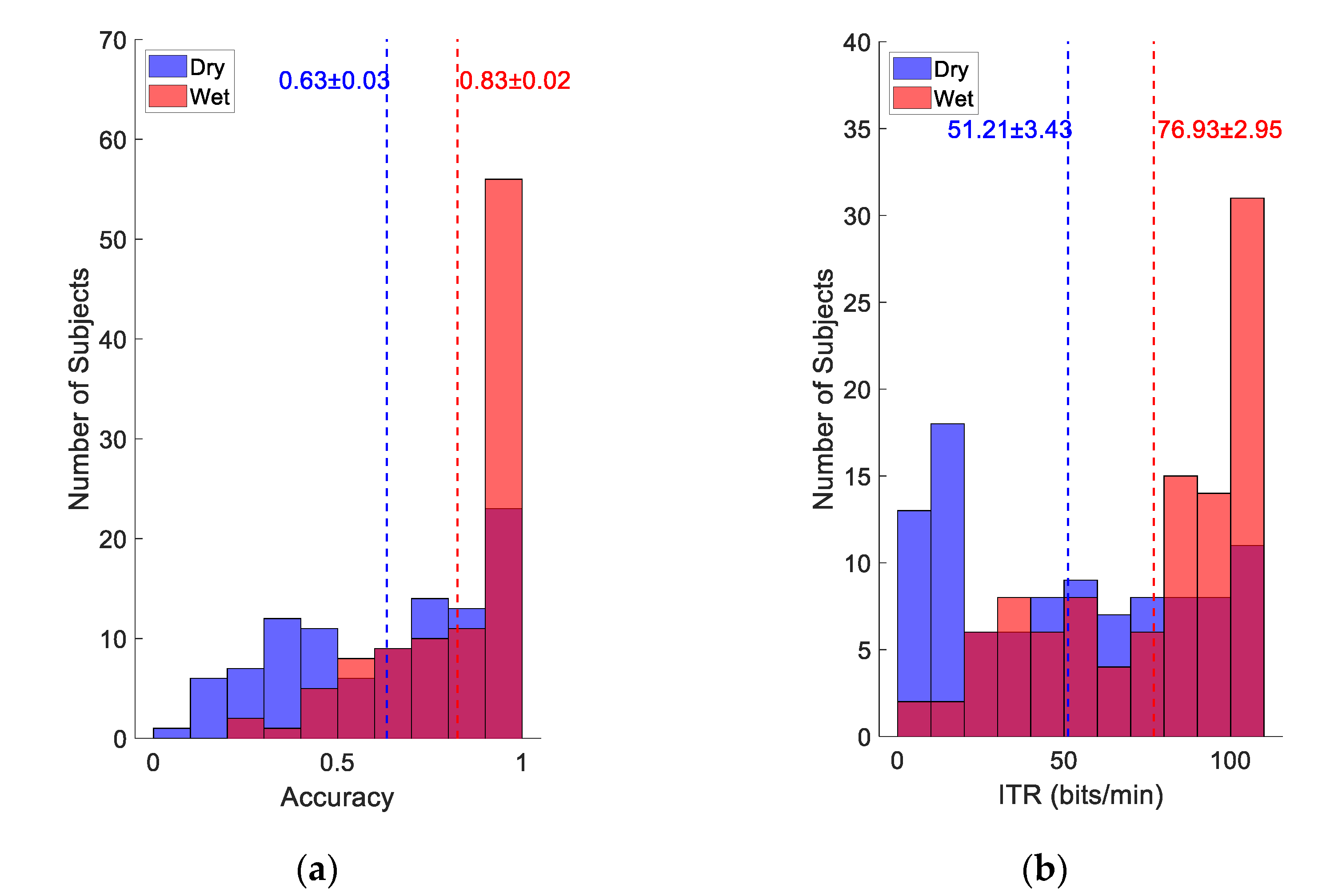
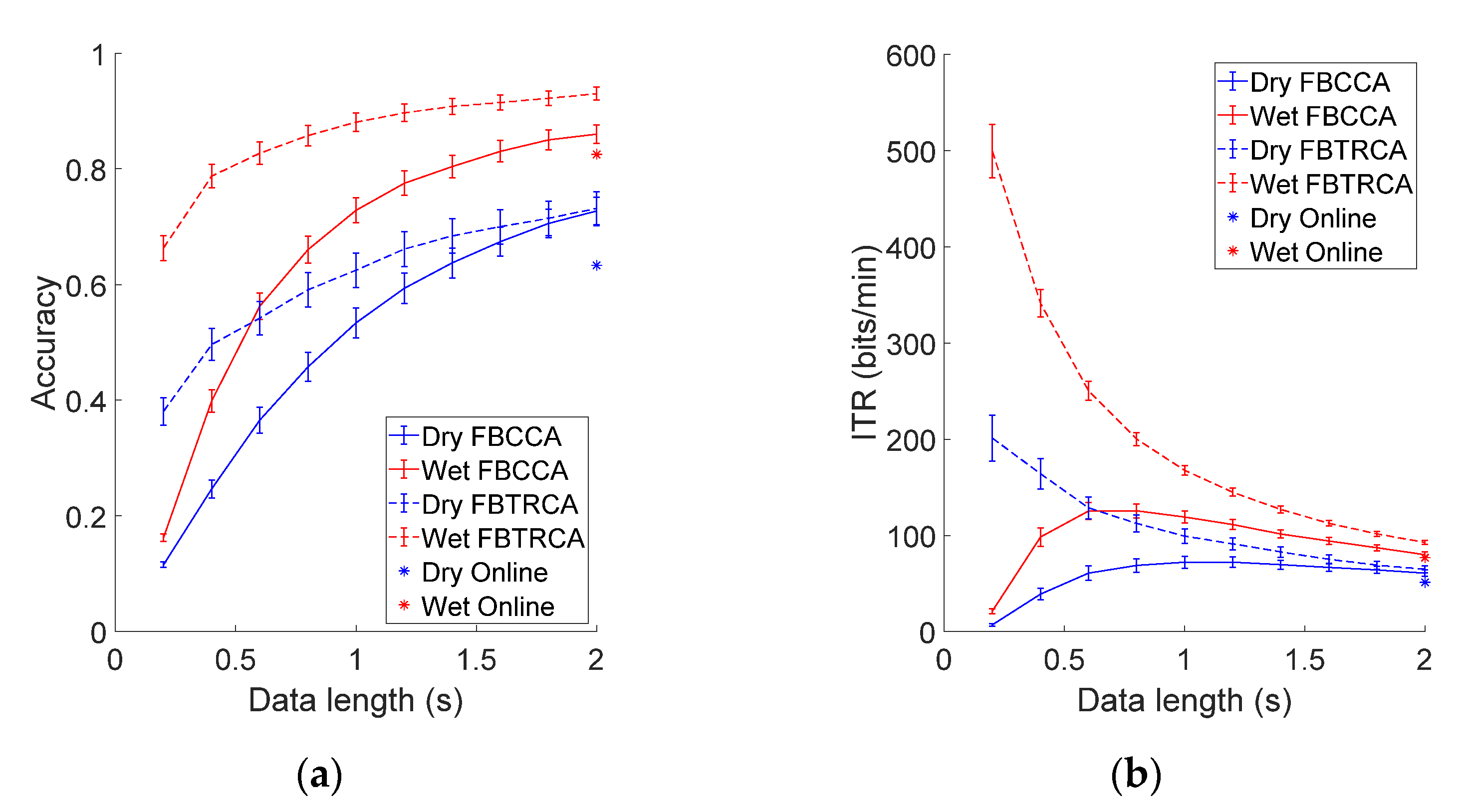
3.2. Online BCI Performance
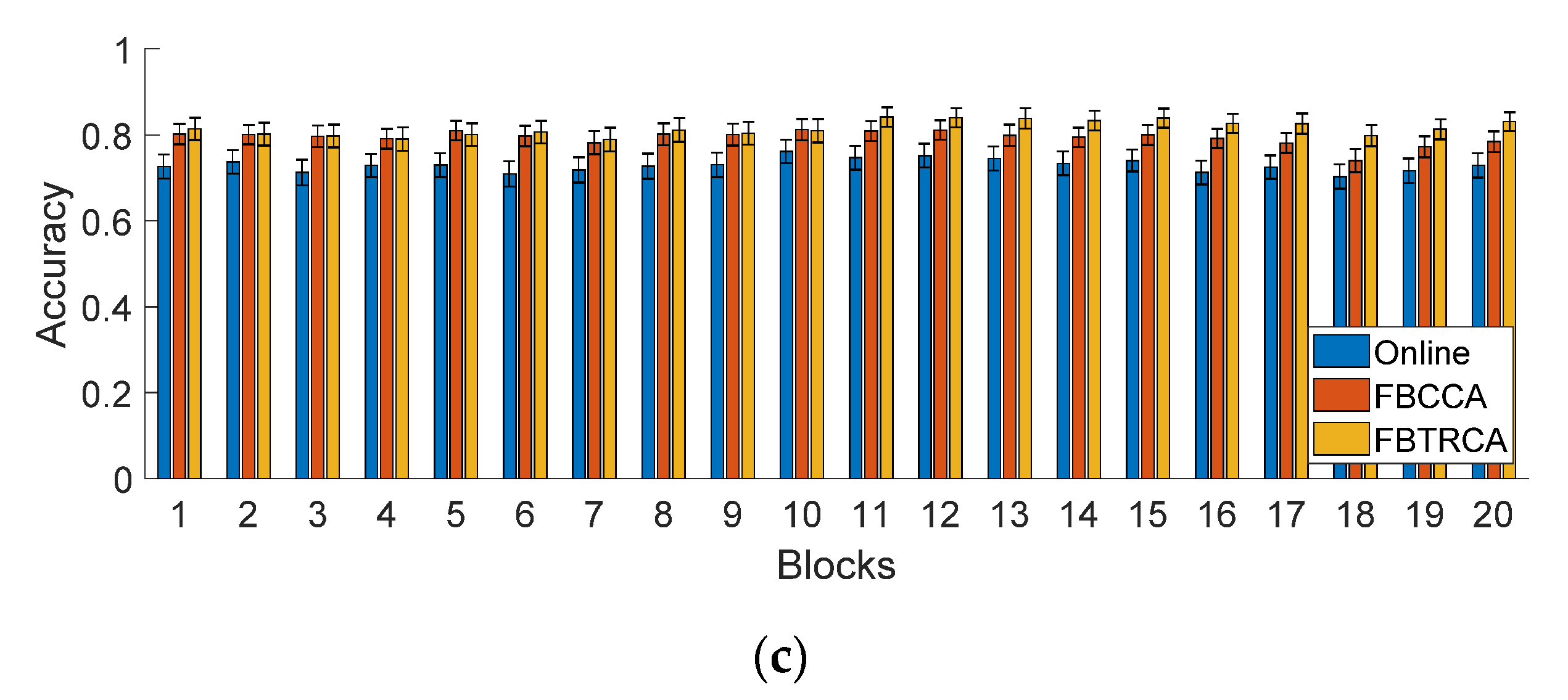
3.3. Offline Analysis
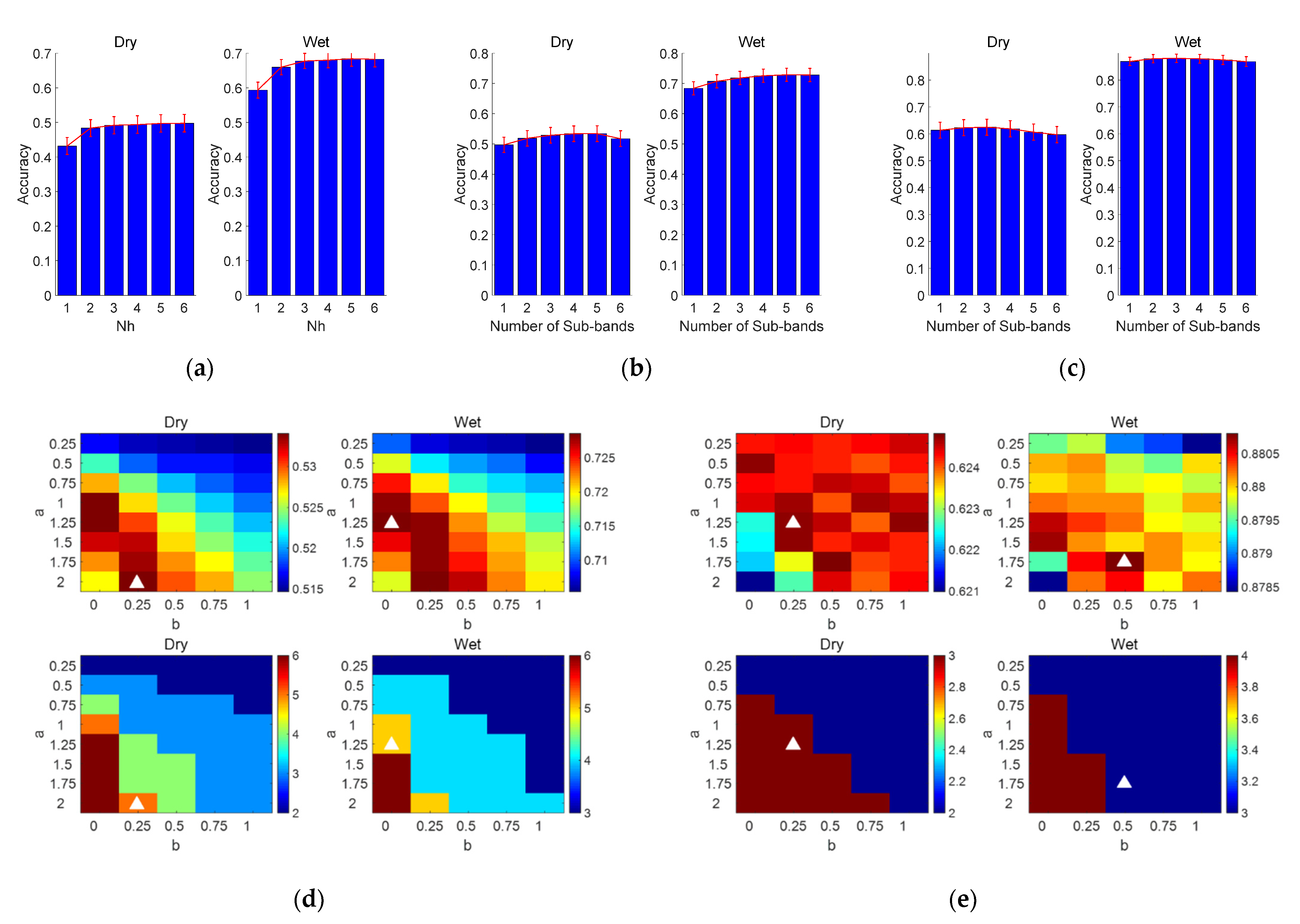
3.3.1. FBCCA Method
3.3.2. FBTRCA Method
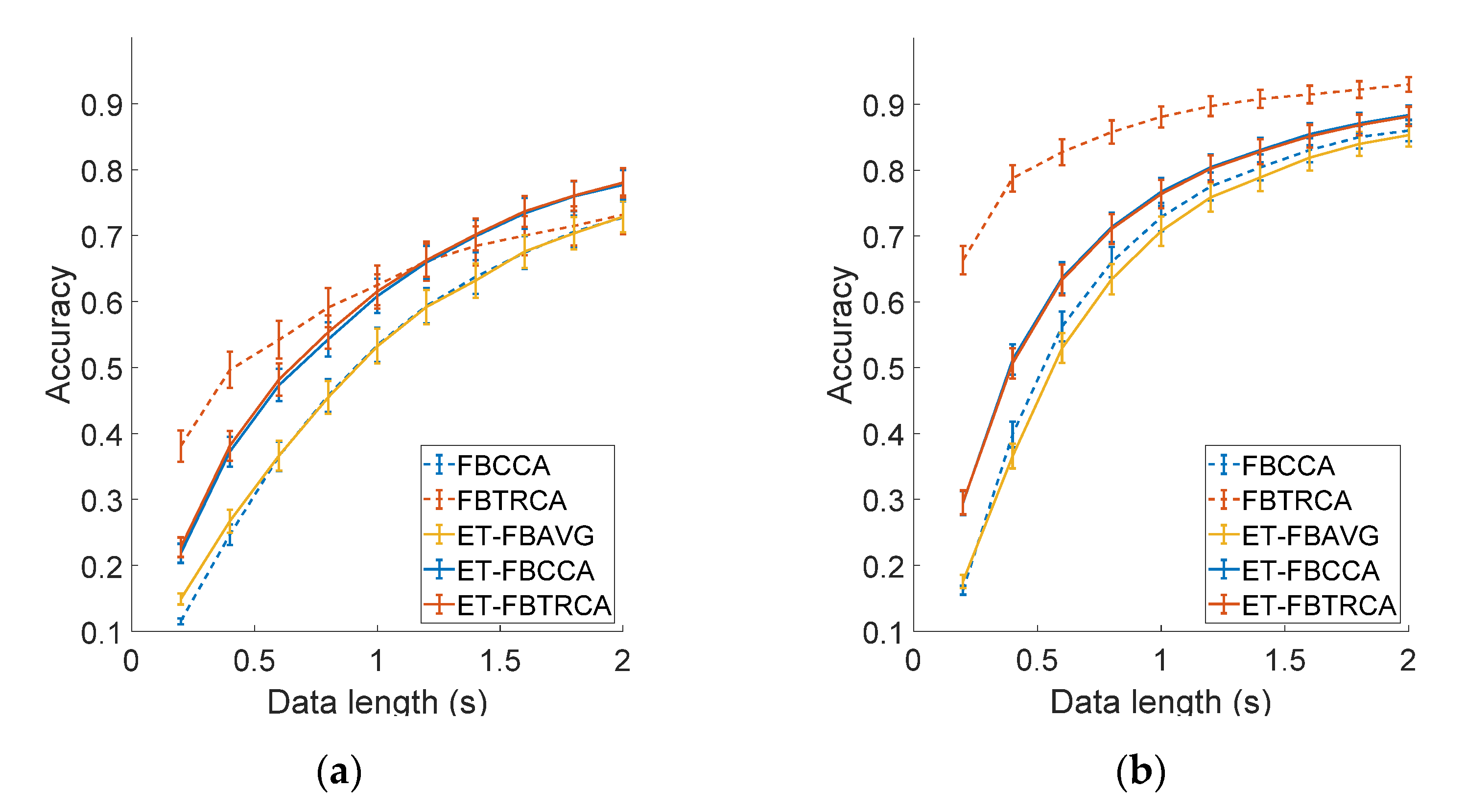
3.3.3. Performance Comparison
3.4. Individual Difference
3.5. Electrode Impedance and Classification Accuracy
3.6. Information Transfer across Electrodes
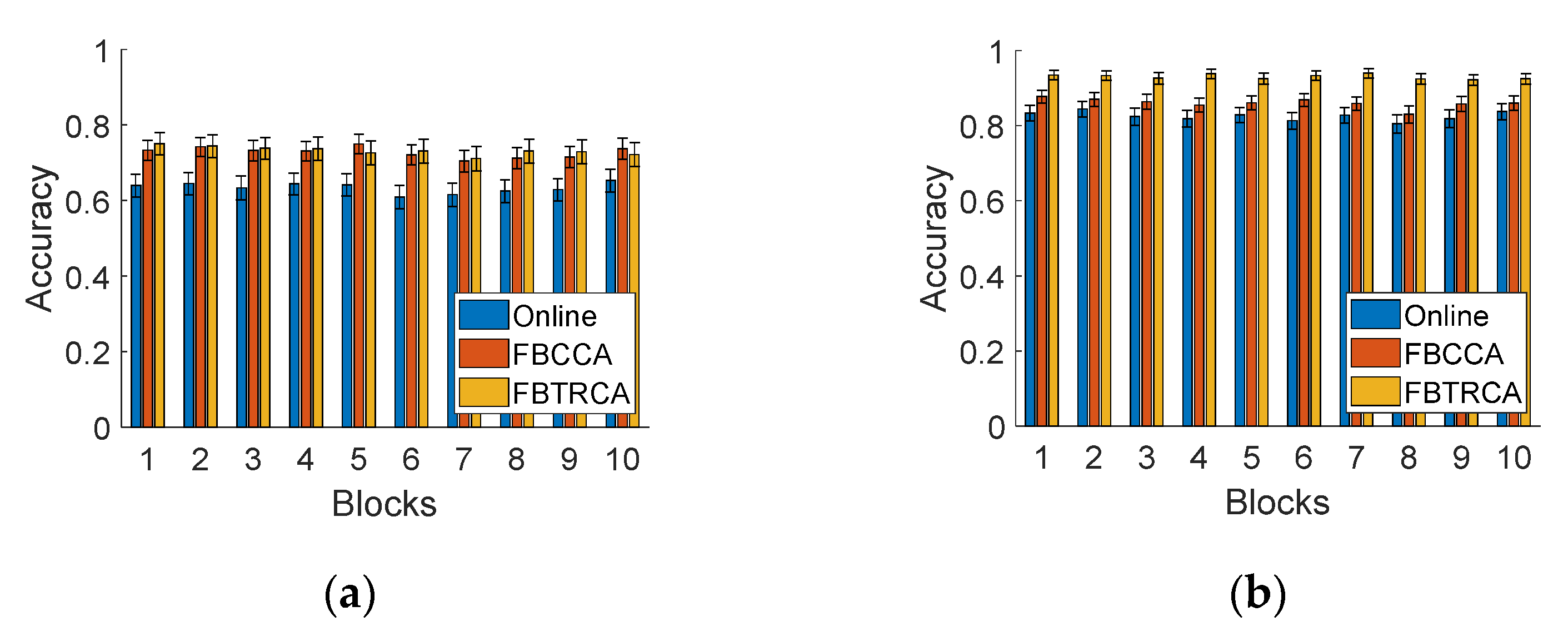
3.7. Time-Variant Effects
3.7.1. Questionnaire
3.7.2. BCI Performance
4. Conclusions and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Hong, B. Visual and Auditory Brain-Computer Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.-P.; Pompili, D.; Elisevich, K.; Soltanian-Zadeh, H. Optimized Deep Learning for EEG Big Data and Seizure Prediction BCI via Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2017, 3, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.R.; Xu, D.F.; Cheng, M.; Gao, S.K. A BCI-based environmental controller for the motion-disabled. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Gao, X.; Jung, T.-P.; Gao, S. High-speed spelling with a noninvasive brain-computer interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6058–E6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandarinath, C.; Nuyujukian, P.; Blabe, C.H.; Sorice, B.L.; Saab, J.; Willett, F.R.; Hochberg, L.R.; Shenoy, K.V.; Henderson, J.M. High performance communication by people with paralysis using an intracortical brain-computer interface. eLife 2017, 6, e18554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Wan, F.; Wong, C.M.; da Cruz, J.N.; Hu, Y. Objective evaluation of fatigue by EEG spectral analysis in steady-state visual evoked potential-based brain-computer interfaces. Biomed. Eng. Online 2014, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Wong, C.M.; Wang, Z.; Wan, F.; Vai, M.I.; Mak, P.U.; Hu, Y.; Rosa, A.C. Fatigue Evaluation Using Multi-Scale Entropy of EEG in SSVEP-Based BCI. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 108200–108210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Hong, B.; Jia, C.; Gao, S. Brain-computer interfaces based on visual evoked potentials—Feasibility of practical system designs. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2008, 27, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialatte, F.-B.; Maurice, M.; Dauwels, J.; Cichocki, A. Steady-state visually evoked potentials: Focus on essential paradigms and future perspectives. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 90, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; Gao, X. A high-ITR SSVEP-based BCI speller. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 2014, 1, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, G.; Gao, X.; Yan, Z.; Hong, B.; Gao, S. An online multi-channel SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using a canonical correlation analysis method. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Jung, T.-P.; Gao, X. Filter bank canonical correlation analysis for implementing a high-speed SSVEP-based brain-computer interface. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.-T.; Gao, X.; Jung, T.-P. Enhancing Detection of SSVEPs for a High-Speed Brain Speller Using Task-Related Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Wei, C.-S.; Chiang, K.-J.; Jung, T.-P. Facilitating Calibration in High-Speed BCI Spellers via Leveraging Cross-Device Shared Latent Responses. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Wan, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Nan, W.; Lao, K.F.; Mak, P.U.; Vai, M.I.; Rosa, A. Learning across multi-stimulus enhances target recognition methods in SSVEP-based BCIs. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 016026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Gao, X.R.; Gao, S.G.; Xu, D.F. Design and implementation of a brain-computer interface with high transfer rates. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z. SSVEP Extraction Based on the Similarity of Background EEG. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Sullivan, T.J. A user-friendly SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using a time-domain classifier. J. Neural Eng. 2010, 7, 026010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wittevrongel, B.; Khachatryan, E.; Hnazaee, M.F.; Camarrone, F.; Carrette, E.; De Taeye, L.; Meurs, A.; Boon, P.; Van Roost, D.; Van Hulle, M.M. Decoding Steady-State Visual Evoked Potentials From Electrocorticography. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friman, O.; Volosyak, I.; Graeser, A. Multiple channel detection of steady-state visual evoked potentials for brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalunga, E.K.; Chevallier, S.; Barthelemy, Q.; Djouani, K.; Monacelli, E.; Hamam, Y. Online SSVEP-based BCI using Riemannian geometry. Neurocomputing 2016, 191, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, N.-S.; Mueller, K.-R.; Lee, S.-W. A convolutional neural network for steady state visual evoked potential classification under ambulatory environment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, X.; Gao, S. A Benchmark Dataset for SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-K.; Lee, Y.-E.; Williamson, J.; Fazli, S.; Lee, S.-W. EEG dataset and OpenBMI toolbox for three BCI paradigms: An investigation into BCI illiteracy. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, X. BETA: A Large Benchmark Database Toward SSVEP-BCI Application. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Tomita, Y.; Horiuchi, T. Clinical application of an active electrode using an operational amplifier. IEEE Trans. Bio-Med. Eng. 1992, 39, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, L.A.; Steinberg, R.; Wise, G. Dry electrodes and holder for electro-oculography. Med. Biol. Eng. 1973, 11, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes, L.F.; Day, J.L.; Kennedy, L. The response of human skin to long-term space flight electrodes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1967, 49, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sellers, E.W.; Turner, P.; Sarnacki, W.A.; McManus, T.; Vaughan, T.M.; Matthews, R. A Novel Dry Electrode for Brain-Computer Interface. In Human-Computer Interaction, Pt II: Novel Interaction Methods and Techniques; Jacko, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5611, pp. 623–631. [Google Scholar]
- Kubler, A.; Nijboer, F.; Mellinger, J.; Vaughan, T.M.; Pawelzik, H.; Schalk, G.; McFarland, D.J.; Birbaumer, N.; Wolpaw, J.R. Patients with ALS can use sensorimotor rhythms to operate a brain-computer interface. Neurology 2005, 64, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, J.W.Y.; Griffin, S.; Shen, A.; Patel, S.; Hinrichs, H.; Heinze, H.-J.; Deouell, L.Y.; Knight, R.T. Systematic comparison between a wireless EEG system with dry electrodes and a wired EEG system with wet electrodes. Neuroimage 2019, 184, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubler, A.; Neumann, N.; Kaiser, J.; Kotchoubey, B.; Hinterberger, T.; Birbaumer, N.P. Brain-computer communication: Self-regulation of slow cortical potentials for verbal communication. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morriss, R.K.; Wearden, A.J.; Mullis, R. Exploring the validity of the Chalder fatigue scale in chronic fatigue syndrome. J. Psychosom. Res. 1998, 45, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Costa, E.; Menezes, P.R.; Chalder, T.; Bhugra, D.; Wessely, S. Cross-cultural validation of the Chalder Fatigue Questionnaire in Brazilian primary care. J. Psychosom. Res. 2007, 62, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brainard, D.H. The Psychophysics Toolbox. Spat. Vis. 1997, 10, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.-T.; Mitsukura, Y.; Jung, T.-P. A high-speed brain speller using steady-state visual evoked potentials. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2014, 24, 1450019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Russo, F.; Spinelli, D. Electrophysiological evidence for an early attentional mechanism in visual processing in humans. Vis. Res. 1999, 39, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dry | Wet | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion (%) | Time (h) | Proportion (%) | Time (h) | |
| Level 1 | 20.59 | 0 | 83.33 | 0 |
| Level 2 | 46.08 | 0.61 ± 0.05 | 13.73 | 0.75 ± 0.02 |
| Level 3 | 13.72 | 0.76 ± 0.08 | 2.94 | 1 ± 0 |
| Level 4 | 19.61 | 0.71 ± 0.10 | 0 | / |
| Comfort (%) | Comfort and Convenience (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Dry | 5.89 | 13.72 |
| Wet | 83.33 | 68.63 |
| Either | 10.78 | 17.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, F.; Jiang, L.; Dong, G.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y. An Open Dataset for Wearable SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. Sensors 2021, 21, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041256
Zhu F, Jiang L, Dong G, Gao X, Wang Y. An Open Dataset for Wearable SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041256
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Fangkun, Lu Jiang, Guoya Dong, Xiaorong Gao, and Yijun Wang. 2021. "An Open Dataset for Wearable SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041256
APA StyleZhu, F., Jiang, L., Dong, G., Gao, X., & Wang, Y. (2021). An Open Dataset for Wearable SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. Sensors, 21(4), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041256





