The Feasibility of Equine Field-Based Postural Sway Analysis Using a Single Inertial Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lameness Induction
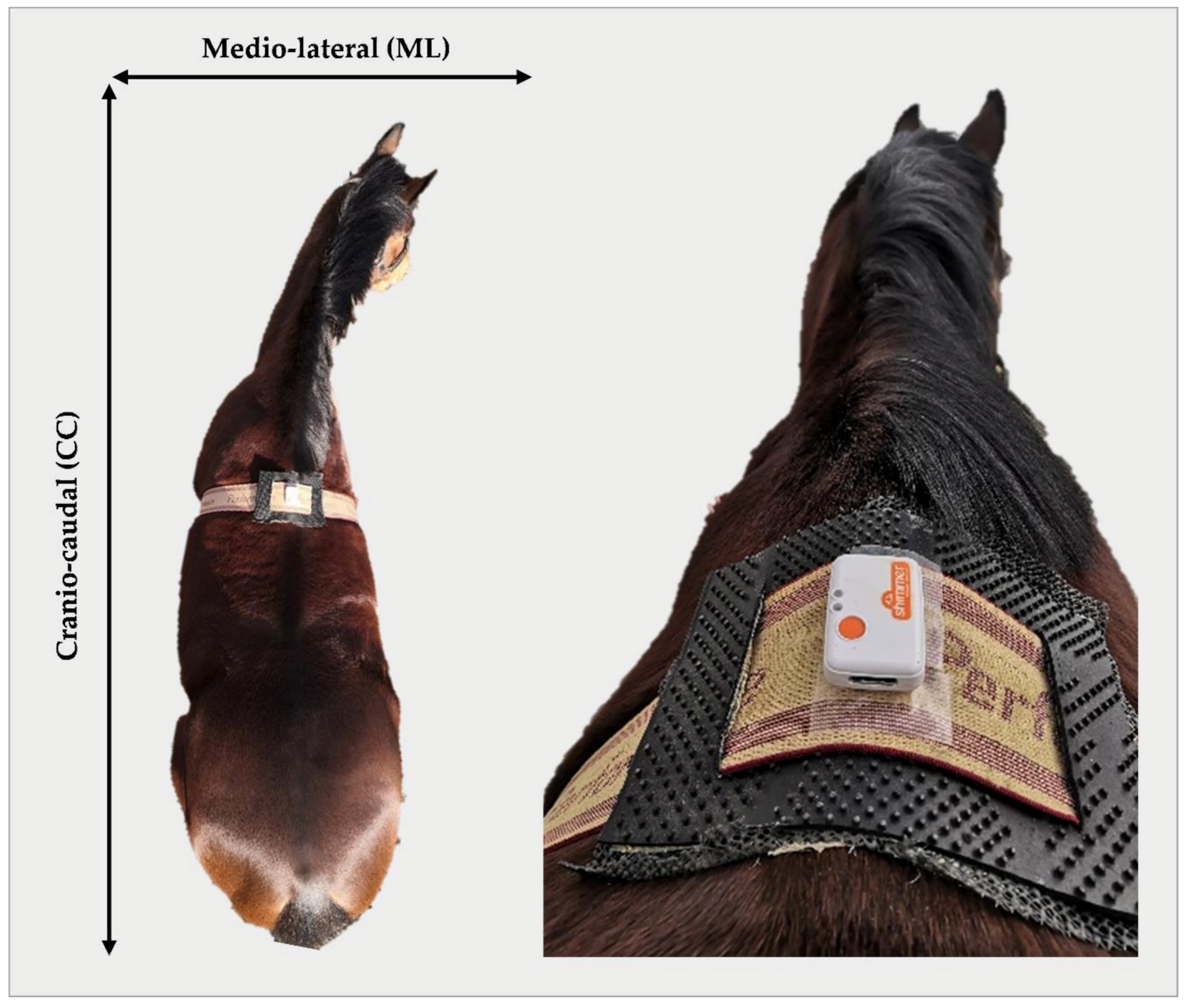
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Quiet Standing: Video Annotation
2.3.2. Quiet Standing: IMU Processing
2.4. Displacement Analysis
2.5. Path Length
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Frequency of Quiet Standing
3.2. Inflammation Markers
3.3. Displacement Analysis
3.4. Path Length
3.5. Stabilograms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuo, A.D.; Speers, R.A.; Peterka, R.J.; Horak, F.B. Effect of altered sensory conditions on multivariate descriptors of human postural sway. Exp. Brain Res. 1998, 122, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollock, A.S.; Durward, B.R.; Rowe, P.J.; Paul, J.P. What is balance? Clin. Rehabil. 2000, 14, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, B.; Costa, B.M.; Hu, K.; Newton, E.; Starobinets, O.; Kang, H.G.; Peng, C.K.; Novak, V.; Lipsitz, L.A. Physiological complexity and system adaptability: Evidence from postural control dynamics of older adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrà, M.F.; Warmerdam, E.; Vila-Chã, N.; Maetzler, W.; Maia, L. Wearable Health Technology to Quantify the Functional Impact of Peripheral Neuropathy on Mobility in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampogna, A.; Mileti, I.; Palermo, E.; Celletti, C.; Paoloni, M.; Manoni, A.; Mazzetta, I.; Dalla Costa, G.; Pérez-López, C.; Camerota, F. Fifteen years of wireless sensors for balance assessment in neurological disorders. Sensors 2020, 20, 3247. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakita, T.; Kuno, S.; Miyake, Y.; Watanabe, S. Body sway induced by depth linear vection in reference to central and peripheral visual field. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2000, 50, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellis, K.L.; King, M.R. Relationship between postural stability and paraspinal muscle adaptation in lame horses undergoing rehabilitation. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 91, 103108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, W.H.; Winter, D.A.; Frank, J.S.; Adkin, A.L. Kinematic and kinetic validity of the inverted pendulum model in quiet standing. Gait Posture 2004, 19, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, R.M.; Ingersoll, C.D.; Stone, M.B.; Krause, B.A. Center-of-pressure parameters used in the assessment of postural control. J. Sport Rehabil. 2002, 11, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghislieri, M.; Gastaldi, L.; Pastorelli, S.; Tadano, S.; Agostini, V. Wearable inertial sensors to assess standing balance: A systematic review. Sensors 2019, 19, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, D.A. Human balance and posture control during standing and walking. Gait Posture 1995, 3, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Abe, M.; Masani, K.; Kawashima, N.; Eto, F.; Haga, N.; Nakazawa, K. Evaluation of postural control in quiet standing using center of mass acceleration: Comparison among the young, the elderly, and people with stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingenen, B.; Janssens, L.; Luyckx, T.; Claes, S.; Bellemans, J.; Staes, F.F. Postural stability during the transition from double-leg stance to single-leg stance in anterior cruciate ligament injured subjects. Clin. Biomech. 2015, 30, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norré, M.; Forrez, G. Posture testing (posturography) in the diagnosis of peripheral vestibular pathology. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 1986, 243, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, M.G.; Murnaghan, C.D.; Inglis, J.T. Shifting the balance: Evidence of an exploratory role for postural sway. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.; De Luca, C. Upright, correlated random walks: A statistical-biomechanics approach to the human postural control system. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 1995, 5, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, H.M.; Bialski, D.E. Assessment of the reliability of a technique to measure postural sway in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 64, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, H.M.; Nauwelaerts, S. Effect of blindfolding on centre of pressure variables in healthy horses during quiet standing. Vet. J. (Lond. Engl. 1997) 2014, 199, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, H.M.; Nauwelaerts, S. Is a single force plate adequate for stabilographic analysis in horses? Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialski, D.; Lanovaz, J.L. Effect of detomidine on postural sway in horses. Equine Comp. Exerc. Physiol. 2004, 1, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, S.; Brama, P.; McGrath, D. Research trends in equine movement analysis, future opportunities and potential barriers in the digital age: A scoping review from 1978–2018. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, H.M.; Buchholz, R.; Nauwelaerts, S. Relationship between morphological and stabilographic variables in standing horses. Vet. J. 2013, 198 (Suppl. 1), e65–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Costa, M.; Roupa, I.; Pequito, M.; Prazeres, J.; Gaivão, M.; Abrantes, J.; Clayton, H.M. The use of pressure plates for static Center of Pressure Analysis in horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doheny, E.P.; McGrath, D.; Greene, B.R.; Walsh, L.; McKeown, D.; Cunningham, C.; Crosby, L.; Kenny, R.A.; Caulfield, B. Displacement of centre of mass during quiet standing assessed using accelerometry in older fallers and non-fallers. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 3300–3303. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, D.; Doheny, E.P.; Walsh, L.; McKeown, D.; Cunningham, C.; Crosby, L.; Kenny, R.A.; Stergiou, N.; Caulfield, B.; Greene, B.R. Taking balance measurement out of the laboratory and into the home: Discriminatory capability of novel centre of pressure measurement in fallers and non-fallers. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 3296–3299. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, C.; Zhao, L.; Ryan, J.; Komaba, Y.; Inomata, A.; Caulfield, B. Quantification of postural control deficits in patients with recent concussion: An inertial-sensor based approach. Clin. Biomech. 2017, 42, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moorman, V.J.; Kawcak, C.E.; King, M.R. Evaluation of a portable media device for use in determining postural stability in standing horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 78, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchner, H.H.; Savelberg, H.H.; Schamhardt, H.C.; Barneveld, A. Bilateral lameness in horses—A kinematic study. Vet. Q. 1995, 17, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, K.G.; MacAllister, C.G.; Wilson, D.A.; Gedon, C.A.; Kramer, J.; Yonezawa, Y.; Maki, H.; Pai, P.F. Comparison of an inertial sensor system with a stationary force plate for evaluation of horses with bilateral forelimb lameness. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, S. Can lameness be graded reliably? Equine Vet. J. 2011, 43, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchner, H.H.F.; Obermüller, S.; Scheidl, M. Body centre of mass movement in the sound horse. Vet. J. 2000, 160, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, N.; Taylor, W.; Baumann, C.R.; Wenderoth, N.; Singh, N.B. Revealing the quality of movement: A meta-analysis review to quantify the thresholds to pathological variability during standing and walking. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egan, S.; Kearney, C.M.; Brama, P.A.J.; Parnell, A.C.; McGrath, D. Exploring stable-based behaviour and behaviour switching for the detection of bilateral pain in equines. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 235, 105214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madgwick, S.O.; Harrison, A.J.; Vaidyanathan, R. Estimation of IMU and MARG orientation using a gradient descent algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lucia, J.; Coverdale, J.; Arnold, C.; Winsco, K. Influence of an intra-articular lipopolysaccharide challenge on markers of inflammation and cartilage metabolism in young horses. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 2693–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.T.; Bolt, D.M.; Ishihara, A.; Rajala-Schultz, P.J.; Bertone, A.L. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of intra-articular injection of triamcinolone acetonide, mepivacaine hydrochloride, or both on lipopolysaccharide-induced lameness in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, B.; Horn, D.; Marclay, S.; Crews, R.T.; Wu, S.; Wrobel, J.S. Assessing Postural Control and Postural Control Strategy in Diabetes Patients Using Innovative and Wearable Technology; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, K.; Rogers, C.W.; Gronqvist, G.; Gee, E.K.; Bolwell, C.F. Anxiety and pain in horses measured by heart rate variability and behavior. J. Vet. Behav. 2017, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, M.G.; Frank, J.S.; Winter, D.A.; Peysar, G.W. Sampling duration effects on centre of pressure summary measures. Gait Posture 2001, 13, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.; Freitas, S.M. Revision of posturography based on force plate for balance evaluation. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2010, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitti, L.; Oosterlinck, M.; Díaz-Bertrana, M.L.; Carrillo, J.M.; Rubio, M.; Sopena, J.; Santana, A.; Vilar, J.M. Assessment of static posturography and pedobarography for the detection of unilateral forelimb lameness in ponies. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stergiou, N.; Harbourne, R.; Cavanaugh, J. Optimal movement variability: A new theoretical perspective for neurologic physical therapy. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2006, 30, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stergiou, N.; Kent, J.A.; McGrath, D. Human movement variability and aging. Kinesiol. Rev. 2016, 5, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greve, L.; Pfau, T.; Dyson, S. Alterations in body lean angle in lame horses before and after diagnostic analgesia in straight lines in hand and on the lunge. Vet. J. 2018, 239, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhea, C.K.; Kiefer, A.W.; Haran, F.; Glass, S.M.; Warren, W.H. A new measure of the CoP trajectory in postural sway: Dynamics of heading change. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lubetzky, A.V.; Harel, D.; Lubetzky, E. On the effects of signal processing on sample entropy for postural control. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Placidi, G.; Avola, D.; Ferrari, M.; Iacoviello, D.; Petracca, A.; Quaresima, V.; Spezialetti, M. A low-cost real time virtual system for postural stability assessment at home. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2014, 117, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Skubic, M.; Abbott, C.; Keller, J.M. Body sway measurement for fall risk assessment using inexpensive webcams. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 2225–2229. [Google Scholar]









| Cranio-Caudal Amplitude of Displacement (mm). | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 24 | 72 | (B)168 | |
| H1 | −47.1389 | −11.9613 | 4.381976 | 20.52378 | −12.3364 | −1.07204 | 4.954598 | 8.725844 | ||
| H2 | 106.2469 | 113.4973 | 66.96512 | 108.7198 | 101.6003 | 185.0028 | 194.7217 | 120.1628 | 148.056 | |
| H3 | 147.4473 | 88.46477 | 66.86672 | 78.10156 | 54.81889 | 146.0614 | 99.52632 | 121.2145 | ||
| H5 | 93.70621 | 69.37689 | 174.8362 | 45.59515 | 117.3788 | 107.8154 | 111.2028 | |||
| H6 | 10.32397 | 10.36763 | 30.9781 | −2.25987 | 8.367317 | 0.397835 | 4.997202 | |||
| H7 | 100.9326 | 94.19014 | 166.9199 | 164.0935 | 106.6934 | 91.54561 | 165.7867 | 132.5918 | 112.0737 | 103.5486 |
| Average | 52.81416 | 85.79335 | 67.74605 | 107.008 | 82.99759 | 70.00182 | 119.4162 | 87.24835 | 78.80398 | 69.9378 |
| SD | 61.05513 | 59.57178 | 54.12221 | 58.22919 | 24.13744 | 66.66681 | 86.84508 | 59.90119 | 55.93903 | 51.81886 |
| Medio-Lateral Amplitude of Displacement (mm) | ||||||||||
| 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 24 | 72 | (B)168 | |
| H1 | 16.34772 | −8.55322 | −4.36109 | −5.72143 | 10.4833 | 5.174975 | 9.216272 | −3.00699 | ||
| H2 | 78.52314 | 91.96439 | 35.15835 | 72.05765 | 69.33291 | 82.08802 | 69.93044 | 77.17923 | 80.33109 | |
| H3 | 55.80658 | 56.02084 | 38.62816 | 51.44049 | 60.04469 | 53.10575 | 40.92368 | 41.90341 | ||
| H5 | 57.27578 | 48.12936 | 74.4663 | 56.4325 | 106.4024 | 75.84028 | 76.68095 | |||
| H6 | −11.7363 | 1.914441 | 33.31275 | 9.042947 | −9.63795 | −5.04264 | 1.037078 | |||
| H7 | 63.91576 | 71.36391 | 98.04188 | 67.3006 | 74.33996 | 52.4736 | 74.58922 | 96.74821 | 80.19373 | 72.48259 |
| Average | 40.86522 | 52.64542 | 39.15063 | 49.34626 | 62.88647 | 47.68047 | 51.18753 | 54.82877 | 46.9104 | 37.81941 |
| SD | 33.42689 | 37.58866 | 34.47014 | 30.38589 | 9.292512 | 24.28905 | 29.86135 | 43.85782 | 34.68301 | 33.90625 |
| Cranio-Caudal Displacement | Medio-Lateral Displacement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4–12 h | 168 h | 4–12 h | 168 h | |
| Mean (mm) | 91.229 | 118.207 | 38.005 | 59.904 |
| Variance | 1444.214 | 241.203 | 172.307 | 55.415 |
| p-value | 0.152 | 0.005 | ** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egan, S.; Brama, P.A.J.; Goulding, C.; McKeown, D.; Kearney, C.M.; McGrath, D. The Feasibility of Equine Field-Based Postural Sway Analysis Using a Single Inertial Sensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041286
Egan S, Brama PAJ, Goulding C, McKeown D, Kearney CM, McGrath D. The Feasibility of Equine Field-Based Postural Sway Analysis Using a Single Inertial Sensor. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041286
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgan, Sonja, Pieter A. J. Brama, Cathy Goulding, David McKeown, Clodagh M. Kearney, and Denise McGrath. 2021. "The Feasibility of Equine Field-Based Postural Sway Analysis Using a Single Inertial Sensor" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041286
APA StyleEgan, S., Brama, P. A. J., Goulding, C., McKeown, D., Kearney, C. M., & McGrath, D. (2021). The Feasibility of Equine Field-Based Postural Sway Analysis Using a Single Inertial Sensor. Sensors, 21(4), 1286. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041286






