Efficiently Updating ECG-Based Biometric Authentication Based on Incremental Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background and Related Works
2.1. Electrocardiogram
2.2. Related Works
2.3. Incremental SVM
3. Proposed ECG-Based Authentication
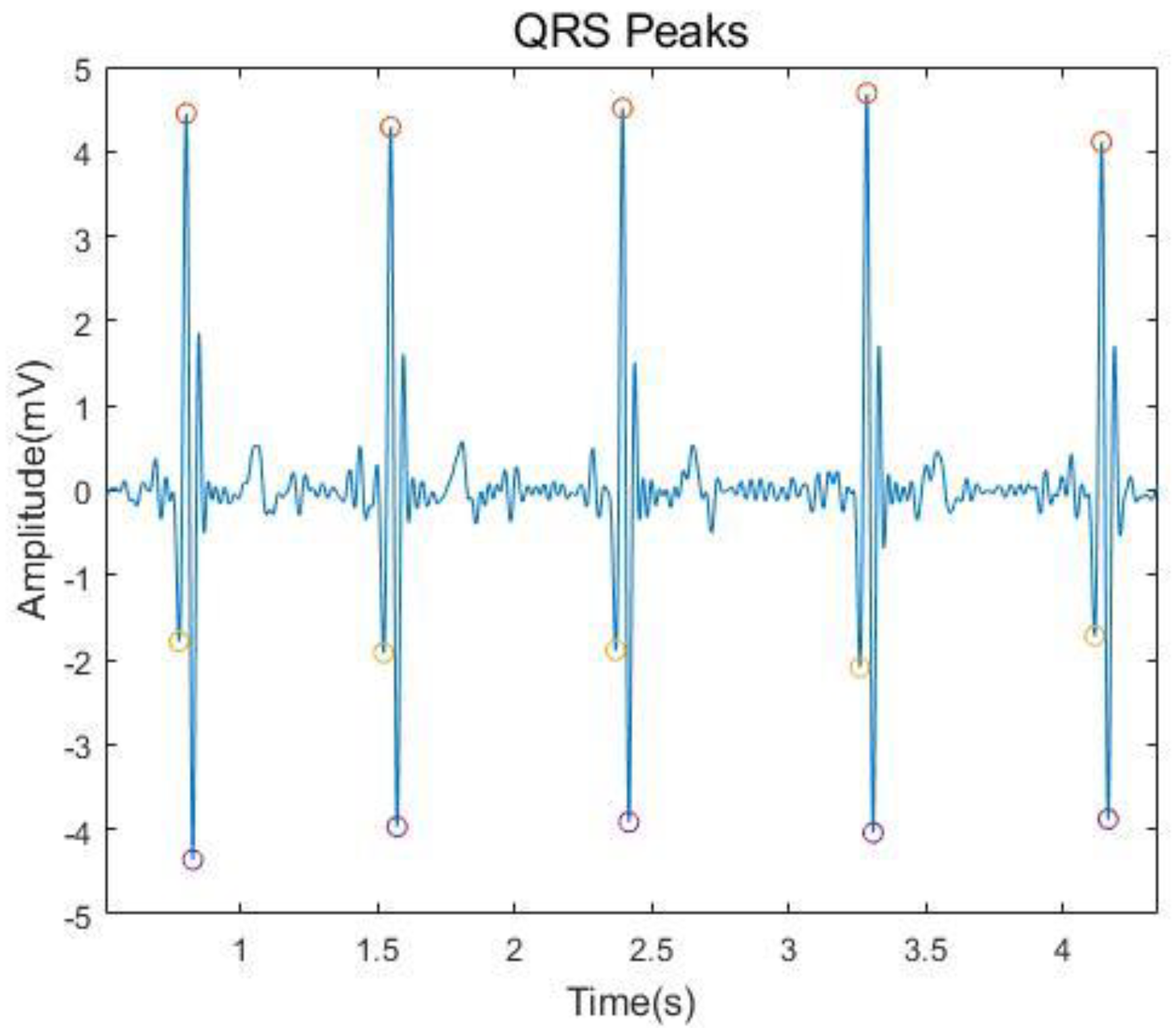
3.1. ECG Signal Acquisition and Preprocessing
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.3. Incremental Learning
3.4. Performance Measures
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frischholz, R.W.; Dieckmann, U. BiolD: A multimodal biometric identification system. Computer 2000, 33, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Hou, R.; Hou, J. ECG Beat Classification on Edge Device. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–6 January 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Holder, J.R.E.H.; Robinson, L.O.; Laub, J.H. The Fingerprint Sourcebook; Dept. Justice, Office Justice Programs, Nat. Inst. Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Prabhakar, S.; Pankanti, S.; Jain, A.K. Biometric recognition:Security and privacy concerns. IEEE Secur. Priv. Mag. Mar. 2003, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Jain, A.K. Human recognition using biometrics: An overview. Ann. Télécommun. Jan. 2007, 62, 11–35. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.J.; Noh, H.K.; Kim, B.; Sim, J.Y.; Park, H.J. An Ultrasonic Scanner to Probe 3-D Finger Skin Structures for Biometric Recognition. IEIE Trans. 2019, 8, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, V.; Sridhar, A.; Baalaaji, A.; Sangeetha, M. A Palm Vein Recognition System based on a Support Vector Machine. IEIE Trans. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, P.; Luo, J.; Ling, Z.; Liu, B.; Fu, X. Fingerprint attack against touch enabled devices. Proc. SPSM 2012, 12, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, N.M.; Minh, B.Q. Your face is not your password. Black Hat. 2009, 4, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, K.; Yan, Q.; Li, Y.; Deng, R.H. Understanding OSN based facial disclosure against face authentication systems. Proc. AS ACCS 2014, 14, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Albacete, S.V.; Tome-Gonzalez, P.; Alonso-Fernandez, F.; Galbally, J.; Fierrez, J.; Ortega-Garcia, J. Direct Attacks Using Fake Images in Iris Verification. In Biometrics and Identity Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Israel, S.A.; Irvine, J.M.; Cheng, A.; Wiederhold, M.D.; Wiederhold, B.K. ECG to identify individuals. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemian, S.Z.; Hatzinakos, D. A new ECG feature extractor for biometric recognition. In Proceedings of the 2009 16th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Santorini, Greece, 5–7 July 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekema, R.; Gérard, G.J.; Van Oosterom, A. Geometrical aspects of the interindividual variability of multilead ECG recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biel, L.; Pettersson, O.; Philipson, L.; Wide, P. ECG analysis: A new approach in human identification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2001, 50, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carreiras, C.; Lourenço, A.; Fred, A.; Ferreira, R. ECG signals for biometric applications—Are we there yet? In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO), Vienna, Austria, 1–3 September 2014; Volume 2, pp. 765–772. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, M.; Luo, G.; Wang, K. Cancelable biometric authentication system based on ECG. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 12, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, G.; Wang, K.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Yin, Y. Robust ECG biometrics using GNMF and sparse representation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 129, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odinaka, I.; Lai, P.; Kaplan, A.D.; O’Sullivan, J.A.; Sirevaag, E.J.; Rohrbaugh, J.W. ECG Biometric Recognition: A Comparative Analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Falconi, J.S.; Al Osman, H.; El Saddik, A. ECG authentication for mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samona, Y.; Pintavirooj, C.; Visitsattapongse, S. Study of ECG variation in daily activity. In Proceedings of the 2017 10th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Hokkaido, Japan, 31 August–2 September 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gepperth, A.; Hammer, B. Incremental learning algorithms and applications. Eur. Symp. Artif. Neural Netw. 2016, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xu, C.; Zou, B.; Tang, Y.Y.; Peng, J.; You, X. New Incremental Learning Algorithm with Support Vector Machines. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utgoff, P.E. Incremental induction of decision trees. Mach. Learn. 1989, 4, 161–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falcari, T.; Saotome, O.; Pires, R.; Campo, A.B. Evaluation of multi-class support-vector machines strategies and kernel adjustment levels in hand posture recognition by analyzing sEMG signals acquired from a wearable device. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2020, 10, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.L.; Wu, Y.S. Classification of atrial fibrillation and normal sinus rhythm based on convolutional neural network. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2020, 10, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. An approach to incremental SVM learning algorithm. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE Internationals Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence. ICTAI 2000, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 15 November 2000; pp. 268–278. [Google Scholar]
- Polikar, R.; Upda, L.; Upda, S.S.; Honavar, V. Learn++: An incremental learning algorithm for supervised neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. C. 2001, 31, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diehl, C.P.; Cauwenberghs, G. SVM incremental learning, adaptation and optimization. Proc. Int. Jt. Conf. Neural Netw. 2003, 4, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Lugovaya, T. Biometric Human Identification Based on Electrocardiogram. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Computing Technologies and Informatics, Electrotechnical University “LETI”, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bousseljot, R.; Kreiseler, D.; Schnabel, A. Nutzung der EKG- Signaldatenbank CARDIODAT der PTB über das Internet. Biomed. Tech. 1995, 1, S317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, H.P.; Lourenço, A.; Fred, A.; Raposo, N.; Aires-deSousa, M. Check your biosignals here: A new dataset for off-the-person ECG biometrics. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. Physiobank physiotoolkit and physionet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, A.D.C.; Hamdy, M.M.; Badre, A.; Badee, V. Wavelet Distance Measure for Person Identification Using Electrocardiograms. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezgui, D.; Lachiri, Z. ECG biometric recognition using SVM-based approach. IEE J. Trans. Electric. Electron. Eng. 2016, 11, S94–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labati, R.D.; Muñoz, E.; Piuri, V.; Sassi, R.; Scotti, F. Deep-ECG: Convolutional neural networks for ECG biometric recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 126, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Lee, B.H.; Yoon, S.R. Biometric authentication using noisy electrocardiograms acquired by mobile sensors. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergin, S.; Uysal, A.K.; Gunal, E.S.; Gunal, S.; Gulmezoglu, M.B. ECG based biometric authentication using ensemble of features. In Proceedings of the 2014 9th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Barcelona, Spain, 18–21 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, M.; Pławiak, P.; Wang, K.; Acharya, U.R. ResNet-Attention model for human authentication using ECG signals. Expert Syst. 2020, 10, e12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Chuang, C.M.; Hsu, C.Y. A Novel Personal Identity Verification Approach Using a Discrete Wavelet Transform of the ECG Signal. In Proceeding of the International Conference on Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering (MUE 2008), Busan, Korea, 24–26 April 2008; pp. 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Laguna, P.; Mark, R.G.; Goldberg, A.; Moody, G.B. A database for evaluation of algorithms for measurement of QT and other waveform intervals in the ECG. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computers in Cardiology, Lund, Sweden, 7–10 September 1997; pp. 673–676. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, J.R.; Cardoso, J.S.; Lourenço, A.; Carreiras, C. Towards a continuous biometric system based on ECG signals acquired on the steering wheel. Sensors 2017, 17, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammad, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K. A novel two-dimensional ECG feature extraction and classi_cation algorithm based on convolution neural network for human authentication. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 101, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, L.; He, C.; Wen, B.; Hong, X.; Li, Y. Amultiscale autoregressive model-based electrocardiogram identication method. IEEE Access. 2018, 6, 18251–18263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasteva, V.; Jekova, I.; Abächerli, R. Biometric verification by cross-correlation analysis of 12-lead ECG patterns: Ranking of the most reliable peripheral and chest leads. J. Electrocardiol. 2017, 50, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Hadhoud, M. A novel biometric based on ECG signals and images for human authentication. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2016, 13, 959–964. [Google Scholar]
- Karimian, N.; Guo, Z.M.; Tehranipoor, M.; Forte, D. Highly Reliable Key Generation from Electrocardiogram (ECG). IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Perkowski, M. Toward Improving Electrocardiogram (ECG) Biometric Verification using Mobile Sensors: A Two-Stage Classifier Approach. Sensors 2017, 17, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathoumvanh, S.; Airphaiboon, S.; Hamamoto, K. Robustness study of ECG biometric identification in heart rate variability conditions. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2014, 9, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalai Zaghouani, E.; Benzina, A.; Attia, R. ECG based authentication for e-healthcare systems: Towards a secured ECG features transmission. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Valencia, Spain, 26–30 June 2017; pp. 1777–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Luz, E.J.D.S.; Moreira, G.J.P.; Oliveira, L.S.; Schwartz, W.R.; Menotti, D. Learning deep off-the-person heart biometrics representations. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, H.M.; Pan, S.B.; Kim, P. A Deep Bidirectional GRU Network Model for Biometric Electrocardiogram Classification Based on Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 145395–145405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, N.L.; Furnell, S.M.; Rodwell, P.M.; Reynolds, P.L. Acceptance of subscriber authentication methods for mobile telephony devices. Comput. Secur. 2002, 21, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, M.; Wang, K. Parallel score fusion of ECG and fingerprint for human authentication based on convolution neural network. Comput. Secur. 2019, 81, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla-Palestina, D.E.; Jimenez-Duarte, J.A.; Ramirez-Cortes, J.M.; Hernandez, A.; Gomez-Gil, P.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J. Embedded System for Bimodal Biometrics with Fiducial Feature Extraction on ECG and PPG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K. Multimodal biometric authentication systems using convolution neural network based on different level fusion of ECG and fingerprint. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 26527–26542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, H.; Wu, D.; Vapnik, V.N. Support vector machines for spam categorization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontil, M.; Verri, A. Support vector machines for 3d object recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Artan, Y.; Haider, M.A.; Langer, D.L.; Van der Kwast, T.H.; Evans, A.J.; Yang, Y.; Wernick, M.N.; Trachtenberg, J.; Yetik, I.S. Prostate Cancer Localization With Multispectral MRI Using Cost-Sensitive Support Vector Machines and Conditional Random Fields. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 2444–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguita, D.; Boni, A.; Pace, S. Fast training of support vector machines for regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE-INNS-ENNS International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. IJCNN 2000. Neural Computing: New Challenges and Perspectives for the New Millennium, Como, Italy, 27–27 July 2000; Volume 5, pp. 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.X.; Krzyzak, A.; Suen, C.Y. Fast SVM Training Algorithm with Decomposition on Very Large Data Sets. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2005, 27, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Domeniconi, C.; Gunopulos, D. Incremental Support Vector Machine Construction. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, San Jose, CA, USA, 29 November–2 December 2014; pp. 589–592. [Google Scholar]
- Cauwenberghs, G.; Poggio, T. Incremental and decremental support vector machine learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2001, 13, 409–415. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Singh, P.; Budhiraja, S. Various Approaches to Minimise Noises in ECG Signal: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2015 Fifth International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies, Haryana, India, 21–22 February 2015; pp. 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A real-time QRS detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. Mar. 1985, 32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, B.J.; Califf, R.M.; Funk, M.; Kaufman, E.S.; Krucoff, M.W.; Laks, M.M.; Macfarlane, P.W.; Sommargren, C.; Swiryn, S.; Van Hare, G.F. Practice standards for electrocardiographic monitoring in hospital settings: An American Heart Association scientific statement from the councils on cardiovascular nursing, clinical cardiology, and cardiovascular disease in the young: Endorsed by the international society of computerized electrocardiology and the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses. Circulation 2004, 110, 2721–2746. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, M.; Maher, A.; Wang, K.; Jiang, F.; Amrani, M. Detection of abnormal heart conditions based on characteristics of ECG signals. Measurement 2018, 125, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.N.; Singh, S.K. Evaluation of Electrocardiogram for Biometric Authentication. J. Inf. Secur. 2012, 3, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2011, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yekkehkhany, B.; Safari, A.; Homayouni, S.; Hasanlou, M.A.; Homayouni, S.; Hasanlou, M. A comparison study of different kernel functions for SVM-based classification of multi-temporal polarimetry SAR data. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences—ISPRS Archives; ISPRS: Hanover, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, A.R.; Snoek, J.; Larochelle, H. Practical Bayesian Optimization of Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the NIPS 2012, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 3–8 December 2012; pp. 2951–2959. [Google Scholar]
- Robnik-Šikonja, M.; Kononenko, I. Theoretical and empirical analysis of relieff and rrelieff. Mach. Learn. 2003, 53, 23–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui, Z.; Yan, Z. A Survey on Biometric Authentication: Toward Secure and Privacy-Preserving Identification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 5994–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.Y. Small Scale Single Pulse ECG-based Authentication using GLRT that Considers T Wave Shift and Adaptive Template Update with Prior Information. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 3038–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Abdiansah, A.; Wardoyo, R. Time complexity analysis of support vector machines (SVM) in LibSVM. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 128, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Authors | Database | Feature Extraction | Authentication Model | Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rezgui et al. [35] | MIT-BIH | 21 Fiducial and 10 morphological descriptors | SVM | ACC: | 98.8% |
| Labati et al. [36] | PTB | CNN | Softmax | ACC: | 100% |
| Juan et al. [20] | PTB self-collected | 8 Fiducial | Template Matching | FAR: | 1.29% 1.41% |
| Choi et al. [37] | MIT-BIH PTB | 8 Fiducial | SVM | ACC: | 95.9% |
| Ergin et al. [38] | MIT-BIH PTB | Fiducial, WT and PSD | Decision tree and BayesNet | F1-score: | 0.972 |
| Hammad et al. [39] | PTB CYBHi | ResNet-Attention | Softmax | ACC: | 98.85% 99.27% |
| Chiu et al. [40] | QT DB [41] | DWT | Euclidean distance | ACC: | 81% |
| Biel et al. [15] | Self-collected | Siemens ECG apparatus | PCA | ACC: | 98% |
| Pinto et al. [42] | Self-collected | DCT | SVM | ACC: | 94.9% |
| Hammad et al. [43] | MIT-BIH | Fiducial | CNN | ACC: | 99% |
| RMSE | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.12346 ± 0.06493 | 0.15085 ± 0.09276 | 0.16848 ± 0.07744 | 0.25785 ± 0.30352 | 0.20714 ± 0.14167 |
| Subject | Incremental Learning | Full Training | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Sample | 10 Samples | 100 Samples | 1 Sample | 10 Samples | 100 Samples | |
| 1 | 0.541 | 3.995 | 27.184 | 2.022 | 20.279 | 241.554 |
| 2 | 0.630 | 3.233 | 25.382 | 0.713 | 7.101 | 82.799 |
| 3 | 0.213 | 3.320 | 17.190 | 2.570 | 25.502 | 322.653 |
| 4 | 0.367 | 5.661 | 35.133 | 1.225 | 12.762 | 192.827 |
| 5 | 0.289 | 4.347 | 34.006 | 1.901 | 18.343 | 229.996 |
| 6 | 0.234 | 2.116 | 13.015 | 1.306 | 13.181 | 161.457 |
| 7 | 0.252 | 3.208 | 26.130 | 2.185 | 21.436 | 262.371 |
| 8 | 0.102 | 2.332 | 20.584 | 1.497 | 15.139 | 187.970 |
| 9 | 0.156 | 1.994 | 17.990 | 3.294 | 31.457 | 401.554 |
| 10 | 0.610 | 4.711 | 28.913 | 0.951 | 9.294 | 107.644 |
| 11 | 0.714 | 3.381 | 21.442 | 1.120 | 9.227 | 113.987 |
| Day | Positive (%) | Negative (%) | Total | Training Time (s) | R | S | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 51.79 ± | 48.21 ± | 10,930 ± | 85.867 ± | 10,348 ± | 37 ± | 544 ± |
| 2 | 51.14 ± | 48.86 ± | 10,525 ± | 157.070 ± | 19,966 ± | 50 ± | 1438 ± |
| 3 | 52.03 ± | 47.97 ± | 10,893 ± | 344.520 ± | 29,739 ± | 62 ± | 2546 ± |
| 4 | 52.21 ± | 47.79 ± | 11,752 ± | 525.066 ± | 40,396 ± | 81 ± | 3623 ± |
| 5 | 50.30 ± | 49.70 ± | 10,254 ± | 569.601 ± | 49,808 ± | 85 ± | 4461 ± |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Yang, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.K.; Park, C. Efficiently Updating ECG-Based Biometric Authentication Based on Incremental Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051568
Kim J, Yang G, Kim J, Lee S, Kim KK, Park C. Efficiently Updating ECG-Based Biometric Authentication Based on Incremental Learning. Sensors. 2021; 21(5):1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051568
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Junmo, Geunbo Yang, Juhyeong Kim, Seungmin Lee, Ko Keun Kim, and Cheolsoo Park. 2021. "Efficiently Updating ECG-Based Biometric Authentication Based on Incremental Learning" Sensors 21, no. 5: 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051568
APA StyleKim, J., Yang, G., Kim, J., Lee, S., Kim, K. K., & Park, C. (2021). Efficiently Updating ECG-Based Biometric Authentication Based on Incremental Learning. Sensors, 21(5), 1568. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051568






