Laser Beam Pointing Stabilization Control through Disturbance Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
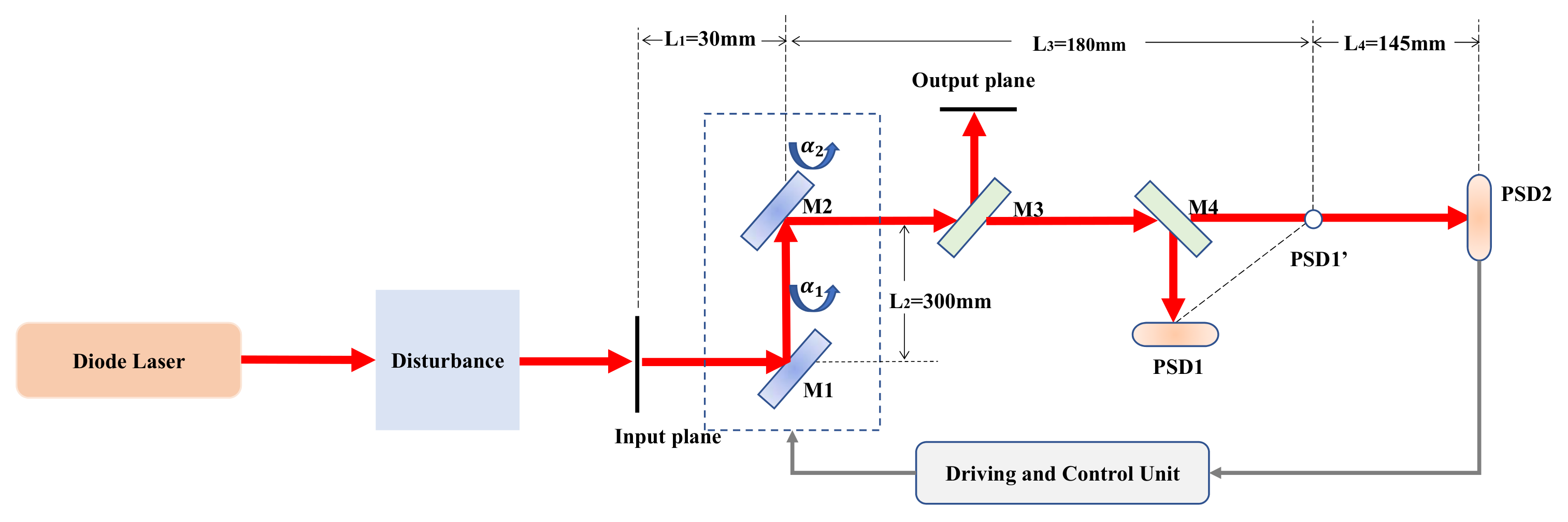
2. Control System Description
3. Modeling Methods
3.1. Optical Model
3.2. Kinematic Model
3.3. Active Motion Based Calibration
3.4. Control Method
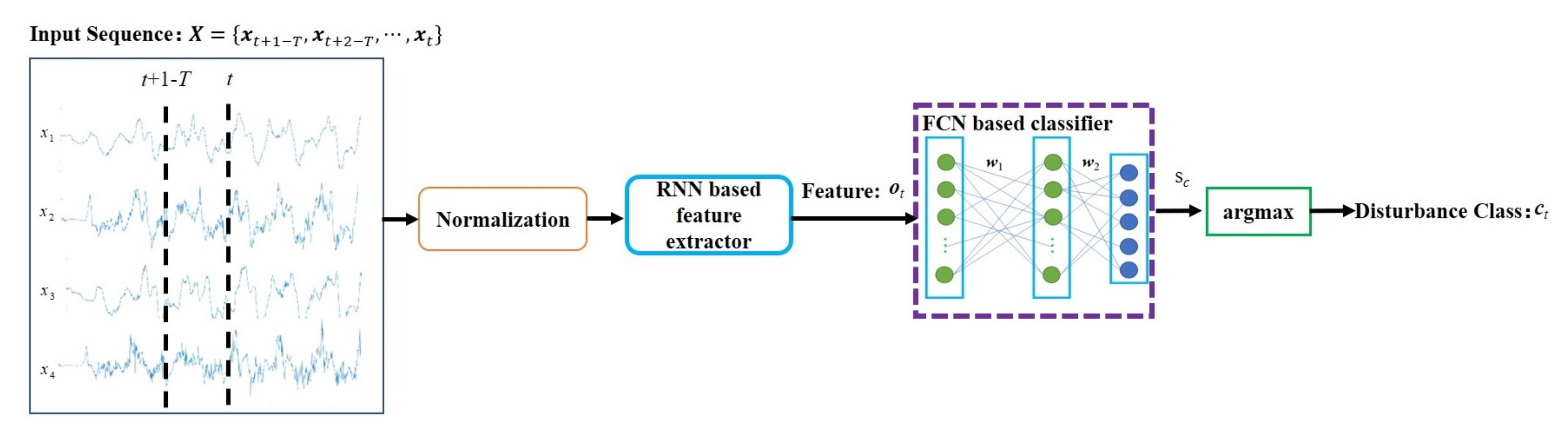
4. Disturbance Source Classification Method
RNN Based Feature Extraction
5. Experimental Results and Discussions
5.1. Kinematic Model Calibration Based on Active Motion
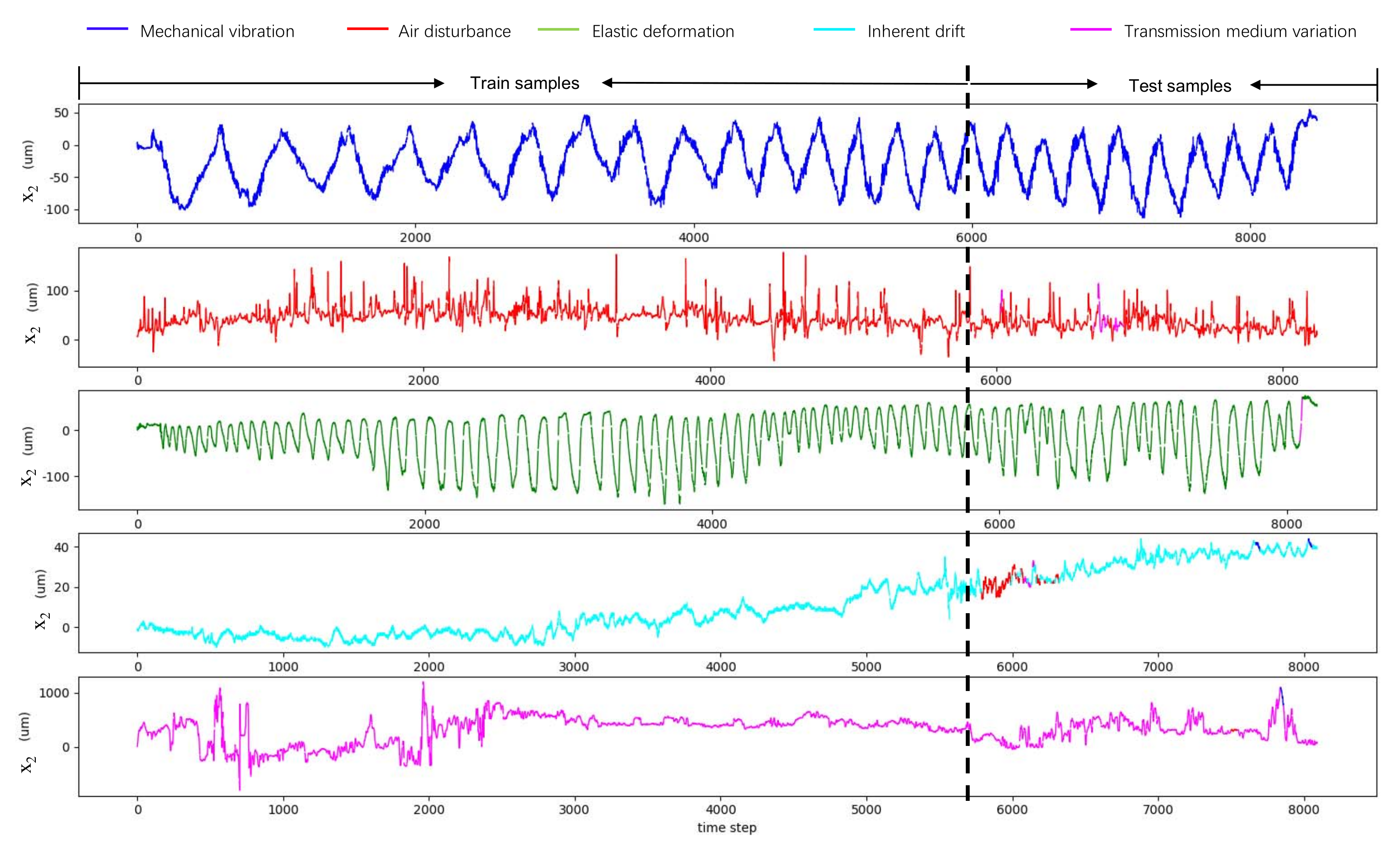
5.2. Disturbance Type Classification
5.2.1. Data Collection
5.2.2. Model Training
5.2.3. Classification Evaluation
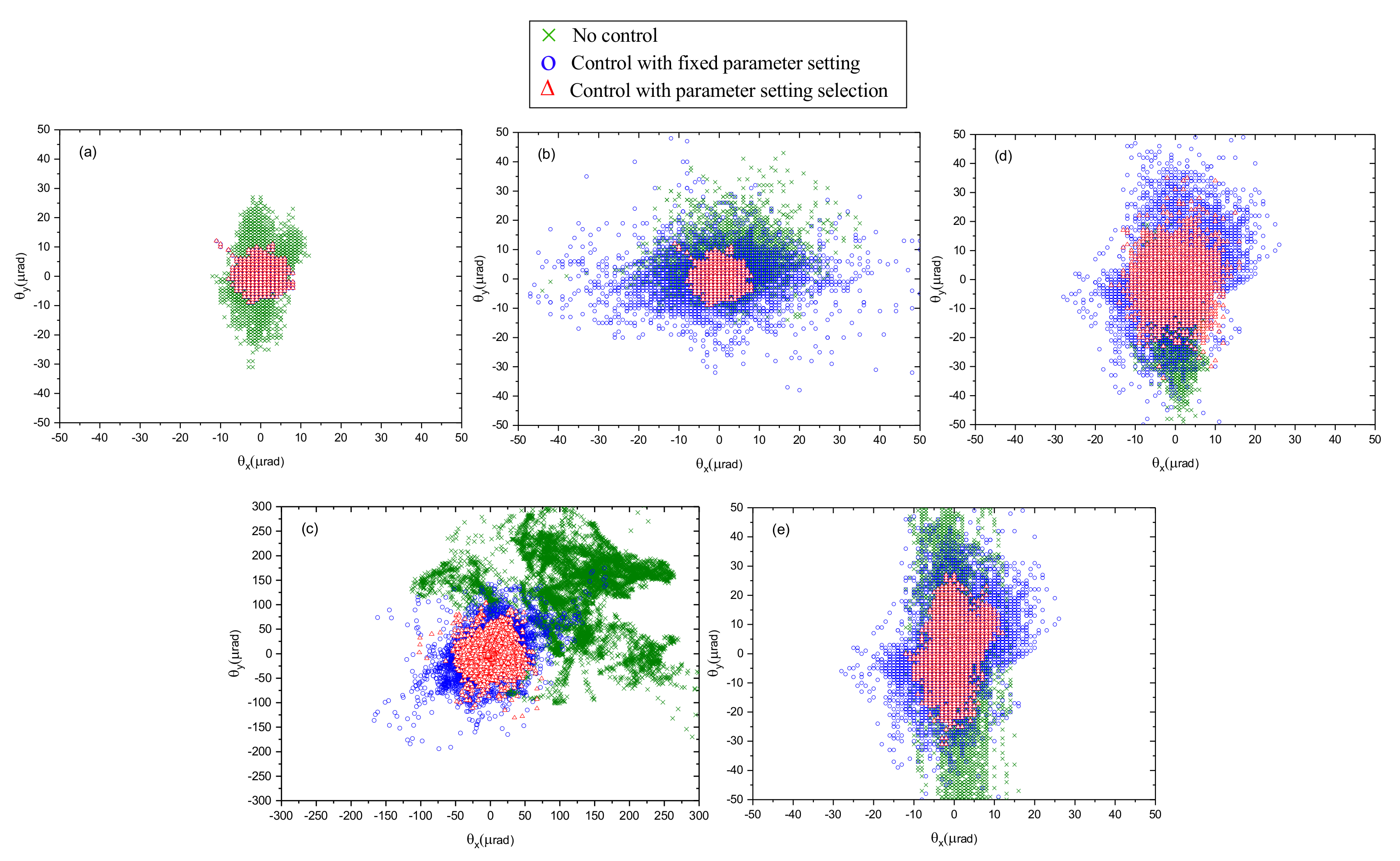
5.3. Beam Pointing Control with Disturbance Source Classification
5.4. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Hou, L.; He, G.; Ren, B.; Zeng, A.; Huang, H. The beam delivery modeling and error sources analysis of beam stabilization system for lithography. Int. Conf. Opt. Instrum. Technol. 2013, 9046, 9046S. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Hou, L.; He, G.; Song, Q.; Huang, H. Study of active beam steering system with a simple method. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2014, 12, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, F.; Zhang, D.; Xing, D.; Xu, D.; Li, J. Laser Beam Pointing Control With Piezoelectric Actuator Model Learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep Learning; MIT Press Cambridge: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alex, K.; Ilya, S.; Geoffrey, E.H. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, M.; William, W. A phrase-based, joint probability model for statistical machine translation. In Proceedings of the ACL-02 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 6–7 July 2002; pp. 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Kai, C.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1310.4546. [Google Scholar]
- Medsker, L.; Jain, L.C. Recurrent Neural Networks: Design and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, K. Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pascanu, R.; Mikolov, T.; Bengio, Y. On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. In International Conference on Machine Learning; PMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1310–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Svelto, O.; Hanna, D.C. Principles of Lasers; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]




| Model | Neuron Number | Accuracy (%) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GRU | 64 | 92.7 | 4.2 |
| GRU | 128 | 92.5 | 4.7 |
| GRU | 256 | 93.9 | 4.8 |
| GRU | 512 | 94.9 | 10.1 |
| LSTM | 64 | 92.1 | 4.4 |
| LSTM | 128 | 91.6 | 4.5 |
| LSTM | 256 | 91.6 | 5.0 |
| LSTM | 512 | 91.8 | 11.3 |
| Disturbance Type | Experiment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inherent drift | A | 21.41 | 2.75 | 21.23 |
| B | 3.28 | 2.12 | 2.43 | |
| C | 3.28 | 2.12 | 2.43 | |
| Air disturbance | A | 11.61 | 7.46 | 8.89 |
| B | 11.94 | 10.03 | 6.47 | |
| C | 3.28 | 2.12 | 2.43 | |
| Transmission medium variation | A | 208.20 | 142.22 | 152.05 |
| B | 46.46 | 29.44 | 35.94 | |
| C | 26.81 | 16.05 | 21.47 | |
| Mechanical vibration | A | 19.04 | 2.60 | 18.86 |
| B | 21.30 | 13.01 | 16.86 | |
| C | 7.58 | 4.34 | 6.21 | |
| Elastic deformation | A | 33.56 | 4.42 | 33.27 |
| B | 15.15 | 7.39 | 13.23 | |
| C | 8.71 | 3.77 | 7.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, H.; Ge, W.-Q.; Wang, H.-C.; Yuan, H.; Fan, Z.-W. Laser Beam Pointing Stabilization Control through Disturbance Classification. Sensors 2021, 21, 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21061946
Chang H, Ge W-Q, Wang H-C, Yuan H, Fan Z-W. Laser Beam Pointing Stabilization Control through Disturbance Classification. Sensors. 2021; 21(6):1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21061946
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Hui, Wen-Qi Ge, Hao-Cheng Wang, Hong Yuan, and Zhong-Wei Fan. 2021. "Laser Beam Pointing Stabilization Control through Disturbance Classification" Sensors 21, no. 6: 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21061946
APA StyleChang, H., Ge, W.-Q., Wang, H.-C., Yuan, H., & Fan, Z.-W. (2021). Laser Beam Pointing Stabilization Control through Disturbance Classification. Sensors, 21(6), 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21061946






