An Experimental Study on the Validity and Reliability of a Smartphone Application to Acquire Temporal Variables during the Single Sit-to-Stand Test with Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
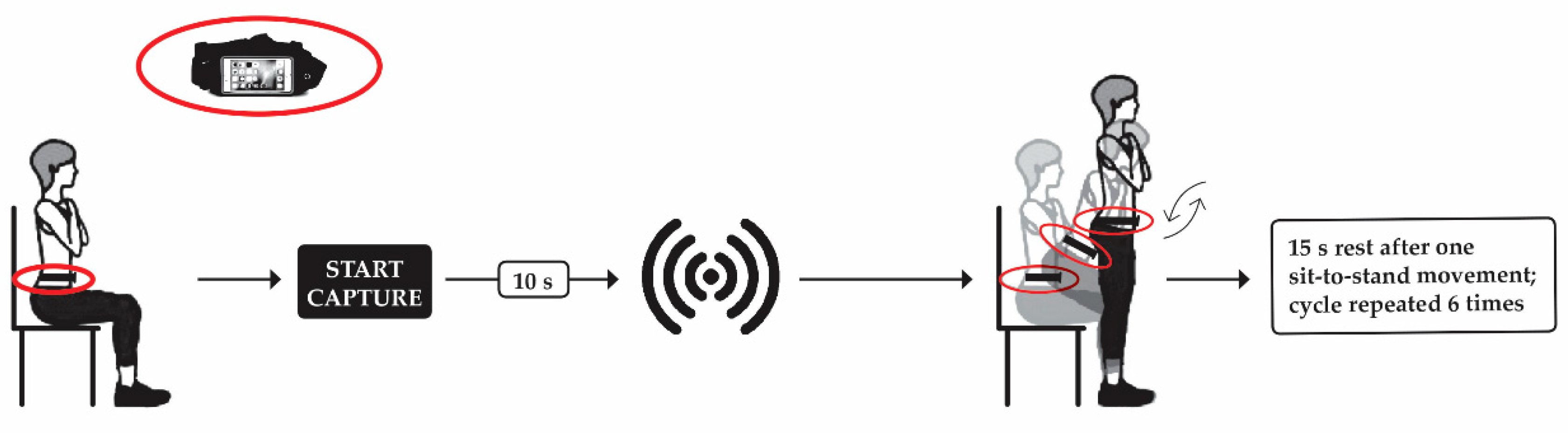
2.3. Sit-to-Stand Test
2.4. Data Acquisition
2.5. Data Analysis
2.5.1. Mobile Application
2.5.2. Video-Camera Recordings
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bloom, D.E.; Canning, D.; Lubet, A. Global Population Aging: Facts, Challenges, Solutions & Perspectives. Chall. Solut. Perspect. Daedalus 2015, 144, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Noury, N.; Quach, K.-A.; Berenguer, M.; Bouzi, M.-J.; Teyssier, H. A feasibility study of using a smartphone to monitor mobility in elderly. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 14th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Beijing, China, 11–13 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dall, P.M.; Kerr, A. Frequency of the sit to stand task: An observational study of free-living adults. Appl. Ergon. 2010, 41, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frykberg, G.E.; Häger, C.K. Movement analysis of sit-to-stand—research informing clinical practice. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2015, 20, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, S.; Nagano, A.; Hay, D.C.; Fukashiro, S. The minimum required muscle force for a sit-to-stand task. J. Biomech. 2012, 45, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadore, E.L.; Izquierdo, M. New Strategies for the Concurrent Strength-, Power-, and Endurance-Training Prescription in Elderly Individuals. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiedemann, A.; Shimada, H.; Sherrington, C.; Murray, S.; Lord, S. The comparative ability of eight functional mobility tests for predicting falls in community-dwelling older people. Age Ageing 2008, 37, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buatois, S.; Miljkovic, D.; Manckoundia, P.; Gueguen, R.; Miget, P.; Vanã§on, G.; Perrin, P.; Benetos, A. FIVE TIMES SIT TO STAND TEST IS A PREDICTOR OF RECURRENT FALLS IN HEALTHY COMMUNITY-LIVING SUBJECTS AGED 65 AND OLDER. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 1575–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusardi, M.M.; Fritz, S.; Middleton, A.; Allison, L.; Wingood, M.; Phillips, E.; Criss, M.; Verma, S.; Osborne, J.; Chui, K.K. Determining Risk of Falls in Community Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Using Posttest Probability. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2017, 40, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minematsu, A.; Hazaki, K.; Harano, A.; Okamoto, N. Association between muscle strength and physical performance in Japanese elderly: The Fujiwara-kyo Study. JCGG 2018, 9, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.M.; Gray, M.; Binns, A. Relationship of Sit-to-Stand Lower-Body Power With Functional Fitness Measures Among Older Adults With and Without Sarcopenia. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2017, 40, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaubert, K.L.; Bohannon, R.W. Reliability and Validity of Three Strength Measures Obtained From Community-Dwelling Elderly Persons. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwannarat, P.; Kaewsanmung, S.; Thaweewannakij, T.; Amatachaya, S. The use of functional performance tests by primary health-care providers to determine walking ability with and without awalking device in community-dwelling elderly. Physiother. Theory Pr. 2021, 37, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, N.; Shimomitsu, T.; Kawanishi, M.; Fukunaga, T.; Kanehisa, H. Relationship between performances of 10-time-repeated sit-to-stand and maximal walking tests in non-disabled older women. J. Physiol. Anthr. 2016, 36, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, C.-J.; Hu, M.-H. Mobility-related performance tests to predict mobility disability at 2-year follow-up in community-dwelling older adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2011, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.S.; Salazar, A.P.; Hennig, E.M.; Spessato, B.C.; Domingo, A.; Pagnussat, A.S. Can We Rely on Mobile Devices and Other Gadgets to Assess the Postural Balance of Healthy Individuals? A Systematic Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P. Smartphone Applications for Patients’ Health and Fitness. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Chan, Y.-F.Y.; McConnell, M.V.; Shaw, S.Y.; Trister, A.D.; Friend, S.H. The Use of Smartphones for Health Research. Acad. Med. 2017, 92, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.; Jayewardene, D. The use of smartphones in clinical practice. Nurs. Manag. (Springhouse) 2014, 21, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.; King, L.; Mancini, M. Role of Body-Worn Movement Monitor Technology for Balance and Gait Rehabilitation. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joundi, R.A.; Brittain, J.-S.; Jenkinson, N.; Green, A.L.; Aziz, T. Rapid tremor frequency assessment with the iPhone accelerometer. Park. Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wile, D.J.; Ranawaya, R.; Kiss, Z.H. Smart watch accelerometry for analysis and diagnosis of tremor. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 230, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A.; Herman, T.; Plotnik, M.; Brozgol, M.; Giladi, N.; Hausdorff, J.M. An instrumented timed up and go: The added value of an accelerometer for identifying fall risk in idiopathic fallers. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, 2003–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Ferrucci, L.; Culham, E.; Metter, E.J.; Guralnik, J.; Deshpande, N. Performance on Five Times Sit-to-Stand Task as a Predictor of Subsequent Falls and Disability in Older Persons. J. Aging Health 2012, 25, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csuka, M.; Mccarty, D.J. Simple method for measurement of lower extremity muscle strength. Am. J. Med. 1985, 78, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, A.; Bisca, G.W.; Machado, F.V.C.; A Hernandes, N.; Pitta, F.; Probst, V.S. Best Protocol for the Sit-to-Stand Test in Subjects With COPD. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, D.L.; Neiva, H.P.; Marinho, D.A.; Marques, M.C. Novel Resistance Training Approach to Monitoring the Volume in Older Adults: The Role of Movement Velocity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar, J.; Losa-Reyna, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, C.; Alfaro-Acha, A.; Rodriguez-Mañas, L.; Ara, I.; García-García, F.J.; Alegre, L.M. The sit-to-stand muscle power test: An easy, inexpensive and portable procedure to assess muscle power in older people. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 112, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, W.G.M.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Horemans, H.L.D.; Stam, H.J. Validity of accelerometry in assessing the duration of the sit-to-stand movement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerrito, A.; Bichsel, L.; Radlinger, L.; Schmid, S. Reliability and validity of a smartphone-based application for the quantification of the sit-to-stand movement in healthy seniors. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H.; Keung, D.T.; Lui, S.Y.; Cheung, R.T. A validation study of a smartphone application for functional mobility assessment of the elderly. Hong Kong Physiother. J. 2016, 35, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, I.; Felizardo, V.; Pombo, N.; Garcia, N.M. Limitations of Energy Expenditure Calculation Based on a Mobile Phone Accelerometer. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation (HPCS), Genoa, Italy, 19–21 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, I.M.; Garcia, N.M.; Pombo, N.; Florez-Revuelta, F. Limitations of the Use of Mobile Devices and Smart Environments for the Monitoring of Ageing People. In Proceedings of the 4th International on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health, Lisbon, Portugal, 27 March 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, S.T.; Metcalfe, J.W.; Liefeith, A.; Jordan, A.R. Validity of various portable devices to measure sit-to-stand velocity and power in older adults. Gait Posture 2020, 76, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Cárdenas, J.D.; Rodríguez-Juan, J.J.; Smart, R.R.; Jakobi, J.M.; Jones, G.R. Validity and reliability of an iPhone App to assess time, velocity and leg power during a sit-to-stand functional performance test. Gait Posture 2018, 59, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán-Baeza, J.A.; González-Sánchez, M.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Using Smartphones to Collect Quantitative Data on Lower Limb Functionality in People Who Have Suffered a Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 3555–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, H.A.G.; Cuevas, P.C.; Figueras, E.E.Z.; Foix, S.C.; Egea, A.J.S. Time measurement characterization of stand-to-sit and sit-to-stand transitions by using a smartphone. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 56, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, E.; Morley, J.E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Woodhouse, L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Fried, L.P.; Woo, J.; Aprahamian, I.; Sanford, A.; Lundy, J.; et al. Physical Frailty: ICFSR International Clinical Practice Guidelines for Identification and Management. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausdorff, J.M.; Edelberg, H.K.; Mitchell, S.L.; Goldberger, A.L.; Wei, J.Y. Increased gait unsteadiness in community-dwelling elderly fallers. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1997, 78, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Rehman, R.Z.U.; Hansen, C.; Maetzler, W.; Del Din, S.; Rochester, L.; Hortobágyi, T.; Lamoth, C.J.C. Classification of Neurological Patients to Identify Fallers Based on Spatial-Temporal Gait Characteristics Measured by a Wearable Device. Sensors 2020, 20, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millor, N.; Lecumberri, P.; Gómez, M.; Martínez-Ramírez, A.; Izquierdo, M. An evaluation of the 30-s chair stand test in older adults: Frailty detection based on kinematic parameters from a single inertial unit. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lummel, R.C.; Walgaard, S.; Maier, A.B.; Ainsworth, E.; Beek, P.J.; van Dieën, J.H. The Instrumented Sit-to-Stand Test (iSTS) Has Greater Clinical Relevance than the Manually Recorded Sit-to-Stand Test in Older Adults. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukadida, A.; Piotte, F.; Dehail, P.; Nadeau, S. Determinants of sit-to-stand tasks in individuals with hemiparesis post stroke: A review. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.; Saini, J.; Pires, I.M.; Miranda, N.; Pitarma, R. Internet of Things for Enhanced Living Environments, Health and Well-Being: Technologies, Architectures and Systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 1132, 616–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleva, R.I.; Garcia, N.M.; Mavromoustakis, C.X.; Dobre, C.; Mastorakis, G.; Stainov, R.; Chorbev, I.; Trajkovik, V. AAL and ELE Platform Architecture. Ambient Assist. Living Enhanc. Living Environ. 2017, 171–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, N.M.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Ambient Assisted Living; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781439869857. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, I.M.; Teixeira, M.C.; Pombo, N.; Garcia, N.M.; Flórez-Revuelta, F.; Spinsante, S.; Goleva, R.; Zdravevski, E. Android Library for Recognition of Activities of Daily Living: Implementation Considerations, Challenges, and Solutions. Open Bioinform. J. 2018, 11, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, I.M.; Garcia, N.M.; Teixeira, M.C.C. Calculation of Jump Flight Time using a Mobile Device. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Health Informatics, Lisabon, Portugal, 12–15 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, P.S.; Sabugueiro, D.; Felizardo, V.; Couto, R.; Pires, I.; Garcia, N.M. mHealth Sensors and Applications for Personal Aid. In Mobile Health; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 5, pp. 265–281. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, I.M.; Hussain, F.; Garcia, N.M.; Zdravevski, E. Improving Human Activity Monitoring by Imputation of Missing Sensory Data: Experimental Study. Futur. Internet 2020, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, D.L.; Neiva, H.P.; Pires, I.M.; Marinho, D.A.; Marques, M.C. Accelerometer data from the performance of sit-to-stand test by elderly people. Data Brief. 2020, 33, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Demura, S.; Takahashi, K. Center of gravity transfer velocity during sit-to-stand is closely related to physical functions regarding fall experience of the elderly living in community dwelling. Health 2013, 5, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viecelli, C.; Graf, D.; Aguayo, D.; Hafen, E.; Füchslin, R.M. Using smartphone accelerometer data to obtain scientific mechanical-biological descriptors of resistance exercise training. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atrsaei, A.; Dadashi, F.; Hansen, C.; Warmerdam, E.; Mariani, B.; Maetzler, W.; Aminian, K. Postural transitions detection and characterization in healthy and patient populations using a single waist sensor. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stack, E.; Agarwal, V.; King, R.; Burnett, M.; Tahavori, F.; Janko, B.; Harwin, W.; Ashburn, A.; Kunkel, D. Identifying balance impairments in people with Parkinson’s disease using video and wearable sensors. Gait Posture 2018, 62, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, A.K.; Ihlen, E.A.F.; Bergquist, R.; Wik, P.B.; Vereijken, B.; Helbostad, J.L. A Physical Activity Reference Data-Set Recorded from Older Adults Using Body-Worn Inertial Sensors and Video Technology—The ADAPT Study Data-Set. Sensors 2017, 17, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A. Signal Processing. In Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 14–44. ISBN 978-0-470-39818-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gandomkar, Z.; Bahrami, F. Method to classify elderly subjects as fallers and non-fallers based on gait energy image. Heal. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Lovell, N.H.; Redmond, S.J.; Wang, K.; Delbaere, K.; Van Schooten, K.S. Deep Learning for Activity Recognition in Older People Using a Pocket-Worn Smartphone. Sensors 2020, 20, 7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, I.M.; Marques, D.; Pombo, N.; Garcia, N.M.; Marques, M.C.; Florez-Revuelta, F. Measurement of the Reaction Time in the 30-S Chair Stand Test using the Accelerometer Sensor Available in off-the-Shelf Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 4th International on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health, Lisbon, Portugal, 27 March 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistics Notes: Measurement error proportional to the mean. BMJ 1996, 313, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vet, H.C.W.; Terwee, C.B.; Mokkink, L.B.; Knol, D.L. Measurement in Medicine; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; ISBN 9780521118200. [Google Scholar]
- Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Martínez-Cava, A.; Morán-Navarro, R.; Escribano-Peñas, P.; Chavarren-Cabrero, J.; González-Badillo, J.J.; Pallarés, J.G. Reproducibility and Repeatability of Five Different Technologies for Bar Velocity Measurement in Resistance Training. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoye, A.H.K.; Mitrzyk, J.R.; Molesky, M.J. Comparative Accuracy of a Wrist-Worn Activity Tracker and a Smart Shirt for Physical Activity Assessment. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2017, 21, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, W.N. Sample Size Calculator (Version 2.0) [Spreadsheet File]. Available online: http://wnarifin.github.io (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Regterschot, G.R.H.; Folkersma, M.; Zhang, W.; Baldus, H.; Stevens, M.; Zijlstra, W. Sensitivity of sensor-based sit-to-stand peak power to the effects of training leg strength, leg power and balance in older adults. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regterschot, G.R.H.; Zhang, W.; Baldus, H.; Stevens, M.; Zijlstra, W. Accuracy and concurrent validity of a sensor-based analysis of sit-to-stand movements in older adults. Gait Posture 2016, 45, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlstra, A.; Mancini, M.; Lindemann, U.; Chiari, L.; Zijlstra, W. Sit-stand and stand-sit transitions in older adults and patients with Parkinson’s disease: Event detection based on motion sensors versus force plates. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Lummel, R.C.; Ainsworth, E.; Lindemann, U.; Zijlstra, W.; Chiari, L.; Van Campen, P.; Hausdorff, J.M. Automated approach for quantifying the repeated sit-to-stand using one body fixed sensor in young and older adults. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| n | Age (Years) | Body Mass (kg) | Height (m) | BMI (kg/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women | 20 | 81.9 ± 8.1 | 65.4 ± 11.6 | 1.49 ± 0.1 | 29.4 ± 5.4 |
| Men | 20 | 76.0 ± 8.2 | 78.0 ± 15.5 | 1.66 ± 0.1 | 28.4 ± 4.7 |
| Total | 40 | 78.9 ± 8.6 | 71.7 ± 15.0 | 1.57 ± 0.1 | 28.9 ± 5.0 |
| Variable | App (s) (Mean ± SD) | Video (s) (Mean ± SD) | Cronbach’s α | ICC (95% CI) | Correlation (ρ) (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stand-up Time (n = 842) | 1.68 ± 0.29 | 1.62 ± 0.30 | 0.97 | 0.92 (0.82–0.96) | 0.94 (0.94–0.95) *** |
| Total Time (n = 892) | 2.81 ± 0.50 | 2.75 ± 0.50 | 0.99 | 0.97 (0.93–0.98) | 0.98 (0.97–0.98) *** |
| Stand-Up Time (n = 842) | Total Time (n = 892) | |
|---|---|---|
| SEM (s) | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| CV (%) | 3.03 | 1.85 |
| MDC (s) | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| APE (%) | 5.79 | 3.90 |
| Accuracy (%) | 94.21 | 96.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, D.L.; Neiva, H.P.; Pires, I.M.; Zdravevski, E.; Mihajlov, M.; Garcia, N.M.; Ruiz-Cárdenas, J.D.; Marinho, D.A.; Marques, M.C. An Experimental Study on the Validity and Reliability of a Smartphone Application to Acquire Temporal Variables during the Single Sit-to-Stand Test with Older Adults. Sensors 2021, 21, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062050
Marques DL, Neiva HP, Pires IM, Zdravevski E, Mihajlov M, Garcia NM, Ruiz-Cárdenas JD, Marinho DA, Marques MC. An Experimental Study on the Validity and Reliability of a Smartphone Application to Acquire Temporal Variables during the Single Sit-to-Stand Test with Older Adults. Sensors. 2021; 21(6):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062050
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Diogo Luís, Henrique Pereira Neiva, Ivan Miguel Pires, Eftim Zdravevski, Martin Mihajlov, Nuno M. Garcia, Juan Diego Ruiz-Cárdenas, Daniel Almeida Marinho, and Mário Cardoso Marques. 2021. "An Experimental Study on the Validity and Reliability of a Smartphone Application to Acquire Temporal Variables during the Single Sit-to-Stand Test with Older Adults" Sensors 21, no. 6: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062050
APA StyleMarques, D. L., Neiva, H. P., Pires, I. M., Zdravevski, E., Mihajlov, M., Garcia, N. M., Ruiz-Cárdenas, J. D., Marinho, D. A., & Marques, M. C. (2021). An Experimental Study on the Validity and Reliability of a Smartphone Application to Acquire Temporal Variables during the Single Sit-to-Stand Test with Older Adults. Sensors, 21(6), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062050













