Decoration of CuO NWs Gas Sensor with ZnO NPs for Improving NO2 Sensing Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth of the CuO NWs
2.2. ZnO NPs Decoration on the CuO NWs Gas Sensor
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Analysis
3.1.1. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) Analyses
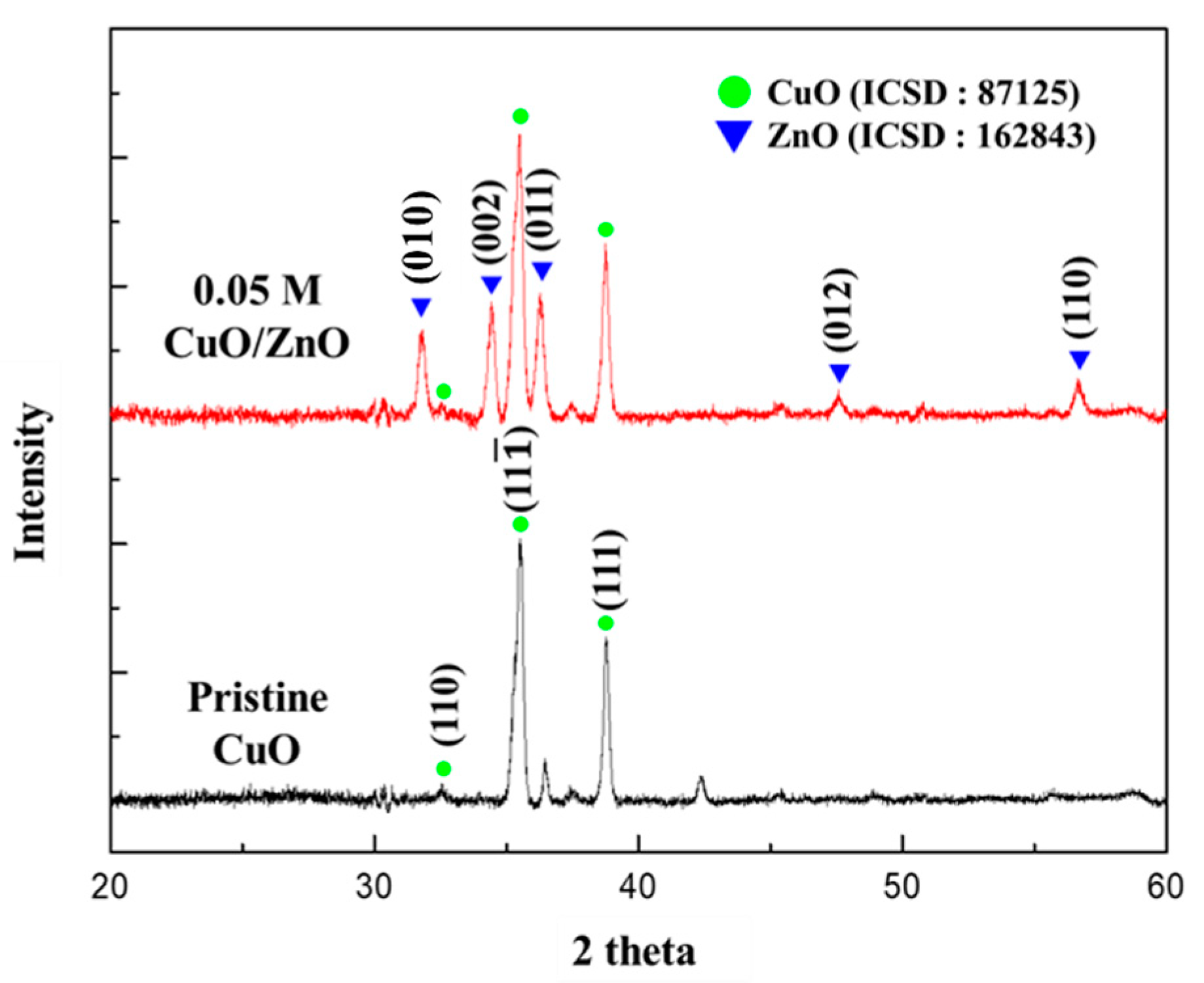
3.1.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
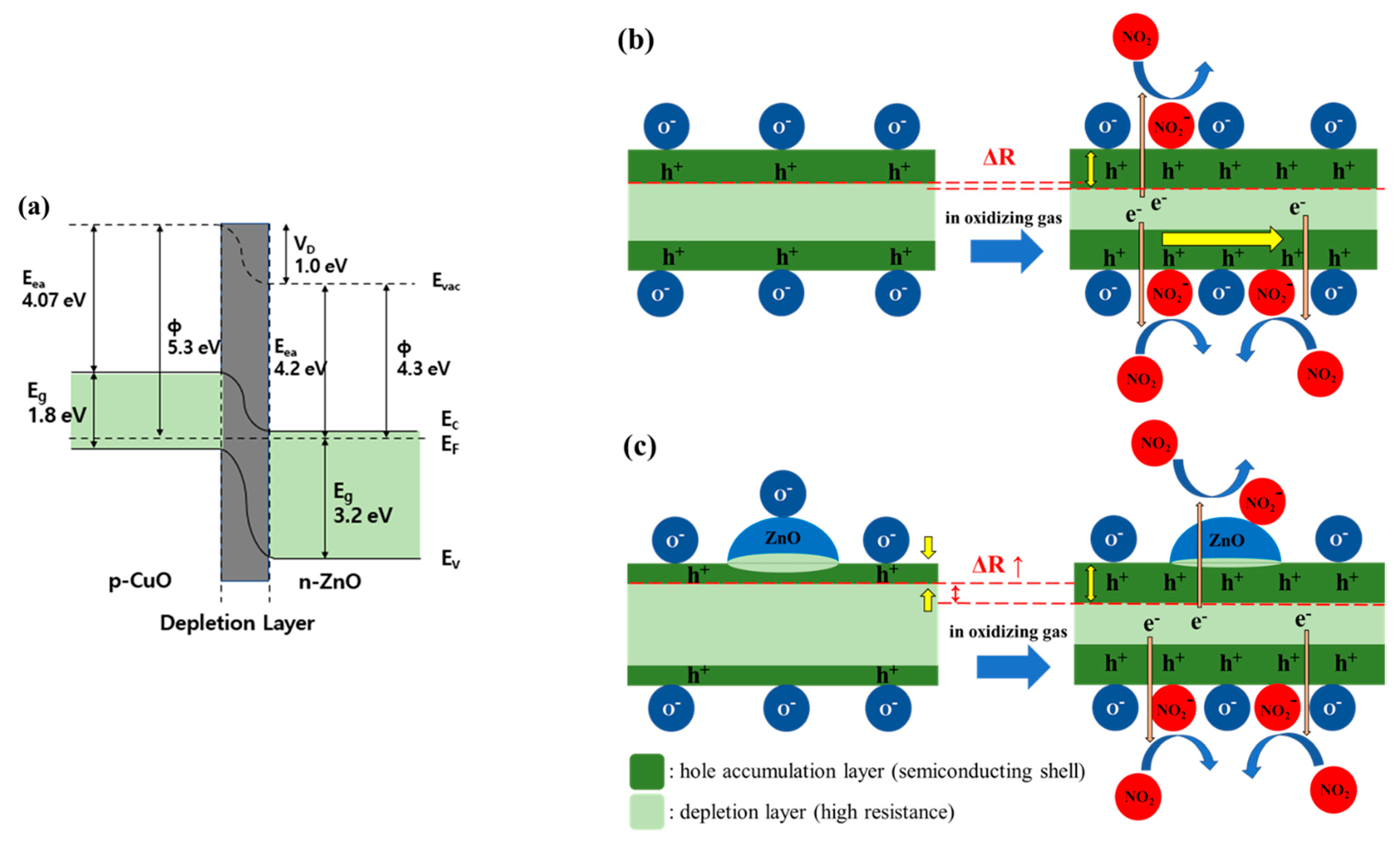
3.2. Effect of the CuO/ZnO Heterojunction on Gas Sensing
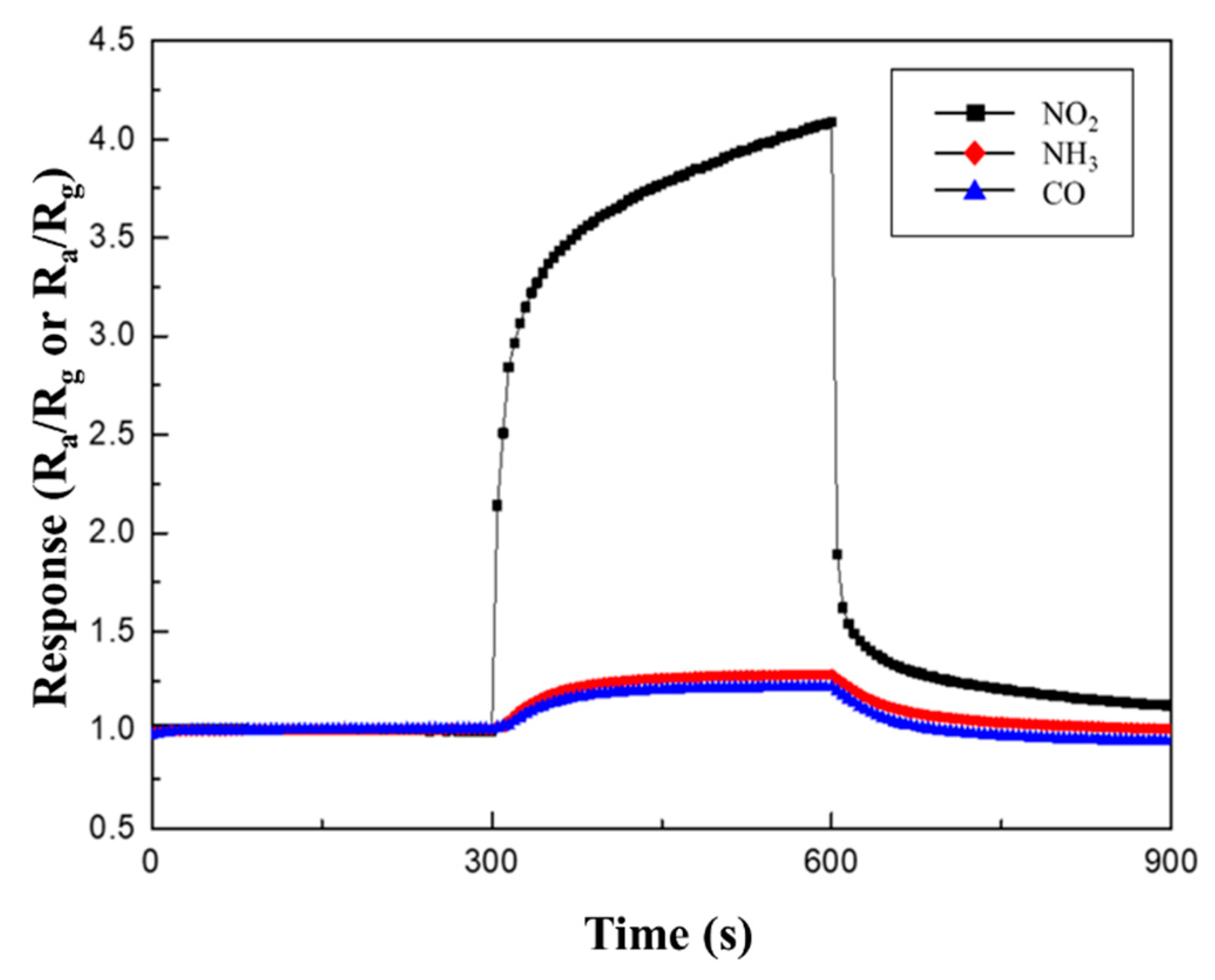
3.3. Gas Sensing Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamazoe, N. Toward innovations of gas sensor technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Kumar, R.; Jayant, R.D.; Nair, M. Nanostructures gas sensors for health care: An Overview. J. Pers. Nanomed. 2015, 1, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.R.; Akbar, S.A.; Morris, P.A. Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, N.; Simon, C.; Heine, T.; Pokhrel, S.; Weimar, U. Modeling of sensing and transduction for p-type semiconducting metal oxide based gas sensors. J. Electroceram. 2010, 25, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaoui, A.; Guerin, J.; Aguir, K. Modeling of a p-type resistive gas sensor in the presence of a reducing gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wlodarski, W.; Galatsis, K.; Moslih, S.h.; Cole, J.; Russo, S.; Rockelmann, N. Gas sensing properties of p-type semiconducting Cr-doped TiO2 thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 83, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Wei, D.; Fang, P.; Shen, Y. Highly selective NO2 sensor based on p-type nanocrystalline NiO thin film prepared by sol-gel dip coating. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisitsoraat, A.; Tuantranont, A.; Comini, E.; Sberveglieri, G.; Wlodarski, W. Characterization of n-type and p-type semiconductor gas sensors based on NiOx doped TiO2 thin films. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Hu, J.; Wu, R.; Lu, J.G. Conductometric chemical sensor based on individual CuO nanowires. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 485502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eranna, G.; Joshi, B.C.; Runthala, D.P.; Gupta, R.P. Oxide Materials for Development of Integrated Gas Sensors-A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 29, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshak, K.; Moore, E.; Lyons, G.M.; Harris, J.; Clifford, S. A review of gas sensors employed in electronic nose applications. Sens. Rev. 2004, 24 No.2, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, Q. LSDA+U study of cupric oxide: Electronic structure and native point defects. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 235206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidowaki, H.; Oku, T.; Akiyama, T.; Suzuki, A.; Jeyadevan, B.; Cuya, J. Fabrication and Characterization of CuO-based Solar Cells. J. Mater. Sci. Res. 2012, 1, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, M.H.; Ghaedi, M.; Avargani, V.M.; Sabzehmeidani, M.M.; Sadeghfar, F.; Jannesar, R. Electrochemical synthesis and efficient photocatalytic degradation of azo dye alizarin yellow R by Cu/CuO nanorods under visible LED light irradiation using experimental design methodology. Polyhedron 2019, 158, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Lu, G. 5.1% Apparent quantum efficiency for stable hydrogen generation over eosin-sensitized CuO/TiO2 photocatalyst under visible light irradiation. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.D.; Quy, N.V.; Tuan, M.A.; Hieu, N.V. Facile synthesis of p-type semiconducting cupric oxide nanowires and their gas-sensing properties. Phys. E 2009, 42, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, O.; Postica, V.; Cretu, V.; Wolff, N.; Duppel, V.; Kienle, L.; Adelung, R. Single and networked CuO nanowires for highly sensitive p-type semiconductor gas sensor applications. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 2016, 10, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.J.; Kouklin, N.; Lu, G.; Lin, I.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Transport, Analyte Detection, and Opto-Electronic Response of p-Type CuO Nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2440–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Jeong, H.M.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, K.I.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Selective Detection of NO2 Using Cr-doped CuO Nanorods. Sensors 2012, 12, 8013–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, C.W.; Woo, H.S.; Lee, J.H. Design of highly sensitive volatile organic compound sensors by controlling NiO loading on ZnO nanowire networks. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.S. Synthesis of SnO2-ZnO core-shell nanofibers via a novel two-step process and their gas sensing properties. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 465603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneti, Y.V.; Zakaria, Q.M.D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Yue, J.; Liu, M.; Jiang, X.; Yu, A. Solvothermal synthesis of ZnO-decorated α-Fe2O3 nanorods with highly enhanced gas-sensing performance toward n-butanol. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13283–13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyadjiev, S.I.; Georgieva, V.; Yordanov, R.; Raicheva, Z.; Szilagyi, I.M. Preparation and characterization of ALD deposited ZnO thin films studied for gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz, A.M.; Sakai, G.; Cornet, A.; Shimanoe, K.; Morante, J.R.; Yamazoe, N. Microstructure control of thermally stable TiO2 obtained by hydrothermal process for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 103, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Woo, C.H.; Shi, S.Q. The effects of oxidative environments on the synthesis of CuO nanowires on Cu substrates. Superlattices Microstruct. 2004, 36, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, S.-Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Woo, K.; Lee, S.; Yi, M. Sensitivity Improvement of Urchin-Like ZnO Nanostructures Using Two-Dimensional Electron Gas in MgZnO/ZnO. Sensors 2019, 19, 5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mali, S.M.; Narwade, S.S.; Navale, Y.H.; Yayade, S.B.; Digraskar, R.V.; Patil, V.B.; Kumbhar, A.S.; Sathe, B.R. Heterostructural CuO-ZnO Nanocomposites: A Highly Selective Chemical and Electrochemical NO2 Sensor. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 20129–20141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, S. CuO nanoparticle decorated ZnO nanorod sensor for low-temperature H2S detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Katoch, A.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.S. A novel approach to improving oxidizing-gas sensing ability of p-CuO nanowires using biased radial modulation of a hole-accumulation layer. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 8911–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, N.; Sakai, G.; Shimanoe, K.; Yamazoe, N. Diffusion equation-based study of thin film semiconductor gas sensor-response transient. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 83, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.N.; Agarwal, R.P. Sensitivity, response and recovery time of SnO2 based thick-film sensor array for H2, CO, CH4 and LPG. Microelectron. J. 1998, 29, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Gas sensors using hierarchical and hollow oxide nanostructures: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Mirzaei, A.; Kang, S.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Bang, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Synthesis, characterization and gas sensing properties of ZnO-decorated MWCNTs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Tao, Z.; Chen, J. CuO particles and plates: Synthesis and gas-sensor application. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 2380–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, I.S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Lee, J.H. CuO nanowire gas sensors for air quality control in automotive cabin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 135, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Choi, N.J.; Kang, H.; Jung, M.Y.; Park, J.W.; Park, K.H.; Lee, D.S. A ppb-level formaldehyde gas sensor based on CuO nanocubes prepared using a polyol process. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Wang, F.; Fan, H.; Xu, L.; Liu, S. Heterojunction CuO@ZnO microcubes for superior p-type gas sensor application. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 672, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


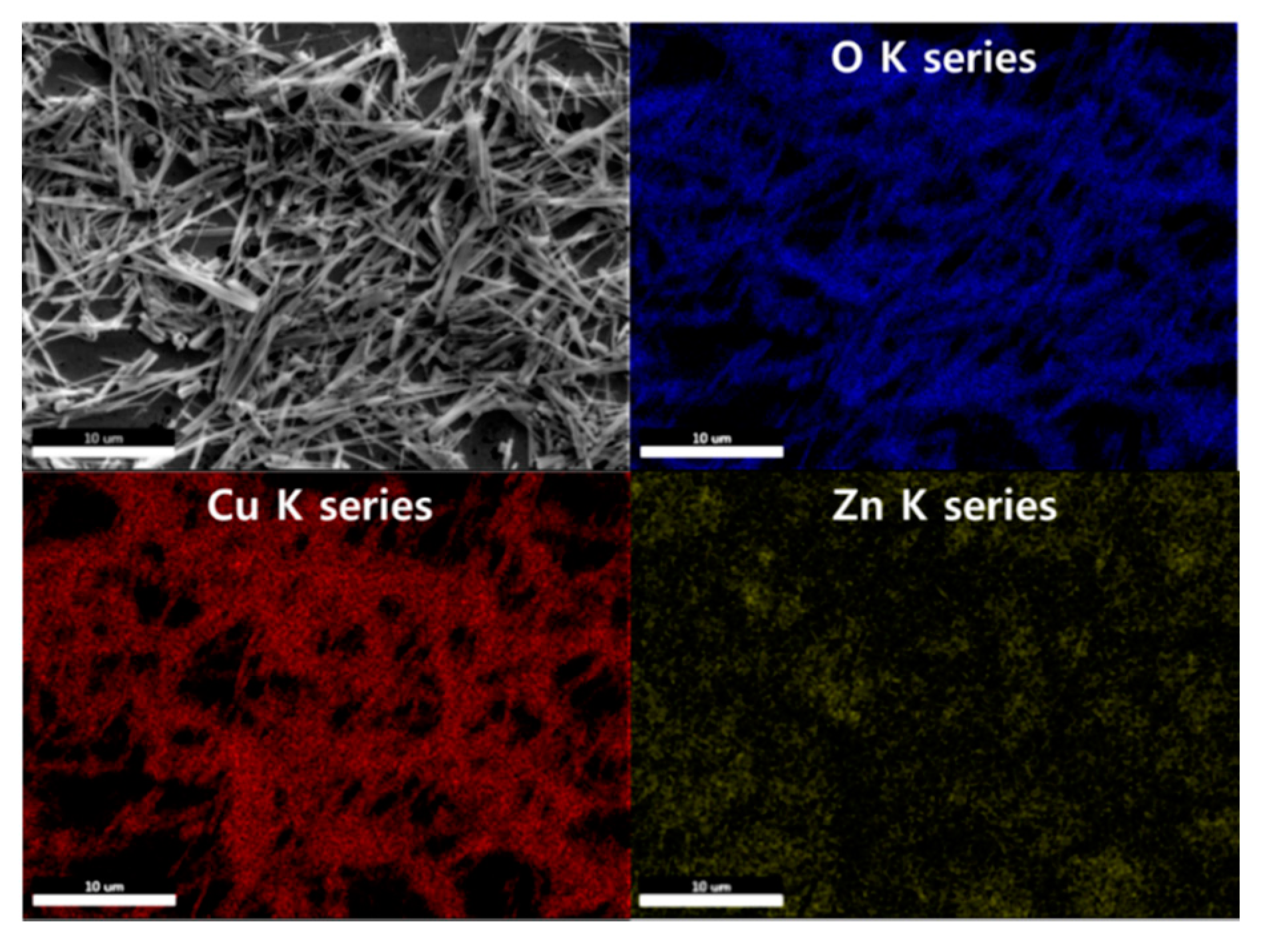





| Pristine CuO | 0.025 M CuO/ZnO | 0.05 M CuO/ZnO | 0.075 M CuO/ZnO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn K Weight % (wt.%) | - | 1.17 | 6.29 | 8.66 |
| Zn K Atomic % (at%) | - | 0.75 | 3.78 | 5.66 |
| Sample | Response (Ra/Rg) | Response Time(s) | Recovery Time(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine CuO | 1.58 | 60 | 225 |
| 0.025 M CuO/ZnO | 2.0 | 65 | 180 |
| 0.05 M CuO/ZnO | 4.1 | 25 | 150 |
| 0.075 M CuO/ZnO | 2.22 | 20 | 180 |
| Pristine CuO | 0.05 M CuO/ZnO | |
|---|---|---|
| NO2 | 1.58 | 4.1 |
| NH3 | 1.21 | 1.28 |
| CO | 1.19 | 1.18 |
| Material | Structure | Method | Target Gas, Concentration (ppm) | Operating Temperature (°C) | Gas Response | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuO | particles | Thermal decomposition | NO2, 100 | 200 | 1.5 | [36] |
| CuO | nanowires | Thermal oxidation | NO2, 4 | 370 | 1.18 | [37] |
| CuO | nanocubes | Polyol process | NO2, 3 | 300 | 0.4 | [38] |
| CuO@ZnO | Core-shell | Two-step solution route | C2H5OH, 50 | 240 | 3.6 | [39] |
| CuO-ZnO | Nanocomposites | Chemical method | NO2, 100 | 200 | 73 % | [29] |
| CuO/ZnO | nanowires | Thermal oxidation | NO2, 100 | 250 | 4.1 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, T.-H.; Bak, S.-Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.H.; Han, Y.-J.; Yi, M. Decoration of CuO NWs Gas Sensor with ZnO NPs for Improving NO2 Sensing Characteristics. Sensors 2021, 21, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062103
Han T-H, Bak S-Y, Kim S, Lee SH, Han Y-J, Yi M. Decoration of CuO NWs Gas Sensor with ZnO NPs for Improving NO2 Sensing Characteristics. Sensors. 2021; 21(6):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062103
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Tae-Hee, So-Young Bak, Sangwoo Kim, Se Hyeong Lee, Ye-Ji Han, and Moonsuk Yi. 2021. "Decoration of CuO NWs Gas Sensor with ZnO NPs for Improving NO2 Sensing Characteristics" Sensors 21, no. 6: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062103
APA StyleHan, T.-H., Bak, S.-Y., Kim, S., Lee, S. H., Han, Y.-J., & Yi, M. (2021). Decoration of CuO NWs Gas Sensor with ZnO NPs for Improving NO2 Sensing Characteristics. Sensors, 21(6), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062103






