Detecting Nuclear Materials in Urban Environments Using Mobile Sensor Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
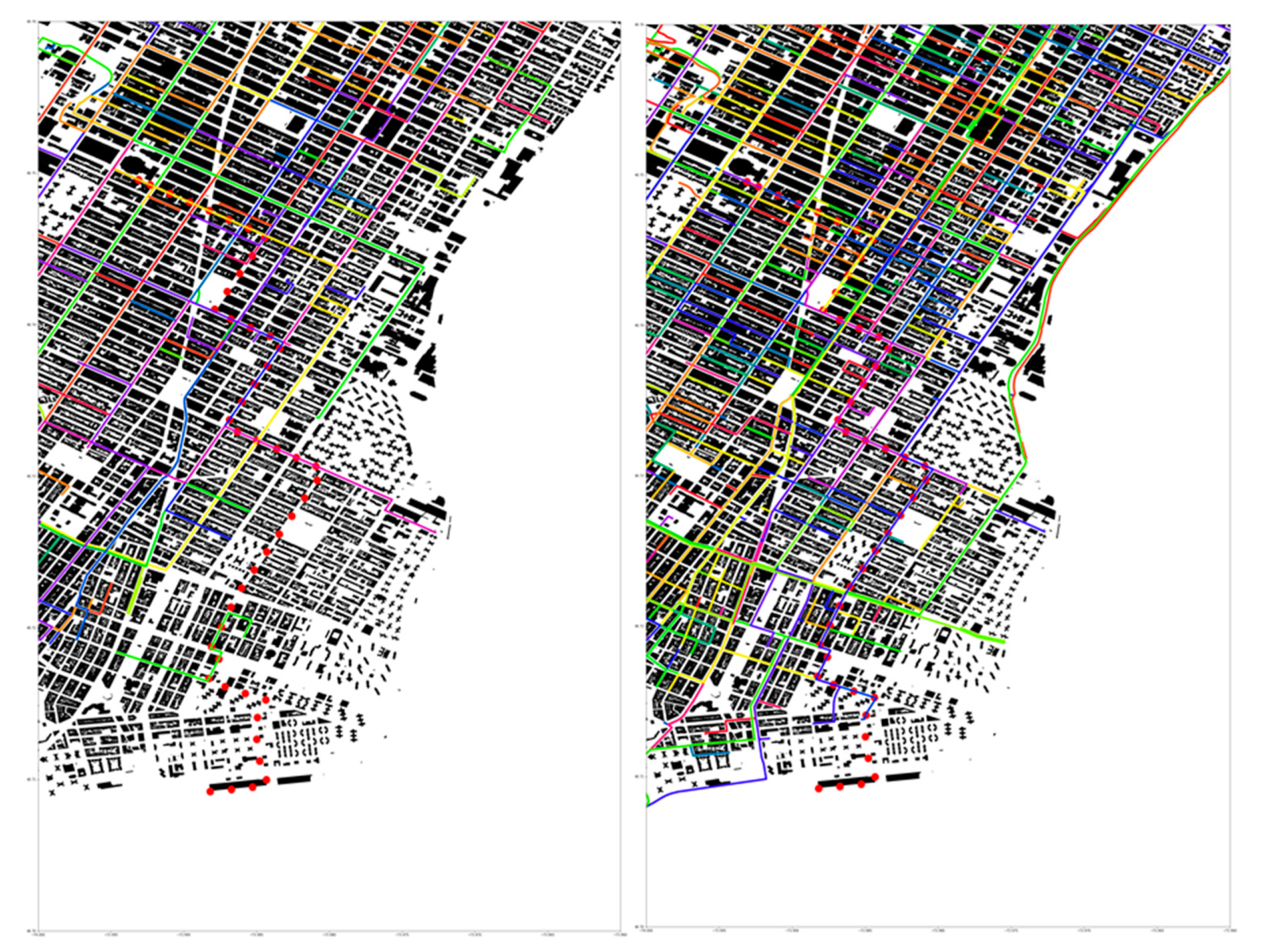
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, M.J. Nuclear Power and Non-Proliferation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981; Available online: http://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:13678654 (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Potter, W.C. Nuclear Power and Nonproliferation: An Interdisciplinary Perspective; Oelgeschlager, Gunn and Hain, Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; Available online: http://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:14738796 (accessed on 18 December 2020).
- Beck, P.; Schmitzer, C.; Duftschmid, K.E.; Arlt, R. Iaea-Cn-86-2P Itrap-International Laboratory and Field Test Site Exercise for Radiation Detection Instruments and Monitoring Systems at Border Crossings; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2001; pp. 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Shattan, M.B. An Analytic-Deliberative Process for the Selection and Deployment of Radiation Detection Systems for Shipping Ports and Border Crossings; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kouzes, R.T. Neutron and gamma ray detection for border security applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 1st International Nuclear and Renewable Energy Conference, INREC’10, Amman, Jordan, 21–24 March 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, S.M.; Mielke, A.M.; Torney, D.C.; Maccabe, A.B. Radiation detection with distributed sensor networks. Computer 2004, 37, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frigo, J.; Brennan, S.; Esch, E.; Jackson, D.; Kulathumani, V.; Rosten, E.; Majerus, P.; Warniment, A.; Mielke, A.; Cai, M. Radiation detection and situation management by distributed sensor networks. Intell. Sens. Situat. Manag. Impact Assess. Cyber-Sens. 2009, 7352, 73520B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wein, L.M.; Atkinson, M.P. The last line of defense: Designing radiation detection-interdiction systems to protect cities from a nuclear terrorist attack. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2007, 54, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.H.; Bunn, J.J.; Chandy, K.M. Sensor networks for the detection and tracking of radiation and other threats in cities. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, IPSN’11, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–14 April 2011; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cortez, R.A.; Tanner, H.G.; Lumia, R. Distributed Robotic Radiation Mapping. Springer Tracts Adv. Robot. 2009, 54, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, M.J.; Harris, B.; Toolin, M.; DuBord, R.M.; Skowronski, V.J.; LuSoto, M.A.; Estep, R.J.; Brennan, S.M.; Cosofret, B.R.; Shokhirev, K.N. An urban environment simulation framework for evaluating novel distributed radiation detection architectures. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security, HST 2010, Waltham, MA, USA, 8–10 November 2010; Volume 01810, pp. 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sullivan, C.J. Urban source detection with mobile sensor networks enhanced with machine learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference and Room-Temperature Semiconductor Detector Workshop, NSS/MIC/RTSD 2016, Strasbourg, France, 29 October–6 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, B. Iterative estimation of location and trajectory of radioactive sources with a networked system of detectors. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2013, 60, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandy, M.; Pilotto, C.; McLean, R. Networked sensing systems for detecting people carrying radioactive material. In Proceedings of the INSS 2008—5th International Conference on Networked Sensing Systems, IKanazawa, Japan, 17–19 June 2008; pp. 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haklay, M.; Weber, P. User-Generated Street Maps. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2008, 7, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- New York Taxi and Limousine Commission. TLC Trip Record Data. 2020. Available online: https://www1.nyc.gov/site/tlc/about/tlc-trip-record-data.page (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- White, O. pyroutelib3 1.6.3. 2020. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/pyroutelib3/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Gillies, S. The Shapely User Manual. Available online: http://sethc23.github.io/wiki/Python/The_Shapely_User_Manual_%E2%80%94_Shapely_1.2_and_1.3_documentation.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Connell, L.W. Dirty Bomb Risk and Impact; U.S. Department of Energy, Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2017. Available online: https://prod-ng.sandia.gov/techlib-noauth/access-control.cgi/2017/179121r.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Frost, R.M. Dirty bombs: Radiological dispersal and emission devices. Adelphi Pap. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosoff, H.; Von Winterfeldt, D. A risk and economic analysis of dirty bomb attacks on the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach. Risk Anal. 2007, 27, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, B.; Olson, K.; Beckes-Talcott, J.; Kadner, S.; Wenderlich, T.; Hoy, M.; Doyle, W.; Koskelo, M. RadNet: Open Protocol for Radiation Data; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1998. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/325781 (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Bandstra, M.S.; Aucott, T.J.; Brubaker, E.; Chivers, D.H.; Cooper, R.J.; Curtis, J.C.; Davis, J.R.; Joshi, T.H.; Kua, J.; Meyer, R.; et al. RadMAP: The Radiological Multi-sensor Analysis Platform. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2016, 840, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, M.H.; Sullivan, C.J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S. Robust abnormality detection methods for spatial search of radioactive materials. Trans. GIS 2019, 23, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandstra, M.S.; Quiter, B.J.; Curtis, J.C.; Bilton, K.J.; Joshi TH, Y.; Meyer, R.; Negut, V.; Vetter, K.; Archer, D.E.; Hornback, D.E.; et al. Attribution of gamma-ray background collected by a mobile detector system to its surroundings using panoramic video. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2020, 954, 161126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NYCDOT. New York City Mobility Report. 2018. Available online: http://www.nyc.gov/html/dot/downloads/pdf/mobility-report-2018-screen-optimized.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2020).
- Sullivan, C.J. Radioactive source localization in urban environments with sensor networks and the Internet of Things. IEEE Int. Conf. Multisens. Fusion Integr. Intell. Syst. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, K. Initiative to enhance radiological resilience. NATO Sci. Peace Secur. Ser. B Phys. Biophys. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovsky, R.; Haefner, A.; Joshi, T.H.; Negut, V.; McManus, K.; Suzuki, E.; Barnowski, R.; Vetter, K. 3-D Radiation mapping in real-time with the localization and mapping platform LAMP from unmanned aerial systems and man-portable configurations. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1901.05038. [Google Scholar]
- Vetter, K.; Barnowski, R.; Cates, J.W.; Haefner, A.; Joshi, T.H.Y.; Pavlovsky, R.; Quiter, B.J. Advances in Nuclear Radiation Sensing: Enabling 3-D Gamma-Ray Vision. Sensors 2019, 19, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Case Number | Speed of Source (m/s) | Speed of Source (mph) | Strength of Source (Ci) | Number of Mobile Detectors | Detection Occurrences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 4.47 | 0.1 | 200 | 86 |
| 2 | 10 | 22.37 | 0.1 | 200 | 68 |
| 3 | 15 | 33.55 | 0.1 | 200 | 62 |
| 4 | 2 | 4.47 | 0.5 | 200 | 238 |
| 5 | 10 | 22.37 | 0.5 | 200 | 147 |
| 6 | 15 | 33.55 | 0.5 | 200 | 119 |
| 7 | 2 | 4.47 | 0.1 | 400 | 101 |
| 8 | 10 | 22.37 | 0.1 | 400 | 93 |
| 9 | 15 | 33.55 | 0.1 | 400 | 72 |
| 10 | 2 | 4.47 | 0.5 | 400 | 357 |
| 11 | 10 | 22.37 | 0.5 | 400 | 306 |
| 12 | 15 | 33.55 | 0.5 | 400 | 154 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flanagan, R.R.; Brandt, L.J.; Osborne, A.G.; Deinert, M.R. Detecting Nuclear Materials in Urban Environments Using Mobile Sensor Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062196
Flanagan RR, Brandt LJ, Osborne AG, Deinert MR. Detecting Nuclear Materials in Urban Environments Using Mobile Sensor Networks. Sensors. 2021; 21(6):2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062196
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlanagan, Robert R., Logan J. Brandt, Andrew G. Osborne, and Mark R. Deinert. 2021. "Detecting Nuclear Materials in Urban Environments Using Mobile Sensor Networks" Sensors 21, no. 6: 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062196
APA StyleFlanagan, R. R., Brandt, L. J., Osborne, A. G., & Deinert, M. R. (2021). Detecting Nuclear Materials in Urban Environments Using Mobile Sensor Networks. Sensors, 21(6), 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062196






