Detecting Bacterial Biofilms Using Fluorescence Hyperspectral Imaging and Various Discriminant Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fluorescence Characteristics of Food Poisoning Bacteria
2.2. Bacterial Biofilm Formation
2.3. Hyperspectral Imaging System
2.4. Acquisition of Hyperspectral Fluorescence Images and Spectra
2.5. Biofilm Detection Algorithm
2.5.1. Decision Tree
2.5.2. k-Nearest Neighbor
2.5.3. Linear Discriminant Analysis
2.5.4. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis
2.5.5. Biofilm Detecting Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluorescence Characteristics of Food Poisoning Bacteria
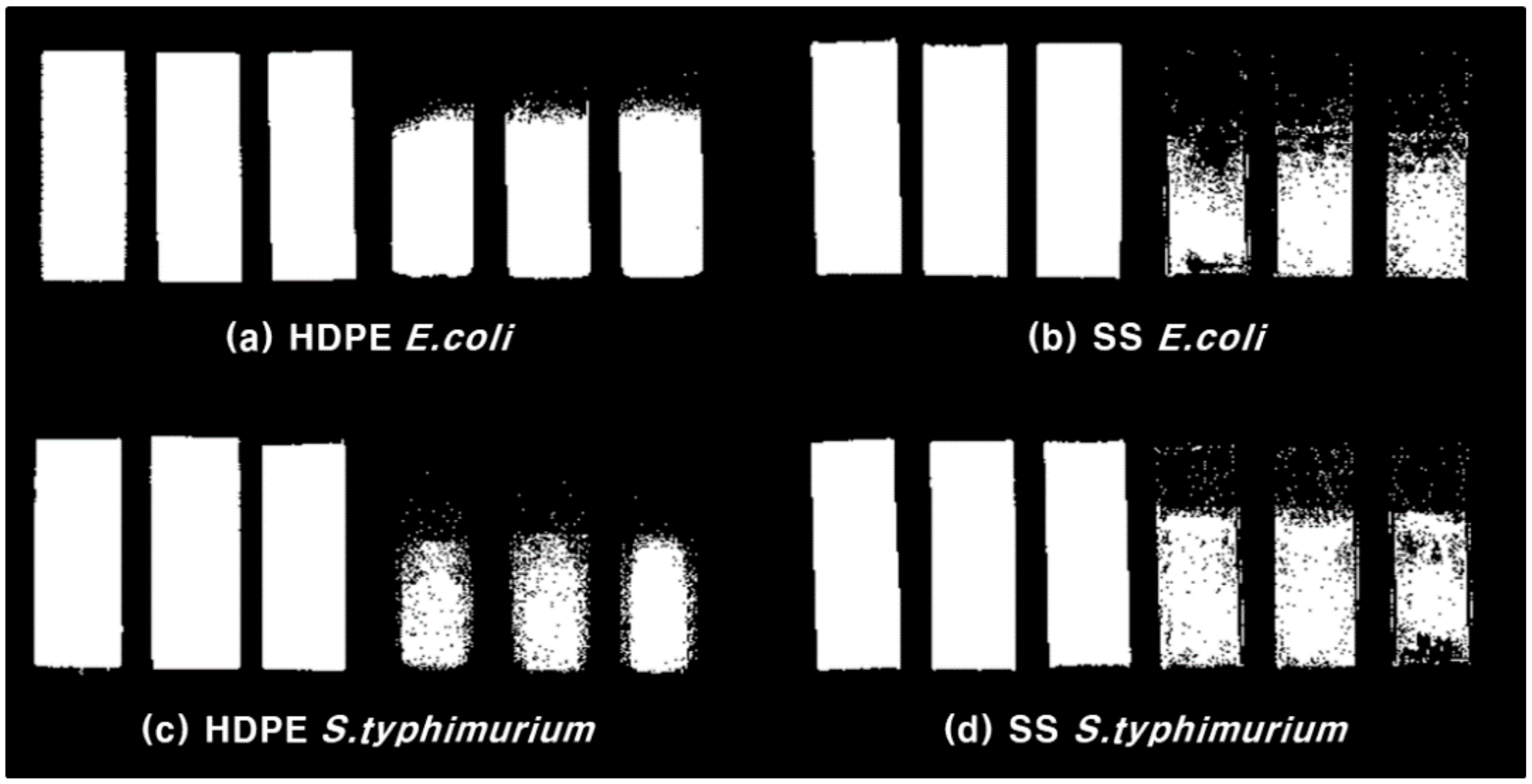
3.2. Food Poisoning Bacteria Biofilm Formation
3.3. Biofilm Detection Model
3.4. Food Poisoning Bacteria Biofilm Detection Result
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srey, S.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.D. Biofilm formation in food industries: A food safety concern. Food Control 2013, 31, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/foodborne-germs.html/ (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/outbreaks-foodborne-illness/foodborne-pathogens (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Soon, J.M.; Brazier, A.K.; Wallace, C.A. Determining common contributory factors in food safety incidents–A review of global outbreaks and recalls 2008–2018. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.-D. A review of microbial biofilms of produce: Future challenge to food safety. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Singleton, I.; San’Ana, A.S. Sources and contamination routes of microbial pathogens to fresh produce during field cultivation: A review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guobjoernsdottir, B.; Einarsson, H.; Thorkelsson, G. Microbial adhesion to processing lines for fish fillets and cooked shrimp: Influence of stainless steel surface finish and presence of gram-negative bacteria on the attachment of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 43, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, K.H.; Flint, S.; Palmer, J.; Andrewes, P.; Bremer, P.; Lindsay, D. Proteolysis produced within biofilms of bacterial isolates from raw milk tankers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galie, S.; García-Gutiérrez, C.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Biofilms in the food industry: Health aspects and control methods. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.; Benoliel, C.; Drider, D.; Dhulster, P.; Chihib, N.E. Biofilm formation and persistence on abiotic surfaces in the context of food and medical environments. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaouris, E.; Heir, E.; Hébraud, M.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Langsrud, S.; Møretrø, T.; Habimana, O.; Desvaux, M.; Renier, S.; Nychas, G.-J. Attachment and biofilm formation by foodborne bacteria in meat processing environments: Causes, implications, role of bacterial interactions and control by alternative novel methods. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zore, A.; Bezek, K.; Jevšnik, M.; Abram, A.; Runko, V.; Slišković, I.; Raspor, P.; Kovačević, D.; Bohinc, K. Bacterial adhesion rate on food grade ceramics and Teflon as kitchen worktop surfaces. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 332, 108764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, A.; Verhoeff-Bakkenes, L.; Nauta, M.; De Jonge, R. Cross-contamination in the kitchen: Effect of hygiene measures. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Liethy, M.A.; Hemdan, B.A.; El-Taweel, G.E. Prevalence of E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria spp. as potential pathogens: A comparative study for biofilm of sink drain environment. Orig. Artic. 2020, 40, e12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Seo, Y.W.; Lim, J.G.; Park, S.B.; Yoo, J.Y.; Kim, B.G.; Kim, G.Y. Detection of E. coli biofilms with hyperspectral imaging and machine learning techniques. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 47, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, M.; Muriana, P.M. Efficacy of Commercial Sanitizers Used in Food Processing Facilities for Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes, E. Coli O157: H7, and Salmonella Biofilms. Foods 2019, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Chen, D.; Xu, Z. Formation and development of Staphylococcus biofilm: With focus on food safety. J. Food Saf. 2017, 37, e12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.J.; Rai, V.R. Bacterial quorum sensing and food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/e-coli (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Gast, R.K.; Porter, R.E.J. Salmonella Infections. In Diseases of Poultry, 14th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 717–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, E.B.; Niemira, B.A.; Sapers, G.M.; Annous, B.A. Biofilm Formation, Cellulose Production, and Curli Biosynthesis by Salmonella Originating from Produce, Animal, and Clinical Sources†. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, C.; Nguyen, T.-A.; Anderson, T.C.; Hancock, T.; Behravesh, C.B. Outbreaks of Human Salmonella Infections Associated with Live Poultry, United States, 1990–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crecencio, R.B.; Brisola, M.C.; Bitner, D.; Frigo, A.; Rampazzo, L.; Borges, K.A.; Furian, T.Q.; Salle, C.T.P.; Moraes, H.L.S.; Faria, G.A.; et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility, biofilm formation and genetic profiles of Escherichia coli isolated from retail chicken meat. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 84, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Tian, Y.; Tan, J.; Salvi, D.; Karwe, M.; Nitin, N. Role of contaminated organic particles in cross-contamination of fresh produce during washing and sanitation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 168, 111283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Galvez, F.; Gil, M.I.; Truchado, P.; Selma, M.V.; Allende, A. Cross-contamination of fresh-cut lettuce after a short-term exposure during pre-washing cannot be controlled after subsequent washing with chlorine dioxide or sodium hypochlorite. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, S.T.; Rossi, B.F.; Bonsaglia, E.C.; Castilho, I.G.; Hernandes, R.T.; Fernandes, A.; Rall, V.L. Cross-contamination and biofilm formation by Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on various cutting boards. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chia, T.; Goulter, R.; McMeekin, T.; Dykes, G.; Fegan, N. Attachment of different Salmonella serovars to materials commonly used in a poultry processing plant. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, T.; Doyle, M.; Rubino, J.; Meng, J. Development of a model for evaluation of microbial cross-contamination in the kitchen. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, E.; Morales-Rueda, A.; García-Gimeno, R.M. Cross-contamination and recontamination by Salmonella in foods: A review. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Sheldon, B.W.; Jaykus, L.A. Transfer of Salmonella and Campylobacter from stainless steel to romaine lettuce. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 2231–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkana, E.; Lianou, A.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Transfer of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium from beef to tomato through kitchen equipment and the efficacy of intermediate decontamination procedures. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateni, G.; Dario, P.; Cavallo, F. Smartphone-based food diagnostic technologies: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayan, H.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Recent development in rapid detection techniques for microorganism activities in food matrices using bio-recognition: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rivas, F.; Ripolles-Avila, C.; Fontecha-Umaña, F.; Ríos-Castillo, A.G.; Rodríguez-Jerez, J.J. Biofilms in the spotlight: Detection, quantification, and removal methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azeredo, J.; Azevedo, N.F.; Briandet, R.; Cerca, N.; Coenye, T.; Costa, A.R.; Desvaux, M.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Hébraud, M.; Jaglic, Z. Critical review on biofilm methods. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 313–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Hyperspectral imaging technique for evaluating food quality and safety during various processes: A review of recent applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-H.; Makino, Y.; Oshita, S.; Martín, J.F.G. Hyperspectral imaging and multispectral imaging as the novel techniques for detecting defects in raw and processed meat products: Current state-of-the-art research advances. Food Control 2018, 84, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakholi, C.; Kandpal, L.M.; Lee, H.; Bae, H.; Park, E.; Kim, M.S.; Mo, C.; Lee, W.H.; Cho, B.K. Rapid assessment of corn seed viability using short wave infrared line-scan hyperspectral imaging and chemometrics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Chao, K.; Kim, M.S.; Lu, R.; Burks, T.F. Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging for evaluating food safety and quality. J. Food Eng. 2013, 118, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Iino, K.; Zhang, S. Monitoring of bacterial contamination on chicken meat surface using a novel narrowband spectral index derived from hyperspectral imagery data. Meat Sci. 2016, 122, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintelas, C.; Mesquita, D.P.; Lopes, J.A.; Ferreira, E.C.; Sousa, C. Near-infrared spectroscopy for the detection and quantification of bacterial contaminations in pharmaceutical products. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 492, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.Q.; Jiang, Q.Q.; Zhang, Z.C.; Shi, P.F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Xi, J.; Chang, S.Z. Hyperspectral Inversion of Petroleum hydrocarbon Contents in Soil Based on Continuum Removal and Wavelet Packet Decomposition. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.Y.; Feng, Y.Z.; Sun, D.W. Recent progress of hyperspectral imaging on quality and safety inspection of fruits and vegetables: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, D.W.; Cheng, J.H.; Han, Z. Hyperspectral imaging sensing of changes in moisture content and color of beef during microwave heating process. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2472–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sun, D.W. Potential of time series-hyperspectral imaging (TS-HSI) for non-invasive determination of microbial spoilage of salmon flesh. Talanta 2013, 111, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElMasry, G.; Wang, N.; Vigneault, C. Detecting chilling injury in Red Delicious apple using hyperspectral imaging and neural networks. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Turner, B.J.; Dury, S.J.; Wallis, I.R.; Foley, W.J. Estimating foliage nitrogen concentration from HYMAP data using continuum removal analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenovský, Z.; Homolová, L.; Zurita-Milla, R.; Lukeš, P.; Kaplan, V.; Hanuš, J.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.-P.; Schaepman, M.E. Retrieval of spruce leaf chlorophyll content from airborne image data using continuum removal and radiative transfer. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R. Application of Hyperspectral Imaging as a Nondestructive Technique for Foodborne Pathogen Detection and Characterization. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foca, G.; Ferrari, C.; Ulrici, A.; Sciutto, G.; Prati, S.; Morandi, S.; Brasca, M.; Lavermicocca, P.; Lanteri, S.; Oliveri, P. The potential of spectral and hyperspectral-imaging techniques for bacterial detection in food: A case study on lactic acid bacteria. Talanta 2016, 153, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, W.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, B.K.; Millner, P.D.; Chao, K.; Chan, D.E. Microbial biofilm detection on food contact surfaces by macro-scale fluorescence imaging. J. Food Eng. 2010, 99, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripatrawan, U.; Makino, Y.; Kawagoe, Y.; Oshita, S. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli contamination in packaged fresh spinach using hyperspectral imaging. Talanta 2011, 85, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Yao, H.; Hruska, Z.; Kincaid, R.; Brown, R.L.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E. Integration of fluorescence and reflectance visible near-infrared (VNIR) hyperspectral images for detection of aflatoxins in corn kernels. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 59, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Chen, Y.R.; Mehl, P.M. Hyperspectral reflectance and fluorescence imaging system for food quality and safety. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavian, S.R.; Landgrebe, D. A survey of decision tree classifier methodology. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1991, 21, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fix, E.; Hodges, J.L. Discriminatory Analysis, Nonparametric Discrimination: Consistency Properties. Int. Stat. Rev. 1951, 57, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.S.; Landau, S.; Leese, M.; Stahl, D. Miscellaneous clustering methods. In Clustering Methods, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 215–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, D.J.; Bang, S.Y. Face recognition using LDA mixture model. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2003, 24, 2815–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Least squares linear discriminant analysis. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML ′07), New York, NY, USA, 20–24 June 2007; pp. 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnama, S.; Ganapathiraju, A. Linear discriminant analysis-a brief tutorial. Inst. Signal Inf. Process. 1998, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, K.J.; Jung, S.Y.; Go, I.H.; Jeong, S.H. Discrimination model for cultivation origin of paper mulberry bast fiber and Hanji based on NIR and MIR spectral data combined with PLS-DA. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 32, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Performance (%) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Average | ||||||||||
| spe | sen | spe | sen | spe | sen | spe | sen | spe | sen | spe | sen | ||||
| HDPE | E. coli | DT | Train | 97.05 | 94.09 | 91.07 | 95.89 | 96.64 | 96.53 | 94.33 | 95.04 | 94.23 | 95.07 | 94.66 | 95.32 |
| Test | 97.06 | 94.86 | 91.33 | 95.79 | 96.52 | 96.04 | 93.53 | 94.88 | 94.03 | 94.61 | 94.49 | 95.24 | |||
| k-NN | Train | 99.99 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.99 | 100 | 99.99 | 100 | 99.99 | 100 | 99.99 | 100 | ||
| Test | 99.97 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.94 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.98 | 100 | |||
| LDA | Train | 99.82 | 100 | 99.81 | 100 | 99.78 | 99.99 | 99.79 | 99.99 | 99.75 | 100 | 99.79 | 100 | ||
| Test | 99.65 | 99.97 | 99.71 | 100 | 99.85 | 99.97 | 99.8 | 100 | 99.91 | 100 | 99.78 | 99.99 | |||
| PLS-DA | Train | 96.76 | 98 | 96.67 | 97.97 | 96.8 | 98.02 | 96.78 | 97.89 | 96.63 | 97.61 | 96.73 | 97.90 | ||
| Test | 96.74 | 98.19 | 96.66 | 97.72 | 96.67 | 97.78 | 96.59 | 97.91 | 97.06 | 97.53 | 96.74 | 97.83 | |||
| HDPE | S. typhimurium | DT | Train | 85.4 | 76.41 | 84.46 | 78.66 | 87.63 | 69.57 | 84.81 | 76.78 | 86.69 | 70.64 | 85.80 | 74.41 |
| Test | 84.07 | 75.89 | 83.71 | 76.79 | 87.48 | 69.84 | 85.18 | 75.89 | 85.85 | 70.22 | 85.26 | 73.73 | |||
| k-NN | Train | 98.9 | 97.24 | 98.86 | 97.36 | 98.94 | 97.21 | 98.97 | 97.21 | 98.85 | 97.22 | 98.90 | 97.25 | ||
| Test | 97.85 | 94.83 | 97.78 | 94.7 | 97.64 | 95.13 | 98.19 | 95.29 | 97.84 | 94.85 | 97.86 | 94.96 | |||
| LDA | Train | 96.47 | 96.26 | 96.52 | 96.46 | 96.61 | 96.29 | 96.5 | 96.27 | 96.46 | 96.42 | 96.51 | 96.34 | ||
| Test | 96.65 | 96.69 | 96.47 | 95.96 | 96.3 | 96.31 | 96.5 | 96.68 | 96.53 | 96.15 | 96.49 | 96.36 | |||
| PLS-DA | Train | 87.17 | 44.95 | 86.92 | 45.42 | 87.15 | 45.11 | 87.01 | 44.68 | 87.23 | 45.19 | 87.10 | 45.07 | ||
| Test | 87.13 | 45.25 | 86.69 | 46.02 | 87.1 | 44.78 | 88.25 | 44.76 | 86.47 | 44.41 | 87.13 | 45.04 | |||
| SS | E. coli | DT | Train | 95.93 | 85.35 | 96.31 | 84.88 | 96.24 | 84.77 | 95.84 | 85.33 | 96.29 | 84.92 | 96.12 | 85.05 |
| Test | 95.55 | 85.81 | 96.18 | 84.26 | 96.46 | 84.73 | 95.9 | 85.88 | 96.24 | 84.13 | 96.07 | 84.96 | |||
| k-NN | Train | 98.41 | 93.43 | 98.32 | 93.31 | 98.38 | 93.51 | 98.35 | 93.37 | 98.67 | 94.31 | 98.43 | 93.59 | ||
| Test | 97.21 | 92.12 | 97.51 | 91.19 | 97.34 | 90.84 | 91.85 | 97.67 | 97.35 | 91.21 | 96.25 | 92.61 | |||
| LDA | Train | 92.15 | 92.9 | 92.09 | 93.2 | 92.01 | 93 | 92 | 92.87 | 92.19 | 92.93 | 92.09 | 92.98 | ||
| Test | 91.9 | 93.16 | 92.46 | 91.9 | 92.47 | 92.62 | 91.86 | 93.52 | 91.94 | 92.95 | 92.13 | 92.83 | |||
| PLS-DA | Train | 91.66 | 89.2 | 91.58 | 89.47 | 91.54 | 89.41 | 91.53 | 89.41 | 91.43 | 89.44 | 91.55 | 89.39 | ||
| Test | 90.14 | 91.39 | 90.96 | 89.26 | 92.05 | 89.06 | 91.39 | 89.48 | 92.01 | 88.99 | 91.31 | 89.64 | |||
| SS | S. typhimurium | DT | Train | 99.19 | 9.17 | 92.82 | 23.26 | 99.18 | 9.2 | 99.41 | 8.43 | 99.45 | 8.41 | 98.01 | 11.69 |
| Test | 99.22 | 9.17 | 92.73 | 21.72 | 99.28 | 9.02 | 99.4 | 8.44 | 99.25 | 8.51 | 97.98 | 11.37 | |||
| k-NN | Train | 94.37 | 58.83 | 94.27 | 58.26 | 94.58 | 58.12 | 94.58 | 58.2 | 94.78 | 58.41 | 94.52 | 58.36 | ||
| Test | 85.65 | 38.29 | 85.67 | 40.77 | 84.42 | 40.36 | 85.26 | 38.41 | 85.75 | 39.5 | 85.35 | 39.47 | |||
| LDA | Train | 91.05 | 26.42 | 90.76 | 26.84 | 91.02 | 26.74 | 91.15 | 26.31 | 91.12 | 26 | 91.02 | 26.46 | ||
| Test | 91.4 | 26.12 | 90.83 | 26.02 | 90.86 | 25.46 | 90.9 | 26.86 | 91.07 | 27.47 | 91.01 | 26.39 | |||
| PLS-DA | Train | 93.89 | 20.81 | 93.64 | 21.27 | 93.93 | 20.82 | 93.93 | 20.88 | 94.02 | 20.55 | 93.88 | 20.87 | ||
| Test | 94.36 | 20.65 | 93.69 | 20.38 | 93.77 | 20.87 | 93.53 | 20.93 | 94.01 | 21.33 | 93.87 | 20.83 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, A.; Park, S.; Yoo, J.; Kang, J.; Lim, J.; Seo, Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, G. Detecting Bacterial Biofilms Using Fluorescence Hyperspectral Imaging and Various Discriminant Analyses. Sensors 2021, 21, 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062213
Lee A, Park S, Yoo J, Kang J, Lim J, Seo Y, Kim B, Kim G. Detecting Bacterial Biofilms Using Fluorescence Hyperspectral Imaging and Various Discriminant Analyses. Sensors. 2021; 21(6):2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062213
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ahyeong, Saetbyeol Park, Jinyoung Yoo, Jungsook Kang, Jongguk Lim, Youngwook Seo, Balgeum Kim, and Giyoung Kim. 2021. "Detecting Bacterial Biofilms Using Fluorescence Hyperspectral Imaging and Various Discriminant Analyses" Sensors 21, no. 6: 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062213
APA StyleLee, A., Park, S., Yoo, J., Kang, J., Lim, J., Seo, Y., Kim, B., & Kim, G. (2021). Detecting Bacterial Biofilms Using Fluorescence Hyperspectral Imaging and Various Discriminant Analyses. Sensors, 21(6), 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062213






