Non-Destructive and Quantitative Evaluation of Rebar Corrosion by a Vibro-Doppler Radar Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
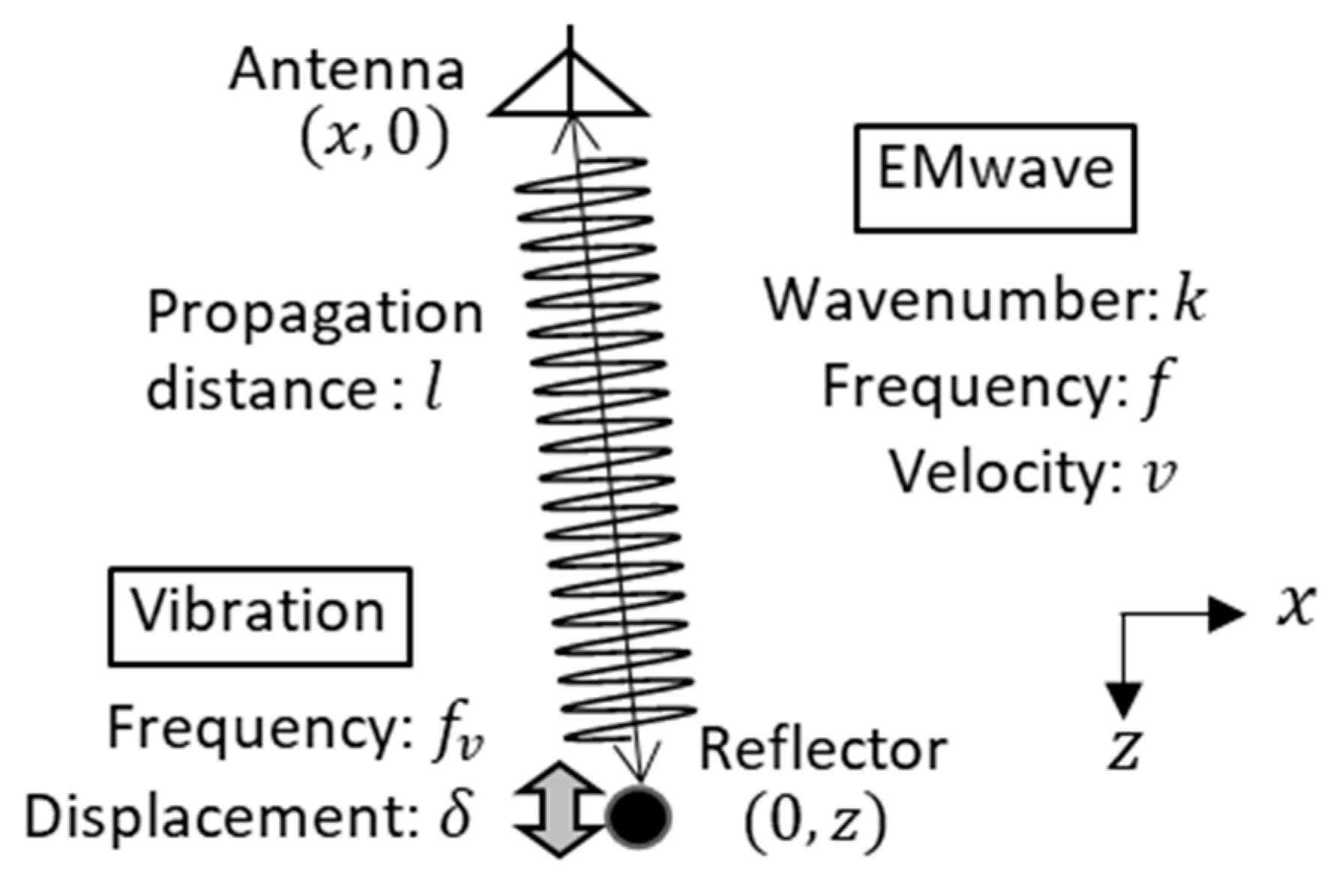
2. Principle of the Vibro-Doppler Radar Method
3. Measurement of Vibration Displacement by Vibro-Doppler Radar
3.1. Vibro-Doppler Radar System
3.2. Rebar Vibration Displacement in Air with Laser Displacement Sensor
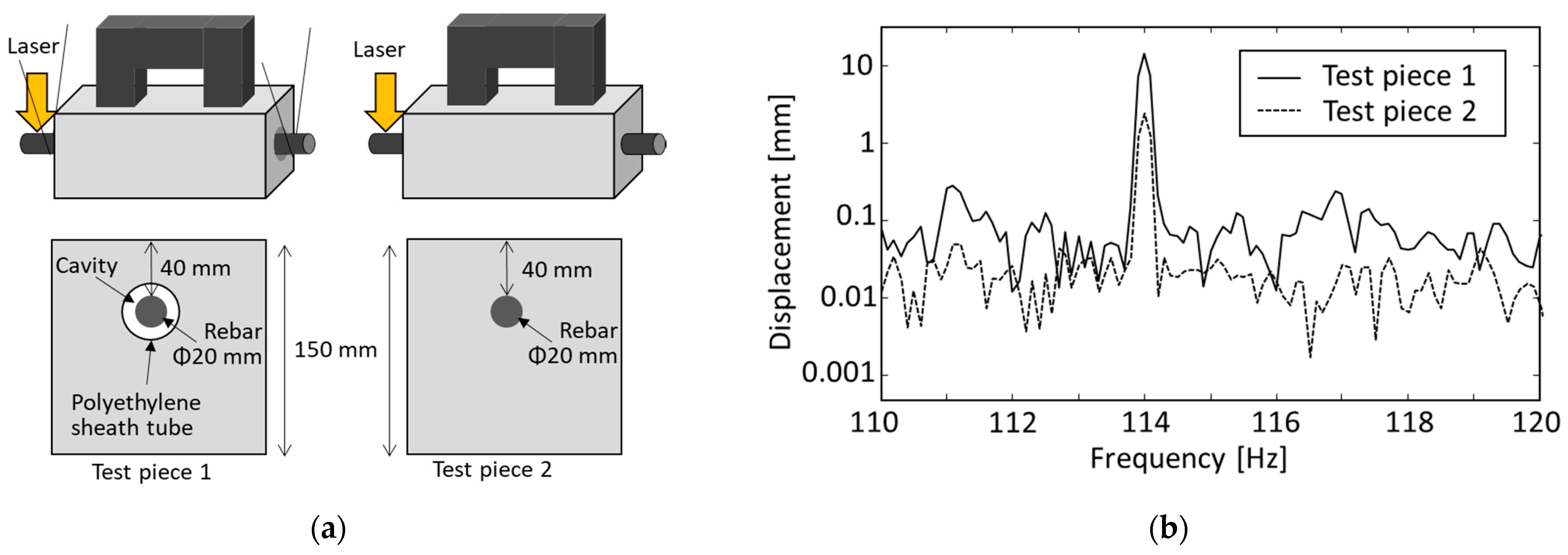
3.3. Rebar Vibration Displacement in Concrete with Laser Displacement Sensor
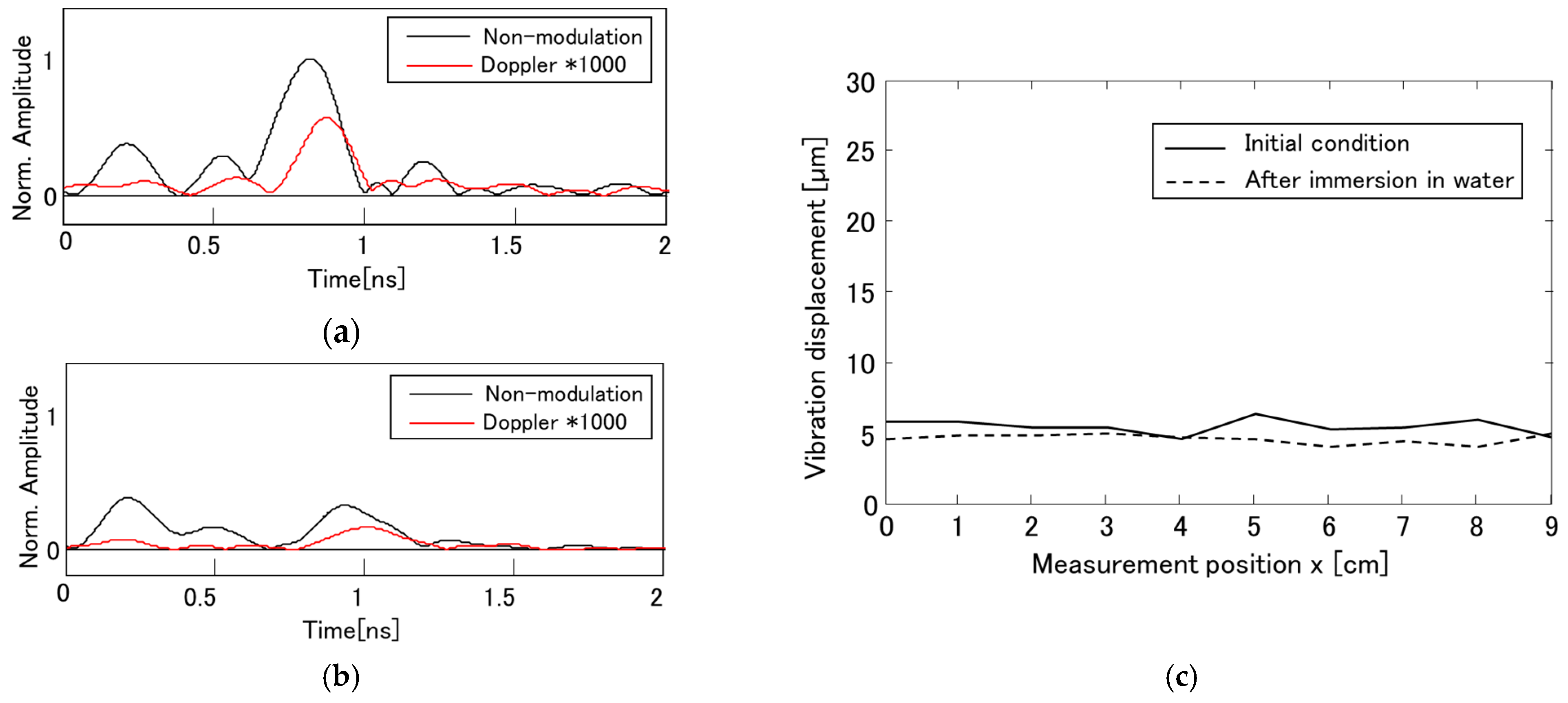
3.4. Measurement of Rebar Vibration Displacement with Vibro-Doppler Radar
4. Measurement of Rebar Vibration Displacement in Electrolytic Corrosion Test
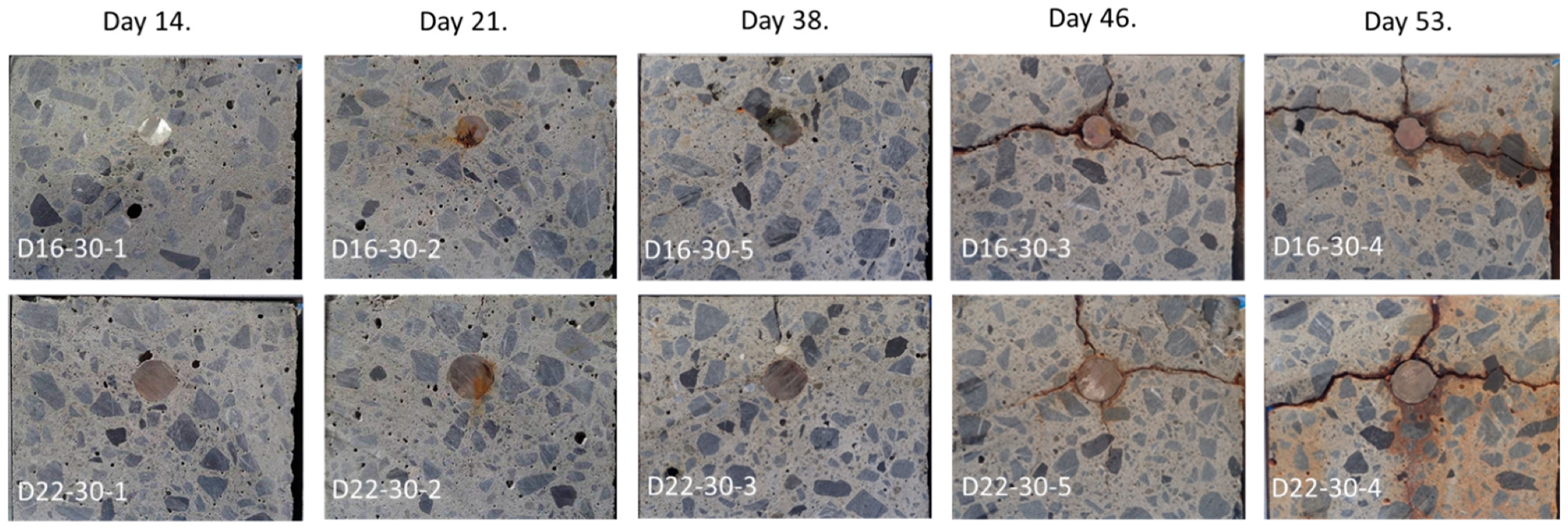
4.1. Overview of the Electrolytic Corrosion Test
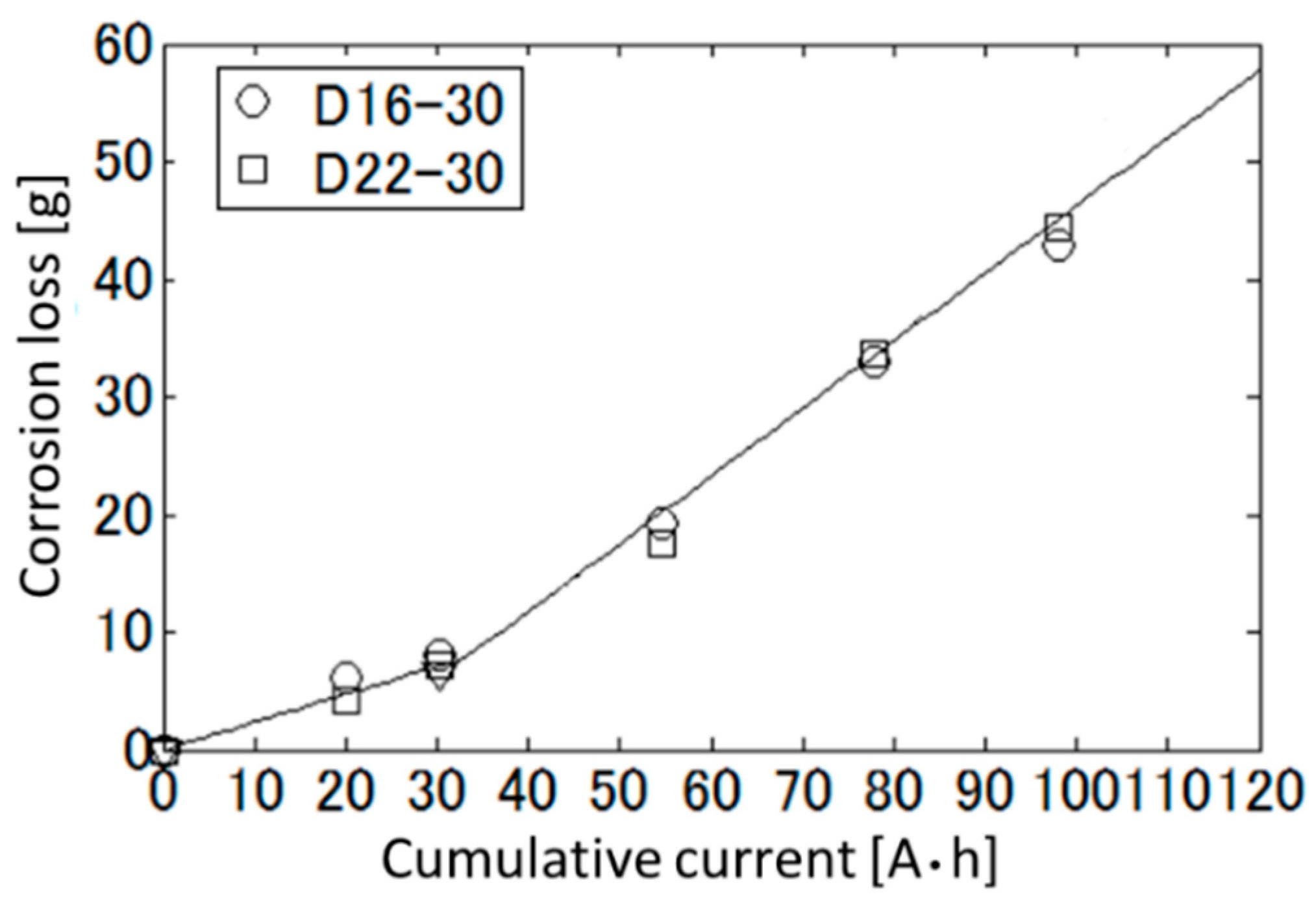
4.2. Curve Fitting of Corrosion Loss as a Function of Cumulative Current
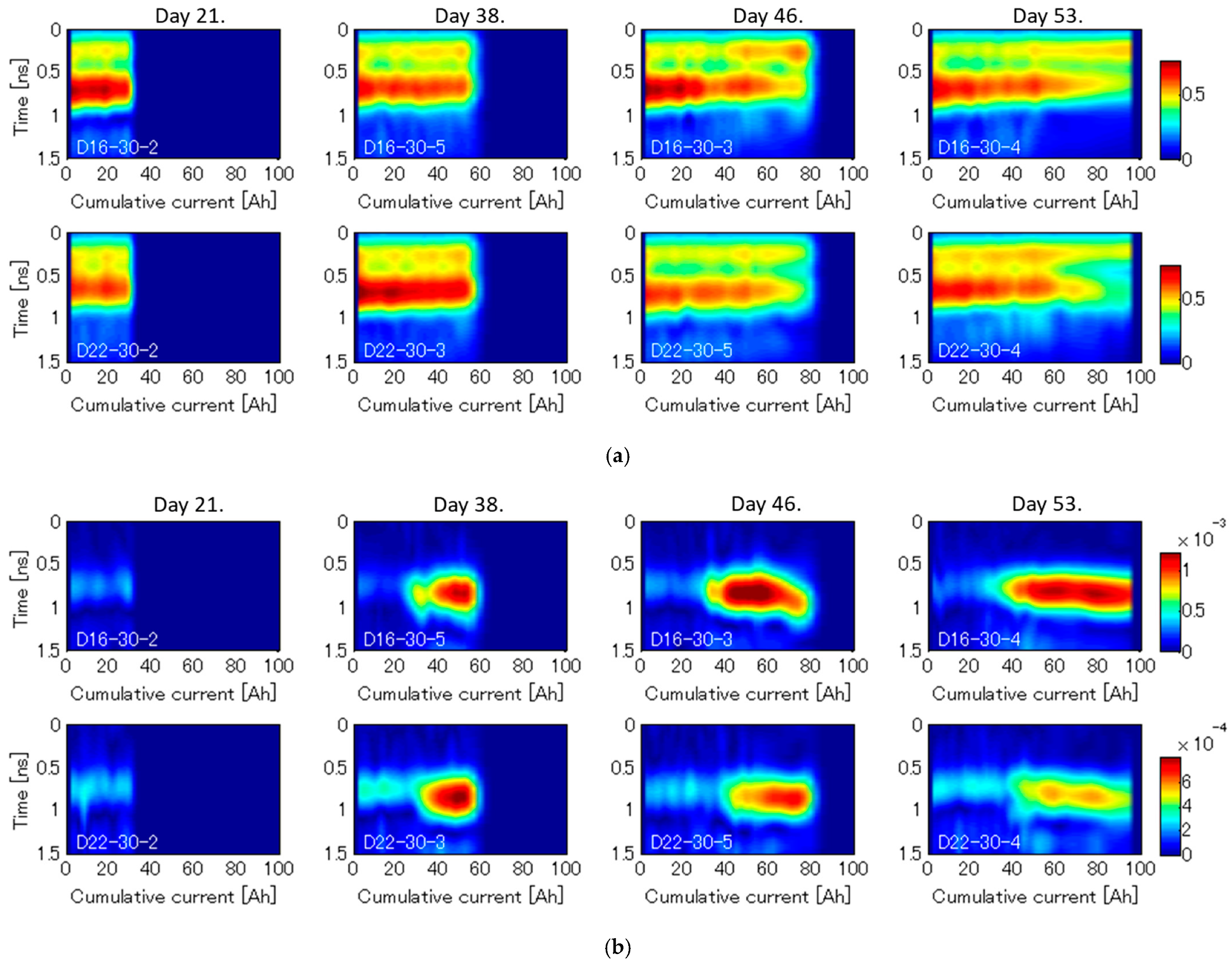
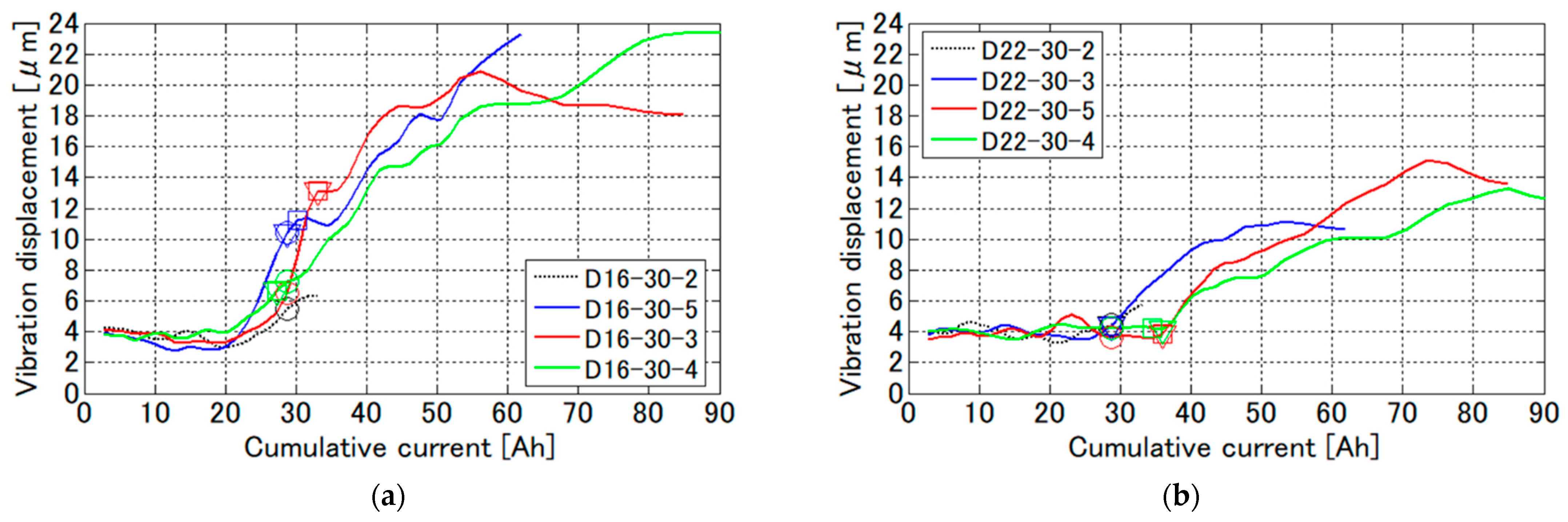
4.3. Result of Rebar Vibration Displacement by Vibro-Doppler Radar
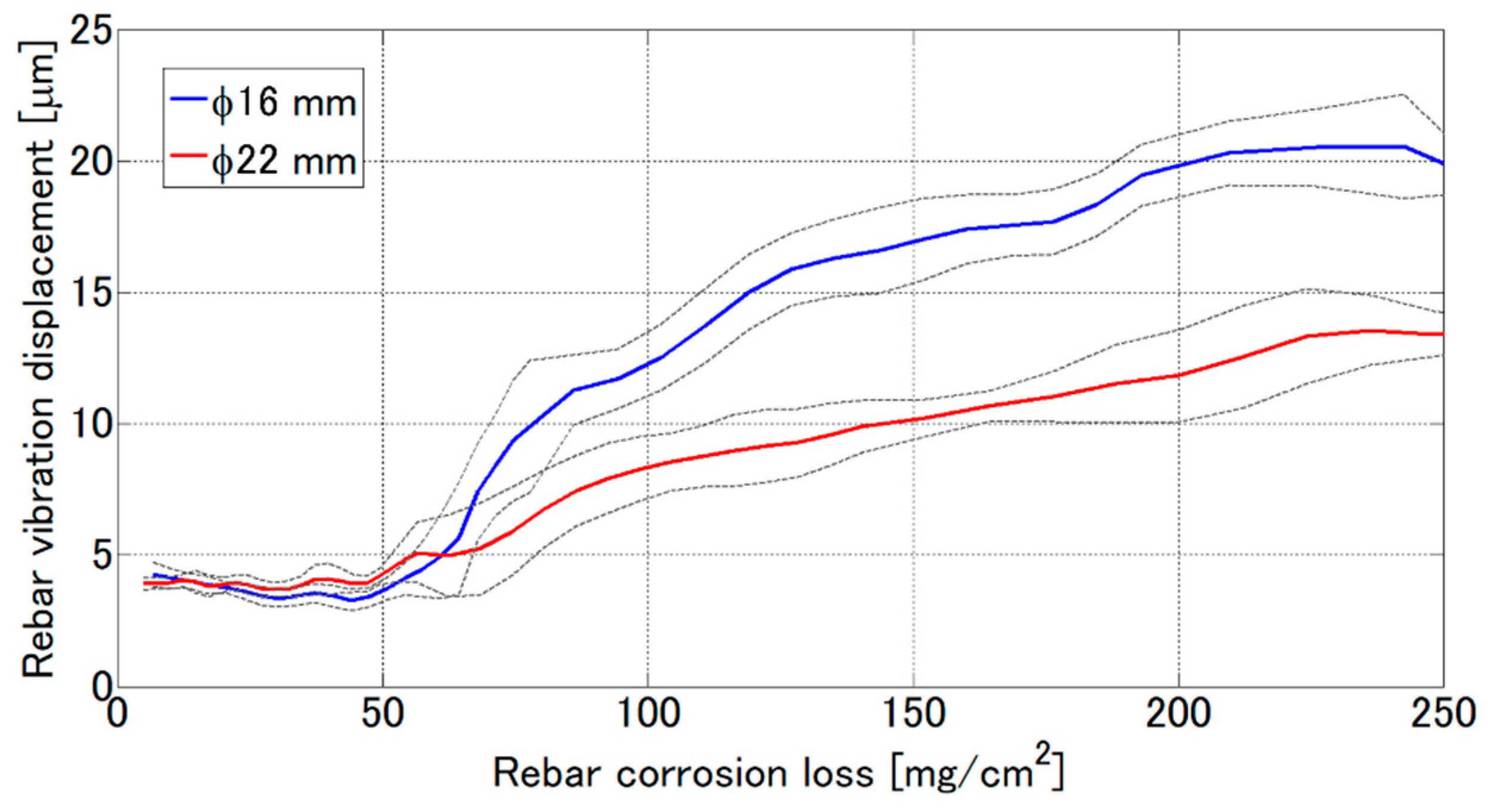
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASTM C876-15. Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. Available online: https://www.astm.org/Standards/C876.htm (accessed on 4 April 2021).
- Elsener, B.; Andrade, C.; Gulikers, J.; Polder, R.; Raupach, M. Half-cell potential measurements—Potential mapping on rein-forced concrete structures. Mater. Struct. 2003, 36, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, L. Methodology for Assessing the Probability of Corrosion in Concrete Structures on the Basis of Half-Cell Potential and Concrete Resistivity Measurements. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medeiros, M.H.F.; Rocha, F.C.; Medeiros, R.A., Jr.; Helene, P. Corrosion potential: Influence of moisture, water-cement ratio, chloride content and concrete cover. Rev. IBRACON Estrut. Mater. 2017, 10, 864–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern, M.; Geary, A.L. Electrochemical polarization I. A theoretical analysis of shape of polarization curves. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1957, 104, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.W.; Saraswathy, V. Corrosion Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Structures—A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2007, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Figueira, R.B. Electrochemical Sensors for Monitoring the Corrosion Conditions of Reinforced Concrete Structures: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, D.D.; El-Tantawy, Y.A.; Rocha-Filho, R.C. Evaluation of Electrochemical Impedance Techniques for Detecting Corrosion on Rebar in Reinforced Concrete. Available online: http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/shrp/SHRP-91-524.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2021).
- Ribeiro, D.; Abrantes, J. Application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) to monitor the corrosion of reinforced concrete: A new approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.G.; Kahraman, R.; Alnuaimi, N.A.; Gencturk, B.; Alnahhal, W.; Dawood, M.; Belarbi, A. Electrochemical behavior of mild and corrosion resistant concrete reinforcing steels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, P.J. Nondestructive Evaluation: Theory, Techniques and Applications; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinacci, G.; Tamburrino, A.; Ventre, S. Concrete rebars inspection by eddy current testing. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2007, 25, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alcantara, J.N.P.; Da Silva, F.M.; Guimarães, M.T.; Pereira, M.D. Corrosion Assessment of Steel Bars Used in Reinforced Concrete Structures by Means of Eddy Current Testing. Sensors 2015, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baek, S.; Xue, W.; Feng, M.Q.; Kwon, S. Nondestructive Corrosion Detection in RC Through Integrated Heat Induction and IR Thermography. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2012, 31, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirca, G.F.; Adeli, H. Infrared Thermography For Detecting Defects In Concrete Structures. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2018, 24, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic Principles of Ground Penetrating Radar. In Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 3–40. [Google Scholar]
- Blindow, N.; Eisenburger, D.; Illich, B.; Petzold, H.; Richter, T. Ground Penetrating Radar. In Environmental Geology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 283–335. [Google Scholar]
- Roqueta, G.; Jofre, L.; Feng, M.Q. Analysis of the Electromagnetic Signature of Reinforced Concrete Structures for Nonde-structive Evaluation of Corrosion Damage. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaki, A.; Johari, M.A.M.; Hussin, W.M.A.W.; Jusman, Y. Experimental Assessment of Rebar Corrosion in Concrete Slab Using Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR). Int. J. Corros. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, I.; Yazdani, N. An Experimental Study for Quantitative Estimation of Rebar Corrosion in Concrete Using Ground Penetrating Radar. J. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hugenschmidt, J.; Loser, R. Detection of chlorides and moisture in concrete structures with ground penetrating radar. Mater. Struct. 2007, 41, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senin, S.; Hamid, R. Ground penetrating radar wave attenuation models for estimation of moisture and chloride content in concrete slab. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tešić, K.; Baričević, A.; Serdar, M. Non-Destructive Corrosion Inspection of Reinforced Concrete Using Ground-Penetrating Radar: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lubecke, V.M.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lin, J. A Review on Recent Advances in Doppler Radar Sensors for Noncontact Healthcare Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2046–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, N.T.P.; Tang, L.; Demir, V.; Hasan, S.F.; Minh, N.D.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Review-Microwave Radar Sensing Systems for Search and Rescue Purposes. Sensors 2019, 19, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moll, J.; Krozer, V. Radar-based Mechanical Vibration Sensing for Structural Health Monitoring Applications: A Comparison of Radar Transceiver Measurements at 24 GHz and 100 GHz. In Proceedings of the 7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, Bilbao, Spain, 5–8 July 2016. [Google Scholar]







| Excitation Current [A] | Vibration Displacement [μm] |
|---|---|
| 8 | 6.7 |
| 9 | 8.6 |
| 10 | 11.5 |
| Instrument | Item | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vector network analyzerRohde & Schwarz ZVL-13 | Center frequency | 5 GHz |
| Span | 8 GHz | |
| Power | −8 dBm | |
| IF bandwidth | 10 Hz | |
| Number of points | 151 | |
| Image canceling mixer | Output power | 25 dBm |
| Bandwidth | 1.5–12 GHz |
| Water | Cement | W/C | Coarse Aggregate | Fine Aggregate | Fine Aggregate Ratio | Air | Slump | Dry Density | Compressive Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [kg/m3] | [kg/m3] | [%] | [kg/m3] | [kg/m3] | [%] | [%] | [cm] | [Kg/m3] | [N/mm2] |
| 168 | 305 | 55 | 947 | 864 | 48 | 4.5 | 12 | 2329 | 41.2 |
| Test Piece No. | Cover of Concrete [mm] | Diameter of Rebar [mm] | Period of Electrolytic Corrosion Test [Day] | Cumulative Current [Ah] | Amount of Corrosion Loss [g] | Corrosion Loss [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D16-30-1 | 30 | 16 | 14 | 20 | 6.2 | 2.1 |
| D16-30-2 | 21 | 30 | 8.1 | 2.7 | ||
| D16-30-5 | 38 | 55 | 19.3 | 6.5 | ||
| D16-30-3 | 46 | 77 | 32.9 | 11.1 | ||
| D16-30-4 | 53 | 98 | 43.0 | 14.6 | ||
| D22-30-1 | 22 | 14 | 20 | 4.3 | 0.8 | |
| D22-30-2 | 21 | 30 | 7.2 | 1.3 | ||
| D22-30-3 | 38 | 55 | 17.6 | 3.0 | ||
| D22-30-5 | 46 | 77 | 33.8 | 6.0 | ||
| D22-30-4 | 53 | 98 | 44.3 | 7.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miwa, T. Non-Destructive and Quantitative Evaluation of Rebar Corrosion by a Vibro-Doppler Radar Method. Sensors 2021, 21, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072546
Miwa T. Non-Destructive and Quantitative Evaluation of Rebar Corrosion by a Vibro-Doppler Radar Method. Sensors. 2021; 21(7):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072546
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiwa, Takashi. 2021. "Non-Destructive and Quantitative Evaluation of Rebar Corrosion by a Vibro-Doppler Radar Method" Sensors 21, no. 7: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072546
APA StyleMiwa, T. (2021). Non-Destructive and Quantitative Evaluation of Rebar Corrosion by a Vibro-Doppler Radar Method. Sensors, 21(7), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072546





