Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Drinking Water by a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy Immunosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
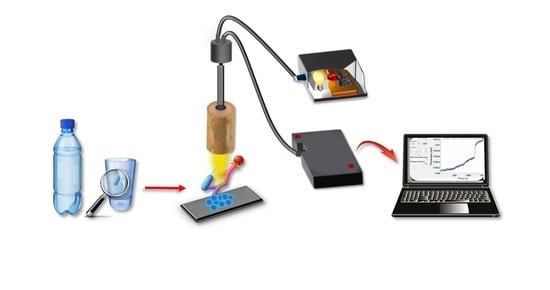
2.2. WLRS Instrumentation
2.3. Bacteria Culturing and Counting
2.4. Calibrators/Water Samples Preparation
2.5. Preparation and Biofunctionalization of the Chip
2.6. Competitive Immunodetection of S. typhimurium with the WLRS Chip
2.7. ELISA Method for the Detection of S. typhimurium in Water Samples
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Assay
3.2. Analytical Characteristics
3.3. Regeneration
3.4. Comparison with Other Immunosensors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newell, D.G.; Koopmans, M.; Verhoef, L.; Duizer, E.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Sprong, H.; Opsteegh, M.; Langelaar, M.; Threfall, J.; Scheutz, F.; et al. Food-borne diseases—The challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2010, 139, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, J.P.S. Water microbiology. Bacterial pathogens and water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3657–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Highlights from the 2017 Surveillance Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fdoss/annual-reports/2017-report-highlights.html (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Shen, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Biosensors for rapid detection of Salmonella in food: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 149–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashazadeh, P.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Hejazi, M.; Hashemi, M.; de la Guardia, M. Nano-materials for use in sensing of salmonella infections: Recent advances. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B. Nanomaterial-based sensors for detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens and toxins as well as pork adulteration in meat products. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsougeni, K.; Papadakis, G.; Gianneli, M.; Grammoustianou, A.; Constantoudis, V.; Dupuy, B.; Petrou, P.S.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Tserepi, A.; Gizeli, E.; et al. Plasma nanotextured polymeric lab-on-a-chip for highly efficient bacteria capture and lysis. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Runyon, M.; Herrman, T.J.; Phillips, R.; Hsieh, J. Review of Salmonella detection and identification methods: Aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. Food Control 2015, 47, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Biswas, A.; Choi, K.; Pal, U. Methods for rapid detection of foodborne pathogens: An overview. Am. J. Food Technol. 2011, 6, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, G.; Sithebe, A.; Enitan, A.M.; Kumari, S.; Bux, F.; Stenström, T.A. Comparison of droplet digital PCR and quantitative PCR for the detection of Salmonella and its application for river sediments. J. Water Health 2017, 15, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.I.; McQuillan, J.; Taiwo, M.; Parks, R.; Stenton, C.A.; Morgan, H.; Mowlem, M.C.; Lees, D.N. A highly specific Escherichia coli qPCR and its comparison with existing methods for environmental waters. Water Res. 2017, 126, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radhika, M.; Saugata, M.; Murali, H.; Batra, H. A novel multiplex PCR for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella enterica and Shigella species. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdivieso-Garcia, A.; Riche, E.; Abubakar, O.; Waddell, T.E.; Brooks, B.W. A double antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of Salmonella using biotinylated monoclonal antibodies. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Song, S.; Tang, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. A highly sensitive ELISA and immunochromatographic strip for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium in milk samples. Sensors 2015, 15, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jasim, I.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, L.; Dweik, M.; Zhang, S.; Almasri, M. A microfluidic based biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella in food products. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhunia, A.K. Biosensors and bio-based methods for the separation and detection of foodborne pathogens. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2008, 54, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Salazar, J.K. Culture-independent rapid detection methods for bacterial pathogens and toxins in food matrices. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, S.; Chuang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Shen, T.Y.; Chang, C.A.; Lin, C. Disposable amperometric immunosensing strips fabricated by Au nanoparticles-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes for the detection of foodborne pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.; Tu, S. Enzyme-linked immunomagnetic electrochemical detection of live Escherichia coli O157:H7 in apple juice. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelada-Guillen, G.A.; Bhosale, S.V.; Riu, J.; Rius, F.X. Real-time potentiometric detection of bacteria in complex samples. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9254–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ying, W.; Alocilja, E.C.; Downes, F.P. Sensitivity and specificity performance of a direct-charge transfer biosensor for detecting Bacillus cereus in selected food matrices. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 99, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, M.; Ma, Q.; Ai, S. A label-free electrochemical impedance immunosensor based on AuNPs/PAMAM-MWCNT-Chi nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode for detection of Salmonella typhimurium in milk. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, Q.K.; Tran, Q.H.; Vu, N.P.; Anh, T.-L.; Dang, T.T.L.; Tonezzer, M.; Nguyen, T.H.H. A label-free electrochemical biosensor based on screen-printed electrodes modified with gold nanoparticles for quick detection of bacterial pathogens. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgione, A.; Cimafonte, M.; Della Ventura, B.; Iannaccone, M.; Ambrosino, C.; Capuano, F.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Velotta, R.; Capparelli, R. QCM-based immunosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 16137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salam, F.; Uludag, Y.; Tothill, I.E. Real-time and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using an automated quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) instrument with nanoparticles amplification. Talanta 2013, 115, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Chen, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; An, H.; Duan, Y. Novel Ω-shaped fiber-optic probe-based localized surface Plasmon resonance biosensor for real-time detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13640–13646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.C.; Bridgman, R.C. Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in romaine lettuce using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, S.; Grant, S.A. A novel FRET-based optical fiber biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.R.; Kim, G.; Kothapalli, A.; Morgan, M.T.; Ess, D. Detection of Salmonella Enteritidis using a miniature optical surface plasmon resonance biosensor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 61, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Si, C.; Ying, Y. Monitoring of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in food samples using lectin based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.K.; Lee, W.; Chun, B.S.; Bae, Y.M.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.W. The fabrication of protein chip based on surface plasmon resonance for detection of pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.D.; Ladd, J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, S.; Homola, J.; Jiang, S. Quantitative and simultaneous detection of four foodborne bacterial pathogens with a multi-channel SPR sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisocherová-Lísalová, H.; Víšová, I.; Ermini, M.L.; Špringer, T.; Song, X.C.; Mrázek, J.; Lamačová, J.; Scott Lynn, N., Jr.; Šedivák, P.; Homola, J. Low-fouling surface plasmon resonance biosensor for multi-step detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens in complex food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagkali, V.; Petrou, P.S.; Makarona, E.; Peters, J.; Haasnoot, W.; Jobst, G.; Moser, I.; Gajos, K.; Budkowski, A.; Economou, A.; et al. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin B 1, fumonisin B 1 and deoxynivalenol in beer samples with a label-free monolithically integrated optoelectronic biosensor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 5, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, M.; Petrou, P.S.; Makarona, E.; Haasnoot, W.; Moser, I.; Jobst, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Lees, M.; Kalatzi, K.; Raptis, I.; et al. Ultrafast multiplexed-allergen detection through advanced fluidic design and monolithic interferometric silicon chips. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9559–9567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.H.; Brackett, R.E.; Hartman, N.F.; Campbell, D.P. Development of a Rapid Response Biosensor for Detection of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, M.; Koba, M.; Celebańska, A.; Bock, W.J.; Śmietana, M. Live E. coli bacteria label-free sensing using a microcavity in-line Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, J.; González-Guerrero, A.B.; Domínguez, C.; Lechuga, L.M. Label-free bimodal waveguide immunosensor for rapid diagnosis of bacterial infections in cirrhotic patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouvinos, G.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Drygiannakis, D.; Raptis, I.; Stefanitsis, G.; Martini, S.; Nikita, D.; Goustouridis, D.; Moser, I.; et al. Simultaneous determination of CRP and D-dimer in human blood plasma samples with White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 84, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsounidi, D.; Koukouvinos, G.; Petrou, P.; Misiakos, K.; Zisis, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.E. Rapid and sensitive label-free determination of aflatoxin M1 levels in milk through a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy immunosensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 282, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavra, E.; Petrou, P.S.; Koukouvinos, G.; Kiritsis, C.; Pirmettis, I.; Papadopoulos, M.; Goustouridis, D.; Economou, A.; Misiakos, K.; Raptis, I.; et al. Simultaneous determination of paraquat and atrazine in water samples with a white light reflectance spectroscopy biosensor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouvinos, G.; Goustouridis, D.; Misiakos, K.; Kakabakos, S.; Raptis, I.; Petrou, P. Rapid C-reactive protein determination in whole blood with a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy label-free immunosensor for Point-of-Care applications. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 260, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouvinos, G.; Petrou, P.; Goustouridis, D.; Misiakos, K.; Kakabakos, S.; Raptis, I. Development and bioanalytical applications of a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy label-free sensing platform. Biosensors 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barlen, B.; Mazumdar, S.; Lezrich, O.; Kämpfer, P.; Keusgen, M. Detection of Salmonella by surface plasmon resonance. Sensors 2007, 7, 1427–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, Y.; Hoffmann, W.C.; Zheng, X. Using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium in chicken carcass. J. Bionic Eng. 2008, 5, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Yi, S.Y.; Woubit, A.; Kim, M. A Portable Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 2016, 25, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokken, G.C.A.M.; Corbee, R.J.; Knapen, F.; Bergwerff, A.A. Immunochemical detection of Salmonella group B, D and E using an optical surface plasmon resonance biosensor. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 22, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, B.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, K.W.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, J.W. Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhneva, E.; Farka, Z.; Skládal, P.; Zajíčková, L. Cyclopropylamine plasma polymer surfaces for label-free SPR and QCM immunosensing of Salmonella. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2018, 276, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukose, J.; Shetty, V.; Ballal, M.; Chidangil, S.; Sinha, R.K. Real-time and rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium using an inexpensive lab-built surface plasmon resonance setup. Laser Phys. Lett. 2018, 15, 075701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Park, B. Label-free screening of foodborne Salmonella using Surface Plasmon Resonance imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5455–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, S.; Pandey, A.; Tiwari, U.K.; Sinha, R.K. A label-free fiber optic biosensor for Salmonella typhimurium detection. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 46, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Park, I.; Kim, W. Salmonella detection with a direct-binding optical grating coupler immunosensor. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2007, 121, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Park, B.; Huang, Y.-W.; Zhao, Y.; Kwon, Y. Label-free SERS detection of Salmonella typhimurium on DNA aptamer modified AgNR substrates. Food Meas. 2017, 11, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, B.; Wang, P.; Mills, A.; Pang, S.; McLandsborough, L.; He, L. Innovative sandwich assay with dual optical and SERS sensing mechanisms for bacterial detection. Anal. Method 2017, 9, 4732–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Ranganathan, V.; DeRosac, M.C.; Mohan Murari, B. Label-free aptasensors based on fluorescent screening assays for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 559, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Sample | Amount Added (CFU/mL) | Amount Determined (CFU/mL) | % Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 8 × 103 | 8.2 × 103 | 102 |
| 8 × 104 | 7.9 × 104 | 98.7 | |
| 8 × 105 | 7.6 × 105 | 95.0 | |
| Bottled water (Vikos) | 8 × 103 | 8.6 × 103 | 108 |
| 8 × 104 | 7.6 × 104 | 95.0 | |
| 8 × 105 | 8.2 × 105 | 102 | |
| Bottled water (Zagori) | 8 × 103 | 7.6 × 103 | 95.0 |
| 8 × 104 | 8.1 × 104 | 101 | |
| 8 × 105 | 7.5 × 105 | 93.8 | |
| Bottled water (Avra) | 8 × 103 | 7.4 × 103 | 92.5 |
| 8 × 104 | 7.7 × 104 | 96.2 | |
| 8 × 105 | 8.4 × 105 | 105 |
| Immunosensor/Device | Sample Type | LOD (CFU/mL) | Assay Time (min) | Ref. # |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPR | romaine lettuce | 4.7 × 105 | <6 | [27] |
| SPR | milk | 2.5 × 105 | ~100 | [44] |
| SPR | chicken carcass | 1 × 106 | ~17 | [45] |
| Portable SPR | buffer | 107 | ~60 | [46] |
| SPR | buffer | 1.7 × 103 | 22 | [47] |
| SPR | assay buffer | 106 | ≤120 | [48] |
| SPR | buffer | 105 | 10 | [49] |
| SPR | buffer | - | 6–7 | [50] |
| SPR imaging | buffer chicken carcass rinse | 2.1 × 106 7.6 × 106 | 20 | [51] |
| Ω-shaped fiber-optic LSPR | buffer | <128 | 100 | [26] |
| Fiber-optic | milk | 247 | <20 | [52] |
| Hartman interferometry | assay buffer chicken carcass | 104 | 10 | [36] |
| Optical-grating coupler | buffer | 1.3 × 103 | 60 | [53] |
| SERS | buffer | 108 | - | [54] |
| SERS | buffer | 100 | 75 | [55] |
| FRET aptasensor | buffer | 733 | 120 | [56] |
| WLRS immunosensor developed | tap and bottled water | 320 | 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelopoulou, M.; Tzialla, K.; Voulgari, A.; Dikeoulia, M.; Raptis, I.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Petrou, P. Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Drinking Water by a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy Immunosensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082683
Angelopoulou M, Tzialla K, Voulgari A, Dikeoulia M, Raptis I, Kakabakos SE, Petrou P. Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Drinking Water by a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy Immunosensor. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082683
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelopoulou, Michailia, Konstantina Tzialla, Angeliki Voulgari, Mary Dikeoulia, Ioannis Raptis, Sotirios Elias Kakabakos, and Panagiota Petrou. 2021. "Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Drinking Water by a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy Immunosensor" Sensors 21, no. 8: 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082683
APA StyleAngelopoulou, M., Tzialla, K., Voulgari, A., Dikeoulia, M., Raptis, I., Kakabakos, S. E., & Petrou, P. (2021). Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium in Drinking Water by a White Light Reflectance Spectroscopy Immunosensor. Sensors, 21(8), 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082683