Viscosity Measurement Sensor: A Prototype for a Novel Medical Diagnostic Method Based on Quartz Crystal Resonator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Quartz Crystal Resonator
2.2. Measurement Setup
2.3. Samples
2.3.1. Artificial Synovial Fluid
2.3.2. Artificial Cerebrospinal Fluid
3. Results
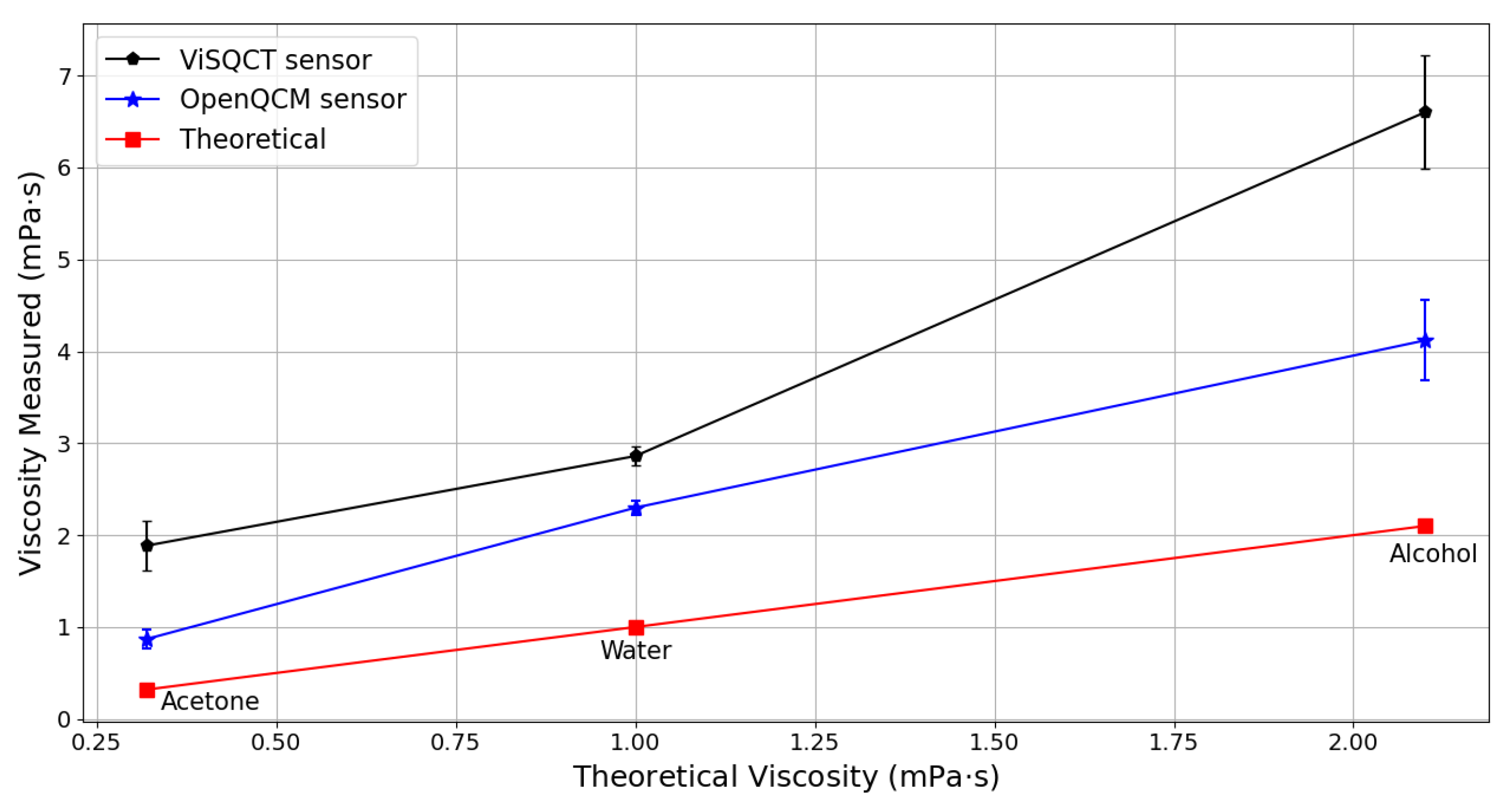
3.1. Pure Fluids: Water, Alcohol, and Acetone
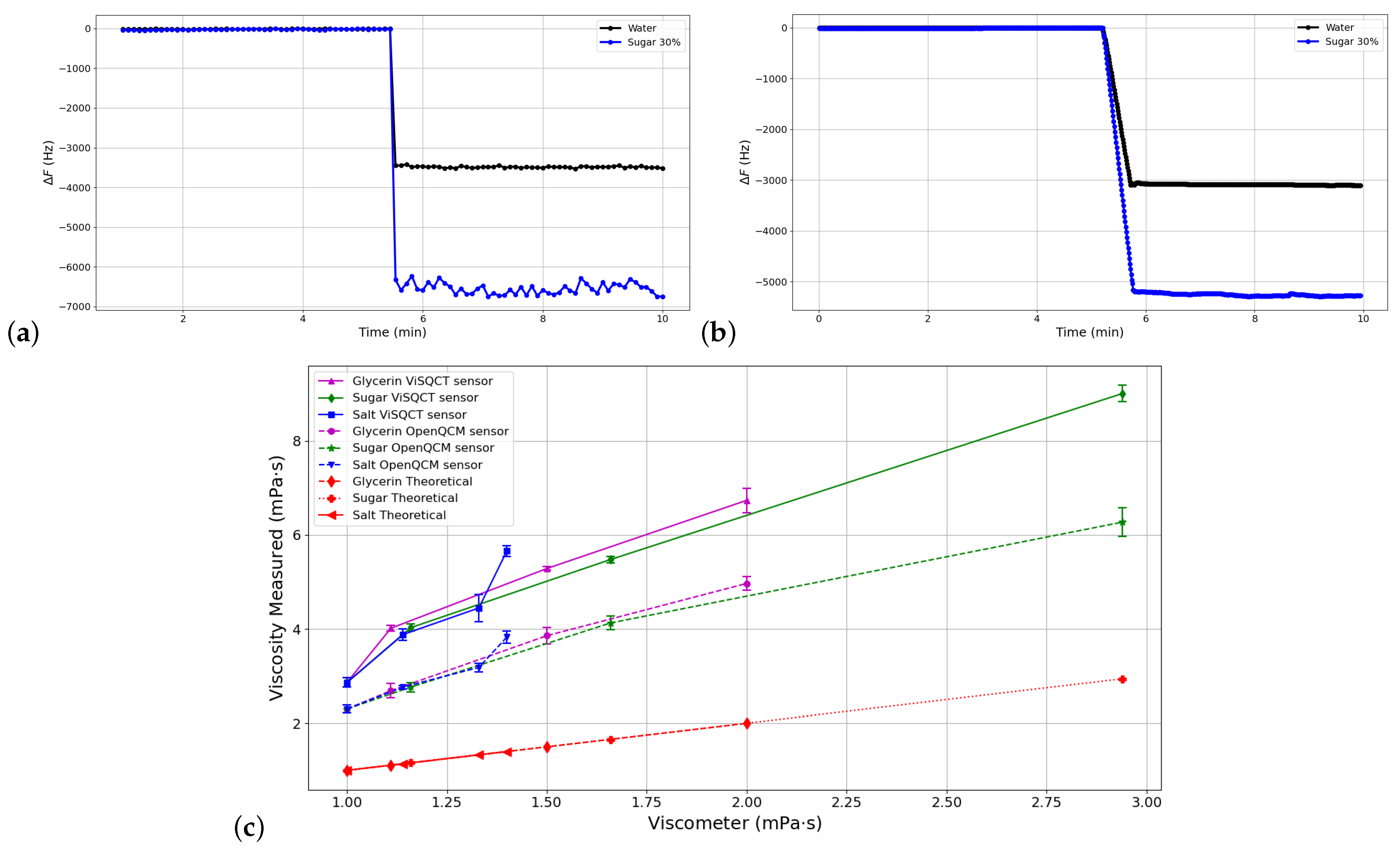
3.2. Test Dilutions: Glycerin, Sugar, and Salt Dilutions
3.3. aSF Results
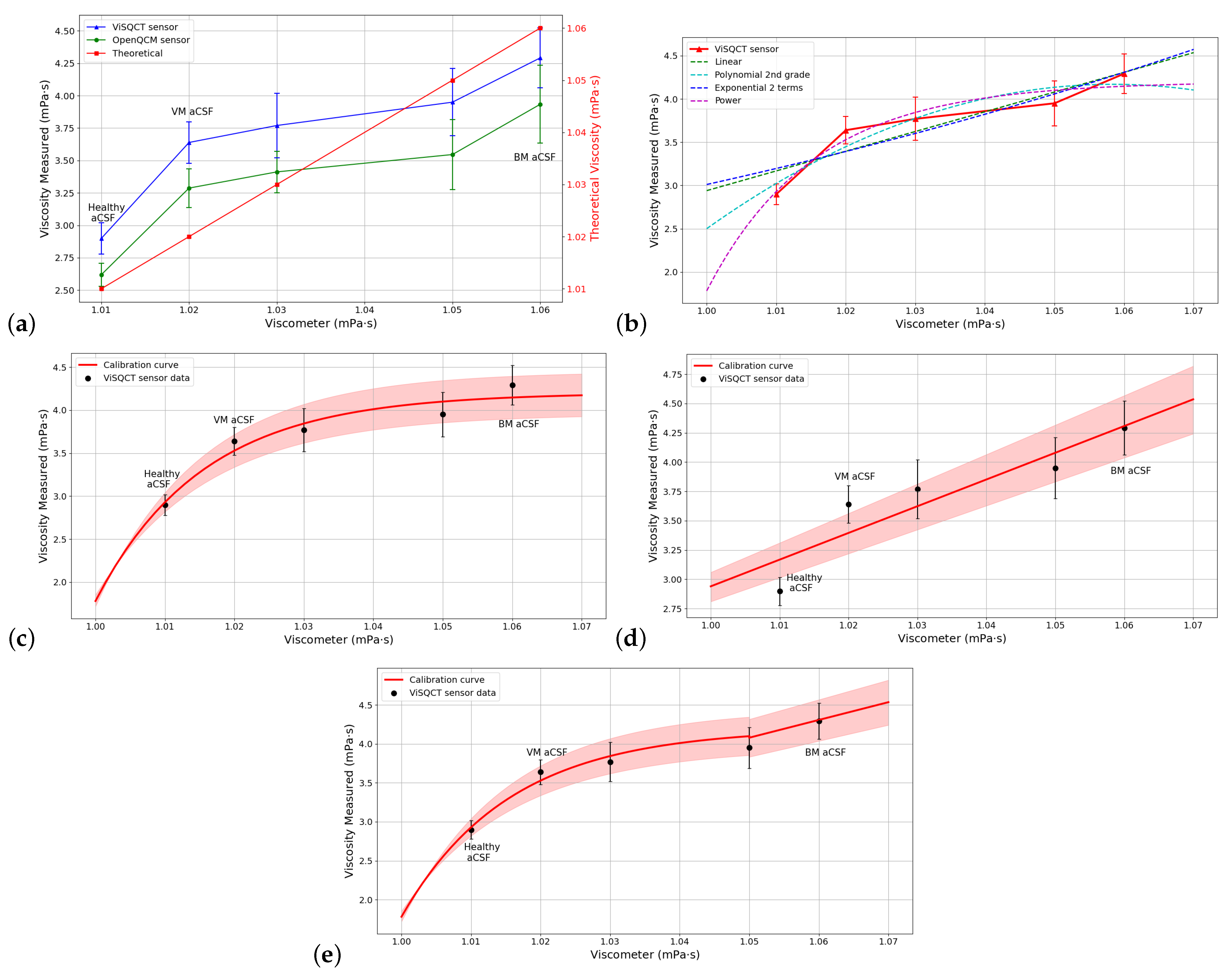
3.4. aCSF Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brannan, S.R.; Jerrard, D.A. Synovial fluid analysis. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 30, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafford, C.T.; Niedermeier, W.; Holley, H.L.; Pigman, W. Studies on the concentration and intrinsic viscosity of hyaluronic acid in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatic diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1964, 23, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetkin, F.; Kayabas, U.; Ersoy, Y.; Bayindir, Y.; Toplu, S.A.; Tek, I. Cerebrospinal fluid viscosity: A novel diagnostic measure for acute meningitis. South. Med. J. 2010, 103, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Castillo, A.; Núñez, C.; Cabiedes, J. Synovial fluid analysis. Reumatol. ClíNica 2010, 6, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, L.; Coll, G.; Chazal, J. Anatomy and physiology of cerebrospinal fluid. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2011, 128, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, J.; Bardin, T. Synovial fluid. EMC-Rhumatol.-Orthop. 2004, 1, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, O. Epidemiology of rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C. Estudio del Liquido Sinovial; Guías de Procedimientos en Reumatología: Bogotá, Colombia, 2011; pp. 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- West, S.G.; Kolfenbach, J. Rheumatology Secrets, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, B.L.C.; Lai, J.T.F.; Sinclair, A.J. Cerebrospinal fluid and lumbar puncture: A practical review. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1530–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, M.C.; Tunkel, A.R.; van de Beek, D. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and antimicrobial treatment of acute bacterial meningitis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, D.R. Viral meningitis. Br. Med. Bull. 2005, 75–76, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirri, F.; Palomba, E.; Longobardo, A.; Zampetti, E.; Saggin, B.; Scaccabarozzi, D. A review of quartz crystal microbalances for space applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 287, 48–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, T.; Szulczyński, B.; Wojciechowski, M.; Kamysz, W.; Gębicki, J. A Highly Selective Biosensor Based on Peptide Directly Derived from the HarmOBP7 Aldehyde Binding Site. Sensors 2019, 19, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migoń, D.; Wasilewski, T.; Suchy, D. Application of QCM in Peptide and Protein-Based Drug Product Development. Molecules 2020, 25, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Bai, Q.; Hu, J.; Hou, D. A practical model of quartz crystal microbalance in actual applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, A.; Panzardi, E.; Vignoli, V.; Tani, M.; Landi, E.; Mugnaini, M.; Vaccarella, P. An adaptive measurement system for the simultaneous evaluation of frequency shift and series resistance of QCM in liquid. Sensors 2021, 21, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittle, J.; Levin, J.; Levin, N. Water Content of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Films Measured by Quartz Crystal Microbalance and Deuterium Oxide Exchange. Sensors 2021, 21, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kömpf, D.; Held, J.; Müller, S.F.; Drechsel, H.R.; Tschan, S.C.; Northoff, H.; Gehring, F.K. Real-time measurement of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocyte cytoadhesion with a quartz crystal microbalance. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberfrank, S.; Drechsel, H.; Sinn, S.; Northoff, H.; Gehring, F.K. Utilisation of quartz crystal microbalance sensors with dissipation (QCM-D) for a clauss fibrinogen assay in comparison with common coagulation reference methods. Sensors 2016, 16, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Luo, R.; Maitz, M.F.; Huang, N. Immobilization of serum albumin and peptide aptamer for EPC on polydopamine coated titanium surface for enhanced in-situ self-endothelialization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 60, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, J.; Ding, Y. A label-free immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of ketamine based on quartz crystal microbalance. Sensors 2015, 15, 8540–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Lim, S.I.; Cho, Y.Y.; Choi, S.; Song, J.Y.; An, D.J. Detection of H3N2 canine influenza virus using a Quartz Crystal Microbalance. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 208, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Saha, T.; Tey, B.T.; Tan, W.S.; Ooi, C.W. Quartz crystal microbalance-based biosensors as rapid diagnostic devices for infectious diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 168, 112513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, D.C.; Joyce, M.J.; Barnes, C.; Booth, C.J.; Jefferies, A.C. Viscosity measurement of industrial oils using the droplet quartz crystal microbalance. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2003, 14, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Paz, A.M.; Rodríguez-Pardo, L.; Fariña, J.; Marcos-Acevedo, J. Resolution in QCM sensors for the viscosity and density of liquids: Application to lead acid batteries. Sensors 2012, 12, 10604–10620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, F.; Qiu, D.-Y.; Guo, L.-P.; Ye, P.; Zeng, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.C. Separate density and viscosity measurements of unknown liquid using quartz crystal microbalance. Aip Adv. 2016, 6, 095313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada, L.A.; González, M.X.; Sandoval, O.L.; Olmedo, J.J. Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid Dilutions at Different Concentrations Using a Quartz Crystal Resonator (QCR) for the Potential Diagnosis of Arthritic Diseases. Sensors 2016, 16, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerbrey, G. Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Z. für Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, K.K.; Gordon, J.G., II. The oscillation frequency of a quartz resonator in contact with liquid. Anal. Chim. Acta 1985, 175, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsmann, D. Viscoelastic, mechanical, and dielectric measurements on complex samples with the quartz crystal microbalance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 4516–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiède, M.; Daridon, J.L.; Paillol, J.H.; Pauly, J. Characterization of the behaviour of a quartz crystal resonator fully immersed in a Newtonian liquid by impedance analysis. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, T.; Moriizumi, T. A Theory of a Quartz Crystal Microbalance Based upon a Mason Equivalent Circuit. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 29, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Songkhla, S.; Nakamoto, T. Interpretation of Quartz Crystal Microbalance Behavior with Viscous Film Using a Mason Equivalent Circuit. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songkhla, S.N.; Nakamoto, T. Signal Processing of Vector Network Analyzer Measurement for Quartz Crystal Microbalance With Viscous Damping. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 10386–10392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal Ahumada, L.A.; Peña Pérez, N.; Herrera Sandoval, O.L.; del Pozo Guerrero, F.; Serrano Olmedo, J.J. A new way to find dielectric properties of liquid sample using the quartz crystal resonator (QCR). Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 239, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open QCM. Available online: https://openqcm.com/about-openqcm-q-1 (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- Swan, A.; Amer, H.; Dieppe, P. The value of synovial fluid assays in the diagnosis of joint disease: A literature survey. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, R.; Snodgrass, S.R.; Johanson, C.E. A balanced view of the cerebrospinal fluid composition and functions: Focus on adult humans. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 273, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Sadhu, K.K. Two instantaneous fluorogenic steps for detection of nanomolar amyloid beta monomer and its interaction with stoichiometric copper(II) ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 303, 127086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudell, J.B.; Rechs, A.J.; Jelman, T.J.; Ross-Inta, C.M.; Hao, S.; Gietzen, D.W. The Anterior Piriform Cortex Is Sufficient for Detecting Depletion of an Indispensable Amino Acid, Showing Independent Cortical Sensory Function. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, R.M. Interpretación del líquido cefalorraquídeo. An. Pediatr. Contin. 2014, 12, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codina, M.G.; de Cueto, M.; Vicente, D.; Echevarría, J.E.; Prats, G. Diagnóstico microbiológico de las infecciones del sistema nervioso central. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. ClíNica 2011, 29, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fluid | H. A. Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Healthy aSF | 3.5 |
| aSF3 | 3.0 |
| aSF2 | 2.0 |
| OA aSF | 1.3 |
| aSF1 | 1.0 |
| RA aSF | 0.84 |
| Fluid | NaCl Concentration (mg/mL) | Concentration (mg/mL) | Albumin Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy aCSF | 7.25 | 2.18 | 0.0 |
| VM aCSF | 7.25 | 2.18 | 0.5 |
| aCSF1 | 7.25 | 2.18 | 1.0 |
| aCSF2 | 7.25 | 2.18 | 2.0 |
| BM aCSF | 7.25 | 2.18 | 3.0 |
| Fluid | Density (Theory) (mg/mL) | Viscosity (Theory) (mPa · s) | ViSQCT | Open QCM® | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference Theory vs. ViSQCT (%) | (Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference Theory vs. Open QCM (%) | |||
| Water | 1000 | 1.0 | 3416 ± 62 | 2.86 ± 0.10 | 186 | 3062 ± 54 | 2.298 ± 0.08 | 129 |
| Alcohol Isopropanol | 786 | 2.1 | 4601 ± 218 | 6.602 ± 0.62 | 214 | 3634 ± 196 | 4.119 ± 0.44 | 96 |
| Acetone | 791 | 0.32 | 2467 ± 179 | 1.886 ± 0.27 | 489 | 1676 ± 95 | 0.87 ± 0.10 | 171 |
| Fluid | Density (mg/mL) | Viscometer (mPa · s) | ViSQCT | Open QCM® | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference vs. Viscometer (%) | (Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference vs. Viscometer (%) | |||
| Glycerin 10% | 1034 | 1.11 | 4115 ± 34 | 4.015 ± 0.06 | 261 | 3367 ± 95 | 2.687 ± 0.15 | 142 |
| Glycerin 20% | 1064 | 1.50 | 4789 ± 20 | 5.284 ± 0.04 | 252 | 4091 ± 96 | 3.856 ± 0.18 | 157 |
| Glycerin 30% | 1091 | 2.00 | 5475 ± 106 | 6.735 ± 0.26 | 236 | 4702 ± 67 | 4.968 ± 0.14 | 148 |
| Sugar 10% | 1045 | 1.16 | 4144 ± 46 | 4.028 ± 0.08 | 247 | 3432 ± 64 | 2.763 ± 0.10 | 138 |
| Sugar 20% | 1096 | 1.66 | 4949 ± 34 | 5.478 ± 0.07 | 230 | 4296 ± 74 | 4.128 ± 0.14 | 148 |
| Sugar 30% | 1139 | 2.94 | 6469 ± 65 | 9.007 ± 0.18 | 206 | 5398 ± 135 | 6.271 ± 0.30 | 113 |
| Salt 10% | 1088 | 1.14 | 4150 ± 64 | 3.880 ± 0.12 | 240 | 3502 ± 25 | 2.763 ± 0.04 | 142 |
| Salt 20% | 1145 | 1.33 | 4557 ± 149 | 4.446 ± 0.29 | 234 | 3855 ± 56 | 3.182 ± 0.09 | 139 |
| Salt 30% | 1194 | 1.40 | 5249 ± 52 | 5.657 ± 0.11 | 304 | 4317 ± 76 | 3.826 ± 0.13 | 173 |
| H. A. Concentration (mg/mL) | Density (mg/mL) | Viscosity (mPa · s) | ViSQCT | Open QCM® | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| || (Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference vs. Viscometer (%) | || (Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference vs. Viscometer (%) | |||
| 0.84 (RA aSF) | 1007 | 94 | 3322 ± 31 | 2.686 ± 0.05 | 97 | 3103 ± 88 | 2.344 ± 0.13 | 97 |
| 1.0 | 1008 | 109 | 3417 ± 36 | 2.839 ± 0.06 | 97 | 3104 ± 99 | 2.343 ± 0.15 | 98 |
| 1.3 (OA aSF) | 1009 | 141 | 3439 ± 34 | 2.873 ± 0.06 | 98 | 3170 ± 75 | 2.441 ± 0.11 | 98 |
| 2.0 | 1013 | 342 | 3468 ± 48 | 2.91 ± 0.08 | 99 | 3146 ± 70 | 2.395 ± 0.10 | 99 |
| 3.0 | 1022 | 716 | 3525 ± 54 | 2.98 ± 0.10 | 99 | 3162 ± 78 | 2.398 ± 0.12 | 99 |
| 3.5 (Healthy aSF) | 1028 | 1133 | 3569 ± 69 | 3.037 ± 0.11 | 99 | 3216 ± 77 | 2.466 ± 0.12 | 99 |
| Fitting Curve Type | Function | Parameters | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | f(x) = ax + b | a = b = 2.784 | 0.0728 |
| Polynomial 2nd grade | f(x) = + bx + c | a = b = c = 2.737 | 0.0747 |
| Exponential (2 terms) | a = 2.855 b = c = −7414 d = −0.1128 | 0.0073 | |
| Power | a = b = −2.438 c = 2.984 | 0.0563 |
| H. A. Concentration (mg/mL) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Viscosity Calibrated (mPa · s) | Viscosity with Viscometer (mPa · s) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.84 (RA aSF) | 2.686 | 94.007 | 94 | 0.007 |
| 1.0 | 2.839 | 109.13 | 109 | 0.119 |
| 1.3 (OA aSF) | 2.873 | 130.70 | 141 | 7.305 |
| 2.0 | 2.91 | 341.50 | 342 | 0.146 |
| 3.0 | 2.98 | 767.00 | 716 | 7.123 |
| 3.5 (Healthy aSF) | 3.037 | 1106.00 | 1133 | 2.383 |
| H. A. Concentration (mg/mL) | Density (mg/mL) | Viscosity (mPa · s) | ViSQCT | Open QCM® | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| || (Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference vs. Viscometer (%) | || (Hz) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Difference vs. Viscometer (%) | |||
| 0.0 (aCSF) | 1008 | 1.01 | 3452 ± 75 | 2.898 ± 0.12 | 187 | 3281 ± 61 | 2.618 ± 0.09 | 159 |
| 0.5 (VM aCSF) | 1010 | 1.02 | 3872 ± 86 | 3.639 ± 0.16 | 256 | 3680 ± 88 | 3.287 ± 0.15 | 222 |
| 1.0 | 1012 | 1.03 | 3945 ± 134 | 3.77 ± 0.25 | 266 | 3753 ± 91 | 3.412 ± 0.16 | 231 |
| 2.0 | 1013 | 1.05 | 4040 ± 136 | 3.95 ± 0.26 | 276 | 3828 ± 145 | 3.546 ± 0.27 | 237 |
| 3.0 (BM aCSF) | 1017 | 1.06 | 4220 ± 118 | 4.292 ± 0.23 | 285 | 4040 ± 182 | 3.934 ± 0.30 | 271 |
| Fitting Curve Type | Function | Parameters | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | f(x) = ax + b | a = 22.8 b = −19.86 | 0.2382 |
| Polynomial 2nd grade | a = −489.9 b = 1037 c = −544.6 | 0.2253 | |
| Exponential (2 terms) | a = 0.00768 b = 5.971 c = 0 d = −216.9 | 0.4358 | |
| Power | a = −2.422 b = −64.6 c = 4.203 | 0.1760 |
| Albumin (mg/mL) | Viscosity Obtained (mPa · s) | Viscosity Calibrated (mPa · s) | Viscosity with Viscometer (mPa · s) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 (aCSF) | 2.898 | 1.009 | 1.01 | 0.099 |
| 0.5 (VM aCSF) | 3.639 | 1.022 | 1.02 | 0.196 |
| 1.0 | 3.77 | 1.027 | 1.03 | 0.291 |
| 2.0 | 3.95 | 1.035 | 1.05 | 1.428 |
| 3.0 (BM aCSF) | 4.292 | 1.059 | 1.06 | 0.094 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda-Martínez, A.; Rivera-González, M.X.; Zeinoun, M.; Carvajal-Ahumada, L.A.; Serrano-Olmedo, J.J. Viscosity Measurement Sensor: A Prototype for a Novel Medical Diagnostic Method Based on Quartz Crystal Resonator. Sensors 2021, 21, 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082743
Miranda-Martínez A, Rivera-González MX, Zeinoun M, Carvajal-Ahumada LA, Serrano-Olmedo JJ. Viscosity Measurement Sensor: A Prototype for a Novel Medical Diagnostic Method Based on Quartz Crystal Resonator. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082743
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda-Martínez, Andrés, Marco Xavier Rivera-González, Michael Zeinoun, Luis Armando Carvajal-Ahumada, and José Javier Serrano-Olmedo. 2021. "Viscosity Measurement Sensor: A Prototype for a Novel Medical Diagnostic Method Based on Quartz Crystal Resonator" Sensors 21, no. 8: 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082743
APA StyleMiranda-Martínez, A., Rivera-González, M. X., Zeinoun, M., Carvajal-Ahumada, L. A., & Serrano-Olmedo, J. J. (2021). Viscosity Measurement Sensor: A Prototype for a Novel Medical Diagnostic Method Based on Quartz Crystal Resonator. Sensors, 21(8), 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082743







