Pilot Study on Analysis of Electroencephalography Signals from Children with FASD with the Implementation of Naive Bayesian Classifiers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
- Diagnosed epilepsy and/or treatment with anti-epileptic medications;
- Other neurological disease that can affect the bioelectrical activity of the brain (neurometabolic diseases, known structural defects of the central nervous system or other CNS defects);
- Systemic conditions that could temporarily affect the EEG signal abnormalities in the general condition at the time of the test (active infectious disease);
- High body temperature (fever, dehydration).
2.2. Experimental Setup
- Resting activity, in which the patient stayed for a specified time with eyes open and then with the eyes closed;
- Activation tests, in which photo-stimulation was used with flashing lights of various frequency ranges (2–30 Hz) for 2 min 30 s together with hyperventilation, which required patient’s cooperation, i.e., taking slow, deep breathing for about 3 min.
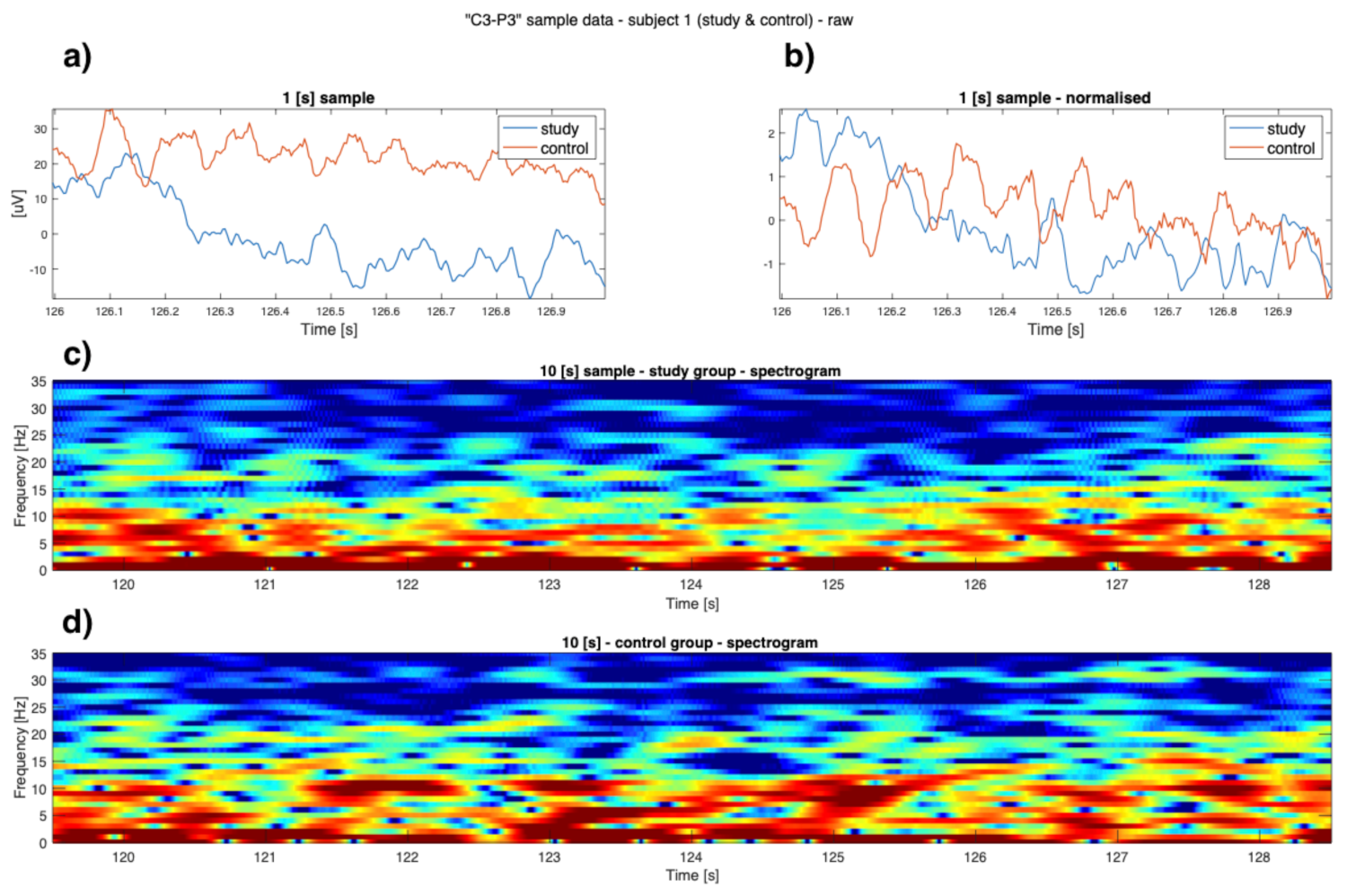
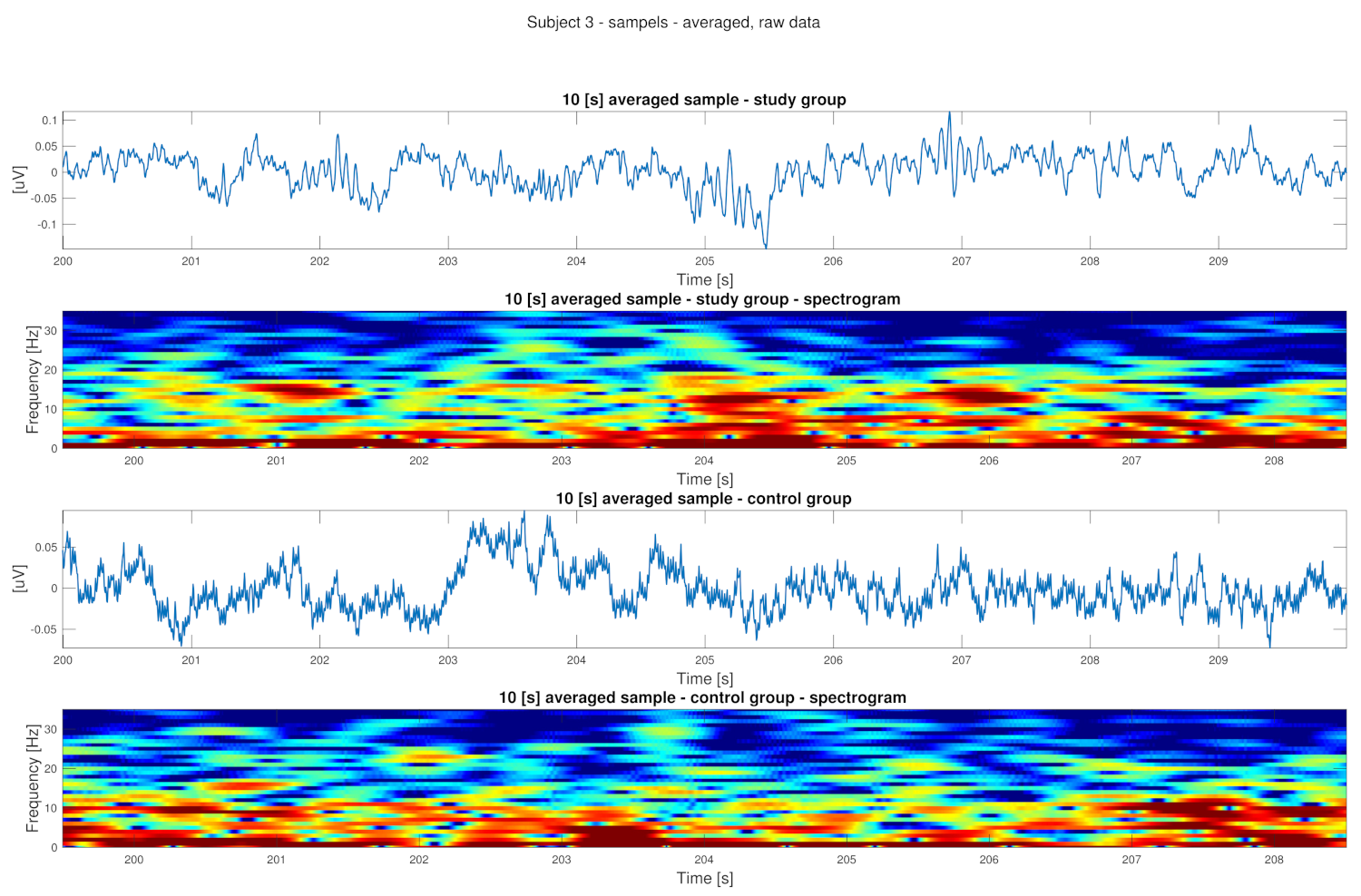
2.3. Data Analysis
- Root-mean-square level,
- Skewness,
- Kurtosis,
- Peak-magnitude-to-RMS ratio,
- Peak to peak,
- Power of lower and high envelop,
- Power of the signal,
- Minimum and maximum value of the signal.
- are the described attributes;
- c are classes;
- is the posterior probability of class c given predictor x;
- is the prior probability of that class;
- is the likelihood which is the probability of the predictor for the given class;
- is the prior probability of the predictor.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Limitations of This Study
5.2. Further Research Plans
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burns, J.; Badry, D.E.; Harding, K.D.; Roberts, N.; Unsworth, K.; Cook, J.L. Comparing outcomes of children and youth with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) in the child welfare system to those in other living situations in Canada: Results from the Canadian National FASD Database. Child Care Health Dev. 2021, 47, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, K.D.; Ryan, L.M.; Akkaya-Hocagil, T.; Cook, R.J.; Richardson, G.A.; Day, N.L.; Coles, C.D.; Olson, H.C.; Jacobson, S.W.; Jacobson, J.L. Bayesian structural equation modeling for data from multiple cohorts. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.12085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Paolozza, A.; Tseng, P.H.; Reynolds, J.N.; Munoz, D.P.; Itti, L. Detection of children/youth with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder through eye movement, psychometric, and neuroimaging data. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, K.; Smith, D. Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet 1973, 302, 999–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Smith, D.; Ulleland, C.; Streissguth, A. Pattern of malformation in offspring of chronic alcoholic mothers. Lancet 1973, 301, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyme, H.E.; May, P.A.; Kalberg, W.O.; Kodituwakku, P.; Gossage, J.P.; Trujillo, P.M.; Buckley, D.G.; Miller, J.H.; Aragon, A.S.; Khaole, N.; et al. A practical clinical approach to diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Clarification of the 1996 institute of medicine criteria. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Itti, L.; Tseng, P.H.; Paolozza, A.; Reynolds, J.N.; Munoz, D.P. Machine Learning-Based Screening for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the AI for Social Good NeurIPS2018 Workshop, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Roozen, S.; Peters, G.J.Y.; Kok, G.; Townend, D.; Nijhuis, J.; Curfs, L. Worldwide prevalence of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: A systematic literature review including meta-analysis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, S.; Lange, S.; Probst, C.; Gmel, G.; Rehm, J. Estimation of national, regional, and global prevalence of alcohol use during pregnancy and fetal alcohol syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e290–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodituwakku, P.W. A neurodevelopmental framework for the development of interventions for children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol 2010, 44, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okulicz-Kozaryn, K.; Borkowska, M.; Brzózka, K. FASD prevalence among schoolchildren in Poland. J. Appl. Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2017, 30, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, P.A.; Chambers, C.D.; Kalberg, W.O.; Zellner, J.; Feldman, H.; Buckley, D.; Kopald, D.; Hasken, J.M.; Xu, R.; Honerkamp-Smith, G.; et al. Prevalence of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in 4 US communities. JAMA 2018, 319, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabenne, A.; Moon, C.; Ojo, C.; Khogali, A.; Nepal, B.; Sharma, S. Biomarkers in fetal alcohol syndrome. Biomarkers Genom. Med. 2014, 6, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bager, H.; Christensen, L.P.; Husby, S.; Bjerregaard, L. Biomarkers for the detection of prenatal alcohol exposure: A review. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, K.A.; Eastman, E.; Howells, F.M.; Adnams, C.; Riley, E.P.; Woods, R.P.; Narr, K.L.; Stein, D.J. Neuroimaging effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on the developing human brain: A magnetic resonance imaging review. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015, 27, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okulicz-Kozaryn, K.; Maryniak, A.; Borkowska, M.; Śmigiel, R.; Dylag, K.A. Diagnosis of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs): Guidelines of Interdisciplinary Group of Polish Professionals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, M.N.; Nothacker, M.; Heinen, F. Diagnosis of fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): German guideline version 2013. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2013, 17, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watkins, R.E.; Elliott, E.J.; Wilkins, A.; Mutch, R.C.; Fitzpatrick, J.P.; Payne, J.M.; O’Leary, C.M.; Jones, H.M.; Latimer, J.; Hayes, L.; et al. Recommendations from a consensus development workshop on the diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in Australia. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoyme, H.E.; Kalberg, W.O.; Elliott, A.J.; Blankenship, J.; Buckley, D.; Marais, A.S.; Manning, M.A.; Robinson, L.K.; Adam, M.P.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; et al. Updated clinical guidelines for diagnosing fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20154256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chudley, A.E.; Conry, J.; Cook, J.L.; Loock, C.; Rosales, T.; LeBlanc, N. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: Canadian guidelines for diagnosis. Cmaj 2005, 172, S1–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astley, S.J. Validation of the fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) 4-Digit Diagnostic Code. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 20, e416–e467. [Google Scholar]
- Lilley, C.M.; Lukas, M.R.; Ruthven, M.L.; Walsh, S. Handbook for the Diagnosis of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder; Sunny Hill Health Centre–BC Children’s Hospital: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart, F.; Roozen, S.; Verbeek, J.; Koek, G.; Kok, G.; van Kranen, H.; Evelo, C.T.; Curfs, L.M. Review and gap analysis: Molecular pathways leading to fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlett, C.R.; Horn, K.H. Mechanisms of alcohol-induced damage to the developing nervous system. Alcohol Res. Health 2001, 25, 175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bell, S.H.; Stade, B.; Reynolds, J.N.; Rasmussen, C.; Andrew, G.; Hwang, P.A.; Carlen, P.L. The remarkably high prevalence of epilepsy and seizure history in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuffrey, L.C.; Myers, M.M.; Isler, J.R.; Lucchini, M.; Sania, A.; Pini, N.; Nugent, J.D.; Condon, C.; Ochoa, T.; Brink, L.; et al. Association between prenatal exposure to alcohol and tobacco and neonatal brain activity: Results from the safe passage study. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e204714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicita, F.; Verrotti, A.; Pruna, D.; Striano, P.; Capovilla, G.; Savasta, S.; Spartà, M.V.; Parisi, P.; Parlapiano, G.; Tarani, L.; et al. Seizures in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Evaluation of clinical, electroencephalographic, and neuroradiologic features in a pediatric case series. Epilepsia 2014, 55, e60–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boronat, S.; Vicente, M.; Lainez, E.; Sanchez-Montanez, A.; Vazquez, E.; Mangado, L.; Martínez-Ribot, L.; Del Campo, M. Seizures and electroencephalography findings in 61 patients with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 60, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, W.; Phillips, E.; Riley, E.; Ehlers, C. EEG findings in fetal alcohol syndrome and Down syndrome children. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1996, 98, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, T. Analysis and Processing of EEG Signal: A Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Data Intelligence (ICSMDI 2021), Kongunadu, India, 29–30 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rakshit, A.; Khasnobish, A.; Tibarewala, D. A Naïve Bayesian approach to lower limb classification from EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Energy & Communication (CIEC), Kolkata, India, 28–30 January 2016; pp. 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Wade, J.W.; Bian, D.; Key, A.P.; Warren, Z.E.; Mion, L.C.; Sarkar, N. A Step towards EEG-based brain computer interface for autism intervention. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 3767–3770. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, M.P.; Hosseini, A.; Ahi, K. A Review on machine learning for EEG Signal processing in bioengineering. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinek, R.; Ladrova, M.; Sidikova, M.; Jaros, R.; Behbehani, K.; Kahankova, R.; Kawala-Sterniuk, A. Advanced Bioelectrical Signal Processing Methods: Past, Present and Future Approach—Part II: Brain Signals. Sensors 2021, 21, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, N.; Tapani, K.; Lauronen, L.; Vanhatalo, S. A dataset of neonatal EEG recordings with seizure annotations. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenzweig, I.; Fogarasi, A.; Johnsen, B.; Alving, J.; Fabricius, M.E.; Scherg, M.; Neufeld, M.Y.; Pressler, R.; Kjaer, T.W.; van Emde Boas, W.; et al. Beyond the double banana: Improved recognition of temporal lobe seizures in long-term EEG. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.R.; Barry, R.J.; McCarthy, R.; Selikowitz, M. EEG-defined subtypes of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, C.D.; Platzman, K.A.; Raskind-Hood, C.L.; Brown, R.T.; Falek, A.; Smith, I.E. A comparison of children affected by prenatal alcohol exposure and attention deficit, hyperactivity disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsengelidou, E. Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Learning Disabilities. In Proceedings of the Dialog Intercultural Polono-Moldovenesc, Chisinau-Cracovia, Poland, 14–15 May 2021; Volume 4, pp. 366–370. [Google Scholar]
- Goodlett, C.R.; Horn, K.H.; Zhou, F.C. Alcohol teratogenesis: Mechanisms of damage and strategies for intervention. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomidou, C.; Bittigau, P.; Ishimaru, M.J.; Wozniak, D.F.; Koch, C.; Genz, K.; Price, M.T.; Stefovska, V.; Hörster, F.; Tenkova, T.; et al. Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrome. Science 2000, 287, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, J.; Valenzuela, C. Ethanol modulation of GABAergic transmission: The view from the slice. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovinger, D.M.; White, G.; Weight, F.F. NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic excitation selectively inhibited by ethanol in hippocampal slice from adult rat. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirkner, K.; Poelchen, W.; Köles, L.; Mühlberg, K.; Scheibler, P.; Allgaier, C.; Illes, P. Ethanol-induced inhibition of NMDA receptor channels. Neurochem. Int. 1999, 35, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jung, S.C.; Clemens, A.M.; Petralia, R.S.; Hoffman, D.A. Regulation of dendritic excitability by activity-dependent trafficking of the A-type K+ channel subunit Kv4. 2 in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 2007, 54, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, H.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.J. The emerging concept of intrinsic plasticity: Activity-dependent modulation of intrinsic excitability in cerebellar Purkinje cells and motor learning. Exp. Neurobiol. 2018, 27, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, M.B.; Paiva, M.; Siler-Marsiglio, K. Ethanol influences on Bax translocation, mitochondrial membrane potential, and reactive oxygen species generation are modulated by vitamin E and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guizzetti, M.; Zhang, X.; Goeke, C.; Gavin, D.P. Glia and neurodevelopment: Focus on fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Topper, L.A.; Baculis, B.C.; Valenzuela, C.F. Exposure of neonatal rats to alcohol has differential effects on neuroinflammation and neuronal survival in the cerebellum and hippocampus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantacorps, L.; Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Moscoso-Castro, M.; Cuitavi, J.; Gracia-Rubio, I.; López-Arnau, R.; Escubedo, E.; Guerri, C.; Valverde, O. Maternal alcohol binge drinking induces persistent neuroinflammation associated with myelin damage and behavioural dysfunctions in offspring mice. Neuropharmacology 2017, 123, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galindo, R.; Zamudio, P.A.; Valenzuela, C.F. Alcohol is a potent stimulant of immature neuronal networks: Implications for fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autti-Rämö, I.; Autti, T.; Korkman, M.; Kettunen, S.; Salonen, O.; Valanne, L. MRI findings in children with school problems who had been exposed prenatally to alcohol. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meintjes, E.; Narr, K.; Van Der Kouwe, A.; Molteno, C.; Pirnia, T.; Gutman, B.; Woods, R.; Thompson, P.; Jacobson, J.; Jacobson, S. A tensor-based morphometry analysis of regional differences in brain volume in relation to prenatal alcohol exposure. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 5, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Mueller, B.A.; Mattson, S.N.; Coles, C.D.; Kable, J.A.; Jones, K.L.; Boys, C.J.; Lim, K.O.; Riley, E.P.; Sowell, E.R. Functional connectivity abnormalities and associated cognitive deficits in fetal alcohol Spectrum disorders (FASD). Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 11, 1432–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, F.C.; Narr, K.L.; Molteno, C.D.; Jacobson, J.L.; Jacobson, S.W.; Meintjes, E.M. Prenatal alcohol exposure is associated with regionally thinner cortex during the preadolescent period. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 26, 3083–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leigland, L.A.; Budde, M.D.; Cornea, A.; Kroenke, C.D. Diffusion MRI of the developing cerebral cortical gray matter can be used to detect abnormalities in tissue microstructure associated with fetal ethanol exposure. Neuroimage 2013, 83, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswal, B.; Zerrin Yetkin, F.; Haughton, V.M.; Hyde, J.S. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Taylor, P.A.; Jacobson, S.W.; Molteno, C.D.; Gohel, S.; Biswal, B.B.; Jacobson, J.L.; Meintjes, E.M. Localized reductions in resting-state functional connectivity in children with prenatal alcohol exposure. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5217–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawala-Janik, A.; Pelc, M.; Podpora, M. Method for EEG signals pattern recognition in embedded systems. Elektron. Ir Elektrotechnika 2015, 21, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, V.d.J.; Leger, P.; Contreras, S.; Fukuda, H. Detecting Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder in children using Artificial Neural Network. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.15074. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dyląg, K.A.; Wieczorek, W.; Bauer, W.; Walecki, P.; Bando, B.; Martinek, R.; Kawala-Sterniuk, A. Pilot Study on Analysis of Electroencephalography Signals from Children with FASD with the Implementation of Naive Bayesian Classifiers. Sensors 2022, 22, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010103
Dyląg KA, Wieczorek W, Bauer W, Walecki P, Bando B, Martinek R, Kawala-Sterniuk A. Pilot Study on Analysis of Electroencephalography Signals from Children with FASD with the Implementation of Naive Bayesian Classifiers. Sensors. 2022; 22(1):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010103
Chicago/Turabian StyleDyląg, Katarzyna Anna, Wiktoria Wieczorek, Waldemar Bauer, Piotr Walecki, Bozena Bando, Radek Martinek, and Aleksandra Kawala-Sterniuk. 2022. "Pilot Study on Analysis of Electroencephalography Signals from Children with FASD with the Implementation of Naive Bayesian Classifiers" Sensors 22, no. 1: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010103







