Optical Fiber Bundle-Based High-Speed and Precise Micro-Scanning for Image High-Resolution Reconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
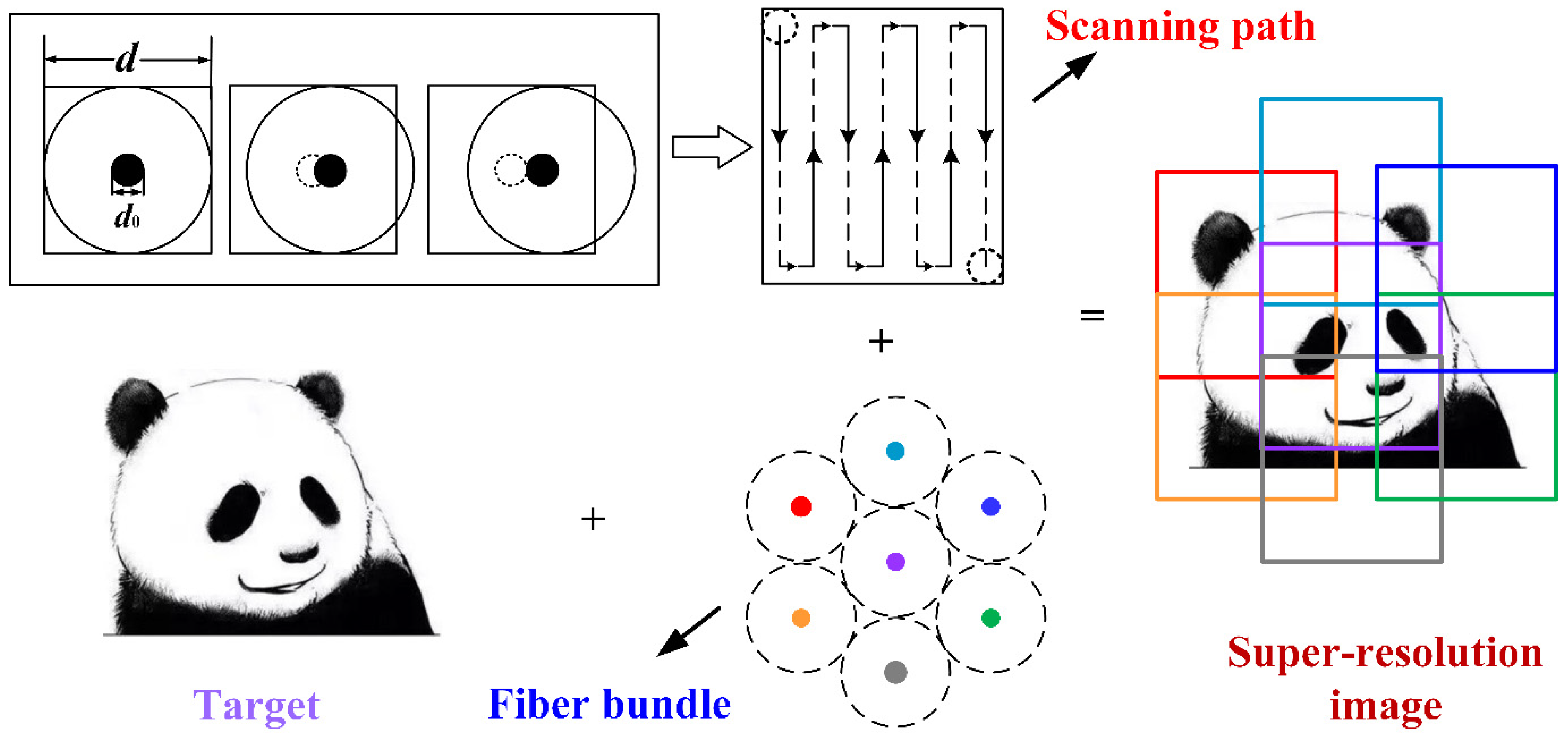
2. Theoretical Analysis
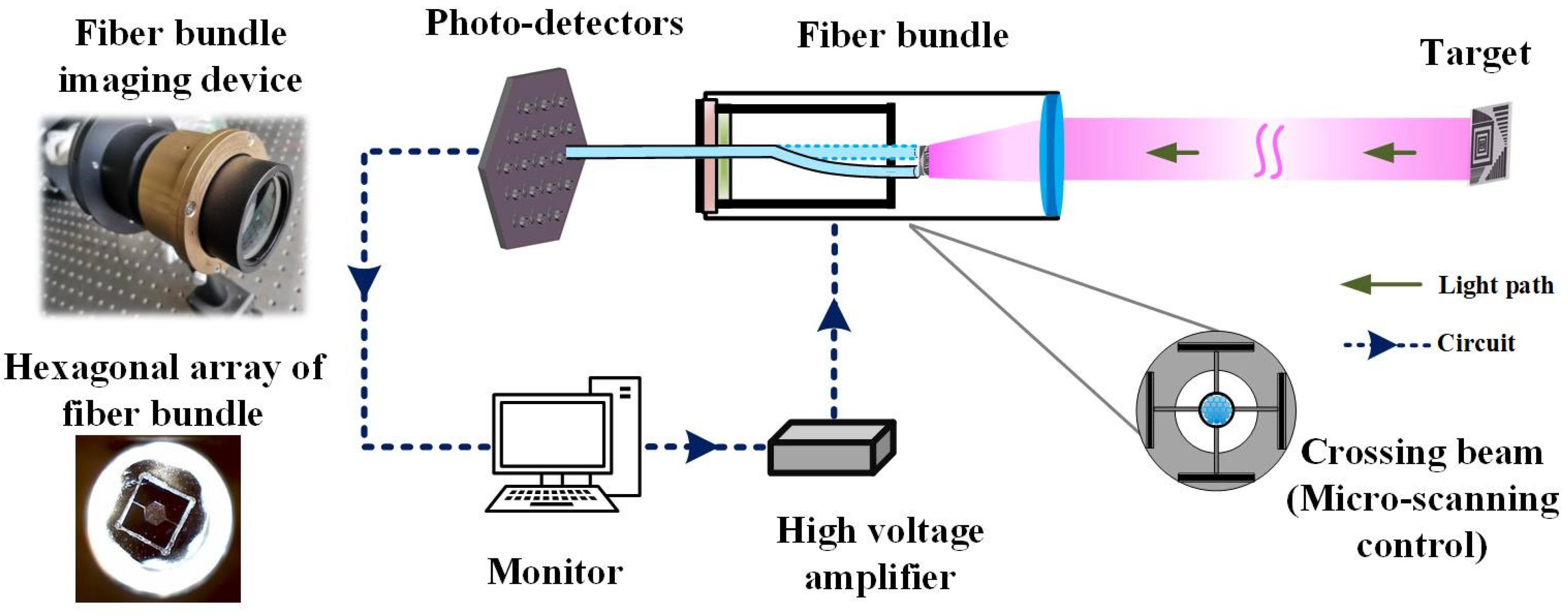
3. Experimental Setup
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Micro-Scanning Step Size
4.2. High-Resolution Image Acquisition and Stitching
4.3. Image Quality Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Group Number | Line Pair (Lp) Line Width (Lw)/μm | Series Number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 0 | Lp/mm | 1 | 1.12 | 1.26 | 1.41 | 1.59 | 1.78 |
| Lw | 500 | 445.45 | 396.85 | 353.55 | 314.98 | 280.62 | |
| 1 | Lp/mm | 2 | 2.24 | 2.52 | 2.83 | 3.17 | 3.56 |
| Lw | 250 | 222.72 | 198.43 | 176.78 | 157.49 | 140.31 | |
| 2 | Lp/mm | 4 | 4.49 | 5.04 | 5.66 | 6.35 | 7.13 |
| Lw | 125 | 111.36 | 99.21 | 88.39 | 78.75 | 70.15 | |
| 3 | Lp/mm | 8 | 8.98 | 10.1 | 11.3 | 12.7 | 14.3 |
| Lw | 62.5 | 55.68 | 49.61 | 44.19 | 39.37 | 35.08 | |
| 4 | Lp/mm | 16 | 17.95 | 20.16 | 22.62 | 25.39 | 28.5 |
| Lw | 31.25 | 27.84 | 24.8 | 22.10 | 19.69 | 17.54 | |
| 5 | Lp/mm | 32 | 36 | 40.3 | 45.3 | 50.8 | 57 |
| Lw | 15.63 | 13.92 | 12.4 | 11.05 | 9.84 | 8.77 | |
References
- Gmitro, A.F.; Aziz, D. Confocal microscopy through a fiber-optic imaging bundle. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morova, B.; Bavili, N.; Yaman, O.; Yigit, B.; Zeybel, M.; Aydin, M.; Dogan, B.; Kasztelanic, R.; Pysz, D.; Buczynski, R.; et al. Fabrication and characterization of large numerical aperture, high-resolution optical fiber bundles based on high-contrast pairs of soft glasses for fluorescence imaging. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 9502–9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, A.; Ploschner, M.; Wilson, E.R.; Maksymov, I.S.; Gibson, B.C. Optical fiber bundles: Ultra-slim light field imaging probes. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Hong, J.; Kim, J.; Shin, H. Fiber bundle-based integrated platform for wide-field fluorescence imaging and patterned optical stimulation for modulation of vasoconstriction in the deep brain of a living animal. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2781–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laemmel, E.; Genet, M.; Le Goualher, G.; Perchant, A.; Le Gargasson, J.; Vicaut, E. Fibered confocal fluorescence microscopy (Cell-viZio™) facilitates extended imaging in the field of microcirculation. J. Vasc. Res. 2004, 41, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, S.M.; Walt, D.R. A fibre-optic chemical sensor with discrete sensing sites. Nature 1991, 353, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeggel, S.; Tosi, D.; Duraibabu, D.; Leen, G.; Mcgrath, D.; Lewis, E. Optical fibre pressure sensors in medical applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 17115–17148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelbrecht, C.; Johnston, R.; Seibel, E.; Helmchen, F. Ultra-compact fiber-optic two-photon microscope for functional fluorescence imaging in vivo. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Moon, J.; Kim, M.; Yang, T.; Kim, J.; Chuang, E.; Choi, W. Toward a miniature endomicroscope: Pixelation-free and diffraction-limited imaging through a fiber bundle. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Liao, W.; Liang, R.; Barnard, K. Resolution enhancement for fiber bundle imaging using maximum a posteriori estimation. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 1906–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenbach, K.; Xu, C. Numerical analysis of light propagation in image fibers or coherent fiber bundles. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 2151–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, G.; Cha, J.; Kang, J. Random transverse motion-induced spatial compounding for fiber bundle imaging. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4368–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Reichenbach, K.; Xu, C. Experimental and theoretical analysis of core-to-core coupling on fiber bundle imaging. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 21598–21607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Bai, L.; Chen, Q.; Gu, G. Influencing factors of microscanning performance based on flat optical component. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 052302. Available online: https://www.osapublishing.org/col/abstract.cfm?URI=col-9-5-052302 (accessed on 24 December 2021).
- Barnard, K.; Watson, E.; McManamon, P. Nonmechanical microscanning using optical space-fed phased arrays. Opt. Eng. 1994, 33, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Liang, R.; Barnard, K. Fiber bundle image restoration using deep learning. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Weiss, Y.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W. Understanding blind deconvolution algorithms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2354–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, L.; Nehmetallah, G. Deep learning approach for fourier ptychography microscopy. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 26470–26484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Gao, J.; Qu, T.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, D. Three-dimensional reconstruction of light field based on phase similarity. Sensors 2021, 21, 7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udovich, J.; Kirkpatrick, N.; Kano, A.; Tanbakuchi, A.; Utzinger, U.; Gmitro, A. Spectral background and transmission characteristics of fiber optic imaging bundles. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 4560–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Q.; Gilbert, J. Comparing cross talk in doped scintillating-fiber bundles. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 1536–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.; Han, J. Elimination of honeycomb patterns in fiber bundle imaging by a superimposition method. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.; Chevrette, P.C. Realization of a fast microscanning device for infrared focal plane arrays. In Proceedings of the Aerospace/Defense Sensing and Controls, Orlando, FL, USA, 10 June 1996; Proceedings of SPIE. SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1996; Volume 2743, pp. 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Reichenbach, S.; Howe, J. Cubic convolution for super-resolution from microscanned images. In Proceedings of the Defense and Security, Orlando, FL, USA, 25 May 2005; Proceedings of SPIE. SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5817, pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Huhns, M. Algorithms for subpixel registration. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1986, 35, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.; Li, J.; Karim, M. High-speed image registration algorithm with subpixel accuracy. IEEE Signal Proc. Lett. 2015, 22, 1796–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Geng, C.; Huang, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Qiu, Q. Experimental demonstration of coherent combining with tip/tilt control based on adaptive space-to-fiber laser beam coupling. IEEE Photon. J. 2017, 9, 7102812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.; Luo, W.; Tan, Y.; Liu, H.; Mu, J.; Li, X. Experimental demonstration of using divergence cost-function in SPGD algorithm for coherent beam combining with tip/tilt control. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 25045–25055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plöschner, M.; Tyc, T.; Čižmár, T. Seeing through chaos in multimode fibres. Nat. Photon. 2015, 9, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cižmár, T.; Dholakia, K. Exploiting multimode waveguides for pure fibre-based imaging. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flusberg, B.; Jung, J.; Cocker, E.; Anderson, E.; Schnitzer, M. In vivo brain imaging using a portable 3.9 gram two-photon fluorescence micro-endoscope. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 2272–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Parameters | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Optical fiber lenses | Focus length | 55 mm |
| Aperture diameter | 44 mm | |
| Micro-scanning system | Driving voltage | −450 V–450 V |
| Scanning step size | ~1 μm | |
| Scanning steps | 160 × 160 | |
| Scanning range | x: −58 μm~62 μm | |
| y: −79 μm~73 μm | ||
| Optical fiber bundles | Core/cladding | 4 μm/80 μm |
| Wavelength | 650 nm | |
| Arrangement | Hexagon | |
| Number of fibers | 7 | |
| CCD | Pixel size | 4.4 μm × 4.4 μm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Pan, L.; Pan, Z.; Zou, F.; Li, Z.; Li, F.; Ma, X.; Geng, C.; et al. Optical Fiber Bundle-Based High-Speed and Precise Micro-Scanning for Image High-Resolution Reconstruction. Sensors 2022, 22, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010127
Jiang J, Zhou X, Liu J, Pan L, Pan Z, Zou F, Li Z, Li F, Ma X, Geng C, et al. Optical Fiber Bundle-Based High-Speed and Precise Micro-Scanning for Image High-Resolution Reconstruction. Sensors. 2022; 22(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Jiali, Xin Zhou, Jiaying Liu, Likang Pan, Ziting Pan, Fan Zou, Ziqiang Li, Feng Li, Xiaoyu Ma, Chao Geng, and et al. 2022. "Optical Fiber Bundle-Based High-Speed and Precise Micro-Scanning for Image High-Resolution Reconstruction" Sensors 22, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010127
APA StyleJiang, J., Zhou, X., Liu, J., Pan, L., Pan, Z., Zou, F., Li, Z., Li, F., Ma, X., Geng, C., Zuo, J., & Li, X. (2022). Optical Fiber Bundle-Based High-Speed and Precise Micro-Scanning for Image High-Resolution Reconstruction. Sensors, 22(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010127







