Fusion of Infrared and Visible Images Using Fast Global Smoothing Decomposition and Target-Enhanced Parallel Gaussian Fuzzy Logic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- An effective fusion method for IR and visible images is proposed using the fast global smoother to efficiently extract multi-scale structure information and well suppress the halos around the edges.
- (ii)
- A target-enhanced parallel Gaussian fuzzy logic (TEPGFL)-based fusion rule is proposed to merge the base layers. The TEPGFL-based fusion rule can avoid brightness loss and highlight the significant targets in IR images and the high-brightness regions in the visible images. The fused results are more natural and consistent with the human visual system so that the fused results attract people’s attentions.
- (iii)
- We present a visual saliency map (VSM)-based fusion rule using the Scharr gradient to merge the detail layers with the purpose of extracting rich details and textures. The Scharr gradient reflects the significant structure features of an image, such as edges, outlines, region boundaries, etc. The visual saliency map based on the Scharr gradient has the ability to enhance the detail textures and capture the significant structures of objects. Therefore, the proposed VSM-based fusion rule can obtain a fused image with rich details and high visual fidelity.
- (iv)
- The proposed fusion method has high computational efficiency. The high computational efficiency facilitates the practical applications of the IR and visible image fusion.
2. Related Works
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Multi-Scale Decomposition Using the Fast Global Smoother
3.1.1. Fast Global Smoother
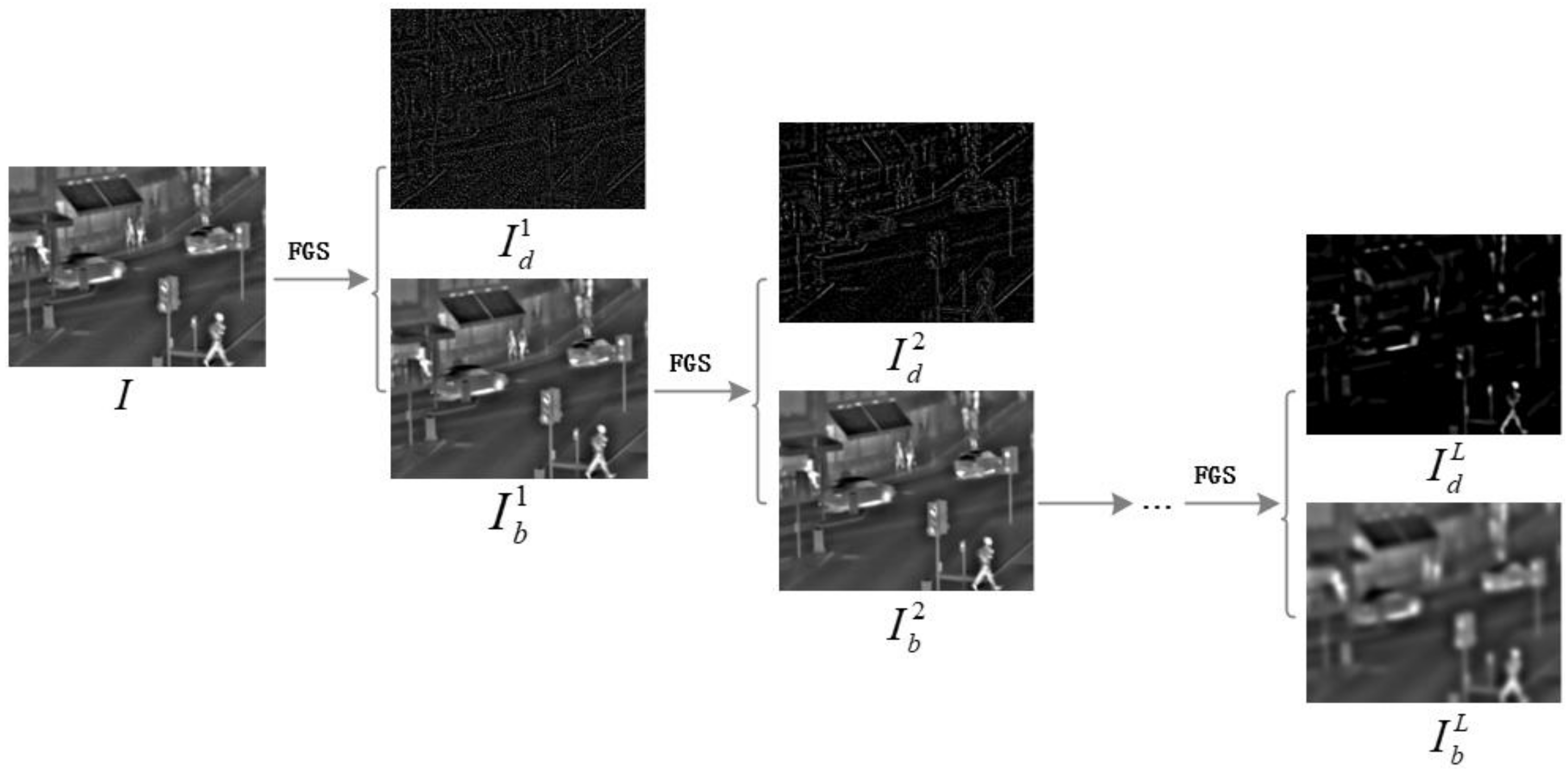
3.1.2. Multi-Scale Decomposition Using FGS
- Step 1:
- For any one of N source images (), = serves as the initial input image.
- Step 2:
- Make use of the fast global smoother to separate progressively larger structures of the input source image, meanwhile maintaining the edges.where denotes FGS filtering, and indicates the l-th base layer image. is the rang parameter at the l-th level, and l is the multi-scale decomposition level currently. Here, (T is the total number of iterations. In our work, T is set to 3 suggested by [46]), and empirically . Additionally, is also regarded as the scale control factor. When the structure scale in the image is smaller than , the structure will be eliminated in according to [50]. Let in Equation (6) for extracting the progressively coarser structures.
- Step 3:
- The l-th level detail layer is obtained by:
- Step 4:
- Iteratively executing Equations (6) and (7), L progressively blurry base layers and L gradually coarse detail layers can be achieved easily at different scales, respectively. With the FGS-based decomposition scheme, a source image can be decomposed into a collection of detail layers and a base layer as follows:
3.2. Base Layer Fusion
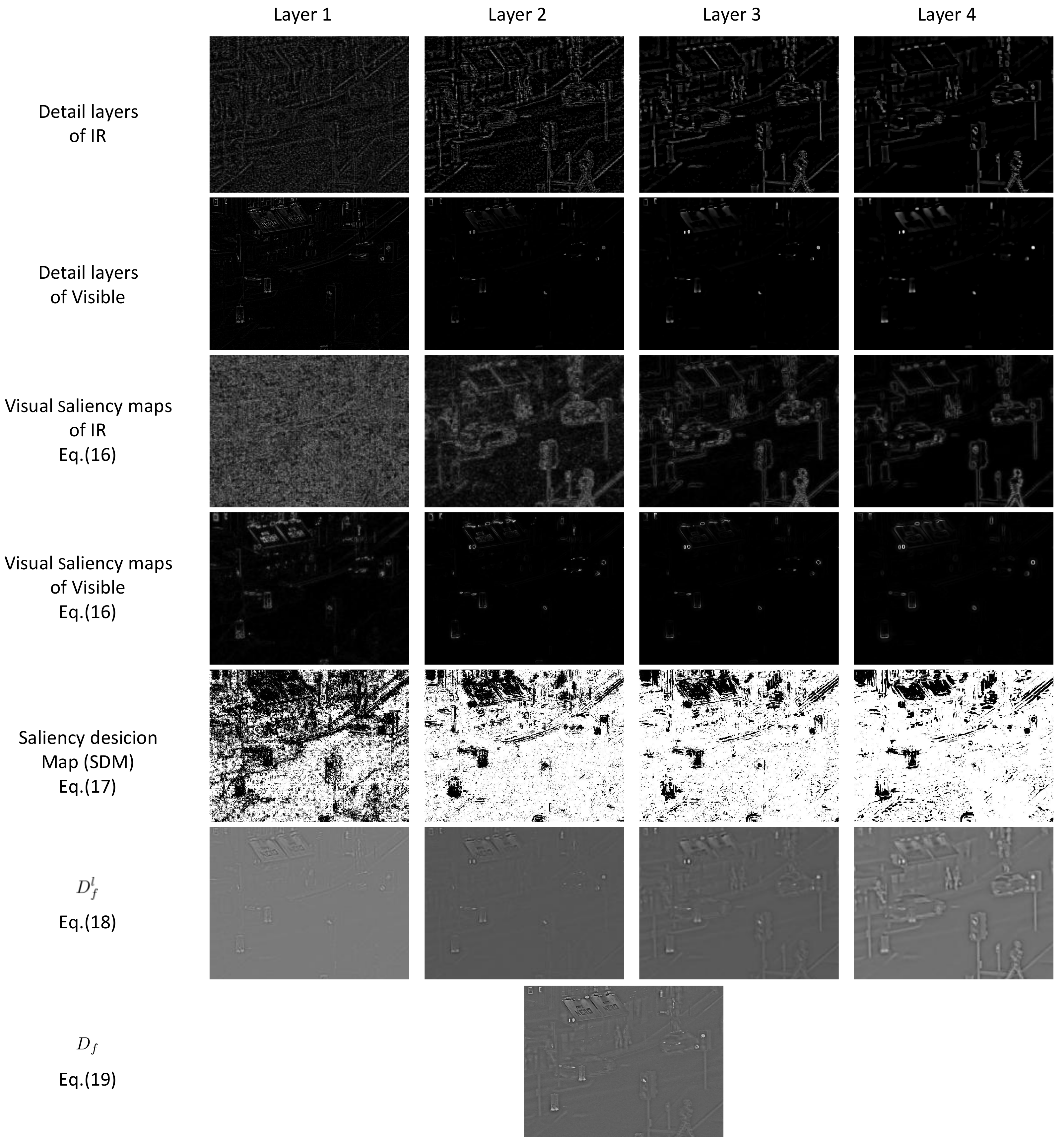
3.3. Detail Layer Fusion
3.4. Reconstruction
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Setting
4.1.1. Other Fusion Methods for Comparison
4.1.2. Image Database
4.1.3. Assessment Metrics
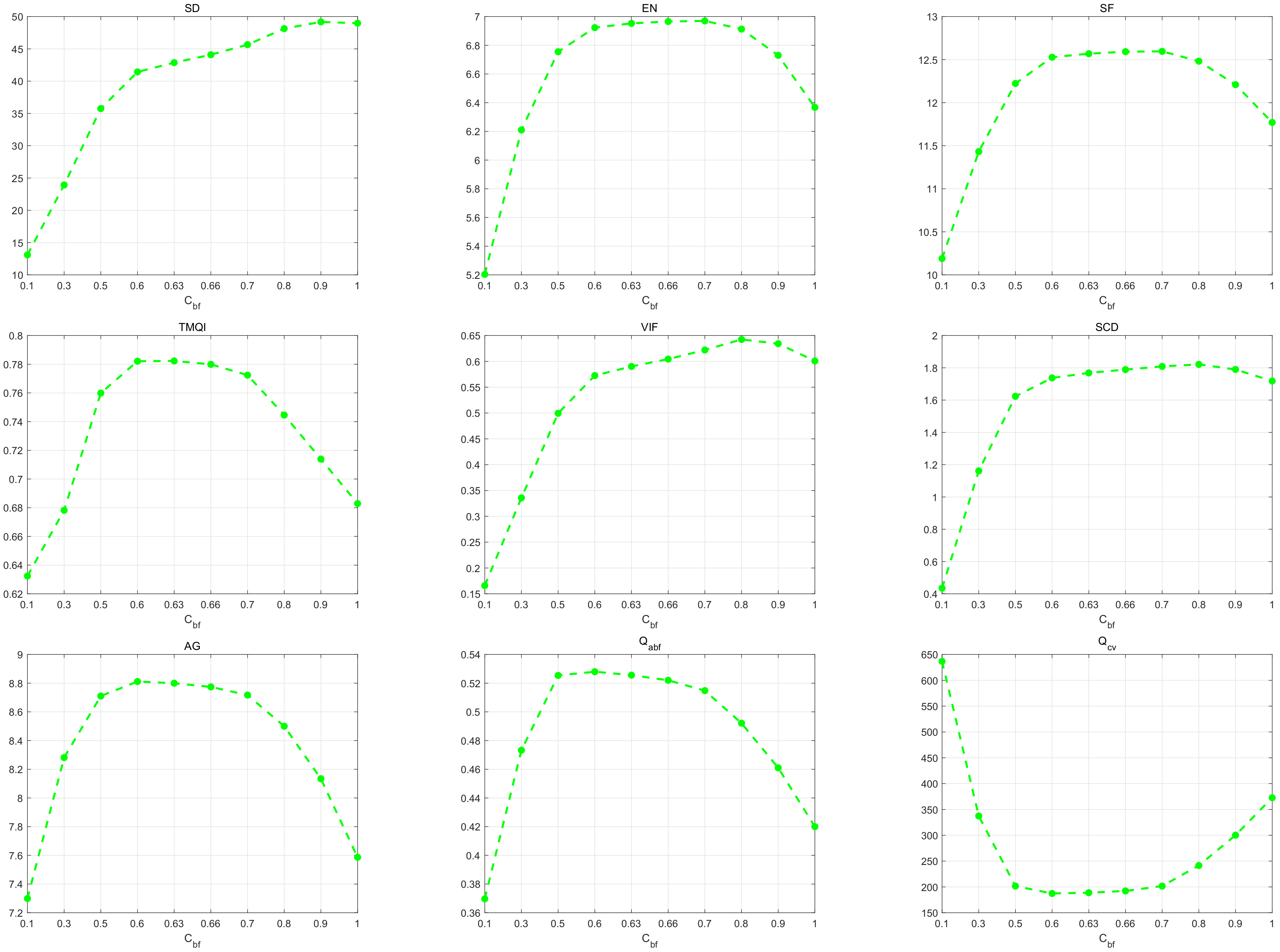
4.1.4. Parameter Analysis
4.2. Quality Performance Comparison on Fusion Rules
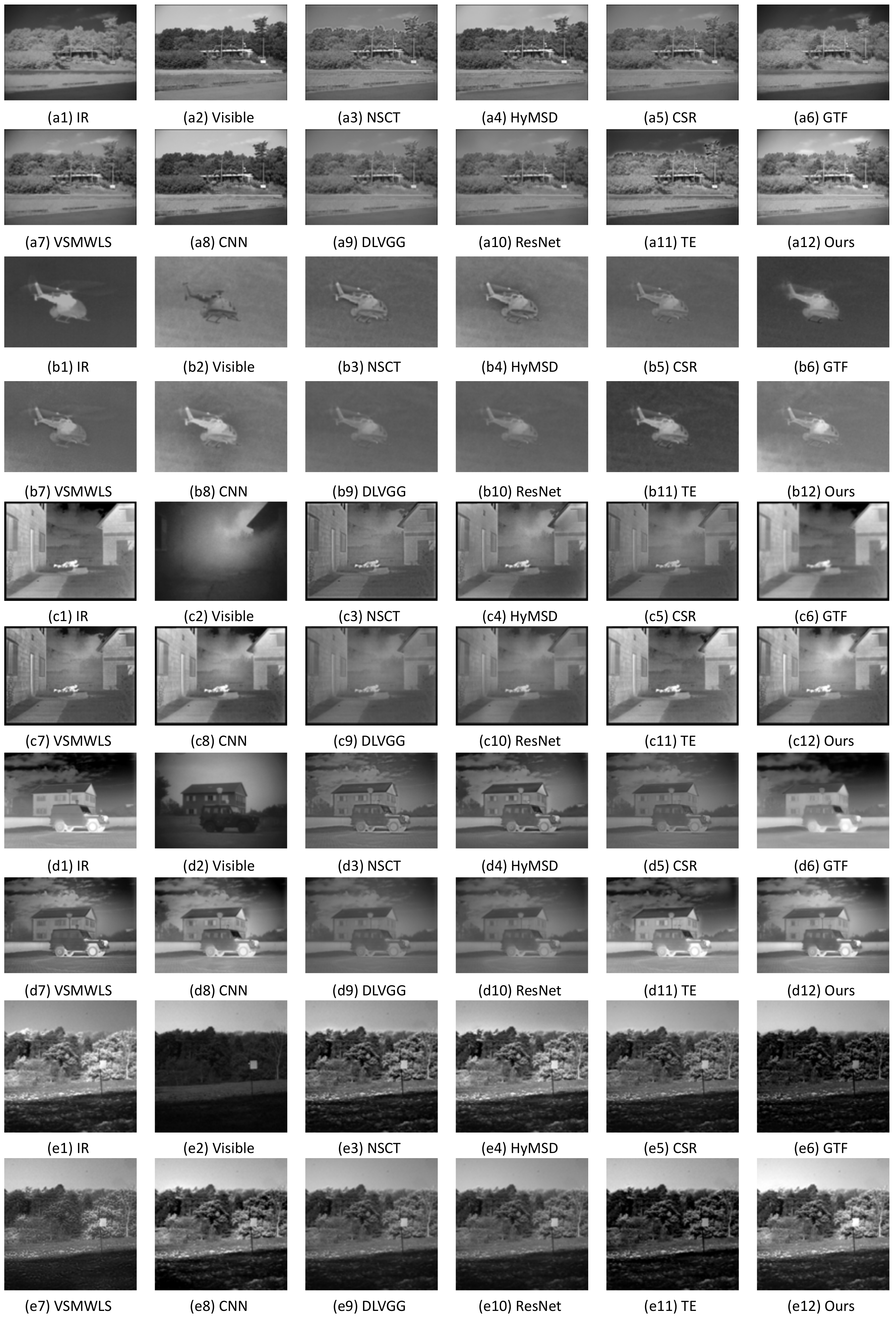
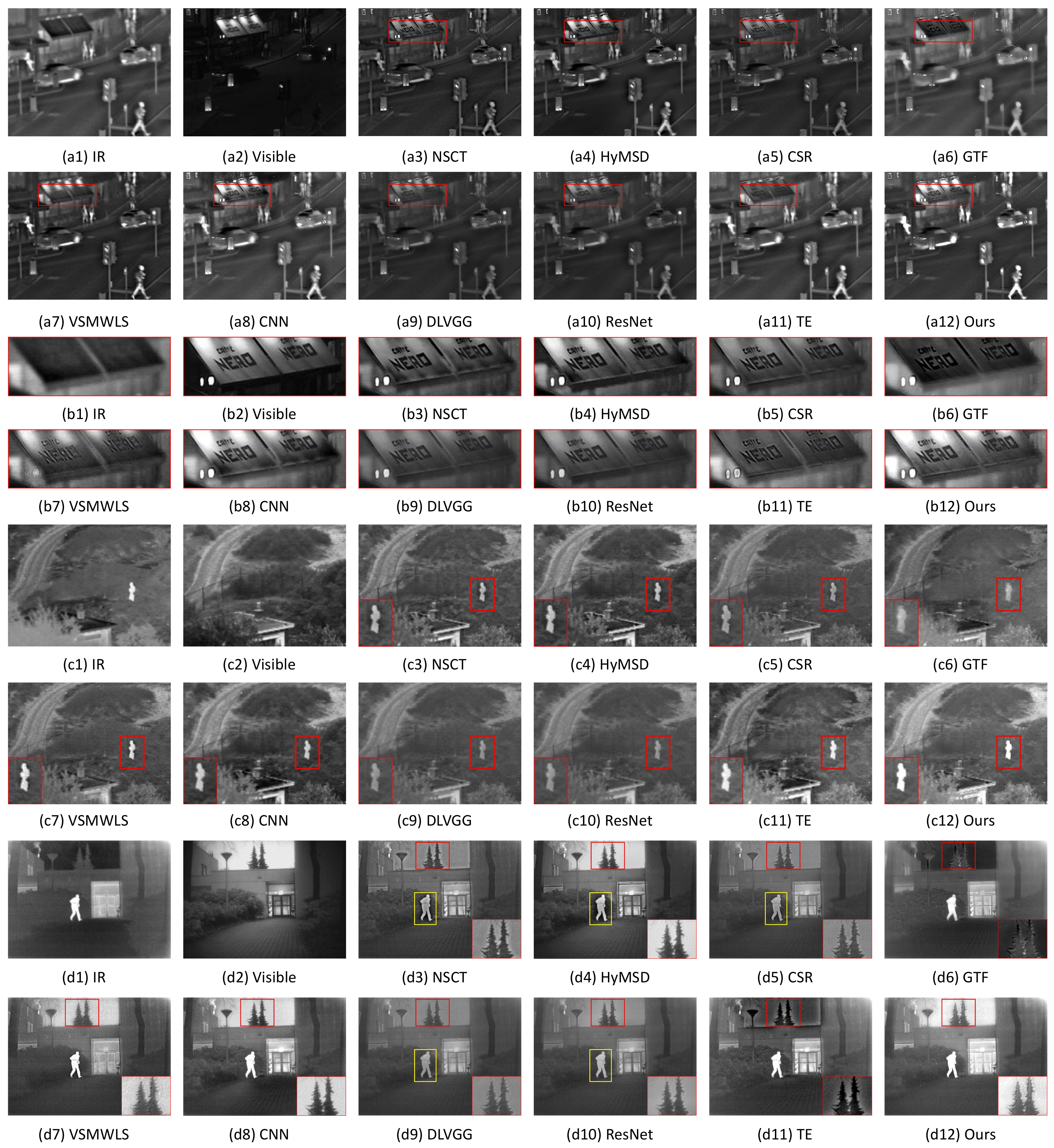
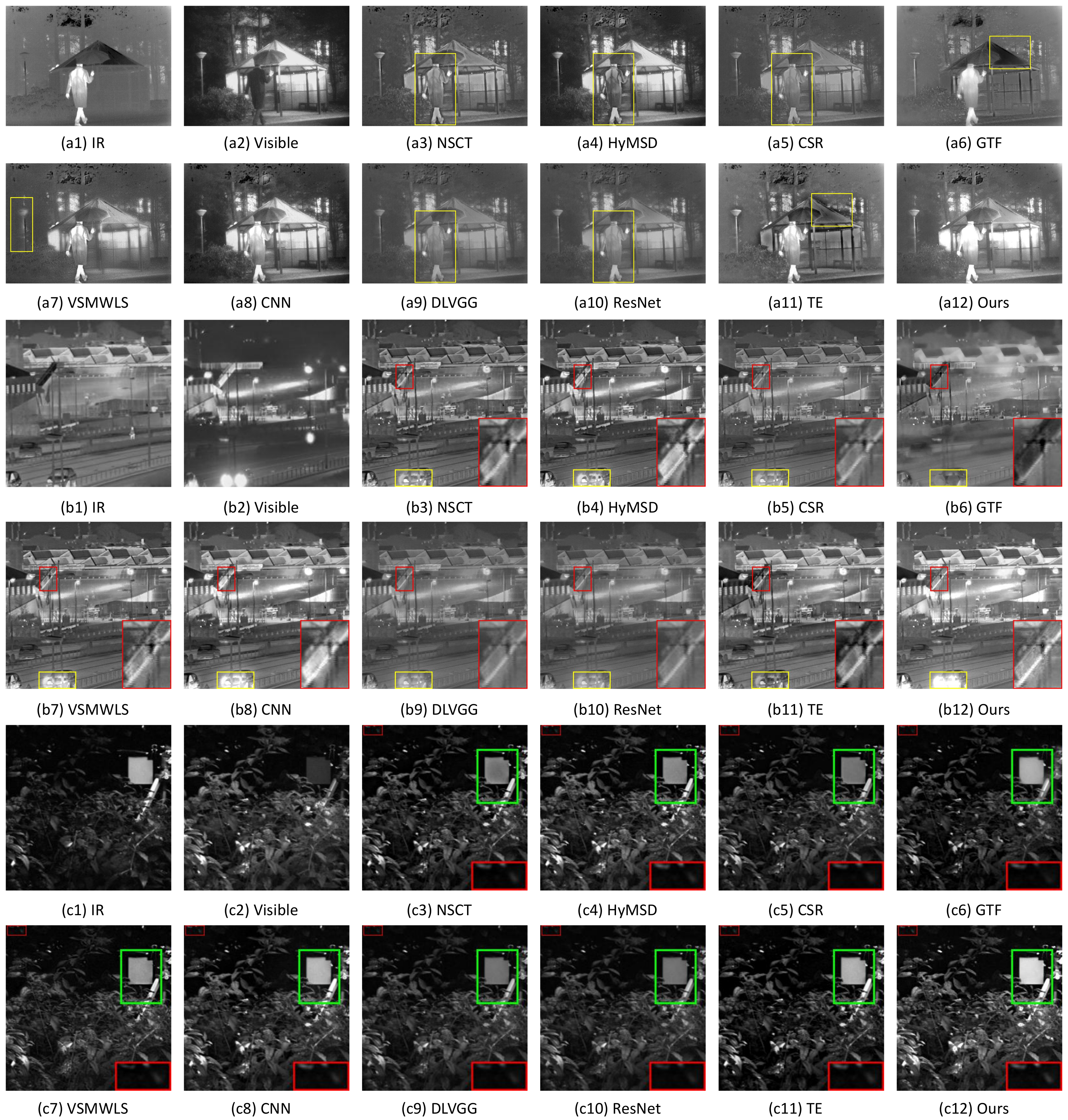
4.3. Subjective and Objective Assessments
4.3.1. Subjective Evaluation on the Fused Results
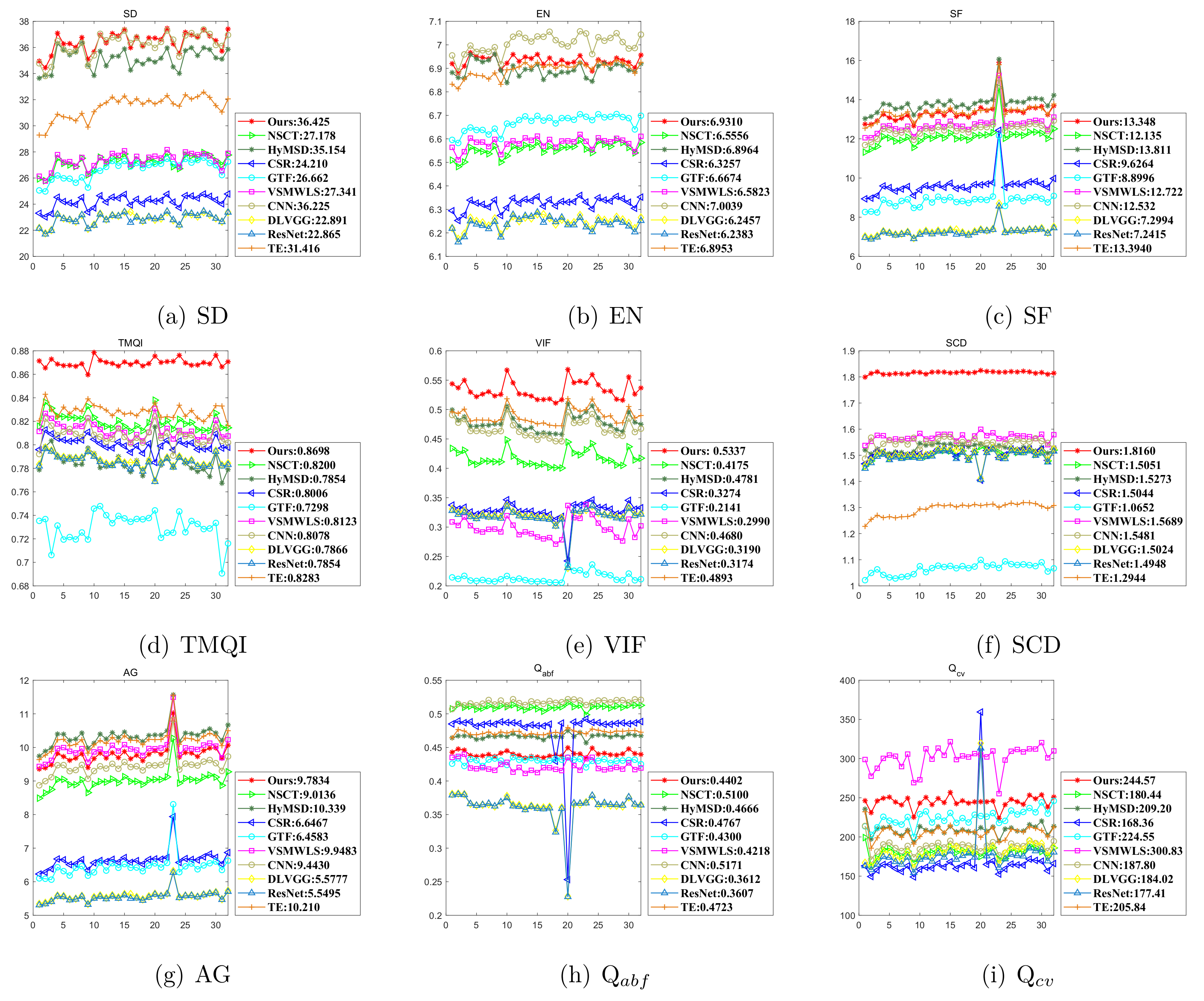
4.3.2. Objective Evaluation on the Fused Results
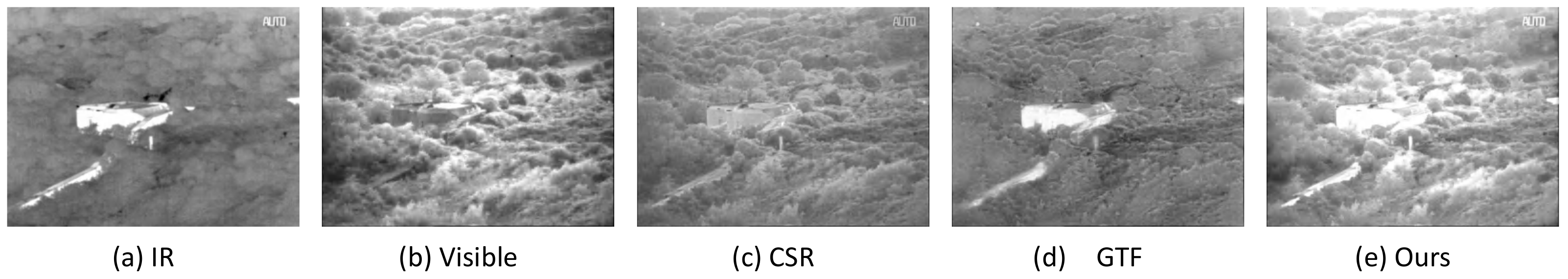
4.4. Experiments on Multiple Images with Different Spectra
4.5. Computational Efficiency
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Jin, X.; Jiang, Q.; Yao, S.; Zhou, D.; Nie, R.; Hai, J.; He, K. A survey of infrared and visual image fusion method. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 85, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, K.; Koundal, D.; Bhatia, S.; Khalid, M.; Rahmani, I.; Tahir, M. Fusion of Infrared and Visible Images Using Fuzzy Based Siamese Convolutional Network. Comput. Mater. Con. 2022, 70, 5503–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2016, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Chaudhary, J.A.; Chaudhary, J. A Review on Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Techniques. In Chapter Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks; Publishing House: Tirunelveli, India, 2020; pp. 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Dhuli, R. Fusion of Infrared and Visible Sensor Images Based on Anisotropic Diffusion and Karhunen-Loeve Transform. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 16, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopdjanan, A.; Machikhin, S.; Bilanchuk, V. Flight study of on-board enhanced vision system for all-weather aircraft landing. In Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics: Atmospheric Phy.; Publishing House: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2014; p. 92920X. [Google Scholar]
- Dogra, A.; Goyal, B.; Agrawal, S. From Multi-Scale Decomposition to Non-Multi-Scale Decomposition Methods: A Comprehensive Survey of Image Fusion Techniques and Its Applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16040–16067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzair, M.; Mahmood, A.; Mian, A.; Mcdonald, C. Periocular region-based person identification in the visible, infrared and hyperspectral imagery. Neurocomputing 2015, 149, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermosilla, G.; Rojas, M.; Mendoza, J.; Farías, G.; Pizarro, F.T.; San, M.C.; Vera, E. Particle Swarm Optimization for the Fusion of Thermal and Visible Descriptors in Face Recognition Systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 42800–42811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Koundal, D.; Kadyan, V. Image Fusion Techniques: A Survey. Arch. Computat. Method E 2021, 28, 4425–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Ma, C.; Cao, J.; Ding, H.; Zhou, D. A Total Variation with Joint Norms for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 3065496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H.B. Saliency-Guided Nonsubsampled Shearlet Transform for Multisource Remote Sensing Image Fusion. Sensors 2021, 21, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xun, C.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Image Fusion With Convolutional Sparse Representation. IEEE Signal Process. Let. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Huang, J. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 2016, 31, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Blum, R.S. A categorization of multiscale-decomposition-based image fusion schemes with a performance study for a digital camera application. Proc. IEEE 1999, 87, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Feng, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, T. Detail enhanced multi-source fusion using visual weight map extraction based on multi scale edge preserving decomposition. Opt. Commun. 2013, 287, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhao, H. Adaptive fusion method of visible light and infrared images based on non-subsampled shearlet transform and fast non-negative matrix factorization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2014, 67, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Blum, R.S.; Han, J.; Tao, D. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2018, 40, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Duan, P.; Liu, W.; Liang, X. A novel infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on shift-invariant dual-tree complex shearlet transform and sparse representation. Neurocomputing 2017, 226, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Yan, L.; Gao, R. A fusion algorithm for infrared and visible images based on adaptive dual-channel unit-linking PCNN in NSCT domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 69, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Dhuli, R. Two-scale image fusion of visible and infrared images using saliency detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, S.; Dong, M. Perceptual fusion of infrared and visible images through a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with Gaussian and bilateral filters. Inf. Fusion 2016, 30, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Zong, H. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, X. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects. Inf. Fusion 2018, 42, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Ma, X.; Huang, Z. Fusion of infrared-visible images using improved multi-scale top-hat transform and suitable fusion rules. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 45, 282–295. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, P.J.; Adelson, E.H. The laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1983, 31, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Xi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hei, X. Fusion of visible and infrared images using multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 71, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Manjunath, B.; Mitra, S. Multi-Sensor Image Fusion using the Wavelet Transform. Graph. Models Image Process. 1995, 57, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.J.; Robert, J.; O’Callaghan, R.J.; Nikolov, S.G.; Bull, D.R.; Canagarajah, N. Pixel- and region-based image fusion with complex wavelets. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencini, F.; Garzelli, A.; Baronti, S.; Alparone, L. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.N.; Vetterli, M. The Contourlet transform: An efficient directional multiresolution image representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, B. Multifocus image fusion using the nonsubsampled Contourlet transform. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Wang, B.; Lei, Y. Technique for infrared and visible image fusion based on non-subsampled shearlet transform and spiking cortical model. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 71, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbman, Z.; Fattal, R.; Lischinski, D.; Szeliski, R. Edge-preserving decompositions for multi-scale tone and detail manipulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Hu, J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, B.K.S. Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter. Signal Image Video Process. 2013, 9, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Jie, M.; Fang, B.; Hu, F.; Quan, S.; Du, H. Multi-scale decomposition based fusion of infrared and visible image via total variation and saliency analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 92, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.T.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion using dual discriminators generative adversarial networks with Wasserstein distance. Inf. Sci. 2020, 529, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.; Kittler, J. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion using a Deep Learning Framework. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 2705–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.J.; Durrani, T.S. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, A.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Huo, H.; Fang, T. IR-MSDNet: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Infrared Features and Multiscale Dense Network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2020, 14, 3426–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network Based on Salient Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Instru. Measu. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Ma, J.; Zhou, H. A Generative Adversarial Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Semantic Segmentation. Entropy 2021, 23, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Han, G.; Liu, P.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, D. An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Method Guided by Saliency and Gradient Information. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 108942–108958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.; Choi, S.; Lu, J.; Ham, B.; Do, M.N. Fast Global Image Smoothing Based on Weighted Least Squares. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 5638–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Jian, S.; Tang, X. Guided Image Filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastal, E.; Oliveira, M.M. Domain Transform for Edge-Aware Image and Video Processing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2011, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lu, C.; Xu, Y.; Jia, J. Image Smoothing via L0 Gradient Minimization. Inf. Fusion 2011, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lindeberg, T. Scale-space theory: A basic tool for analyzing structures at different scales. J. Appl. Stat. 1994, 21, 225–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. IInfrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Cao, L.; Tan, Q.; Jin, G. Infrared and visible image fusion based on NSCT and fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Xi’an, China, 4–7 August 2010; pp. 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. FSIM: A Feature Similarity Index for Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, H. VSI: A Visual Saliency-Induced Index for Perceptual Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 4270–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Wave. Mult. Inf. Process. 2018, 16, 1850018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, B.; Hu, J. Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2011, 12, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. TNO Image Fusion Dataset. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/TN_Image_Fusion_Dataset/1008029 (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Ma, J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Y.; Tian, J. Non-rigid visible and infrared face registration via regularized Gaussian fields criterion. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.E.A. Registration of Thermal and Visible Light Images of Diseased Plants using Silhouette Extraction in the Wavelet Domain. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, H.; Wang, Z. Objective quality assessment of tone-mapped images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslantas, V.; Bendes, E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2015, 69, 1890–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Feng, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y. Detail preserved fusion of visible and infrared images using regional saliency extraction and multi-scale image decomposition. Opt. Commun. 2015, 341, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xydeas, C.S.; Petrovic, V. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron. Lett. 2000, 36, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Varshney, P.K. A human perception inspired quality metric for image fusion based on regional information. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Images | Rules | SD | EN | SF | TMQI | VIF | SCD | AG | Q | Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road | AVG-MAX | 24.413 | 6.0355 | 8.5729 | 0.6659 | 0.4003 | 1.8342 | 4.0542 | 0.4199 | 378.05 |
| AVG-ABSMAX | 24.445 | 6.1007 | 11.907 | 0.6666 | 0.4715 | 1.8230 | 5.9309 | 0.5438 | 228.23 | |
| SGFL-VSM | 38.103 | 5.8504 | 14.140 | 0.6290 | 0.5068 | 1.7169 | 6.6651 | 0.4740 | 323.80 | |
| TEPGFL-VSM | 41.557 | 6.3234 | 13.905 | 0.6966 | 0.7018 | 1.8108 | 6.7974 | 0.5538 | 283.29 | |
| Kayak | AVG-MAX | 16.252 | 5.9252 | 3.5059 | 0.6383 | 0.2179 | 1.5516 | 2.1879 | 0.4537 | 170.13 |
| AVG-ABSMAX | 17.286 | 6.0503 | 5.1000 | 0.6568 | 0.3488 | 1.5228 | 3.5362 | 0.7037 | 171.35 | |
| SGFL-VSM | 32.229 | 6.4433 | 5.1708 | 0.6337 | 0.2105 | 1.4577 | 3.5744 | 0.6590 | 94.326 | |
| TEPGFL-VSM | 22.968 | 6.2697 | 5.2529 | 0.6729 | 0.3935 | 1.6082 | 3.5453 | 0.6958 | 115.43 | |
| Soldiers | AVG-MAX | 21.974 | 6.4668 | 3.9577 | 0.6848 | 0.2962 | 1.8185 | 2.8266 | 0.3782 | 151.94 |
| with jeep | AVG-ABSMAX | 22.460 | 6.5066 | 5.3945 | 0.6979 | 0.4046 | 1.8131 | 4.1455 | 0.4951 | 148.13 |
| SGFL-VSM | 34.533 | 6.9558 | 6.1089 | 0.6849 | 0.4555 | 1.6023 | 4.2572 | 0.4600 | 330.36 | |
| TEPGFL-VSM | 41.343 | 7.2718 | 6.8693 | 0.7534 | 0.8037 | 1.8985 | 4.6329 | 0.5237 | 105.73 | |
| Average | AVG-MAX | 20.880 | 6.1425 | 5.3455 | 0.6630 | 0.3048 | 1.7348 | 3.0229 | 0.4173 | 233.37 |
| AVG-ABSMAX | 21.397 | 6.2192 | 7.4673 | 0.6738 | 0.4083 | 1.7196 | 4.5375 | 0.5809 | 182.57 | |
| SGFL-VSM | 34.955 | 6.4165 | 8.4731 | 0.6492 | 0.3909 | 1.5923 | 4.8322 | 0.5310 | 249.50 | |
| TEPGFL-VSM | 35.290 | 6.6216 | 8.6756 | 0.7076 | 0.6330 | 1.7725 | 4.9919 | 0.5911 | 168.15 |
| SD | EN | SF | TMQI | VIF | SCD | AG | Q | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSCT | 29.581 | 6.5832 | 11.542 | 0.7491 | 0.4636 | 1.5708 | 8.0821 | 0.5943 | 193.23 |
| HyMSD | 39.911 | 6.9397 | 12.563 | 0.7374 | 0.5347 | 1.5497 | 8.7983 | 0.5542 | 231.46 |
| CSR | 27.220 | 6.4358 | 9.6574 | 0.7353 | 0.3656 | 1.5712 | 6.3720 | 0.5618 | 201.50 |
| GTF | 36.240 | 6.6443 | 9.3298 | 0.6871 | 0.2902 | 1.0240 | 6.5414 | 0.4439 | 365.03 |
| VSMWLS | 34.722 | 6.7160 | 11.920 | 0.7634 | 0.4314 | 1.5802 | 8.6299 | 0.4705 | 265.37 |
| CNN | 46.652 | 7.1403 | 11.811 | 0.7507 | 0.5693 | 1.5970 | 8.3758 | 0.6175 | 190.31 |
| DLVGG | 25.848 | 6.3557 | 7.0362 | 0.7296 | 0.3321 | 1.5673 | 4.9591 | 0.4053 | 251.84 |
| ResNet | 26.680 | 6.3977 | 6.9361 | 0.7287 | 0.3372 | 1.5607 | 4.9081 | 0.4067 | 250.51 |
| TE | 37.773 | 6.8414 | 12.300 | 0.7461 | 0.5623 | 1.3772 | 8.7073 | 0.5565 | 197.19 |
| Ours | 42.868 | 6.9528 | 12.569 | 0.7823 | 0.5902 | 1.7684 | 8.7997 | 0.5256 | 188.78 |
| NSCT | HyMSD | CSR | GTF | VSMWLS | CNN | DLVGG | ResNet | TE | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1.8631 | 1.3315 | 61.282 | 1.1098 | 0.8926 | 38.538 | 3.0282 | 1.8516 | 0.0797 | 0.4313 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, C.; Xing, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Fusion of Infrared and Visible Images Using Fast Global Smoothing Decomposition and Target-Enhanced Parallel Gaussian Fuzzy Logic. Sensors 2022, 22, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010040
Duan C, Xing C, Liu Y, Wang Z. Fusion of Infrared and Visible Images Using Fast Global Smoothing Decomposition and Target-Enhanced Parallel Gaussian Fuzzy Logic. Sensors. 2022; 22(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Chaowei, Changda Xing, Yiliu Liu, and Zhisheng Wang. 2022. "Fusion of Infrared and Visible Images Using Fast Global Smoothing Decomposition and Target-Enhanced Parallel Gaussian Fuzzy Logic" Sensors 22, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010040
APA StyleDuan, C., Xing, C., Liu, Y., & Wang, Z. (2022). Fusion of Infrared and Visible Images Using Fast Global Smoothing Decomposition and Target-Enhanced Parallel Gaussian Fuzzy Logic. Sensors, 22(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010040






