Technical Consideration towards Robust 3D Reconstruction with Multi-View Active Stereo Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
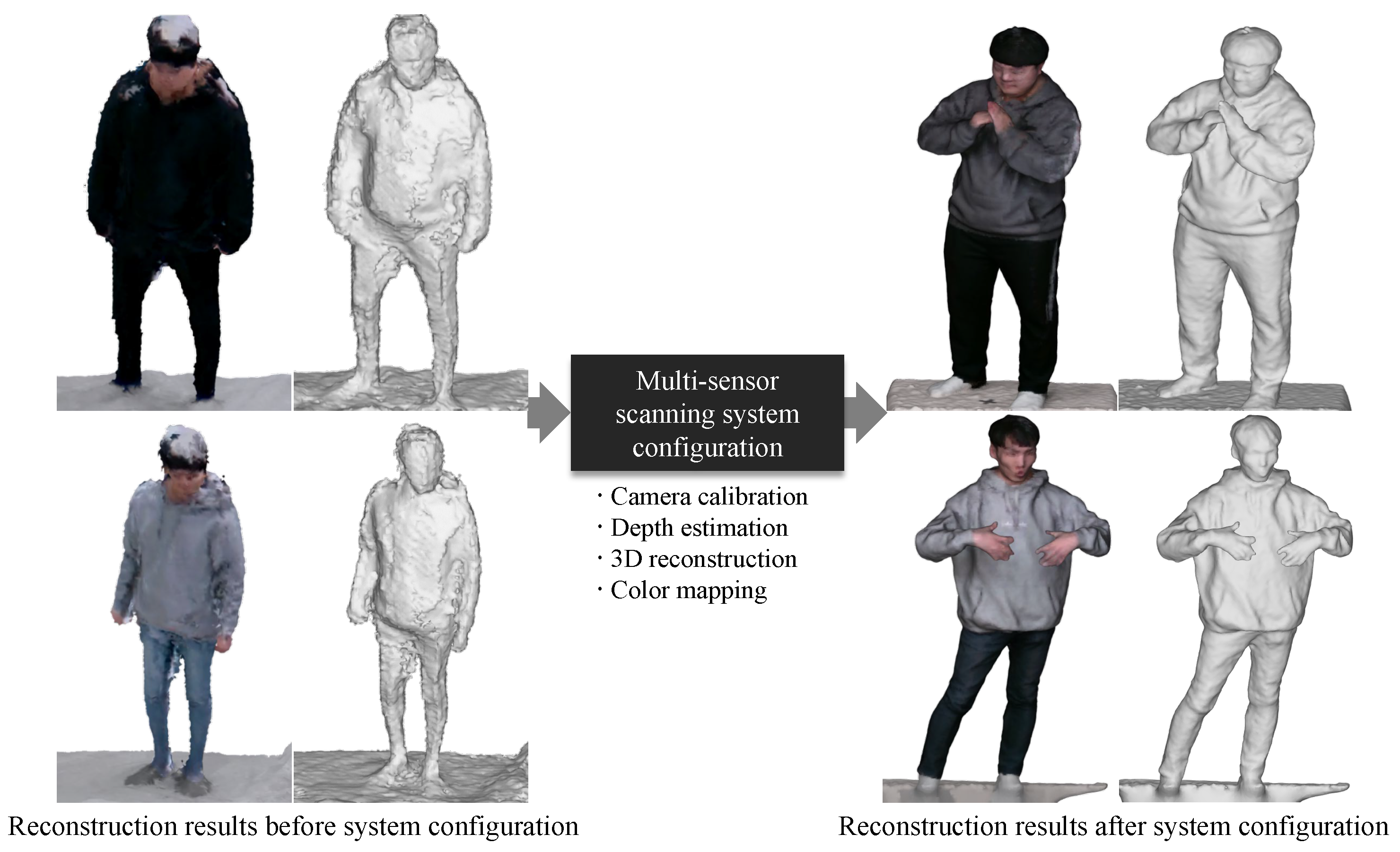
- This paper presents the entire 3D reconstruction pipeline from multi-view active stereo sensors. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first and most detailed set of guidelines for 3D reconstruction with multi-view active stereo sensors.
- The reconstruction pipeline was divided into sub-procedures; various technical factors that could significantly affect the reconstruction accuracy were thoroughly examined in each sub-procedure.
- Through the experiments, this paper provides practical guidelines to reconstruct accurate and reliable 3D objects.
2. Related Work
3. 3D Reconstruction Framework with Multi-View Active Stereo Sensors
4. Technical Considerations toward Robust 3D Reconstruction
4.1. RGB-D Camera Calibration
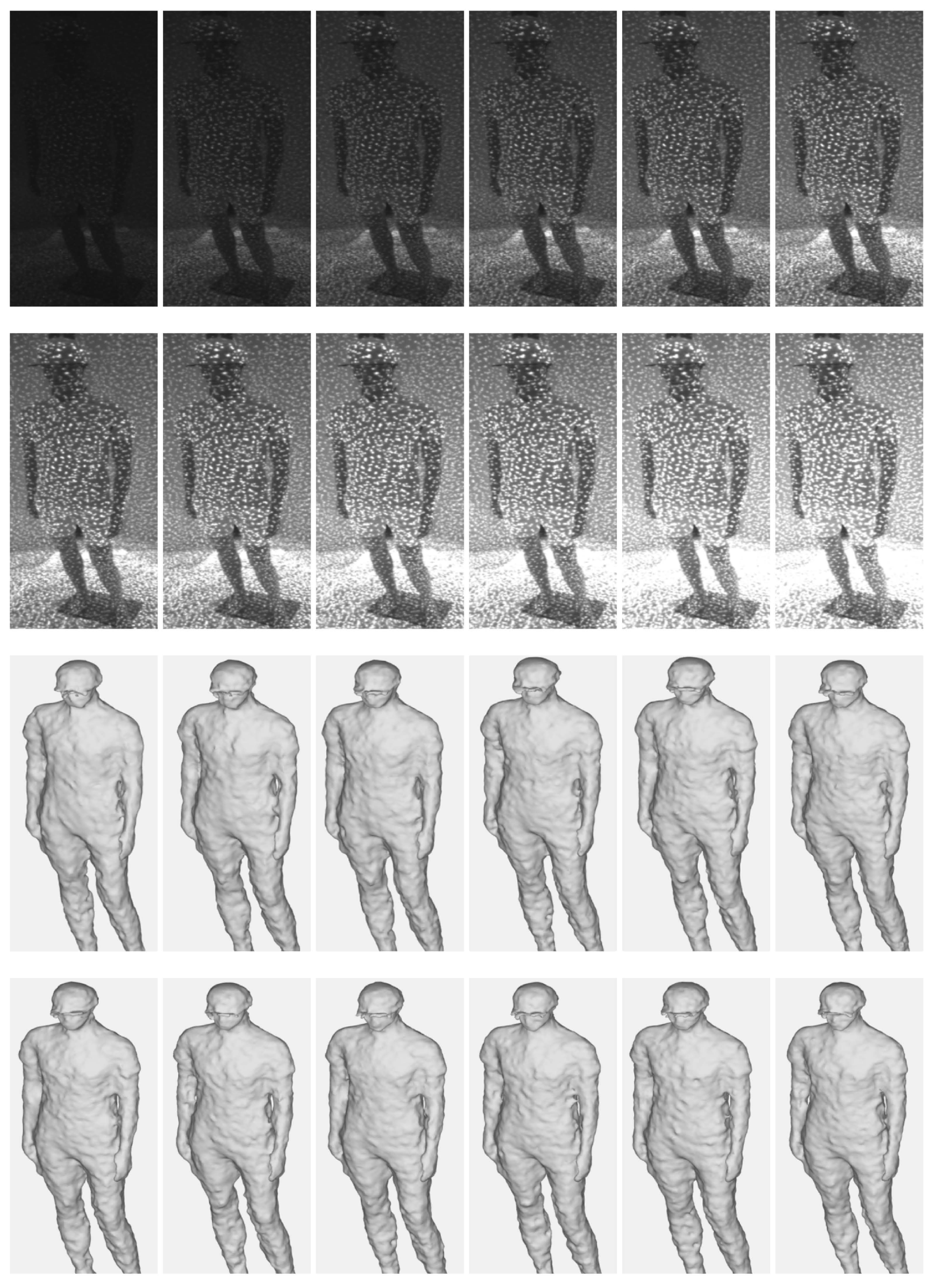
4.2. Projector Intensity
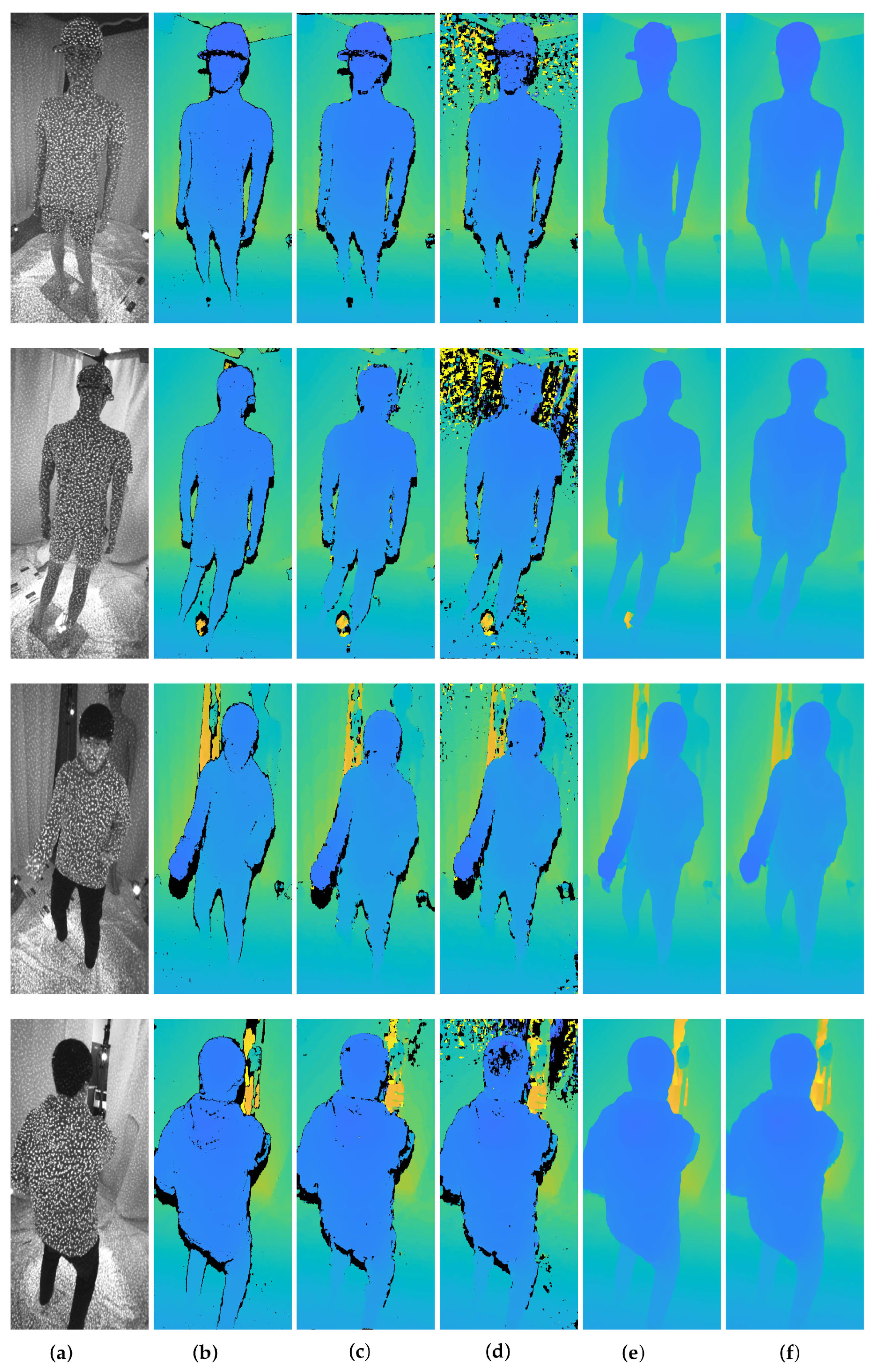
4.3. Stereo Matching Algorithm
4.4. 3D Reconstruction
4.5. Outlier Removal
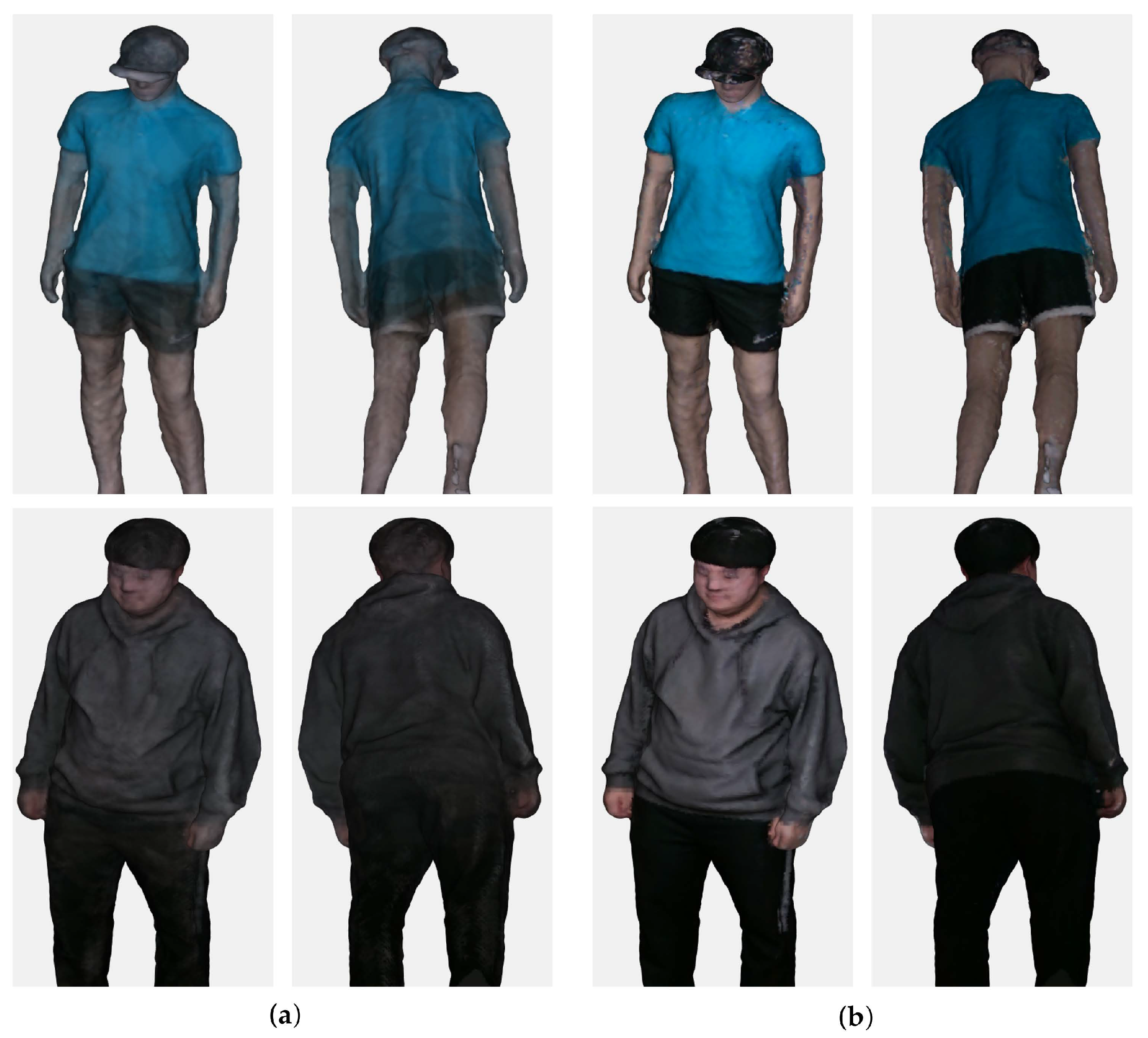
4.6. Color Mapping
4.7. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RGB-D | red, green, blue-depth |
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| 4D | four-dimensional |
| ToF | time-of-flight |
| IR | infrared |
| HD | high definition |
| CPU | central processing unit |
| GPU | graphics processing unit |
| OpenCV | open source computer vision |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| NCC | normalized cross correlation |
| SSD | sum of squared differences |
| AANet | adaptive aggregation networks |
References
- Dou, M.; Khamis, S.; Degtyarev, Y.; Davidson, P.; Fanello, S.R.; Kowdle, A.; Esc, S.O.; Rhemann, C.; Kim, D.; Taylor, J.; et al. Fusion4D: Real-Time Perform. Capture Challenging Scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. 2016, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collet, A.; Chuang, M.; Sweeney, P.; Gillett, D.; Evseev, D.; Calabr, D.; Hoppe, H.; Kirk, A.; Sullivan, S. High-Qual. Streamable Free-Viewp. Video. ACM Trans. Graph. 2015, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.D.; Choi, S.; Kim, W.; Lee, S. GraphX-convolution for point cloud deformation in 2D-to-3D conversion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8628–8637. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Lee, S.; Jang, M.; Leea, S. Gradient Flow Evol. 3D Fusion A Single Depth Sensor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X. Rapid 3D Reconstr. Image Seq. Acquir. UAV Camera. Sensors 2018, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, G.; Han, G. Easy and Fast Reconstruction of a 3D Avatar with an RGB-D Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, Q.; Jiang, Z. 3D Reconstruction of Space Objects from Multi-Views by a Visible Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z. Microsoft kinect sensor and its effect. IEEE Multimed. 2012, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keselman, L.; Iselin Woodfill, J.; Grunnet-Jepsen, A.; Bhowmik, A. Intel Realsense Stereoscopic Depth Cameras. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.W.; Peng, C.C. 3D Face Point Cloud Reconstruction and Recognition Using Depth Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Pape, C.; Reithmeier, E. Scale-Aware Multi-View Reconstruction Using an Active Triple-Camera System. Sensors 2020, 20, 6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Neri, P.; Razion, A.V.; Tambur, F.; Barone, S. Sensor Architectures and Technologies for Upper Limb 3D Surface Reconstruction: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, D.; Lee, S. Microscopic Structure from Motion (SfM) for Microscale 3D Surface Reconstruction. Sensors 2020, 20, 5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, K. FCN-Based 3D Reconstruction with Multi-Source Photometric Stereo. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z. A Multi-View Stereo Algorithm Based on Homogeneous Direct Spatial Expansion with Improved Reconstruction Accuracy and Completeness. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.; Yoon, H.; Lee, S.; Kang, J.; Lee, S. A Comparison and Evaluation of Stereo Matching on Active Stereo Images. Sensors 2022, 22, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Time-of-Flight Camera—An Introduction; Technical White Paper; Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Konolige, K. Projected texture stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M.; Lee, S.; Kang, J.; Lee, S. Active Stereo Matching Benchmark for 3D Reconstruction using Multi-view Depths. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications, Online, 13–15 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Grunnet-Jepsen, A.; Sweetser, J.N.; Winer, P.; Takagi, A.; Woodfill, J. Projectors for Intel® RealSense™ Depth Cameras D4xx; Intel Support, Interl Corporation: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Grunnet-Jepsen, A.; Sweetser, J.N.; Woodfill, J. Best-Known Tuning Intel® RealSense™ D400 Depth Cameras Best Performance; Interl Corporation: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2018; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Grunnet-Jepsen, A.; Tong, D. Depth Post-Processing for Intel® RealSense™ D400 Depth Cameras; New Technology Group; Interl Corporation: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2018; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Corporation, I. Cross-Platform Library for Intel® RealSense™ Depth Cameras. Available online: https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Yoon, H.; Jang, M.; Huh, J.; Kang, J.; Lee, S. Multiple Sensor Synchronization with the RealSense RGB-D Camera. Sensors 2021, 21, 6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradski, G.; Kaehler, A. Learning OpenCV: Computer Vision with the OpenCV Library; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Newton, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svoboda, T.; Martinec, D.; Pajdla, T. A Conv. Multicamera Self-Calibration Virtual Environ. Presence: Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2005, 14, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchelson, J.; Hilton, A. Wand-based multiple camera studio calibration. Center Vision, Speech and Signal Process Technical Report. Guildford, England. 2003. Available online: http://info.ee.surrey.ac.uk/CVSSP/Publications/papers/vssp-tr-2-2003.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Andrew, A.M. Multiple view geometry in computer vision. Kybernetes 2001, 30, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabih, R.; Woodfill, J. Non-parametric local transforms for computing visual correspondence. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Stockholm, Sweden, 2–6 May 1994; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Okutomi, M.; Kanade, T. A multiple-baseline stereo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1993, 15, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.S.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, S.U. Robust Stereo Matching Using Adaptive Normalized Cross-Correlation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 33, 807–822. [Google Scholar]
- Matthies, L.; Kanade, T.; Szeliski, R. Kalman filter-based algorithms for estimating depth from image sequences. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1989, 3, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J. Aanet: Adaptive aggregation network for efficient stereo matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1959–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Duggal, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, W.C.; Hu, R.; Urtasun, R. Deeppruner: Learning efficient stereo matching via differentiable patchmatch. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4384–4393. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, H.; Lin, S.; Dai, J. Deformable convnets v2: More deformable, better results. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 9308–9316. [Google Scholar]
- Kazhdan, M.; Bolitho, M.; Hoppe, H. Poisson Surface Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, Cagliari, Italy, 26–28 June 2006; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Akenine-Möller, T.; Haines, E.; Hoffman, N. Real-Time Rendering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. Competitive Learning of Facial Fitting and Synthesis Using UV Energy. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 2858–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Method | Mean | ±Std. |
| Checkerboard [26] | 0.5132 | 0.1213 |
| Svoboda et al. [27] | 0.8413 | 0.2231 |
| Mitchelson et al. [28] | 0.7482 | 0.2484 |
| Intensity | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 |
| Mean | 2.4596 | 2.4020 | 2.4163 | 2.3736 | 2.3766 | 2.3690 |
| ±Std. | 1.6251 | 1.5846 | 1.6123 | 1.5588 | 1.5700 | 1.5510 |
| Intensity | 210 | 240 | 270 | 300 | 330 | 360 |
| Mean | 2.3503 | 2.3756 | 2.3526 | 2.3326 | 2.3466 | 2.3446 |
| ±Std. | 1.5293 | 1.5325 | 1.5498 | 1.5175 | 1.5356 | 1.5465 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, M.; Lee, S.; Kang, J.; Lee, S. Technical Consideration towards Robust 3D Reconstruction with Multi-View Active Stereo Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 4142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114142
Jang M, Lee S, Kang J, Lee S. Technical Consideration towards Robust 3D Reconstruction with Multi-View Active Stereo Sensors. Sensors. 2022; 22(11):4142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114142
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Mingyu, Seongmin Lee, Jiwoo Kang, and Sanghoon Lee. 2022. "Technical Consideration towards Robust 3D Reconstruction with Multi-View Active Stereo Sensors" Sensors 22, no. 11: 4142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114142
APA StyleJang, M., Lee, S., Kang, J., & Lee, S. (2022). Technical Consideration towards Robust 3D Reconstruction with Multi-View Active Stereo Sensors. Sensors, 22(11), 4142. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114142







