Recent Advances in Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Proteins and Specific DNA Sequences Using a Magnetic Modulation Biosensing System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
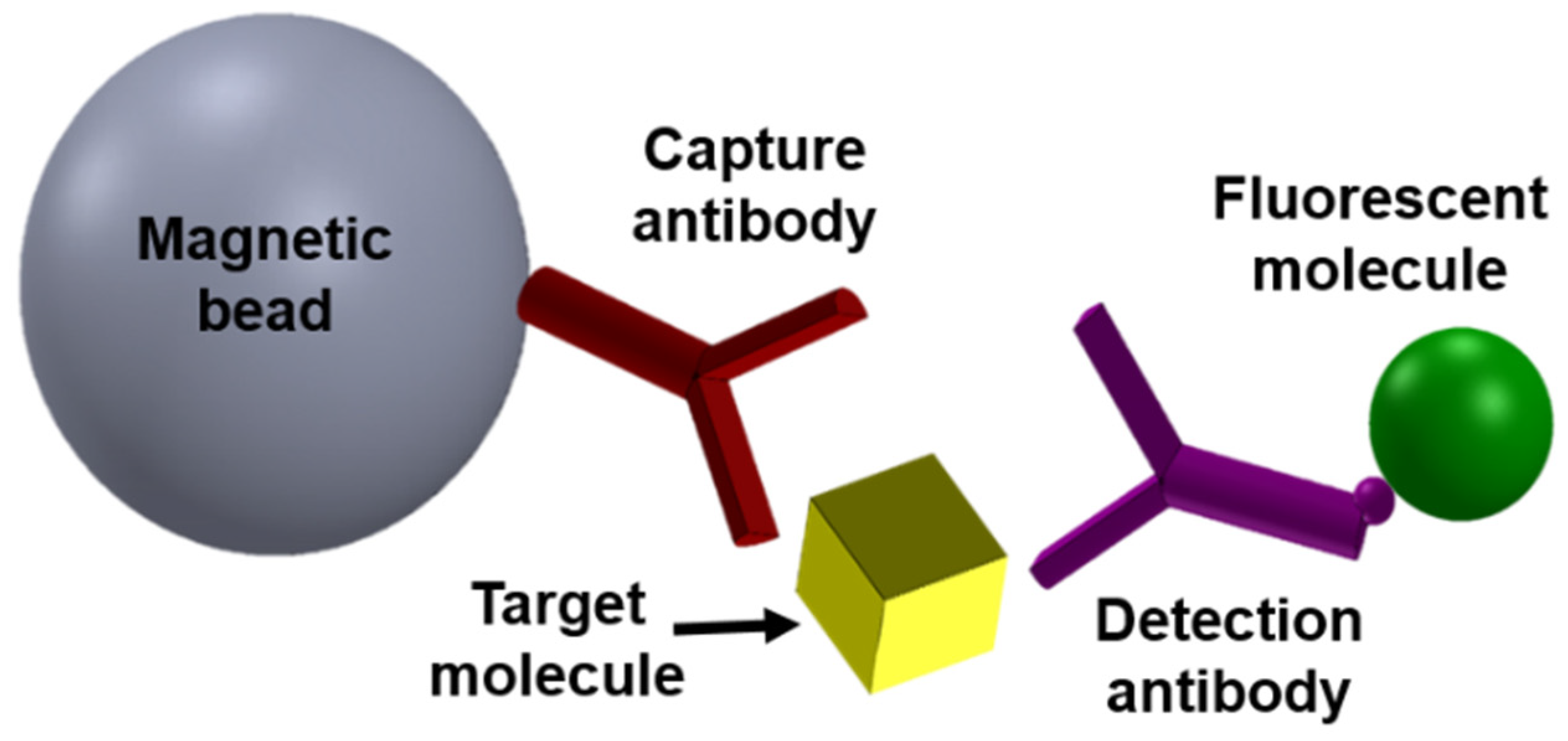
2. Magnetic Modulation Biosensing (MMB) Technology Principles
3. Technology Applications
3.1. Detection of Protein Biomarkers
3.1.1. Serological Assays
3.1.2. Detection of Interleukin-8 (IL-8) in Plasma
3.2. Detection of Interactions
Inhibitor Screening Using the MMB-Based Protein Interaction Assay
3.3. Detection of Specific Nucleic Acid Sequences
3.3.1. MMB-Assisted Sandwich Hybridization Assay (SHA)
3.3.2. Detection of Repetitive Nucleic Acid Sequences
3.3.3. Detecting Low Abundance Nucleic Acid Targets
4. Technology Advancements
4.1. Magnetically Aggregated Biosensors (MAB)
4.2. Optical Modulation Biosensing (OMB)
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Todd, J.; Freese, B.; Lu, A.; Held, D.; Morey, J.; Livingston, R.; Goix, P. Ultrasensitive flow-based immunoassays using single-molecule counting. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, A.H.B.; Fukushima, N.; Puskas, R.; Todd, J.; Goix, P. Development and preliminary clinical validation of a high sensitivity assay for cardiac troponin using a capillary flow (Single molecule) fluorescence detector. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 2157–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat. Biotech. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunbar, S.A. Applications of Luminex® xMAP™ technology for rapid, high-throughput multiplexed nucleic acid detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 363, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Dougan, T.J.; Walt, D.R. High-Throughput, High-Multiplex Digital Protein Detection with Attomolar Sensitivity. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, T.; Cohen, L.; Cheng, C.A.; Lazarovits, R.; Uwamanzu-Nna, A.; Han, I.; Griswold, K., Jr.; Barry, N.; Thompson, D.B.; Kohman, R.E.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assay Using Single Molecule Arrays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 25966–25972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequin, R.M. Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA)/Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2415–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Xie, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. A novel reverse fluorescent immunoassay approach for sensing human chorionic gonadotropin based on silver-gold nano-alloy and magnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.Y.; Huang, T.B.; Tsai, Y.C.; Yeh, C.S.; Lei, H.Y.; Lee, G.B. A microfluidic immunomagnetic bead-based system for the rapid detection of influenza infections: From purified virus particles to clinical specimens. Biomed. Microdevices 2013, 15, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielli, A.; Arie, A.; Porat, N.; Ehrlich, M. Detection of fluorescent-labeled probes at subpicomolar concentrations by magnetic modulation. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 19253–19259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verbarg, J.; Hadass, O.; Olivo, P.D.; Danielli, A. High sensitivity detection of a protein biomarker interleukin-8 utilizing a magnetic modulation biosensing system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Maghsoudlou, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): The basics. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 77, C98–C101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, J.N.; Kopelman, R. Magnetically modulated optical nanoprobes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anker, J.N.; Behrend, C.J.; Huang, H.; Kopelman, R. Magnetically-modulated optical nanoprobes (MagMOONs) and systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, S.; Cohen, M.; Margulis, M.; Roth, S.; Danielli, A. Magnetically aggregated biosensors for sensitive detection of biomarkers at low concentrations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, S.; Zander, I.; Michelson, Y.; Ben-David, Y.; Banin, E.; Danielli, A. Identification of protein-protein interactions using a magnetic modulation biosensing system. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 303, 127228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.; Cohen, M.; Danielli, A. Configuration and Design of Electromagnets for Rapid and Precise Manipulation of Magnetic Beads in Biosensing Applications. Micromachines 2019, 10, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margulis, M.; Ashri, S.; Cohen, M.; Danielli, A. Detecting nucleic acid fragments in serum using a magnetically modulated sandwich assay. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201900104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielli, A.; Porat, N.; Arie, A.; Ehrlich, M. Rapid homogenous detection of the Ibaraki virus NS3 cDNA at picomolar concentrations by magnetic modulation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelson, Y.; Lustig, Y.; Avivi, S.; Schwartz, E.; Danielli, A. Highly sensitive and specific Zika virus serological assays using a magnetic modulation biosensing system. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 219, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Huillier, A.G.; Hamid-Allie, A.; Kristjanson, E.; Papageorgiou, L.; Hung, S.; Wong, C.F.; Stein, D.R.; Olsha, R.; Goneau, L.W.; Dimitrova, K.; et al. Evaluation of Euroimmun Anti-Zika Virus IgM and IgG Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for Zika Virus Serologic Testing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peeling, R.W.; Artsob, H.; Pelegrino, J.L.; Buchy, P.; Cardosa, M.J.; Devi, S.; Enria, D.A.; Farrar, J.; Gubler, D.J.; Guzman, M.G.; et al. Evaluation of diagnostic tests: Dengue. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, S30–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huzly, D.; Hanselmann, I.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Panning, M. High specificity of a novel Zika virus ELISA in European patients after exposure to different flaviviruses. Euro Surveill. 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleton, N.B.; Godeke, G.J.; Reimerink, J.; Beersma, M.F.; van Doorn, H.R.; Franco, L.; Goeijenbier, M.; Jimenez-Clavero, M.A.; Johnson, B.W.; Niedrig, M.; et al. Spot the Difference-Development of a Syndrome Based Protein Microarray for Specific Serological Detection of Multiple Flavivirus Infections in Travelers. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avivi-Mintz, S.; Lustig, Y.; Indenbaum, V.; Schwartz, E.; Danielli, A. Highly Sensitive and Specific SARS-CoV-2 Serological Assay Using a Magnetic Modulation Biosensing System. Biosensors 2022, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.P.; Matthews, J.M. Protein-protein interactions in human disease. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, I.; Lievens, S.; Libert, C.; Tavernier, J.; De Bosscher, K. Modulation of Protein-Protein Interactions for the Development of Novel Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, A.A.; Khuri, F.R.; Fu, H. Targeting protein-protein interactions as an anticancer strategy. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2013, 34, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansour, M.R.; Abraham, B.J.; Anders, L.; Berezovskaya, A.; Gutierrez, A.; Durbin, A.D.; Etchin, J.; Lawton, L.; Sallan, S.E.; Silverman, L.B.; et al. An oncogenic super-enhancer formed through somatic mutation of a noncoding intergenic element. Science 2014, 346, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Transcriptional regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1237–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerabek-Willemsen, M.; Andre, T.; Wanner, R.; Roth, H.M.; Duhr, S.; Baaske, P.; Breitsprecher, D. MicroScale Thermophoresis: Interaction analysis and beyond. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1077, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, C.C.; Lai, W.P.; Leung, Y.C.; Lo, S.C.; Wong, M.S.; Yang, M. Study of substrate-enzyme interaction between immobilized pyridoxamine and recombinant porcine pyridoxal kinase using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1596, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenko, E.; Sarafanov, A.; Greco, N.; Shima, M.; Loster, K.; Schwinn, H.; Josic, D. Use of surface plasmon resonance for studies of protein-protein and protein-phospholipid membrane interactions. Application to the binding of factor VIII to von Willebrand factor and to phosphatidylserine-containing membranes. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 852, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zelmer, A.; Wellmann, S. Visualization of Protein-protein Interaction in Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Fractions by Co-immunoprecipitation and In Situ Proximity Ligation Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 55218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellman, L.M.; Fried, M.G. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) for detecting protein-nucleic acid interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Orenstein, Y.; Golodnitsky, R.; Pellach, M.; Avrahami, D.; Wachtel, C.; Ovadia-Shochat, A.; Shir-Shapira, H.; Kedmi, A.; Juven-Gershon, T.; et al. SELMAP—SELEX affinity landscape MAPping of transcription factor binding sites using integrated microfluidics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhelst, J.; De Vlieger, D.; Saelens, X. Co-immunoprecipitation of the Mouse Mx1 Protein with the Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein. J. Vis. Exp. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, S.; Ideses, D.; Juven-Gershon, T.; Danielli, A. Rapid Biosensing Method for Detecting Protein–DNA Interactions. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philo, J.S.; Aoki, K.H.; Arakawa, T.; Narhi, L.O.; Wen, J. Dimerization of the extracellular domain of the erythropoietin (EPO) receptor by EPO: One high-affinity and one low-affinity interaction. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, M.F.; Peterson, C.L.; Smale, S.T. Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes: Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, S.; Danielli, A. Rapid and Sensitive Inhibitor Screening Using Magnetically Modulated Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Beer, J.C.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Swanson-Mungerson, M.; Desai, U.R. Discovering small-molecule therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, G. COVID-19: Review on latest available drugs and therapies against SARS-CoV-2. Coagulation and inflammation cross-talking. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody, 414–1 (AM001414). Available online: https://www.activemotif.com/catalog/details/91361/sars-cov-2-spike-antibody-am001414 (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Wan, J.; Xing, S.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Gu, C.; Wu, Y.; Rong, B.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, K.; et al. Human-IgG-Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Block the SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) S1 Protein, His Tag. Available online: https://www.acrobiosystems.com/P3103-SARS-CoV-2-%28COVID-19%29-S1-protein-His-Tag.html (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Inhibitor Screening Kit. Available online: https://www.acrobiosystems.com/P3144-SARS-CoV-2-%28COVID-19%29-Inhibitor-screening-Kit.html (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Shackelford, R.E.; Vora, M.; Mayhall, K.; Cotelingam, J. ALK-rearrangements and testing methods in non-small cell lung cancer: A review. Genes Cancer 2014, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, C.; Schielke, A.; Ellerbroek, L.; Johne, R. PCR inhibitors—Occurrence, properties and removal. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.; Willerslev, E.; Hansen, A. Damage and repair of ancient DNA. Mutat. Res. 2005, 571, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieme, D.; Neubauer, P.; Nies, D.H.; Grass, G. Sandwich hybridization assay for sensitive detection of dynamic changes in mRNA transcript levels in crude Escherichia coli cell extracts in response to copper ions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7463–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiddiky, M.J.; Rahman, M.A.; Shim, Y.B. Hydrazine-catalyzed ultrasensitive detection of DNA and proteins. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6886–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, J.; Barken, K.B.; Lahdenpera, J.; Breitenstein, A.; Molin, S.; Neubauer, P. Sandwich hybridisation assay for quantitative detection of yeast RNAs in crude cell lysates. Microb. Cell Fact. 2003, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, D.; Martinez-Salazar, J.; Ortiz, E.; Rodriguez, C.; Valencia-Morales, E. Repeated sequences in bacterial chromosomes and plasmids: A glimpse from sequenced genomes. Res. Microbiol. 1999, 150, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, S.; Goyal, V. Repetitive sequences in plant nuclear DNA: Types, distribution, evolution and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2014, 12, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biscotti, M.A.; Olmo, E.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S. Repetitive DNA in eukaryotic genomes. Chromosome Res. 2015, 23, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautwald-Junghanns, M.E.; Cramer, K.; Fischer, B.; Forster, A.; Galli, R.; Kremer, F.; Mapesa, E.U.; Meissner, S.; Preisinger, R.; Preusse, G.; et al. Current approaches to avoid the culling of day-old male chicks in the layer industry, with special reference to spectroscopic methods. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijnis, M.R.N.; Blok, V.; Stassen, E.N.; Gremmen, H.G.J. Moral “Lock-In” in Responsible Innovation: The Ethical and Social Aspects of Killing Day-Old Chicks and Its Alternatives. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2015, 28, 939–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margulis, M.; Danielli, A. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Repetitive Nucleic Acid Sequences Using Magnetically Modulated Biosensors. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11749–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulis, M.; Erster, O.; Roth, S.; Mandelboim, M.; Danielli, A. A Magnetic Modulation Biosensing-Based Molecular Assay for Rapid and Highly Sensitive Clinical Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulis, M.; Cohen, M.; Burg, S.; Avivi-Mintz, S.; Danielli, A. Optical modulation biosensing system for rapid detection of biological targets at low concentrations. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 5338–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bio-Rad. Bio-Plex Pro™, Human Chemokine Panel; Bio-Rad: Hercules, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, S.; Hadass, O.; Cohen, M.; Verbarg, J.; Wilsey, J.; Danielli, A. Improving the Sensitivity of Fluorescence-Based Immunoassays by Photobleaching the Autofluorescence of Magnetic Beads. Small 2019, 15, 1803751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Application | System | Target | Analytical Parameters | Clinical Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LoD | Dynamic Range | Sensitivity [%] | Specificity [%] | ||||
| Protein assays | SARS-CoV-2 serological assay | MMB | anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 IgG | 129 ng/L | 4-log | 93 | 98 |
| ZIKV serological assay | MMB | anti-ZIKV NS1 IgM | 99 ng/L | 4-log | 88 | 100 | |
| ZIKV serological assay | MMB | anti-ZIKV NS1 IgG | 102 ng/L | 4-log | 97 | 100 | |
| Detection of PPIs | MMB | EPO-EPOR interaction | 42 ng/L | 4-log | - | - | |
| Detection of PPIs | MMB | S1-ACE2 interaction | 1600 ng/L | 4-log | - | - | |
| Inhibition of PPIs | MMB | S1-ACE2 interaction | - | 3-log | - | - | |
| Detection of protein-DNA interactions | MMB | Sp1-wt DNA interaction | 1610 ng/L | 4-log | - | - | |
| Detection of protein biomarkers | MMB | IL-8 | 0.08 ng/L | 6-log | - | - | |
| Molecular assays | Direct detection of specific DNA markers | MMB | EML4-ALK oncogenic translocation | 65.2 ng/L | 3-log | - | - |
| Detection of the repetitive nucleic acid sequences | MMB | XhoI repetitive sequence of the female chicken | - | - | - | - | |
| Clinical diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 | MMB | E-gene | 1.6 target copies/reaction | - | 100 | 100 | |
| Technology advancements | Detection of protein biomarkers | MAB | IL-8 | 0.1 ng/L | 4-log | - | - |
| Detection of protein biomarkers | OMB | IL-8 | 0.02 ng/L | 4-log | - | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roth, S.; Margulis, M.; Danielli, A. Recent Advances in Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Proteins and Specific DNA Sequences Using a Magnetic Modulation Biosensing System. Sensors 2022, 22, 4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124497
Roth S, Margulis M, Danielli A. Recent Advances in Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Proteins and Specific DNA Sequences Using a Magnetic Modulation Biosensing System. Sensors. 2022; 22(12):4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124497
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoth, Shira, Michael Margulis, and Amos Danielli. 2022. "Recent Advances in Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Proteins and Specific DNA Sequences Using a Magnetic Modulation Biosensing System" Sensors 22, no. 12: 4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124497
APA StyleRoth, S., Margulis, M., & Danielli, A. (2022). Recent Advances in Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection of Proteins and Specific DNA Sequences Using a Magnetic Modulation Biosensing System. Sensors, 22(12), 4497. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22124497






