A Novel LiDAR–IMU–Odometer Coupling Framework for Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum (TWIP) Robot Localization and Mapping with Nonholonomic Constraint Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A complete LIDAR–IMU–encoder-coupled state estimation and mapping framework is proposed for a two-wheeled inverted pendulum robot. This method extends the LIDAR–IMU to process odometric measurements and improves the system’s localization accuracy.
- A new nonholonomic factor is proposed to introduce encoder pre-integration constraints and ground constraints, which are naturally coupled to the factor graph optimization of the system.
- Indoor and outdoor experiments demonstrate the improved localization accuracy and robustness of the proposed lidar–IMU–odometry coupling framework when the controller is mounted on a two-wheeled inverted pendulum robot navigating on an approximately flat surface.
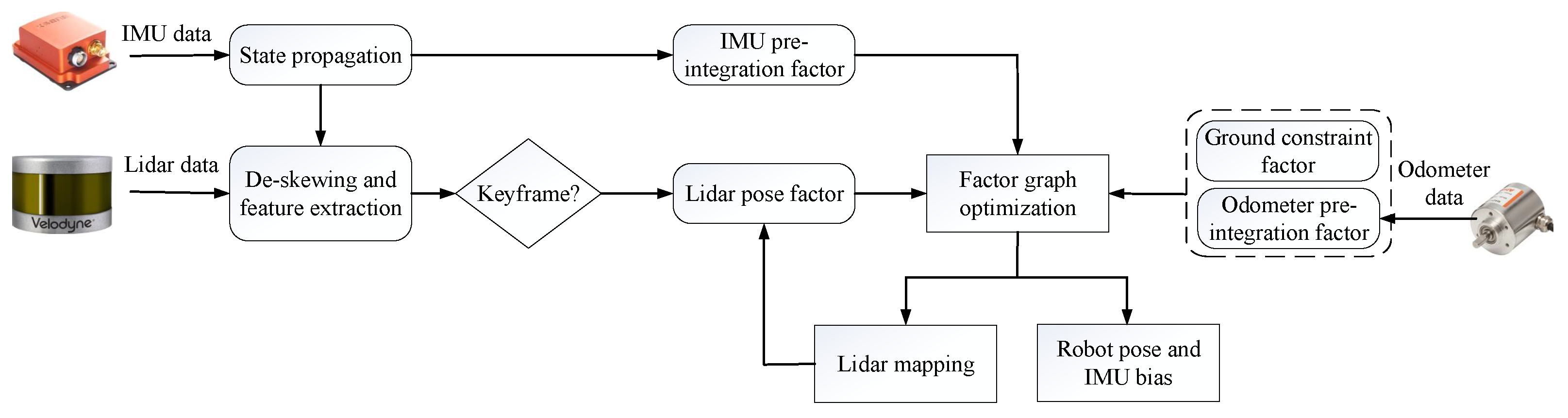
2. Methodology Overview
3. Preliminaries
3.1. On-Manifold Pose Parameterization
3.2. Factor Graph Optimization
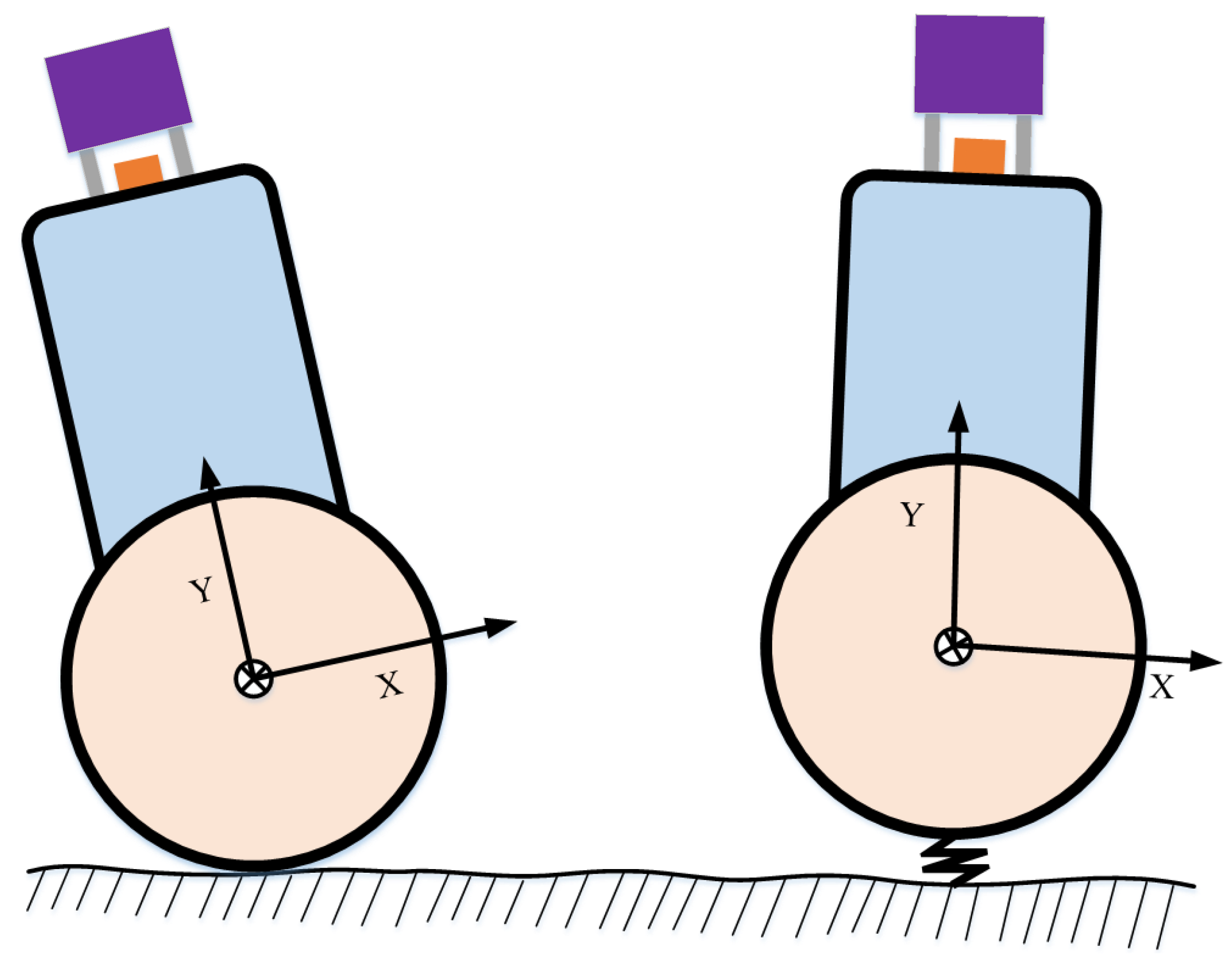
4. State Estimation with Accurate Parameterization of TWIP
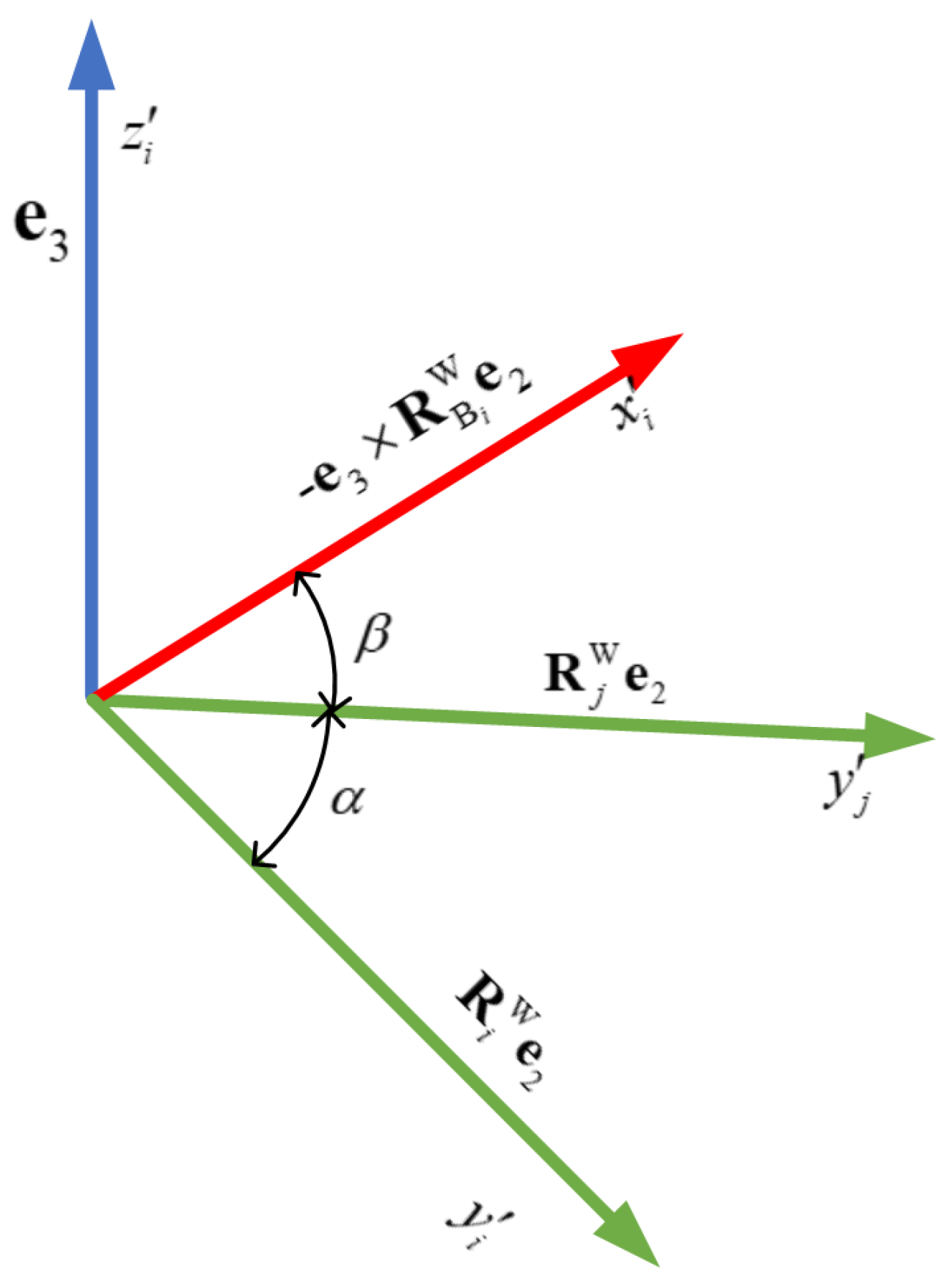
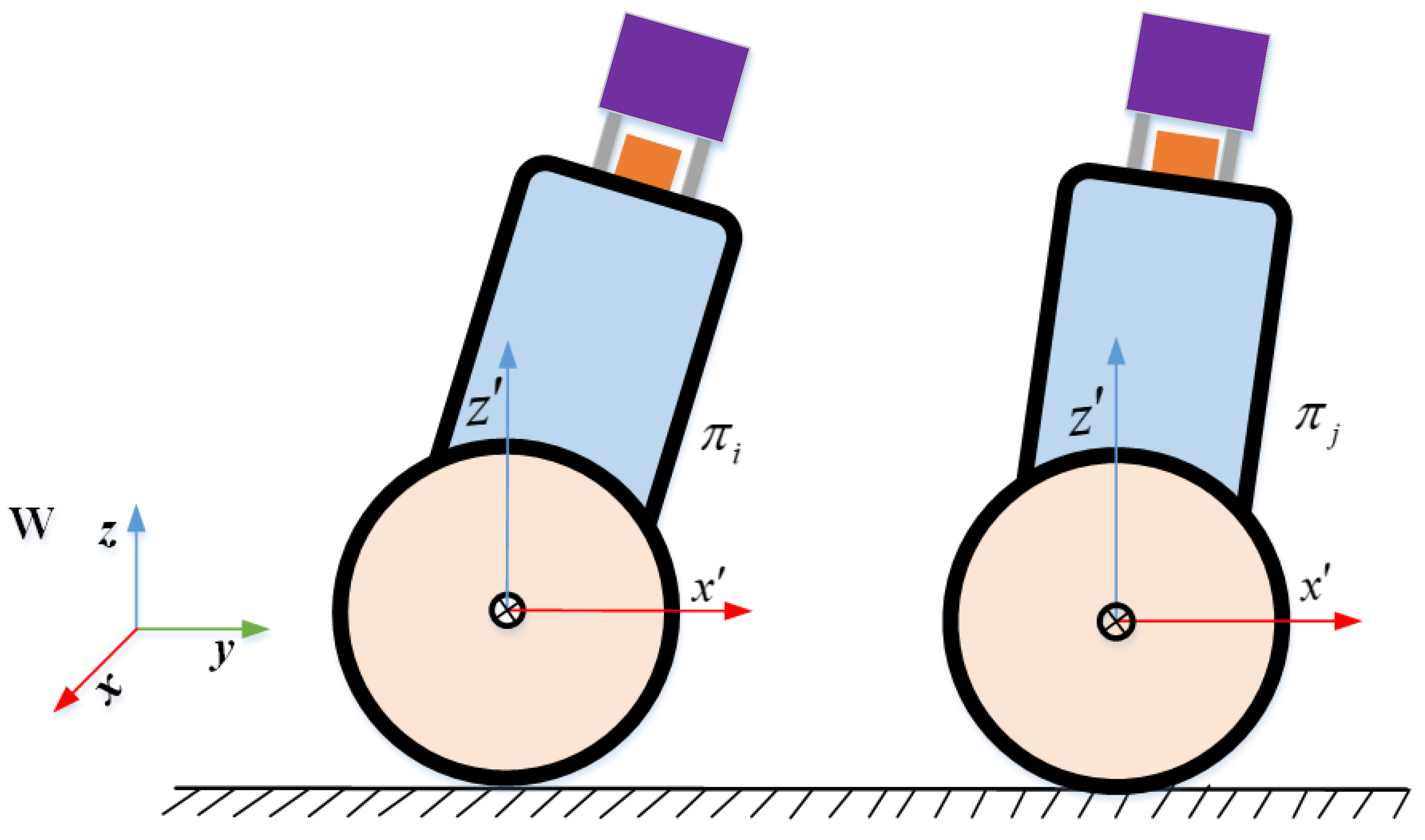
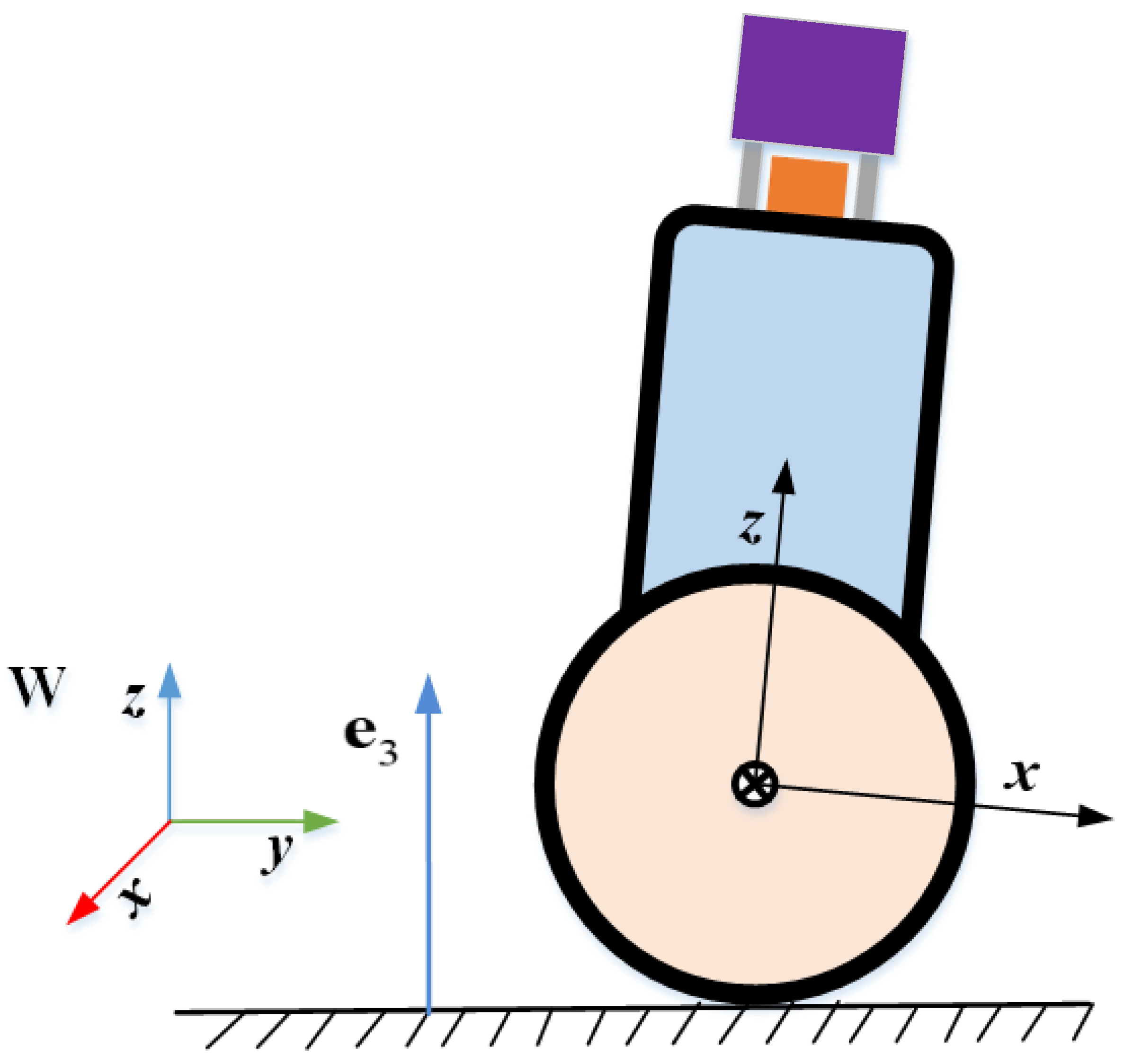
4.1. Pose Parameterization of TWIP
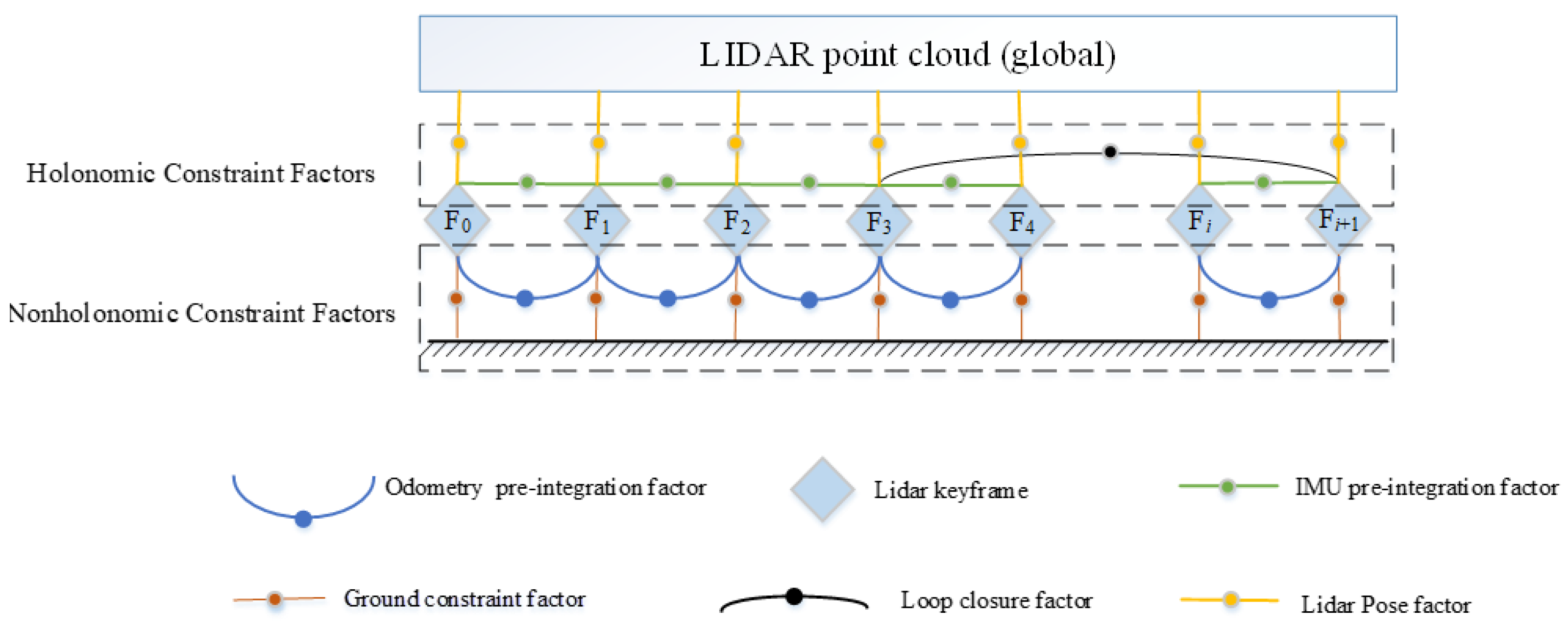
4.2. Coupling of Lidar–IMU–Odometer via Factor Graph
4.2.1. Lidar Pose Factor
4.2.2. IMU Pre-Integration Factor
4.2.3. Odometry Pre-Integration Factor
4.2.4. Ground Constraint Factor
4.2.5. Loop Closure Factor
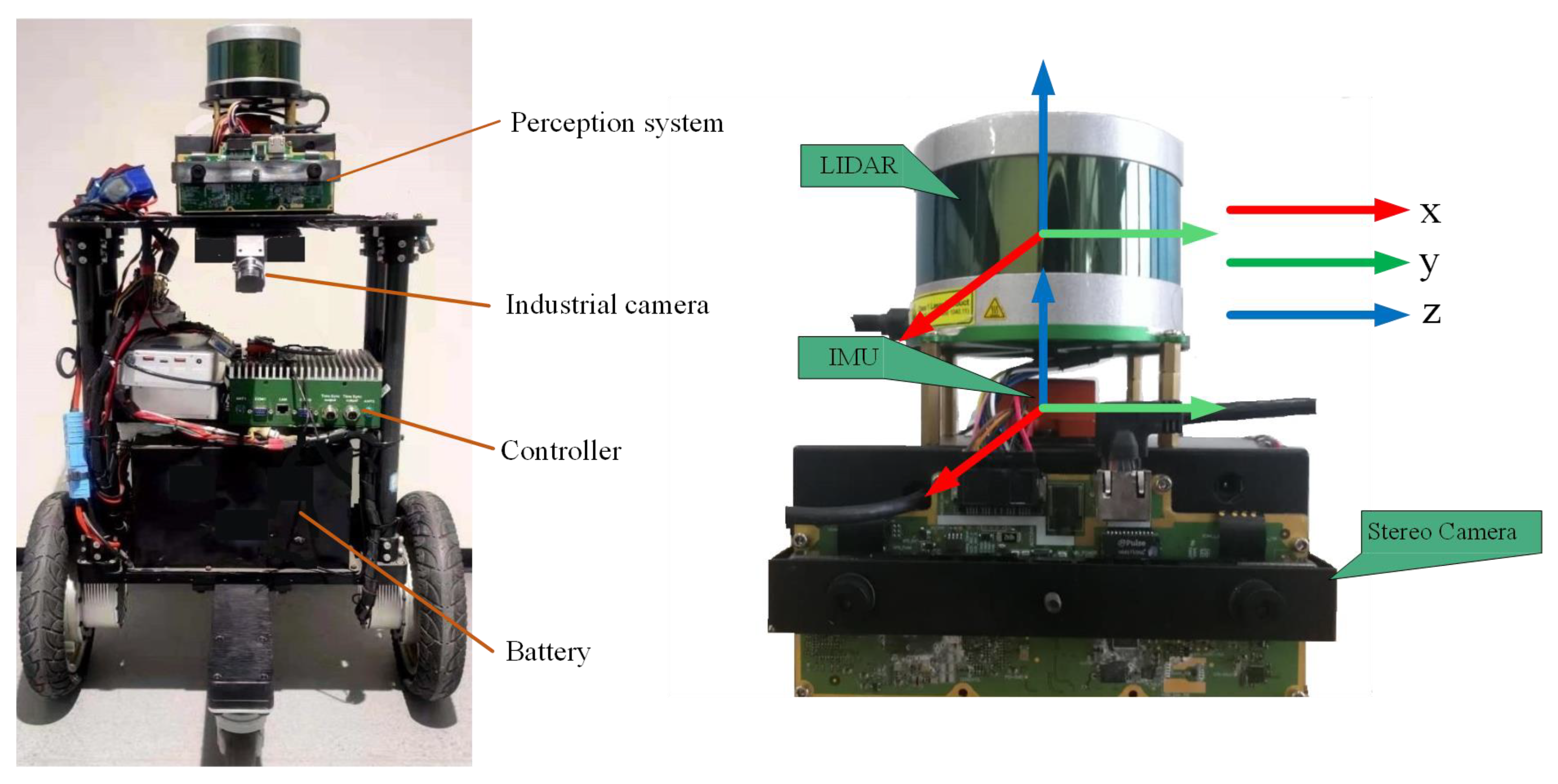
5. Experiment
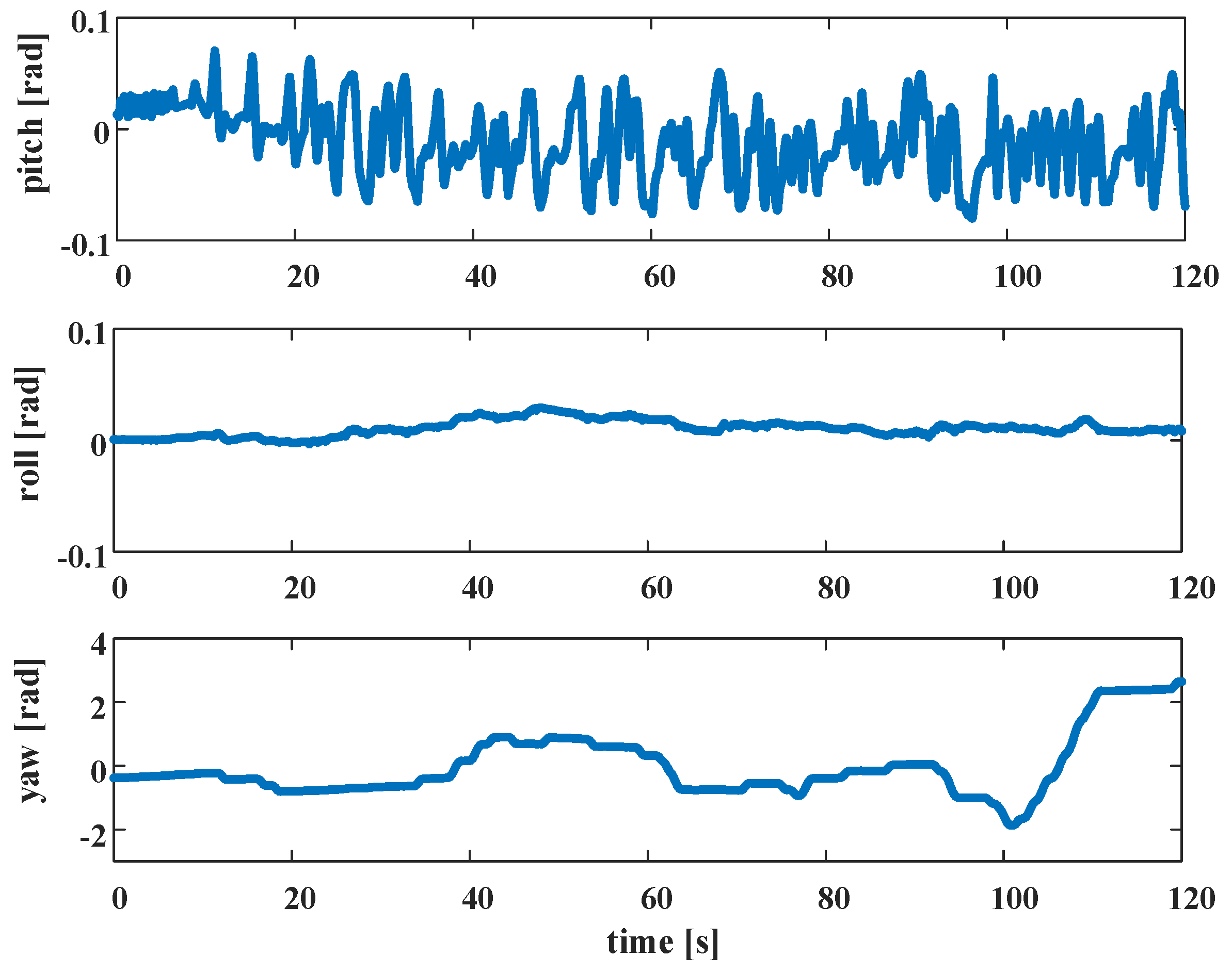
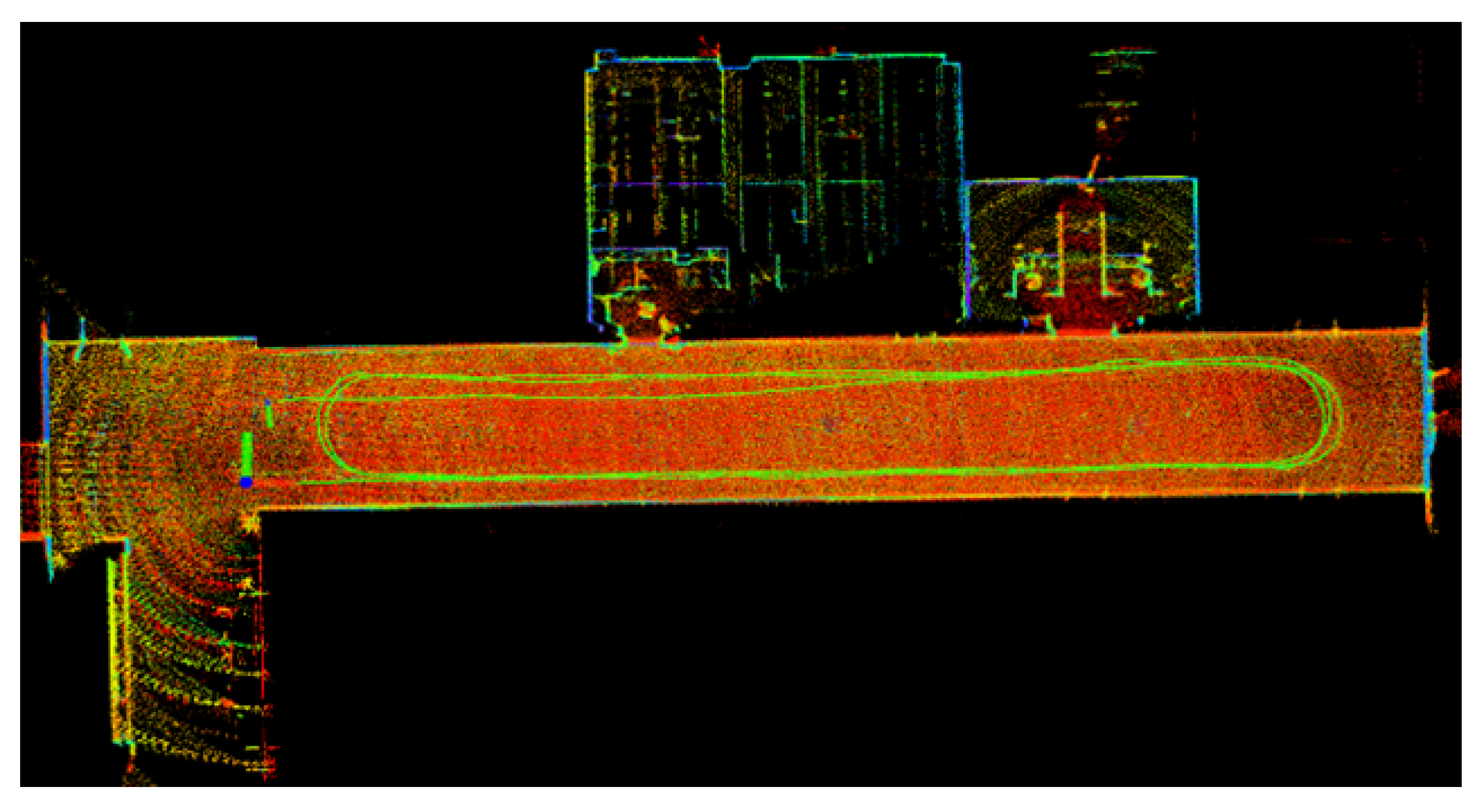
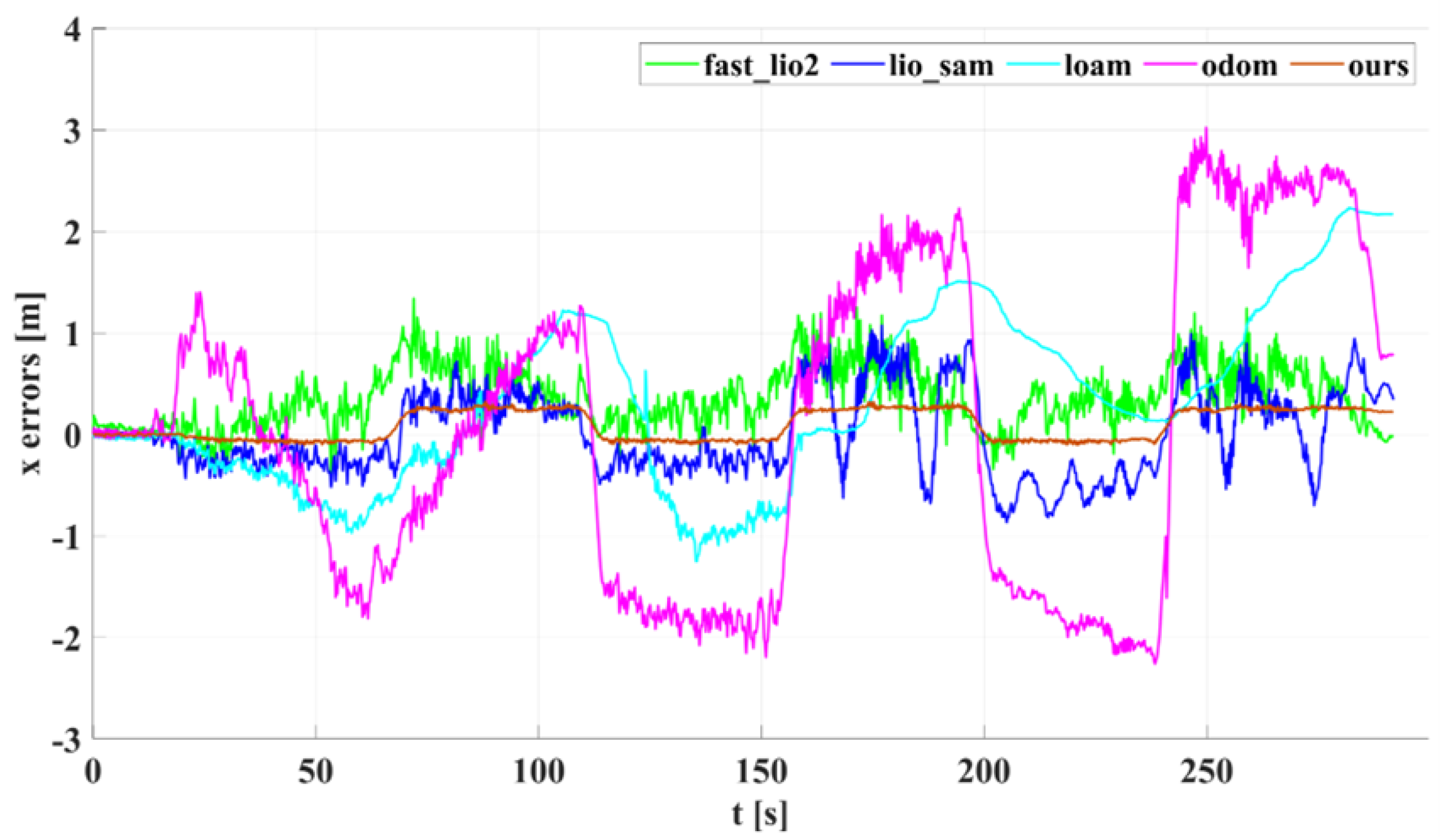
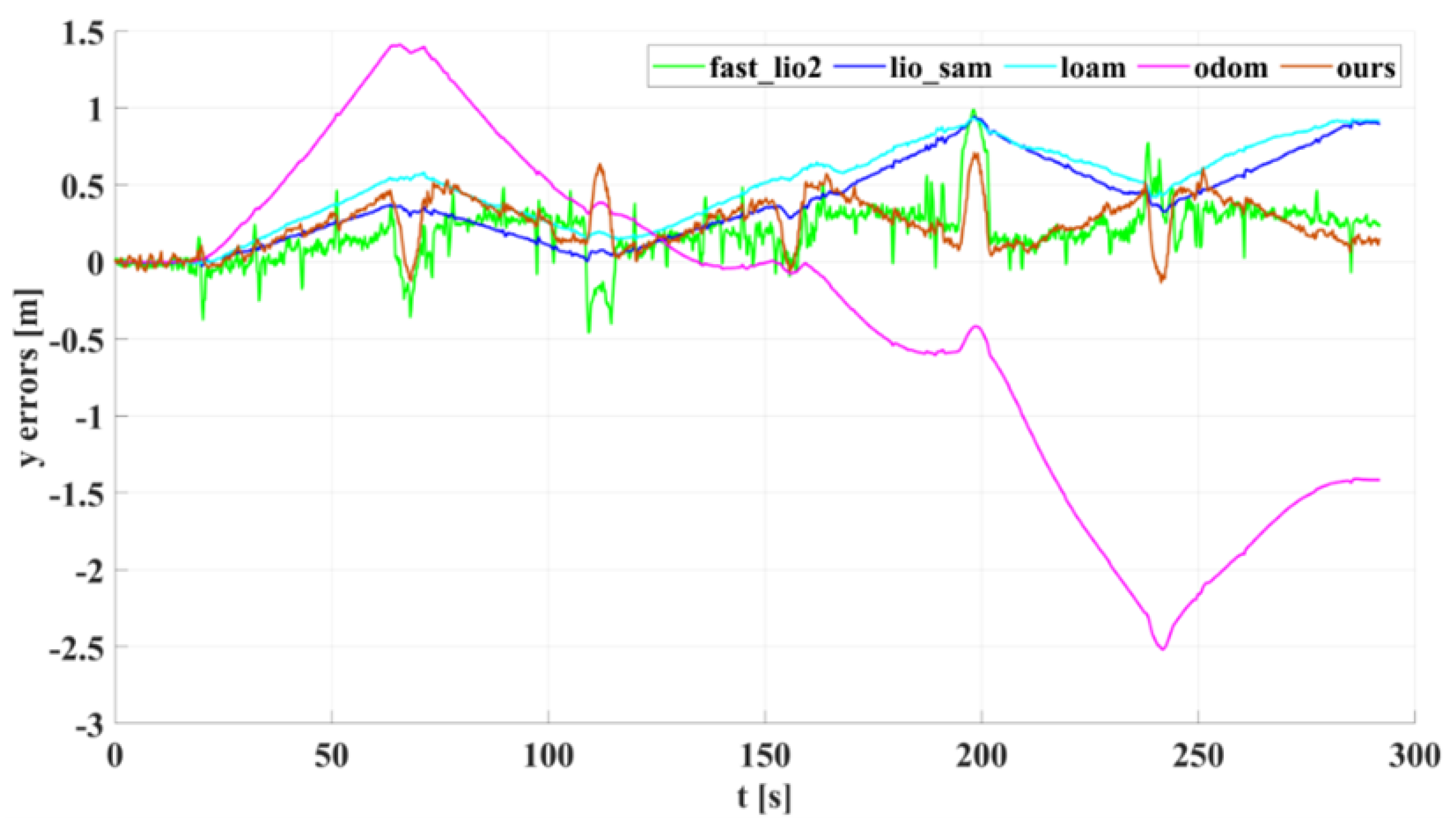
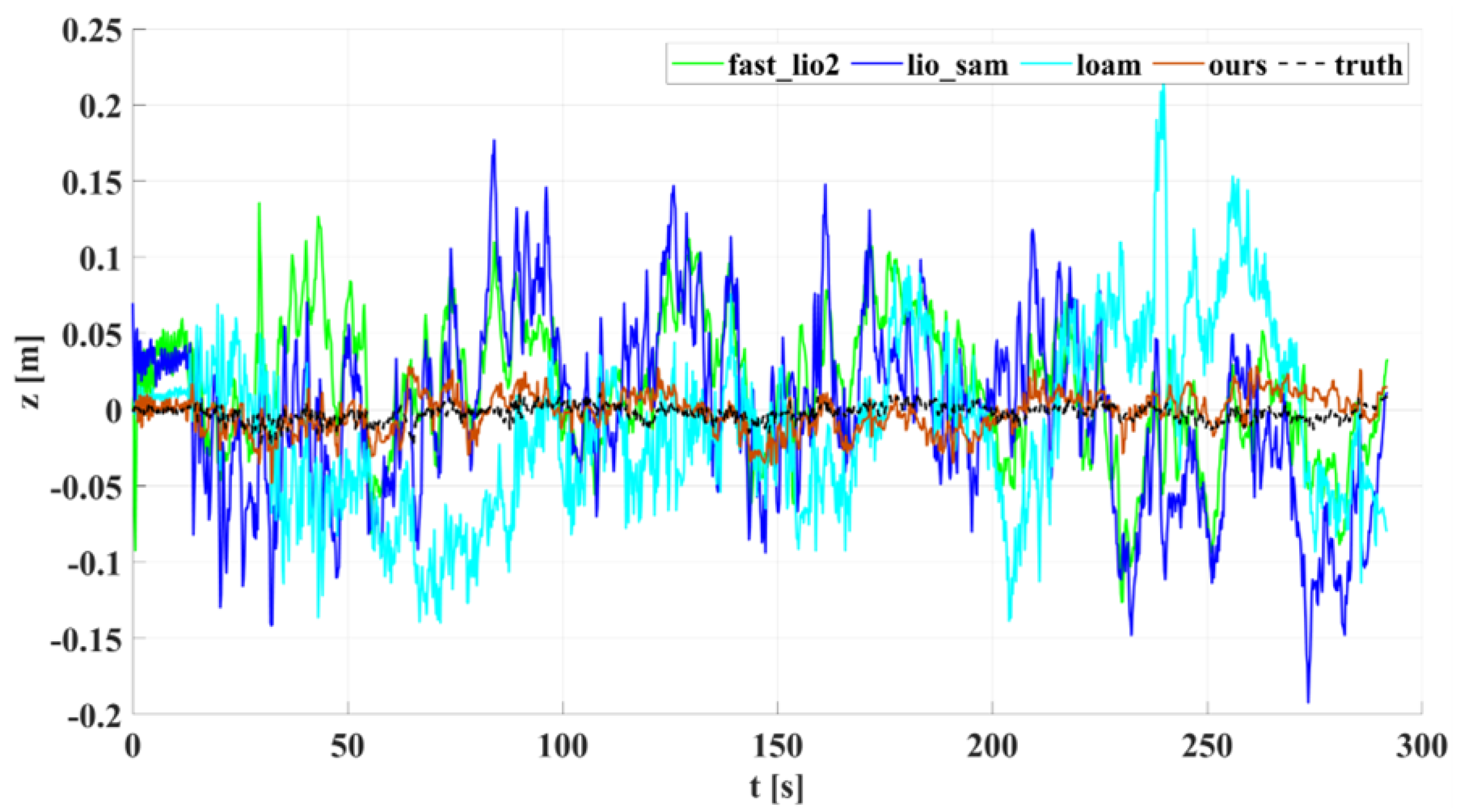
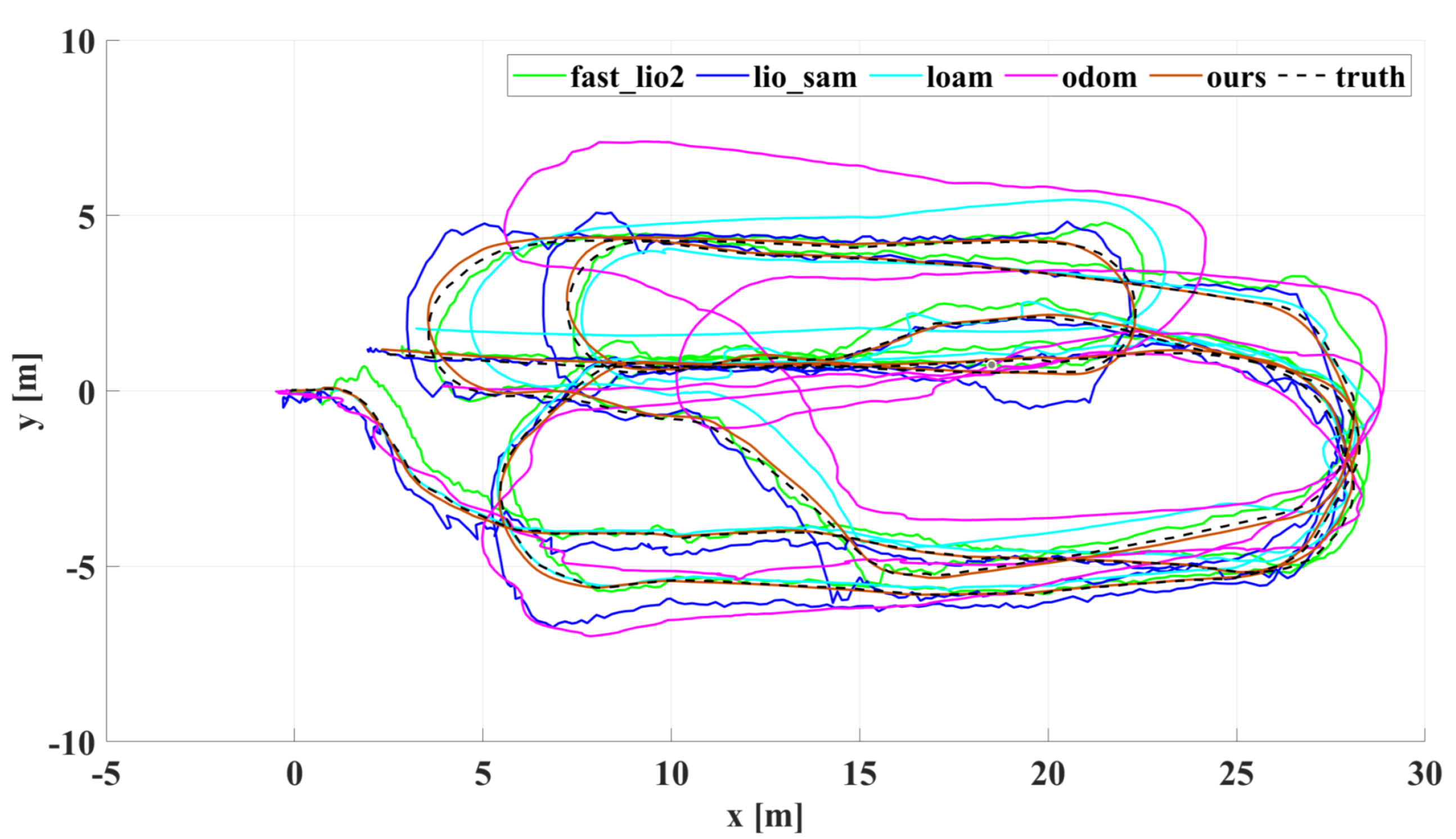
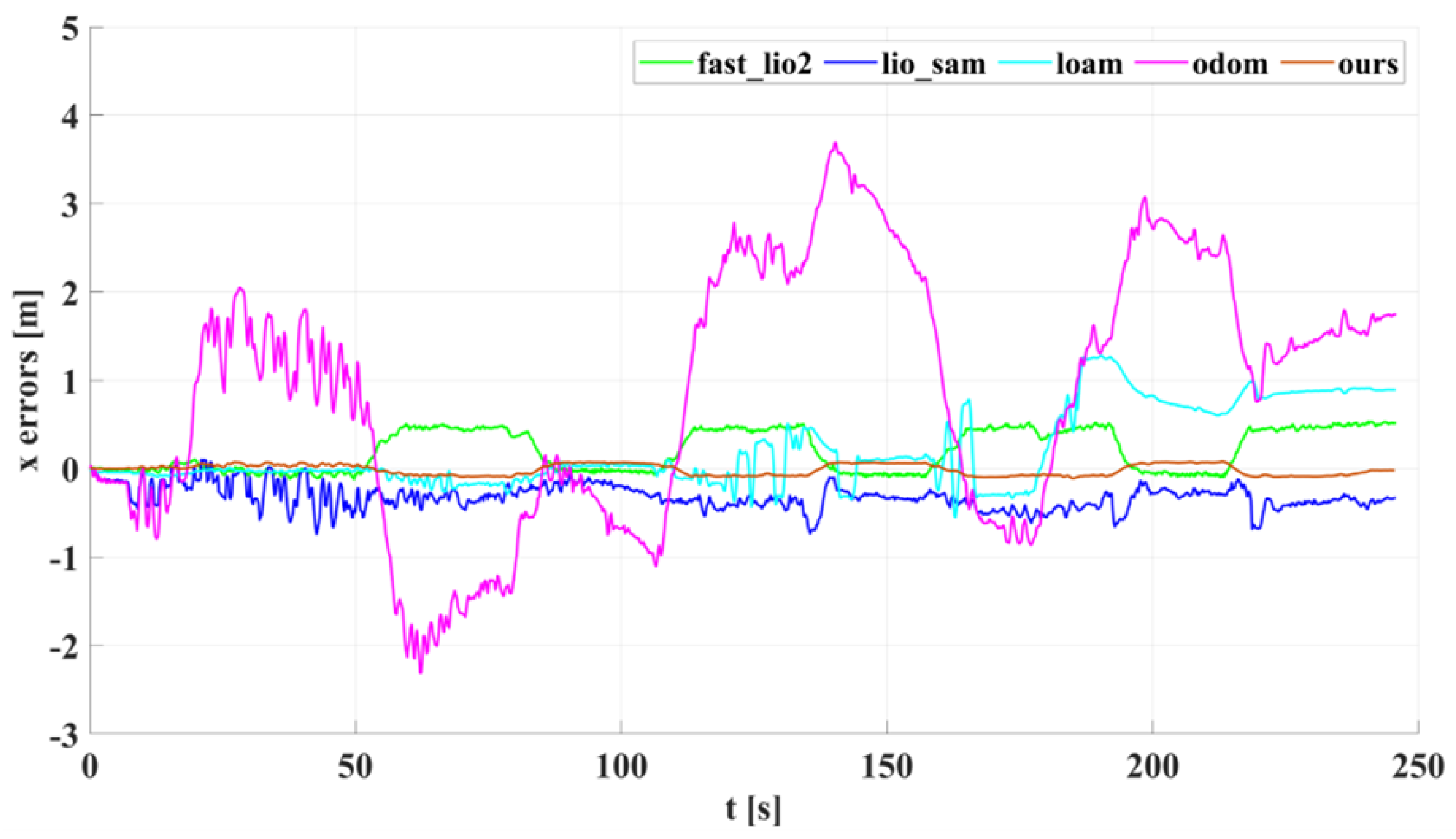
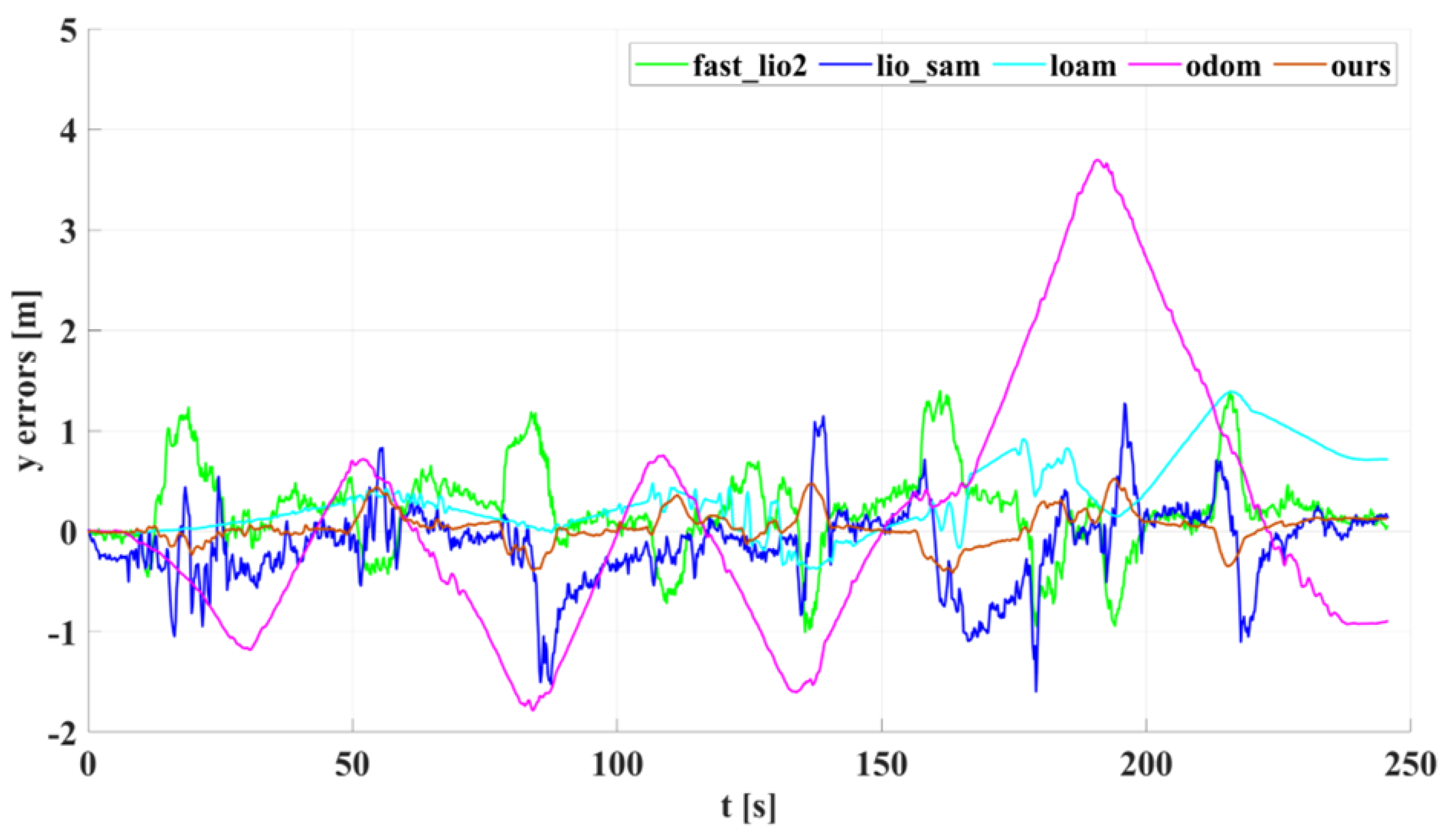
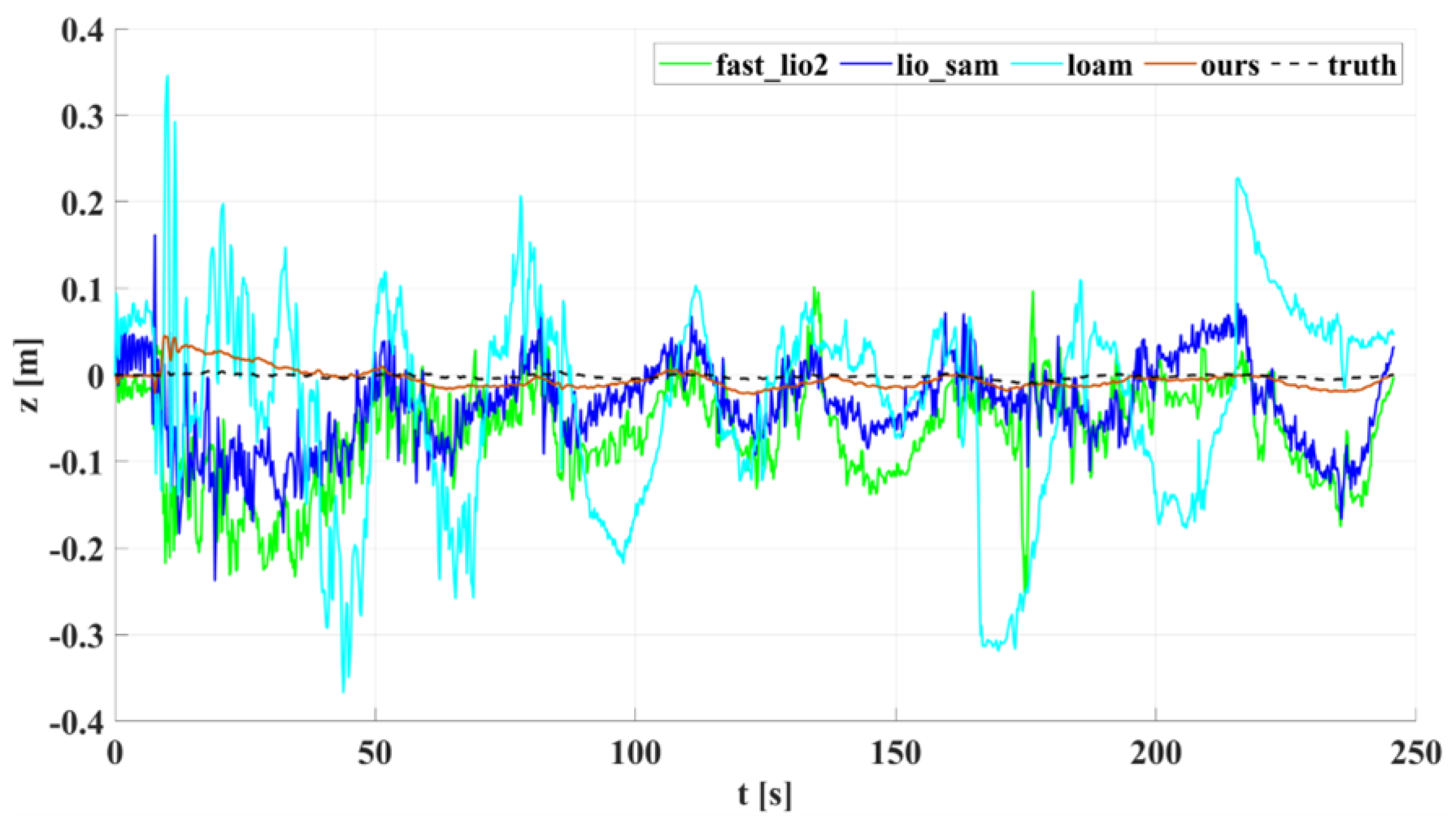
5.1. Experimental Results and Analysis of Indoor Corridors
5.2. Experimental Results and Analysis of Outdoor Structured Environment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Durrant-Whyte, H.; Bailey, T. Simultaneous localization and mapping: Part I. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2006, 13, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, T.; Durrant-Whyte, H. Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM): Part II. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2006, 13, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouman, A.; Ginting, M.F.; Alatur, N.; Palieri, M.; Fan, D.D.; Touma, T.; Kim, S.-K.; Otsu, K.; Burdick, J.; Agha-Mohammadi, A.A. Autonomous Spot: Long-Range Autonomous Exploration of Extreme Environments with Legged Locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 2518–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, M.M.J.; Tardós, D.J. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM2: An Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo, and RGB-D Cameras. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sibley, G.; Matthies, L.; Sukhatme, G. Sliding window filter with application to planetary landing. J. Field Robot. 2010, 27, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Singh, S. LOAM: Lidar Odometry and Mapping in Real-time. Robot. Sci. Syst. 2014, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B. LeGO-LOAM: Lightweight and Ground-Optimized Lidar Odometry and Mapping on Variable Terrain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4758–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, C.-L.; Xie, L. F-LOAM: Fast LiDAR Odometry and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 4390–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palieri, M.; Morrell, B.; Thakur, A.; Ebadi, K.; Nash, J.; Chatterjee, A.; Kanellakis, C.; Carlone, L.; Guaragnella, C.; Agha-Mohammadi, A.A. LOCUS: A Multi-Sensor Lidar-Centric Solution for High-Precision Odometry and 3D Mapping in Real-Time. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria-navarro, A.; Thakker, R.; Fan, D.D.; Morrell, B.; Agha-mohammadi, A.A. Towards resilient autonomous navigation of drones. In International Symposium on Robotics Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Li, P.; Shen, S. VINS-Mono: A Robust and Versatile Monocular Visual-Inertial State Estimator. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodríguez, J.J.G.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM3: An Accurate Open-Source Library for Visual, Visual–Inertial, and Multimap SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynen, S.; Achtelik, M.W.; Weiss, S.; Chli, M.; Siegwart, R. A robust and modular multi-sensor fusion approach applied to MAV navigation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 3923–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Ye, H.; Pranata, C.E.; Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M. LINS: A Lidar-Inertial State Estimator for Robust and Efficient Navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 8899–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Cai, Y.; He, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F. FAST-LIO2: Fast Direct LiDAR-Inertial Odometry. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Tightly Coupled 3D Lidar Inertial Odometry and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 3144–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Meyers, D.; Wang, W.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. LIO-SAM: Tightly-coupled Lidar Inertial Odometry via Smoothing and Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 5135–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J.; Guo, C.X.; Georgiou, G.; Roumeliotis, S.I. VINS on wheels. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 5155–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lategahn, H.; Geiger, A.; Kitt, B. Visual SLAM for autonomous ground vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortín, D.; Montiel, J.M.M. Indoor robot motion based on monocular images. Robotica 2001, 19, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konolige, K.; Grisetti, G.; Kümmerle, R.; Burgard, W.; Limketkai, B.; Vincent, R. Efficient Sparse Pose Adjustment for 2D mapping. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, W.; Kohler, D.; Rapp, H.; Andor, D. Real-time loop closure in 2D LIDAR SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.-H. Odometry-Vision-Based Ground Vehicle Motion Estimation with SE(2)-Constrained SE(3) Poses. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 49, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, Y.-H. Visual-Odometric Localization and Mapping for Ground Vehicles Using SE(2)-XYZ Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 3556–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, C.; Carlone, L.; Dellaert, F.; Scaramuzza, D. On-Manifold Preintegration for Real-Time Visual–Inertial Odometry. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
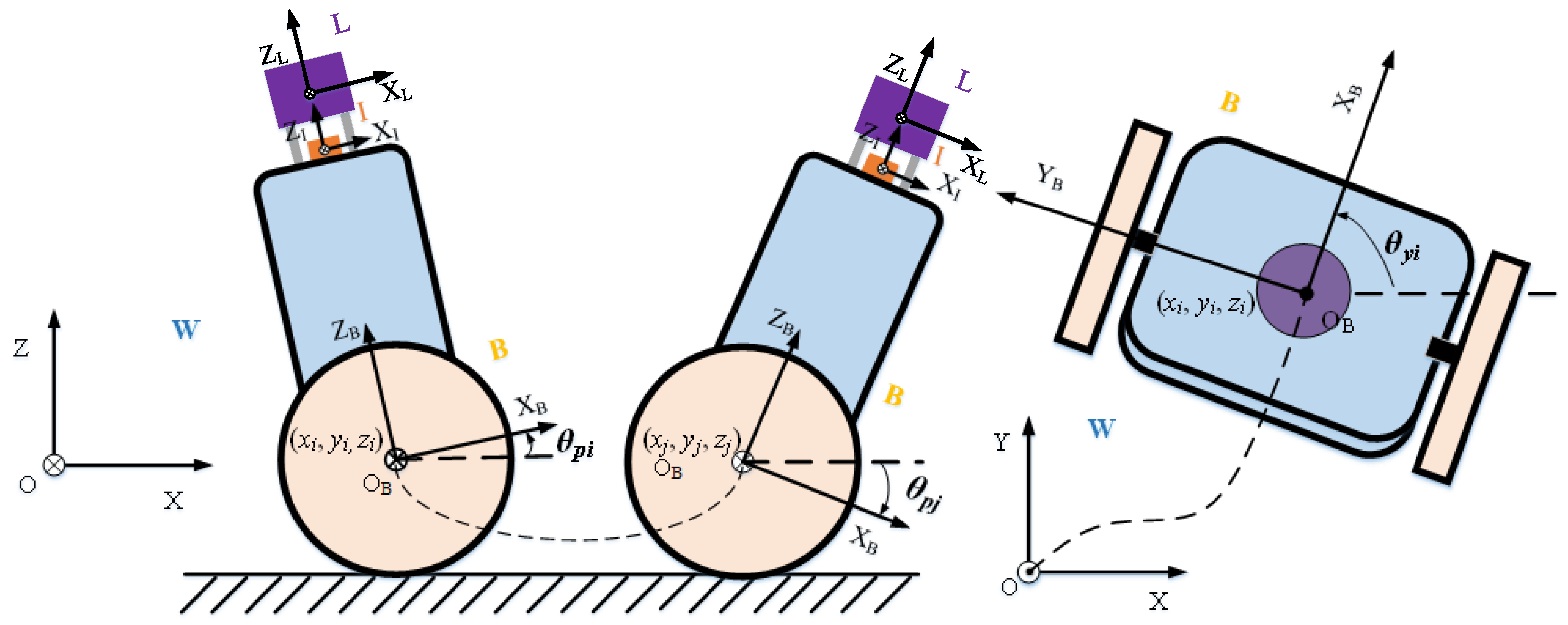



| Symbols | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| The x-axis, z-axis, and origin of the world frame | |
| The x-axis, z-axis, and origin of the robot body frame | |
| The x-axis, z-axis, and origin of the lidar frame | |
| The position of the robot in the world frame at time k (in meters) | |
| The pitch angle of the robot relative to the world frame at time k (in radians) | |
| The yaw angle of the robot relative to the world frame at time k (in radians) |
| Dimension | Fast_lio2 | Lio_sam | Loam | Odom | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4680 | 0.4111 | 0.9218 | 1.5468 | 0.1747 | |
| 0.2636 | 0.4695 | 0.5550 | 1.1035 | 0.2921 | |
| 0.0287 | 0.0420 | 0.0590 | − | 0.0176 | |
| 0.1740 | 0.1810 | 0.3170 | 0.6010 | 0.0970 |
| Dimension | Fast_lio2 | Lio_sam | Loam | Odom | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3113 | 0.3486 | 0.4770 | 1.6786 | 0.0635 | |
| 0.4549 | 0.4213 | 0.4999 | 1.2751 | 0.1625 | |
| 0.0220 | 0.0281 | 0.0282 | − | 0.0172 | |
| 0.2990 | 0.4900 | 0.6170 | 0.9368 | 0.1803 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, Y.; Zhang, S. A Novel LiDAR–IMU–Odometer Coupling Framework for Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum (TWIP) Robot Localization and Mapping with Nonholonomic Constraint Factors. Sensors 2022, 22, 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134778
Zhai Y, Zhang S. A Novel LiDAR–IMU–Odometer Coupling Framework for Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum (TWIP) Robot Localization and Mapping with Nonholonomic Constraint Factors. Sensors. 2022; 22(13):4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134778
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Yanwu, and Songyuan Zhang. 2022. "A Novel LiDAR–IMU–Odometer Coupling Framework for Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum (TWIP) Robot Localization and Mapping with Nonholonomic Constraint Factors" Sensors 22, no. 13: 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134778
APA StyleZhai, Y., & Zhang, S. (2022). A Novel LiDAR–IMU–Odometer Coupling Framework for Two-Wheeled Inverted Pendulum (TWIP) Robot Localization and Mapping with Nonholonomic Constraint Factors. Sensors, 22(13), 4778. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134778






