Study on the Method of Charge Accumulation Suppression of Electrostatic Suspended Accelerometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Model of Charge Distribution and Electrostatic Force in ESA
2.2. Method of Suppressing Charge Accumulation
2.2.1. Charge Noise under AC Signals
2.2.2. Scheme of Suppressing Charge Noise by Actuation with Combined Waveform
2.3. Simulation
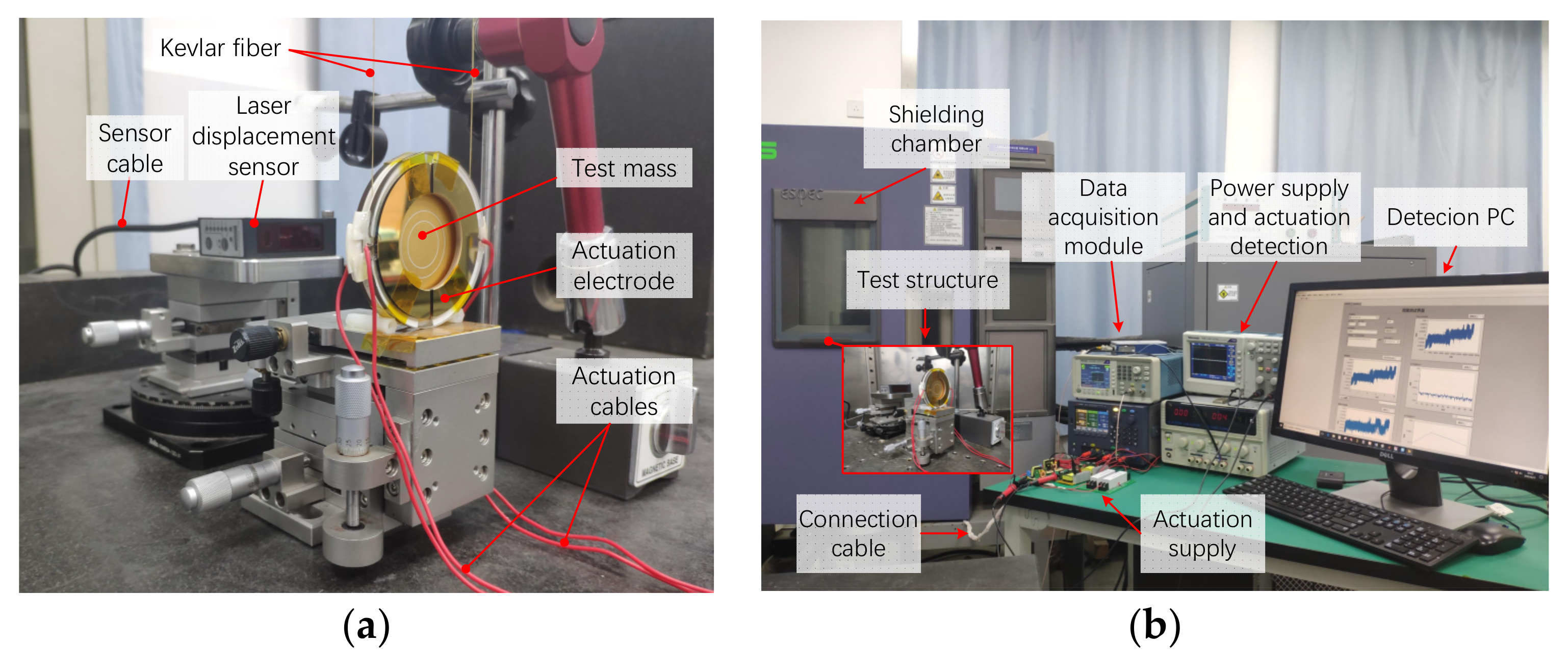
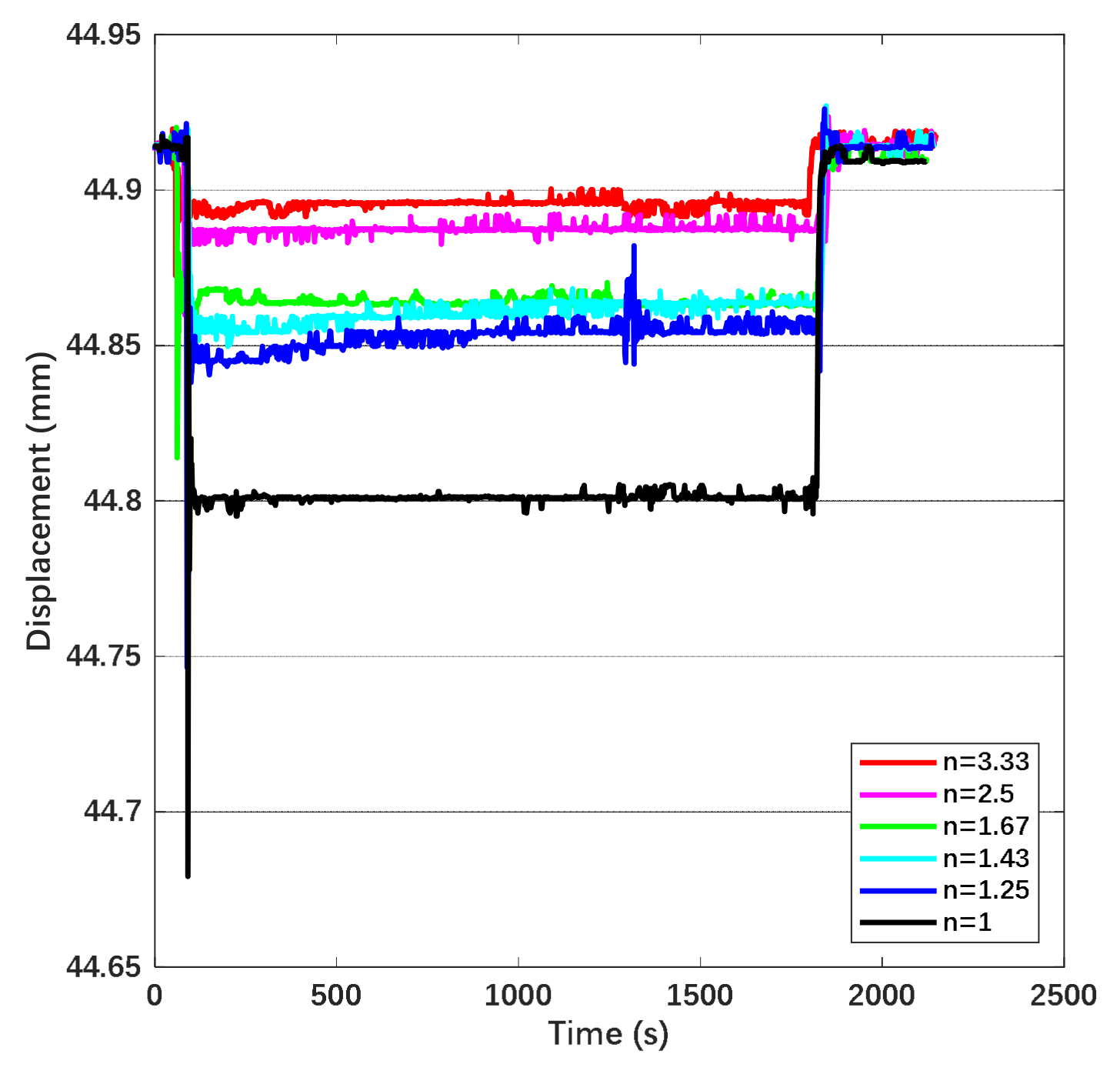
3. Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seel, T.; Kok, M.; McGinnis, R.S. Inertial Sensors—Applications and Challenges in a Nutshell. Sensors 2020, 20, 6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, Q.; Qin, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L. Structural Design and Optimization of a Resonant Micro-Accelerometer Based on Electrostatic Stiffness by an Improved Differential Evolution Algorithm. Micromachines 2022, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, C.; Xie, J. A MEMS Resonant Accelerometer With High Relative Sensitivity Based on Sensing Scheme of Electrostatically Induced Stiffness Perturbation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2021, 30, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; He, C.; Wang, R.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W. A Mathematical Model of a Piezo-Resistive Eight-Beam Three-Axis Accelerometer with Simulation and Experimental Validation. Sensors 2018, 18, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Gao, S.; Niu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, P. Optimal Design of High-g MEMS Piezoresistive Accelerometer Based on Timoshenko Beam Theory. Microsyst. Technol. 2018, 24, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesing, A.L.; Alves, F.D.P.; Paul, S.; Cordioli, J.A. On the Design of a MEMS Piezoelectric Accelerometer Coupled to the Middle Ear as an Implantable Sensor for Hearing Devices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touboul, P.; Foulon, B.; Willemenot, E. Electrostatic Space Accelerometers for Present and Future Missions. Acta Astronaut. 1999, 45, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Qu, S.; Tan, D.; Tu, H.; Wu, S.; Yin, H.; Li, H.; et al. Research and Development of Electrostatic Accelerometers for Space Science Missions at HUST. Sensors 2017, 17, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Huang, T.; Jin, Y.; Pan, J.; Song, K. Fusion of High-Dynamic and Low-Drift Sensors Using Kalman Filters. Sensors 2019, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhiya, R.; Agarwal, P.; Badjatya, S.; Garg, M.; Gaikwad, P.; Sinha, S.; Singh, A.K.; Gopal, R. Design, Modelling and System Level Simulations of DRIE-Based MEMS Differential Capacitive Accelerometer. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3521–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Bai, Y.; Hu, M.; Qu, S.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Z. Amplitude Stability Analysis and Experimental Investigation of an AC Excitation Signal for Capacitive Sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 309, 112020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armano, M.; Audley, H.; Auger, G.; Baird, J.T.; Binetruy, P.; Born, M.; Bortoluzzi, D.; Brandt, N.; Bursi, A.; Caleno, M.; et al. Charge-Induced Force Noise on Free-Falling Test Masses: Results from LISA Pathfinder. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafry, Y.; Sumner, T.J.; Buchman, S. Electrostatic Charging of Space-Borne Test Bodies Used in Precision Experiments. Class. Quantum Gravity 1996, 13, A97–A106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, T.; Araújo, H.; Davidge, D.; Howard, A.; Lee, C.; Rochester, G.; Shaul, D.; Wass, P. Description of Charging/Discharging Processes of the LISA Sensors. Class. Quantum Gravity 2004, 21, S597–S602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Bortoluzzi, D.; Cavalleri, A.; Carbone, L.; Lio, M.D.; Dolesi, R.; Fontana, G.; Hoyle, C.D.; Hueller, M.; Vitale, S. Position Sensors for Flight Testing of LISA Drag-Free Control. In Proceedings of the Gravitational-Wave Detection, SPIE, Bellingham, WA, USA, 26 February 2003; Volume 4856, pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, L.; Cavalleri, A.; Dolesi, R.; Hoyle, C.D.; Hueller, M.; Vitale, S.; Weber, W.J. Achieving Geodetic Motion for LISA Test Masses: Ground Testing Result. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 151101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumner, T.J.; Shaul, D.N.A.; Schulte, M.O.; Waschke, S.; Hollington, D.; Araújo, H. LISA and LISA Pathfinder Charging. Class. Quantum Gravity 2009, 26, 094006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, H.M.; Howard, A.; Davidge, D.; Sumner, T.J. Charging of Isolated Proof Masses in Satellite Experiments Such as LISA. In Proceedings of the Gravitational-Wave Detection, SPIE, Bellingham, WA, USA, 26 February 2003; Volume 4856, pp. 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Christophe, B.; Marque, J.P.; Foulon, B. In-Orbit Data Verification of the Accelerometers of the ESA GOCE Mission. In Proceedings of the SF2A-2010: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the French Society of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Marseille, France, 21–24 June 2010; Volume 1, p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Reigber, C.; Lühr, H.; Schwintzer, P. CHAMP Mission Status. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 30, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Watkins, M.; Reigber, C. The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment: Mission Overview and Early Results. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hewitson, M.; Danzmann, K.; Grote, H.; Hild, S.; Hough, J.; Lück, H.; Rowan, S.; Smith, J.R.; Strain, K.A.; Willke, B. Charge Measurement and Mitigation for the Main Test Masses of the GEO 600 Gravitational Wave Observatory. Class. Quantum Gravity 2007, 24, 6379–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchman, S.; Byer, R.L.; Gill, D.; Robertson, N.A.; Sun, K.-X. Charge Neutralization in Vacuum for Non-Conducting and Isolated Objects Using Directed Low-Energy Electron and Ion Beams. Class. Quantum Gravity 2008, 25, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Bai, Y.; Hong, W.; Sumner, T.J.; Zhou, Z. A Charge Control Method for Space-Mission Inertial Sensor Using Differential UV LED Emission. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 124502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Bai, Y.Z.; Zhou, Z.B.; Yin, H.; Tan, D.Y.; Luo, J. Measurement of the Effect of a Thin Discharging Wire for an Electrostatic Inertial Sensor with a High-Quality-Factor Pendulum. Class. Quantum Gravity 2012, 29, 055010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Bai, Y.; Hong, W.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Sumner, T.J.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z. Investigation of Charge Management Using UV LED Device with a Torsion Pendulum for TianQin. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollington, D.; Baird, J.T.; Sumner, T.J.; Wass, P.J. Characterising and Testing Deep UV LEDs for Use in Space Applications. Class. Quantum Gravity 2015, 32, 235020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, D.N.A.; Araújo, H.M.; Rochester, G.K.; Sumner, T.J.; Wass, P.J. Evaluation of Disturbances Due to Test Mass Charging for LISA. Class. Quantum Gravity 2005, 22, S297–S309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Carbone, L.; Cavalleri, A.; Dolesi, R.; Hoyle, C.D.; Hueller, M.; Vitale, S. Possibilities for Measurement and Compensation of Stray DC Electric Fields Acting on Drag-Free Test Masses. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, F.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X. Design, Fabrication and Levitation Experiments of a Micromachined Electrostatically Suspended Six-Axis Accelerometer. Sensors 2011, 11, 11206–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bai, Y.; Hu, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Z. A Novel Controller Design for the Next Generation Space Electrostatic Accelerometer Based on Disturbance Observation and Rejection. Sensors 2017, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charge and Current Distributions. In Classical Electromagnetic Theory; Vanderlinde, J. (Ed.) Fundamental Theories of Physics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 33–48. ISBN 978-1-4020-2700-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sumner, T.J.; Mueller, G.; Conklin, J.W.; Wass, P.J.; Hollington, D. Charge Induced Acceleration Noise in the LISA Gravitational Reference Sensor. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 045010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Ye, L.; Huang, T.; Yang, Z.; Song, K. The Dead Time Characterization Method of Quartz Flexure Accelerometers Using Monotonicity Number. Sensors 2019, 19, 3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Huang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Song, K. Cold Starting Temperature Time-Related Compensation Model of Inertial Sensors Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 065106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, T.; Ye, L.; Song, K. Cold Starting Temperature Drift Modeling and Compensation of Micro-Accelerometer Based on High-Order Fourier Transform. Micromachines 2022, 13, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wu, S.C.; Zhou, Z.B.; Bai, Y.Z.; Hu, M.; Luo, J. Design and Validation of a High-Voltage Levitation Circuit for Electrostatic Accelerometers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 125004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaver, A.E. An Equation for Charge Decay Valid in Both Conductors and Insulators. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0801.4182. [Google Scholar]
- Pollack, S.E.; Schlamminger, S.; Gundlach, J.H. Temporal Extent of Surface Potentials between Closely Spaced Metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 071101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charge Management for Lisa and Lisa Pathfinder. Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/epdf/10.1142/S0218271808012656 (accessed on 7 November 2021).
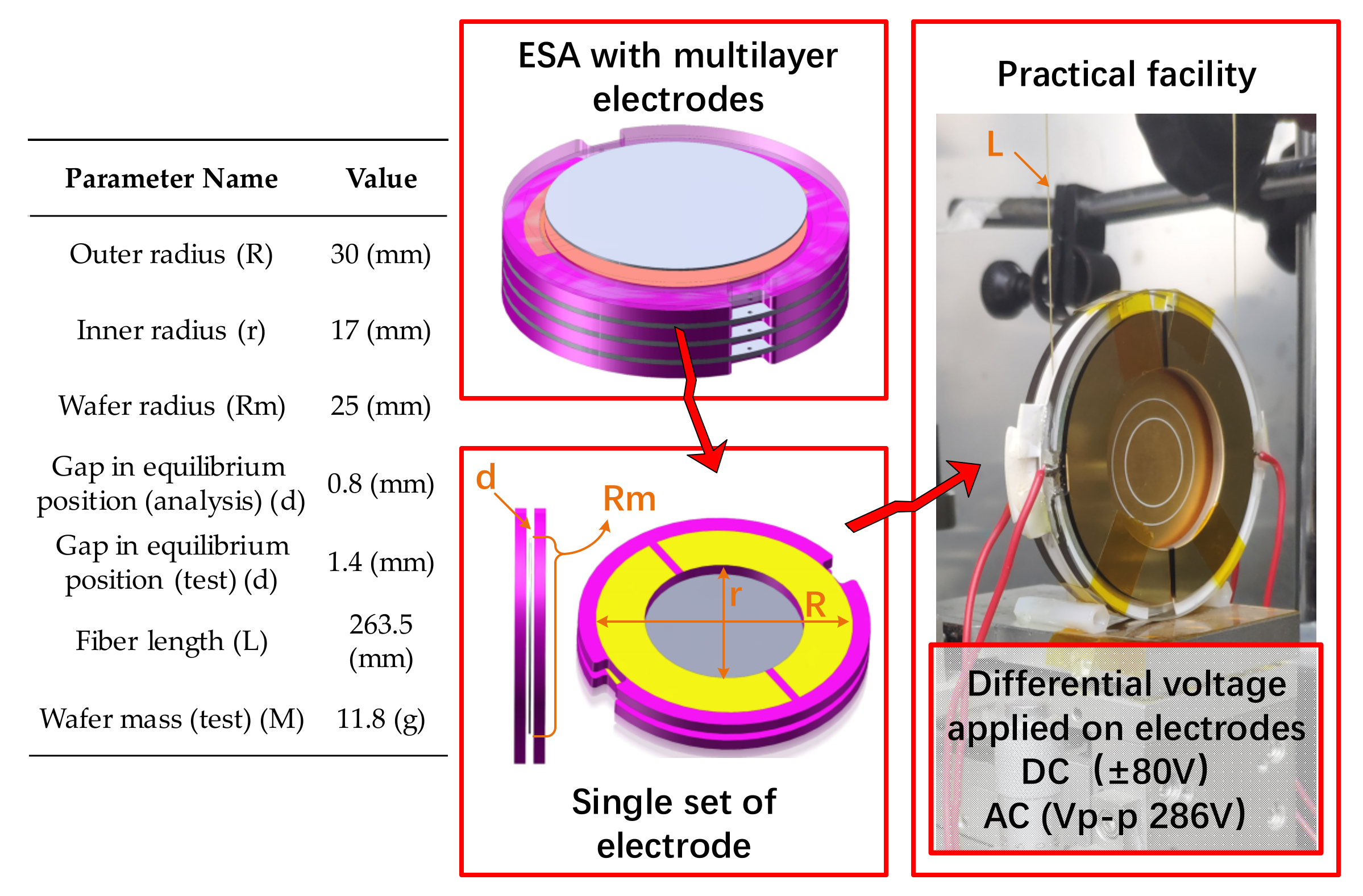
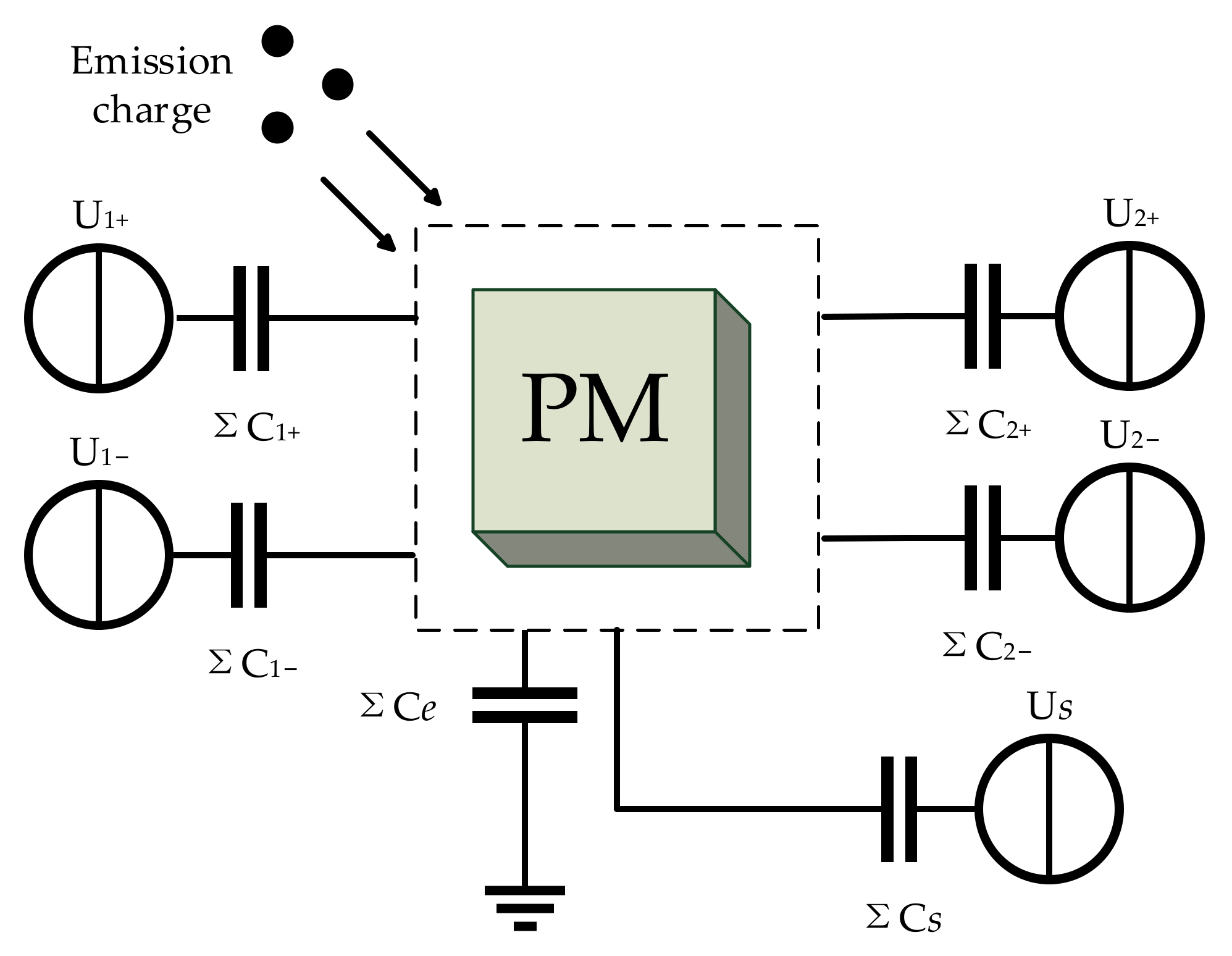





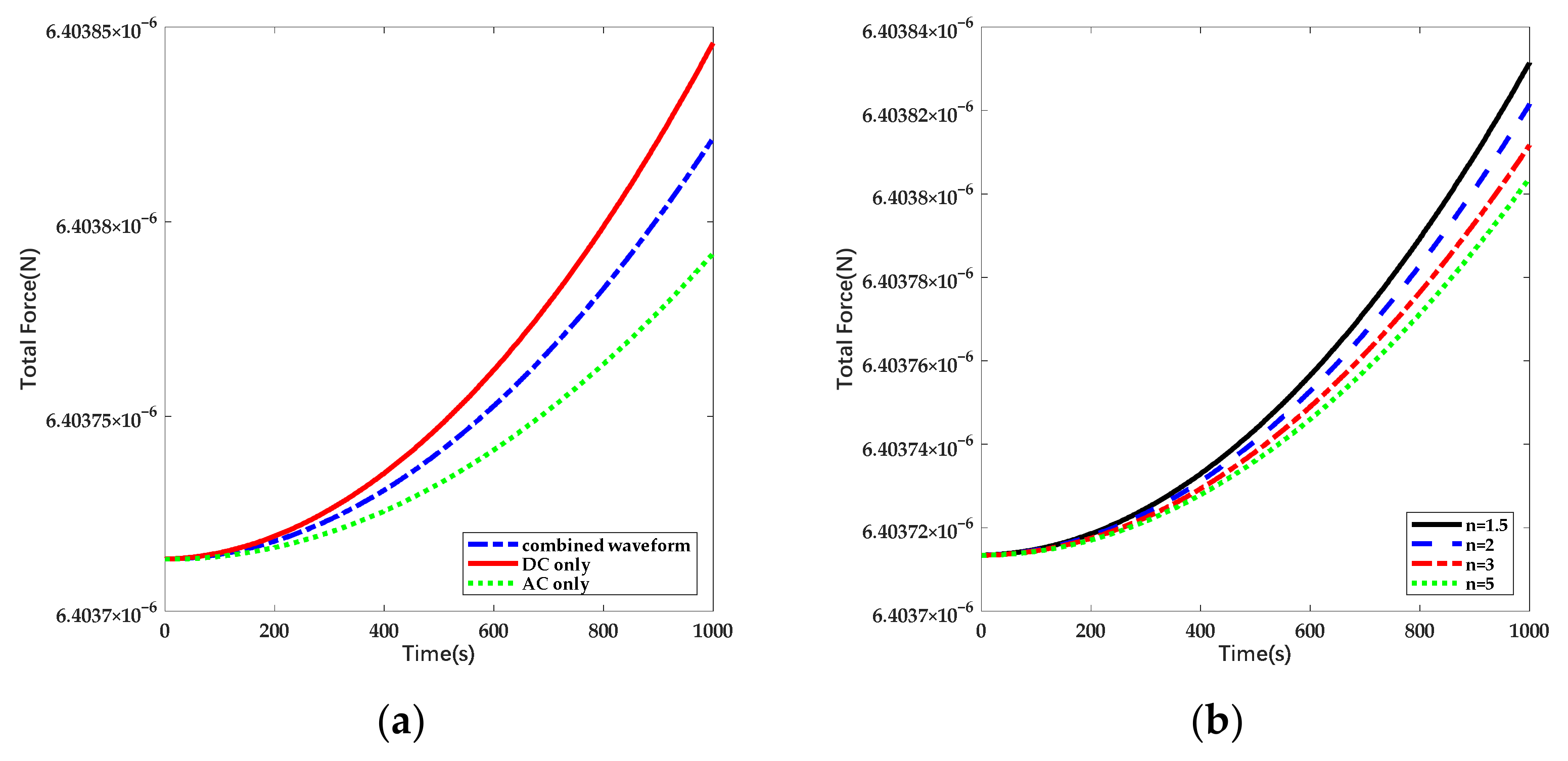

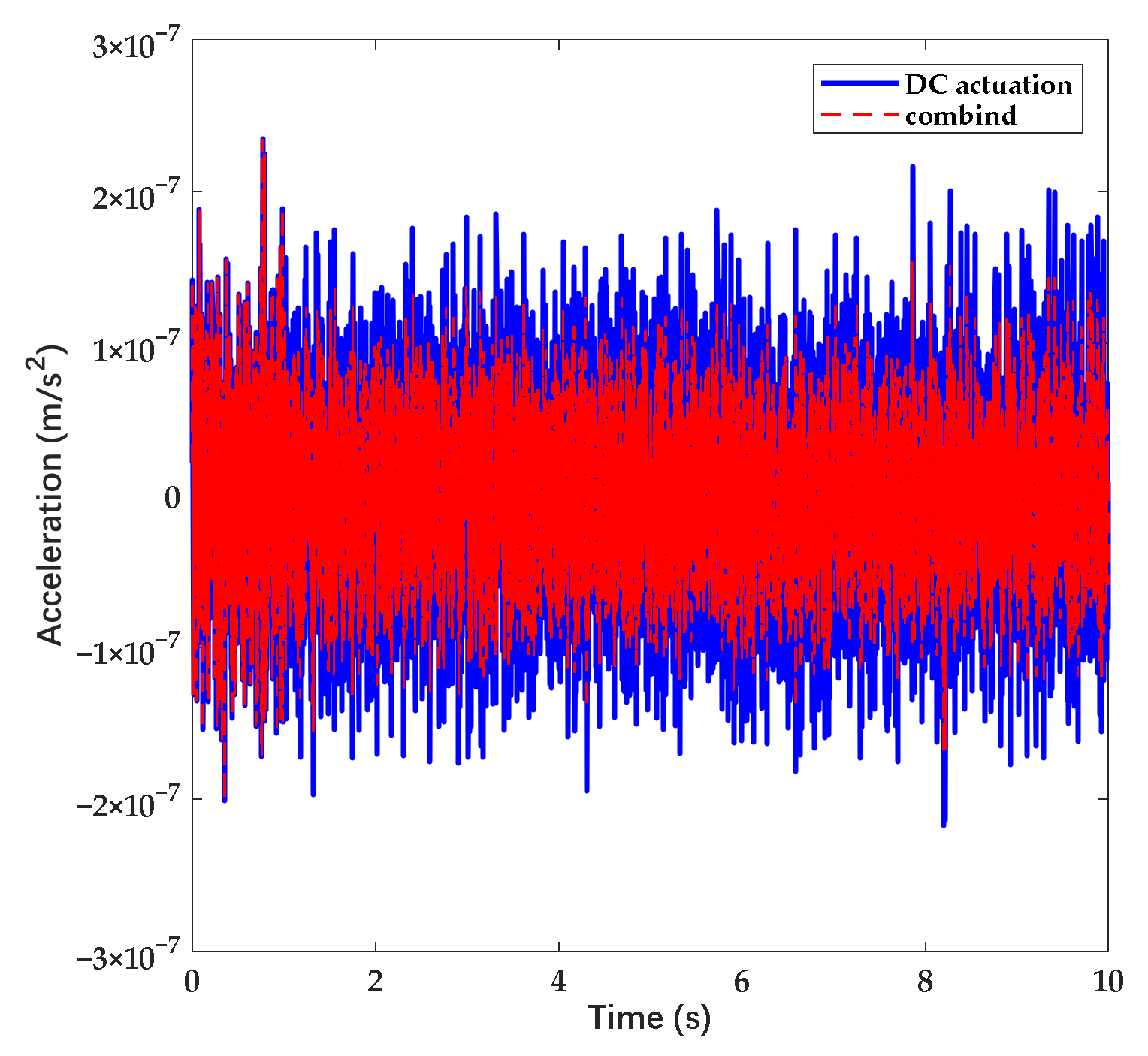
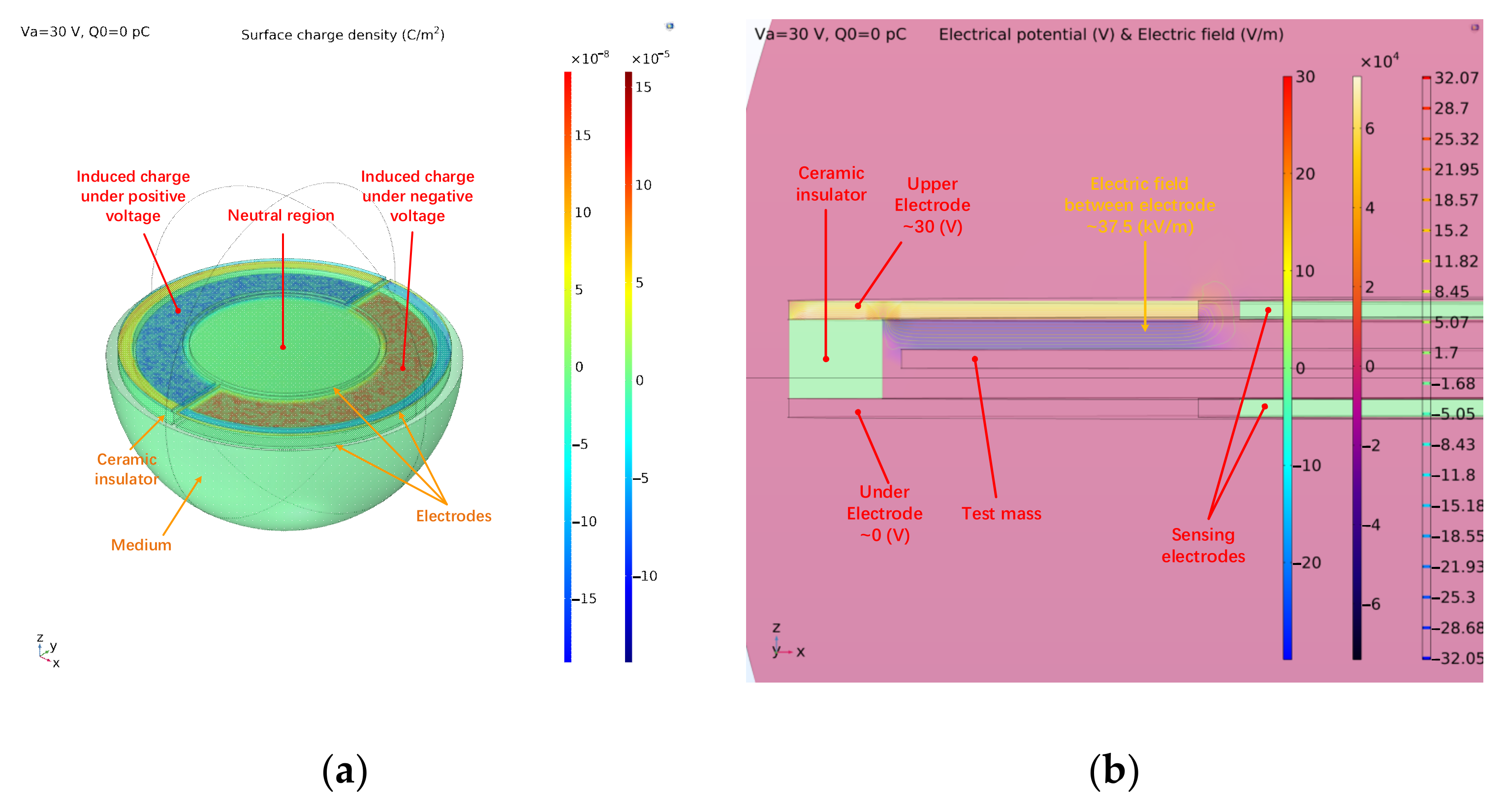
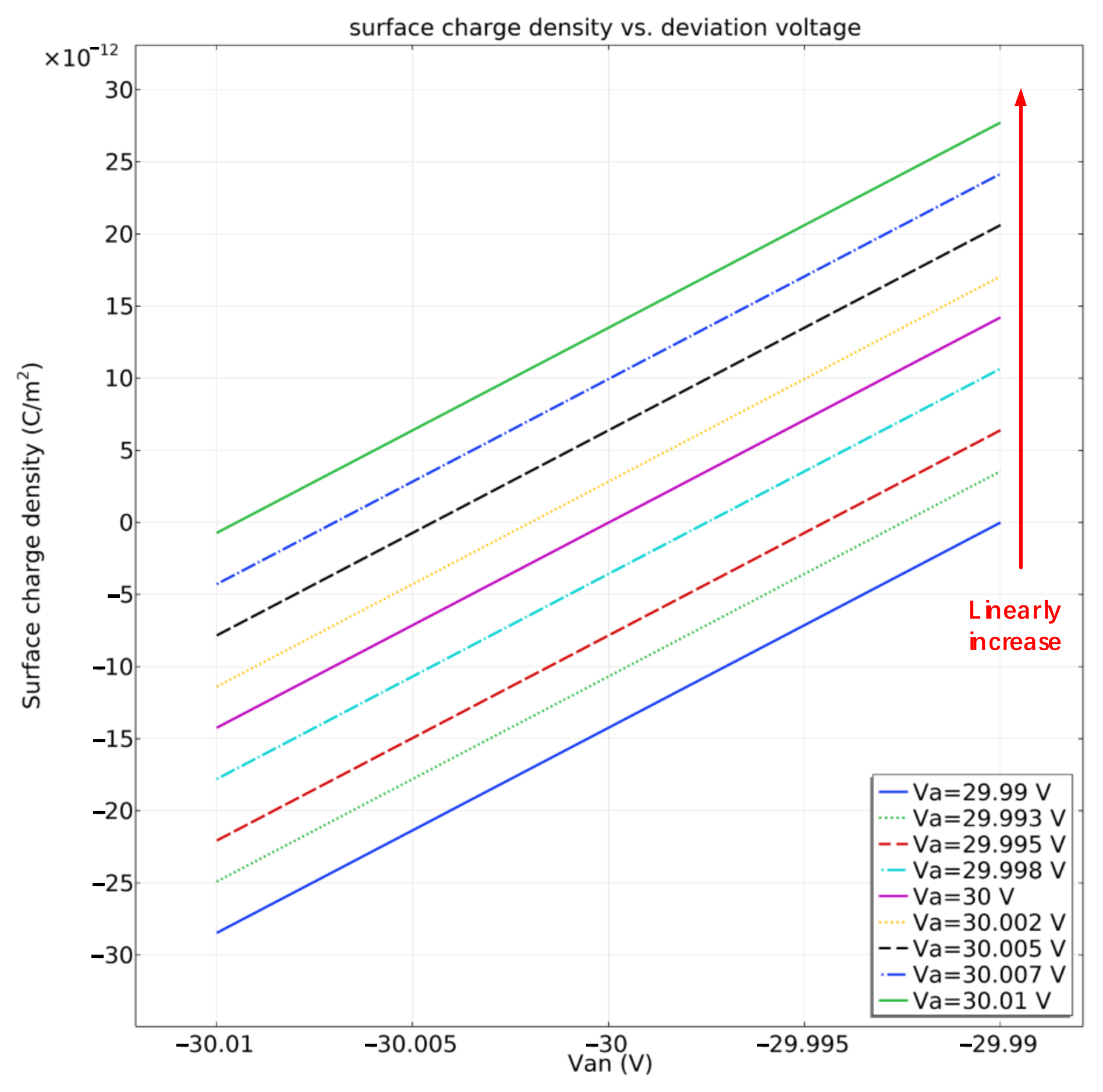
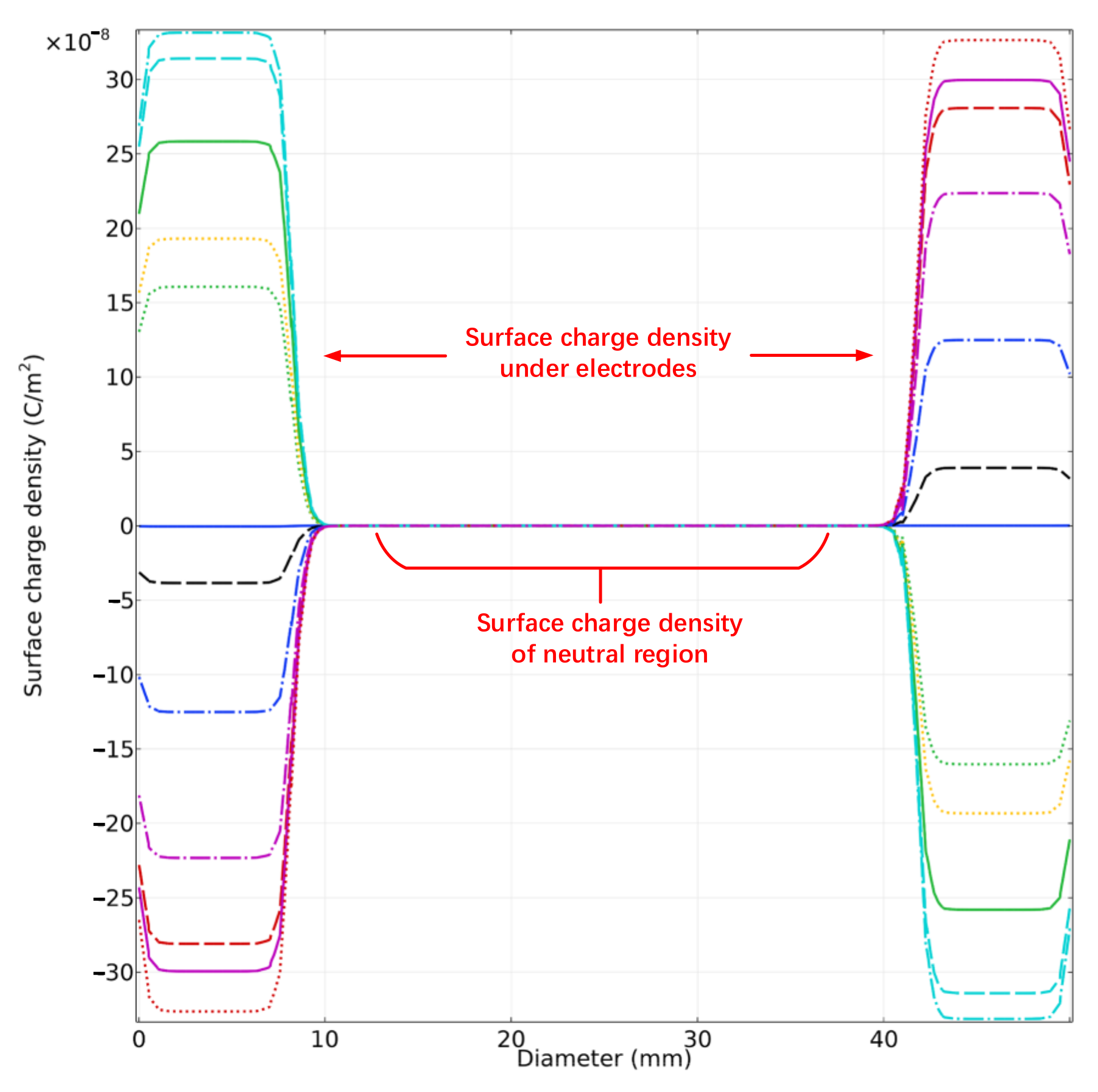
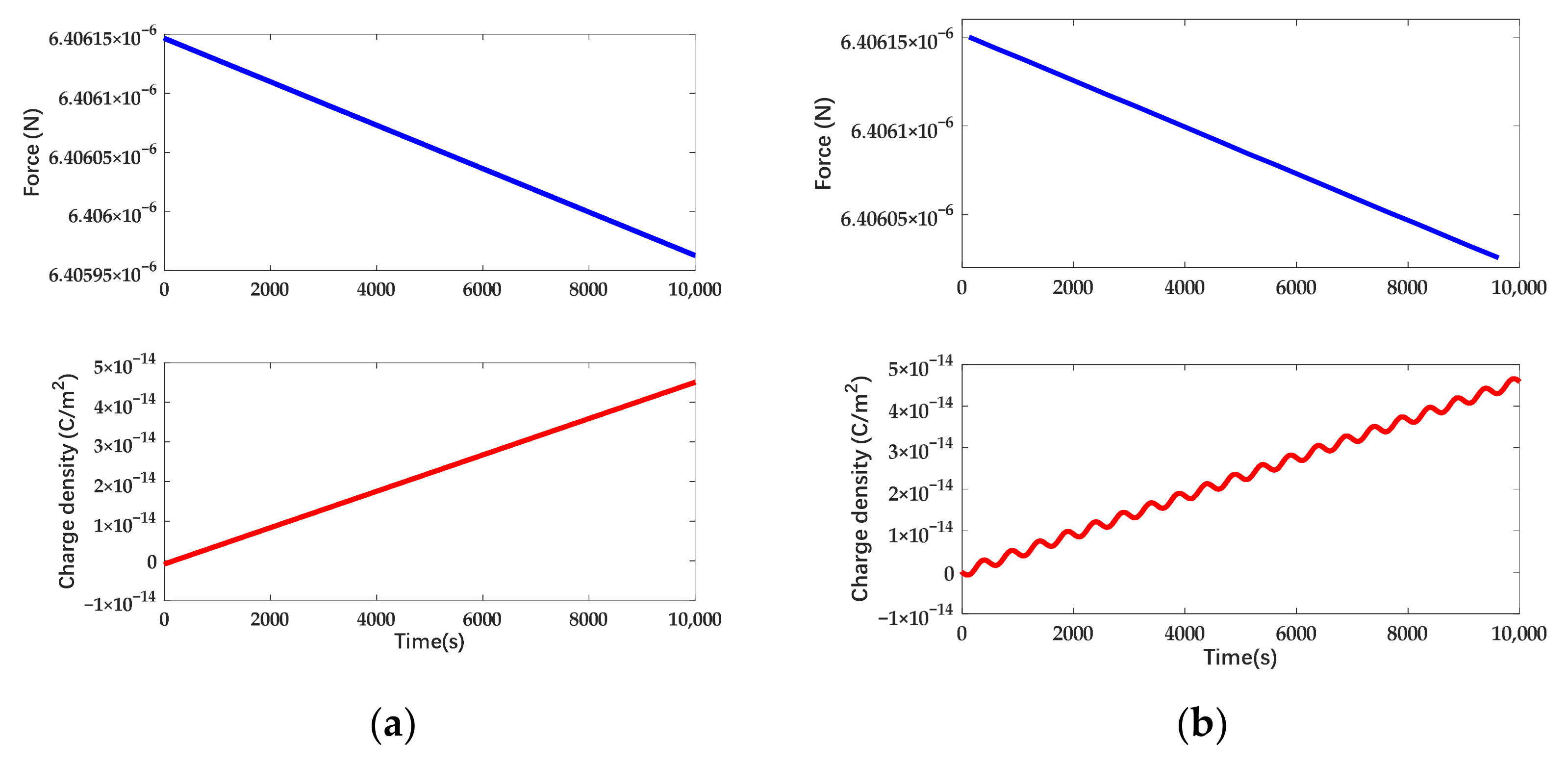
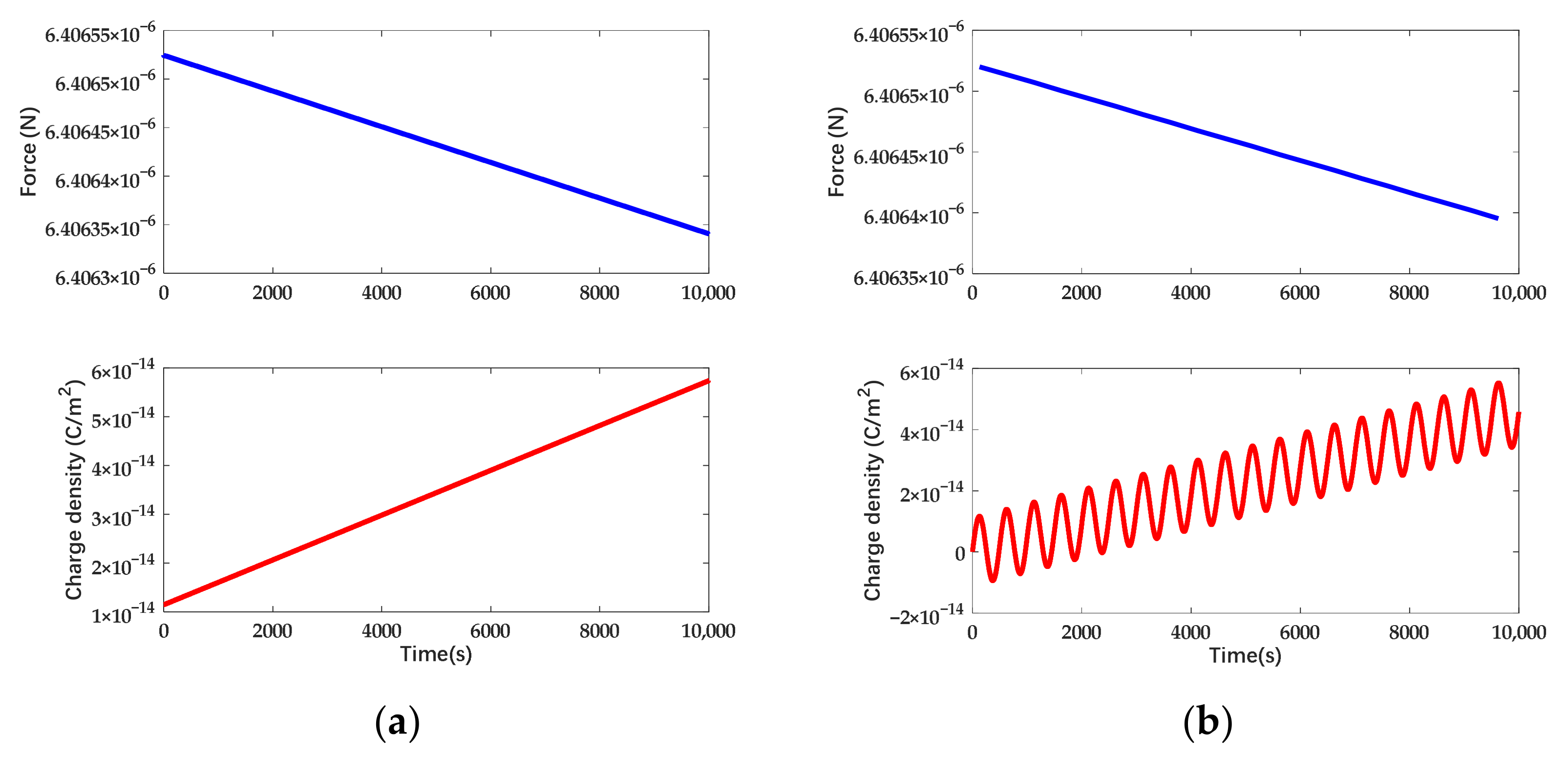
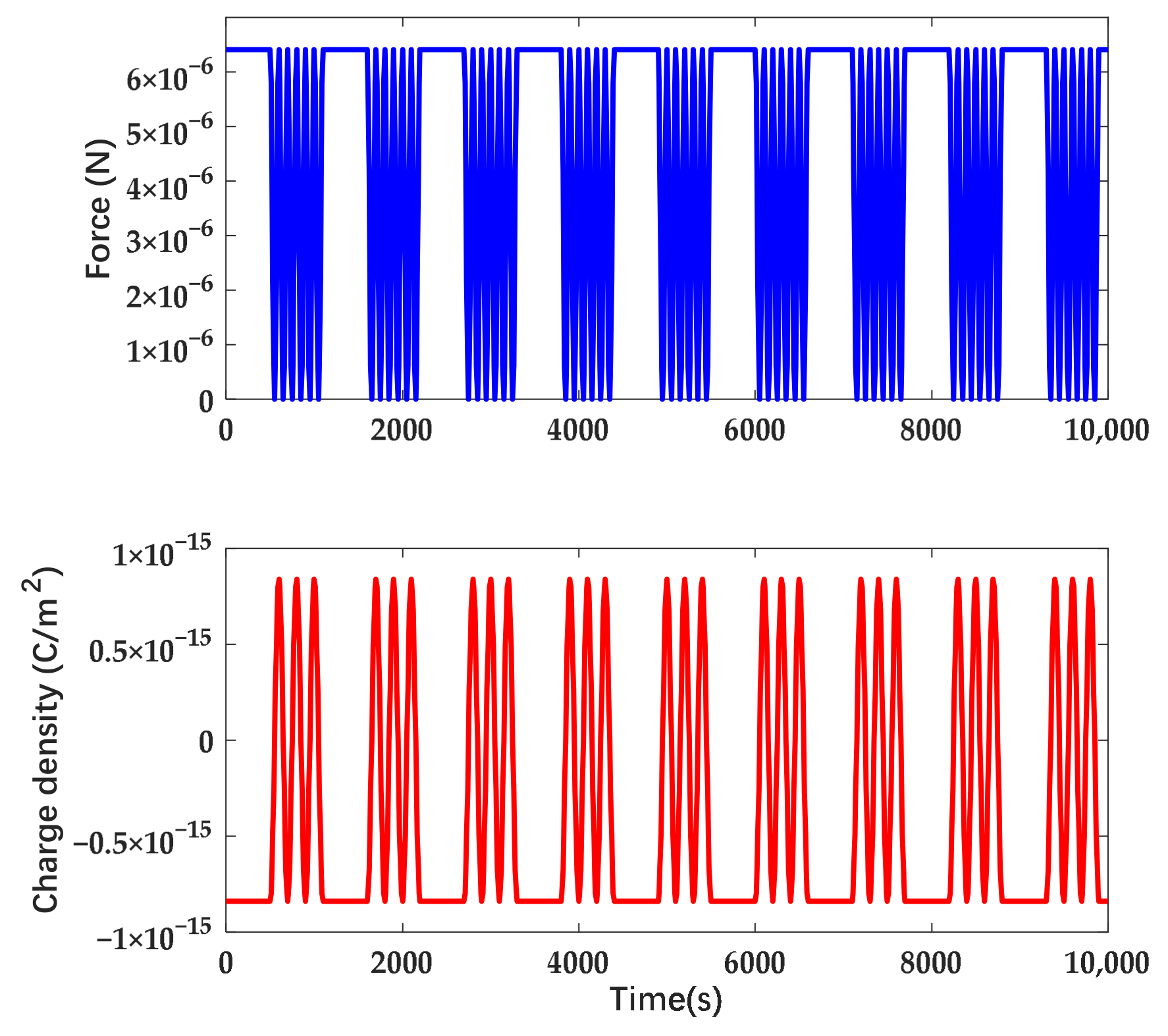
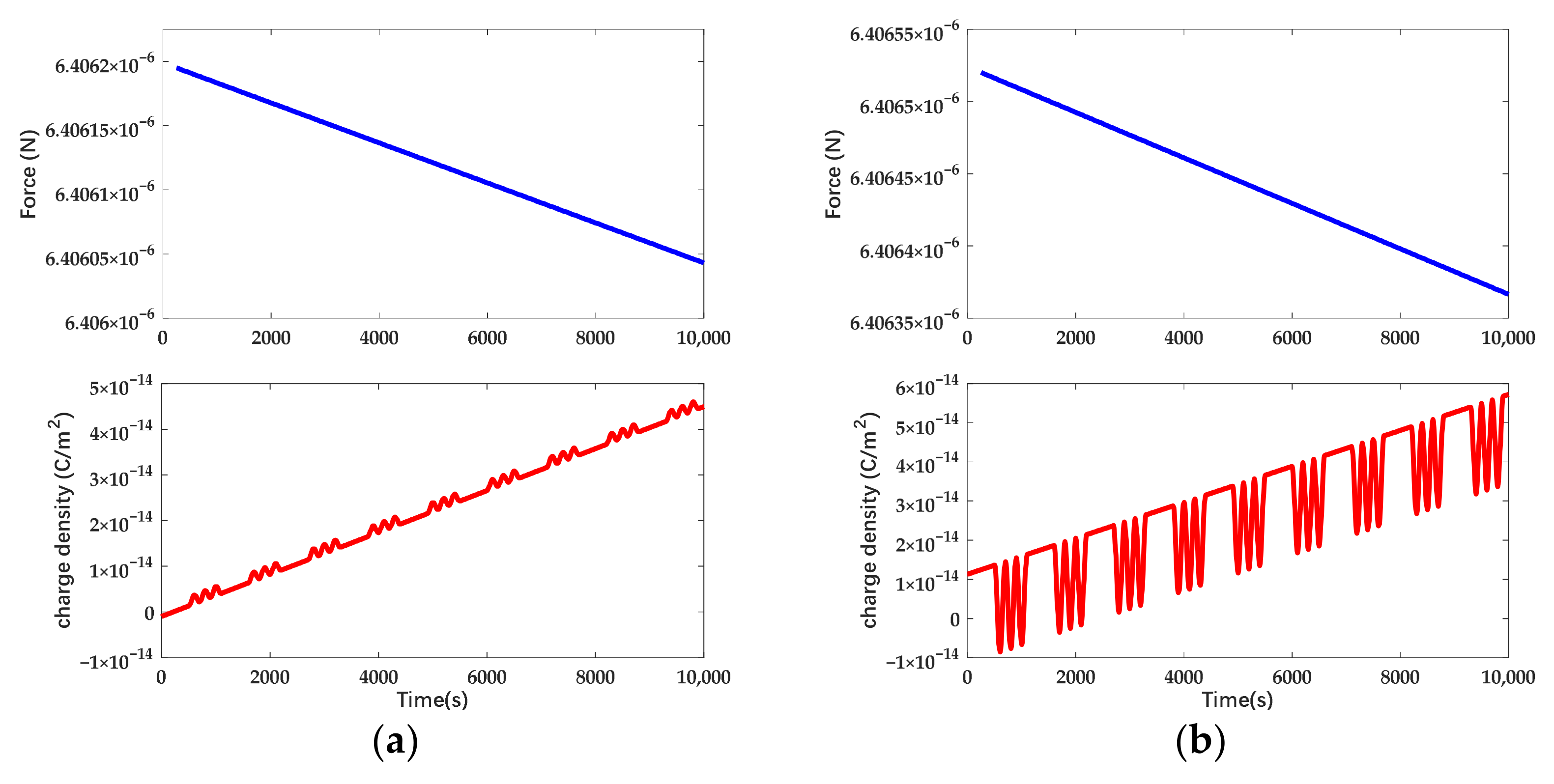


| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Actuation capacitance | 11.384 pF |
| Total capacitance | 40.56 pF |
| Distance | 0.8 mm |
| DC Actuation voltage | 30 V |
| Amplitude of AC signal | 42.4 V |
| Actuation frequency | 500 Hz |
| Voltage deviation | 1 mV |
| Form of Actuation | Deviation Voltage (V) | Suppression Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| DC actuation | 0/0.001/0.05 | 0% |
| AC actuation | 0 | 32% |
| AC actuation | 0.001 | 33.5% |
| AC actuation | 0.05 | 33.6% |
| Combined waveform (n = 2) | 0 | 17.8% |
| Combined waveform (n = 2) | 0.001 | 21.1% |
| Combined waveform (n = 2) | 0.05 | 21.3% |
| Combined waveform (n = 3) | 0.05 | 23.9% |
| Combined waveform (n = 1.5) | 0.05 | 14.6% |
| Coefficient | Time Drift | Equivalent Deposited Charge | Suppression Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00455 mm/h | 13.015 Pc | 0% |
| 1.25 | 0.0042 mm/h | 12.504 Pc | 3.93 % |
| 1.43 | 0.004 mm/h | 12.203 Pc | 6.24 % |
| 1.67 | 0.003 mm/h | 10.568 Pc | 18.8% |
| 2.5 | 0.0021 mm/h | 8.842 Pc | 32.1% |
| 3.33 | 0.0015 mm/h | 7.473 Pc | 42.6% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, B.; Ye, L.; Song, K. Study on the Method of Charge Accumulation Suppression of Electrostatic Suspended Accelerometer. Sensors 2022, 22, 4930. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134930
Dai J, Wang W, Wu B, Ye L, Song K. Study on the Method of Charge Accumulation Suppression of Electrostatic Suspended Accelerometer. Sensors. 2022; 22(13):4930. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134930
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Jiefeng, Wenrui Wang, Bin Wu, Lingyun Ye, and Kaichen Song. 2022. "Study on the Method of Charge Accumulation Suppression of Electrostatic Suspended Accelerometer" Sensors 22, no. 13: 4930. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134930
APA StyleDai, J., Wang, W., Wu, B., Ye, L., & Song, K. (2022). Study on the Method of Charge Accumulation Suppression of Electrostatic Suspended Accelerometer. Sensors, 22(13), 4930. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134930






