An Improved Network Time Protocol for Industrial Internet of Things †
Abstract
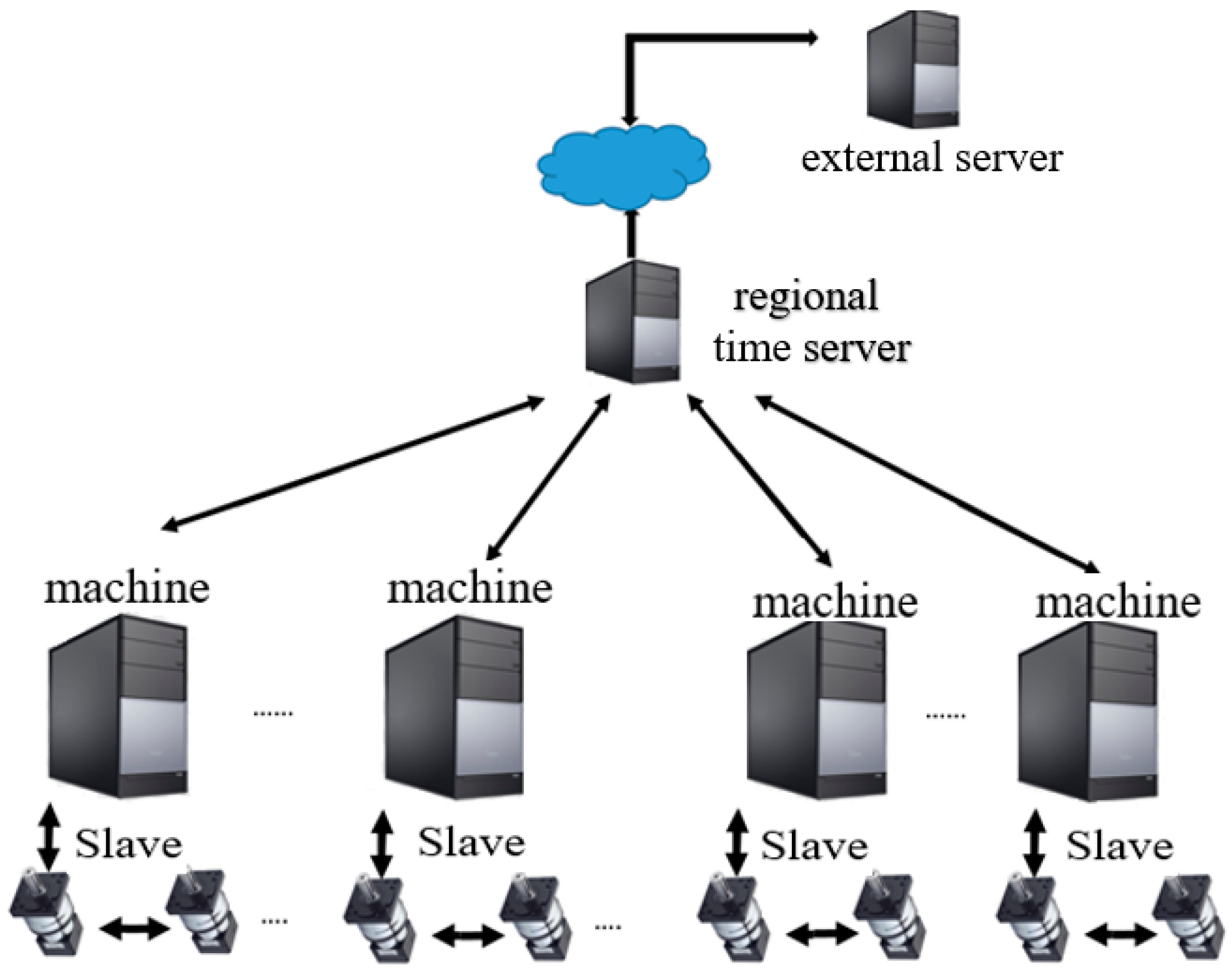
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Methodology to Improve NTP
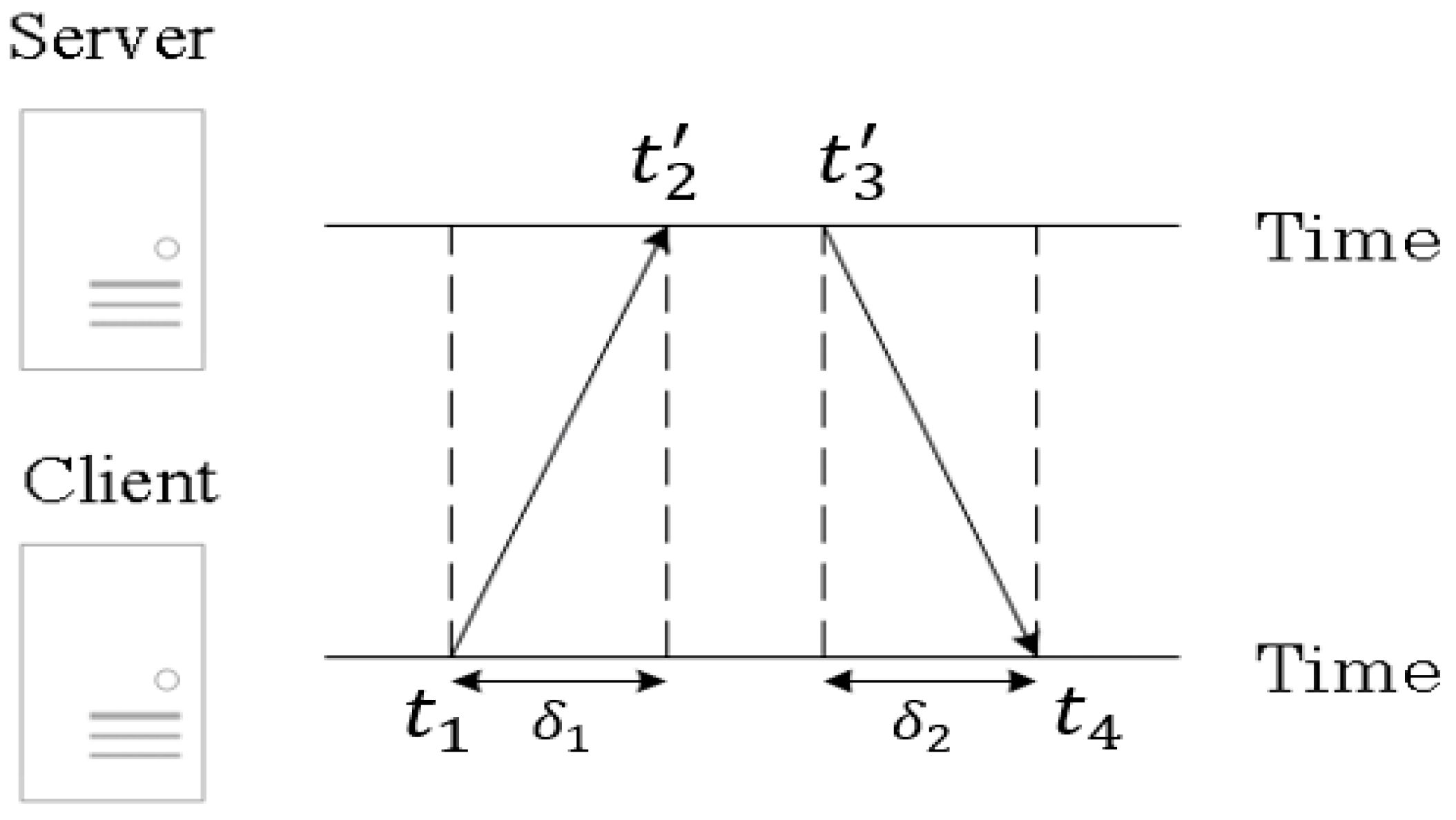
2.1. NTP Princinple
2.2. Clock Skew Measurement
2.3. Adaptive Clock Adjustment
2.4. Determining RTT Threshold
3. Impact of Nullified Offset
3.1. Expected Value and λ
3.2. Fitting of 16 s Inter-Null Distribution with Exponential Distribution
3.3. Fitting of 32 s Inter-Null Distribution with Exponential Distribution
3.4. Comparison with Other Distributions
4. Further Evaluation of the Proposed NTP Improvement
4.1. Adaptive Clock Adjustment and Clock Skew Compensation
4.2. Synchronization between Clients
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrari, P.; Bellagente, P.; Depari, A.; Flammini, A.; Pasetti, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Sisinni, E. Evaluation of the impact on industrial applications of NTP Used by IoT devices. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT, Rome, Italy, 3–5 June 2020; IEEE: Roma, Italy, 2020; pp. 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Borenius, S.; Costa-Requena, J.; Lehtonen, M.; Kantola, R. Providing Network Time Protocol Based Timing for Smart Grid Measurement and Control Devices in 5G Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (Smart Grid Comm), Beijing, China, 21–23 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gore, R.N.; Lisova, E.; Åkerberg, J.; Björkman, M. CoSiWiNeT: A Clock Synchronization Algorithm for Wide Area IIoT Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbank, J.; Mills, D.; Kasch, W. Network Time Protocol Version 4: Protocol and Algorithms Specification, 1st ed.; RFC 5905: Newark, DE, USA, 2010; Available online: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc5905.html (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Ruiqing, P.; Peng, H.; Wenxue, Y.; Min, G.; Bin, Z. The optimization techniques for time synchronization based on NTP. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Future Computer and Communication, Wuhan, China, 21–24 May 2010; Volume 2, pp. 296–299. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, D. Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) Version 4 for IPv4, IPv6 and OSI; RFC 2030: Newark, DE, USA, 1996; Available online: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc4330 (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Mills, D. Measured Performance of the Network Time Protocol in the Internet System; RFC 1128: Newark, DE, USA, 1989; Available online: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc1128.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Aponte-Luis, J.; Gómez-Galán, J.A.; Gómez-Bravo, F.; Sánchez-Raya, M.; Alcina-Espigado, J.; Teixido-Rovira, P.M. An Efficient Wireless Sensor Network for Industrial Monitoring and Control. Sensors 2018, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, D.L. Adaptive Hybrid Clock Discipline Algorithm for the Network Time Protocol. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 1998, 6, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Secilla, J.M.; Palomares, J.M.; Olivares, J. Temperature-Compensated Clock Skew Adjustment. Sensors 2013, 13, 10981–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTP Based on Github. Available online: https://github.com/ntp-project/ntp (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Time Synchronization for Linux. Available online: https://my.oschina.net/myaniu/blog/182959 (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- How to Install and Use Wireshark on Ubuntu. Available online: https://linuxhint.com/install_wireshark_ubuntu/ (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Liu, L.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chu, Y.-S.; Hou, T.-C. Optimization and realization of Network Time Protocol on IIoT. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW 2021), Penghu, Taiwan, 16–18 June 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Ghaffar, H.S. Analysis of synchronization algorithm with time-out control over networks with exponentially symmetric delays. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2002, 10, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, Q.; Serpedin, E.; Qaraqe, K. On maximum likelihood estimation of clock offset and skew in networks with exponential delays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 4, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-Y. Optimization and Implementation of Network Time Synchronization Applied to the Internet of Things. Master’s Thesis, National Chung Cheng University, Chia-Yi, Taiwan, January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, I.-K.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Serpedin, E.; Wu, Y.-C. Clock Synchronization in Wireless Sensor Networks: An Overview. Sensors 2009, 9, 56–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]















| 255 Data in 1 h | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| offset(avg) (ms) | 0.489 | 0.206 | 0.046 |
| offset(max) (ms) | 5.613 | 3.602 | 0.516 |
| RTT(avg) (ms) | 0.949 | 0.604 | 0.411 |
| RTT(max) (ms) | 11.587 | 7.335 | 1.428 |
| Null percentage | - | - | 7.5% |
| Null Threshold | offset(avg) (ms) | offset(max) (ms) | RTT(avg) (ms) | RTT(max) (ms) | Null Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Null | 0.464 | 7.083 | 0.714 | 11.906 | none |
| 1.5 ms | 0.045 | −0.726 | 0.412 | 1.49 | 7.09% |
| 1.6 ms | 0.028 | −0.77 | 0.398 | 1.594 | 4.38% |
| 1.7 ms | 0.023 | 0.656 | 0.387 | 1.683 | 3.34% |
| 1.75 ms | 0.035 | −0.8 | 0.392 | 1.747 | 4.57% |
| 1.8 ms | 0.034 | −0.73 | 0.389 | 1.8 | 2.50% |
| 1.85 ms | 0.037 | −1.19 | 0.399 | 1.847 | 3.46% |
| All Day Threshold 1.7 ms | 16 s Sync | 32 s Sync |
|---|---|---|
| offset(avg) (ms) | 0.023 | 0.054 |
| offset(max) (ms) | 0.656 | −0.716 |
| RTT(avg) (ms) | 0.387 | 0.375 |
| RTT(max) (ms) | 1.683 | 1.675 |
| Null Percentage | 3.34% | 4.02% |
| Adaptive Clock Adj. | w/o | w/ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clock Skew Comp. | w/o | w/ | w/o | w/ |
| offset(avg) (ms) | 0.224 | 0.261 | 0.109 | 0.043 |
| offset(max) (ms) | −5.64 | 11.577 | 0.759 | −0.679 |
| Null | w/o | w/o | 5.3% | 4.3% |
| All Day 5400 Data | Client A | Client B | A-B |
|---|---|---|---|
| offset(max) (ms) | −0.104 | 0.131 | −0.12 |
| offset(avg) (ms) | 0.019 | 0.02 | 0.023 |
| All Day 2725 Data | Client A | Client B | A-B |
|---|---|---|---|
| offset(max) (ms) | −0.066 | 0.077 | −0.084 |
| offset(avg) (ms) | 0.008 | 0.012 | 0.013 |
| All Day 1370 Data | Client A | Client B | A-B |
|---|---|---|---|
| offset(max) (ms) | 0.079 | 0.062 | −0.075 |
| offset(avg) (ms) | 0.013 | 0.012 | 0.019 |
| All Day 680 Data | Client A | Client B | A-B |
|---|---|---|---|
| offset(max) (ms) | 0.128 | 0.18 | 0.214 |
| offset(avg) (ms) | 0.03 | 0.037 | 0.058 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, T.-C.; Liu, L.-H.; Lan, Y.-K.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chu, Y.-S. An Improved Network Time Protocol for Industrial Internet of Things. Sensors 2022, 22, 5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22135021
Hou T-C, Liu L-H, Lan Y-K, Chen Y-T, Chu Y-S. An Improved Network Time Protocol for Industrial Internet of Things. Sensors. 2022; 22(13):5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22135021
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Ting-Chao, Lin-Hung Liu, Yan-Kai Lan, Yi-Ting Chen, and Yuan-Sun Chu. 2022. "An Improved Network Time Protocol for Industrial Internet of Things" Sensors 22, no. 13: 5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22135021
APA StyleHou, T.-C., Liu, L.-H., Lan, Y.-K., Chen, Y.-T., & Chu, Y.-S. (2022). An Improved Network Time Protocol for Industrial Internet of Things. Sensors, 22(13), 5021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22135021





