Driving Mode Selection through SSVEP-Based BCI and Energy Consumption Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
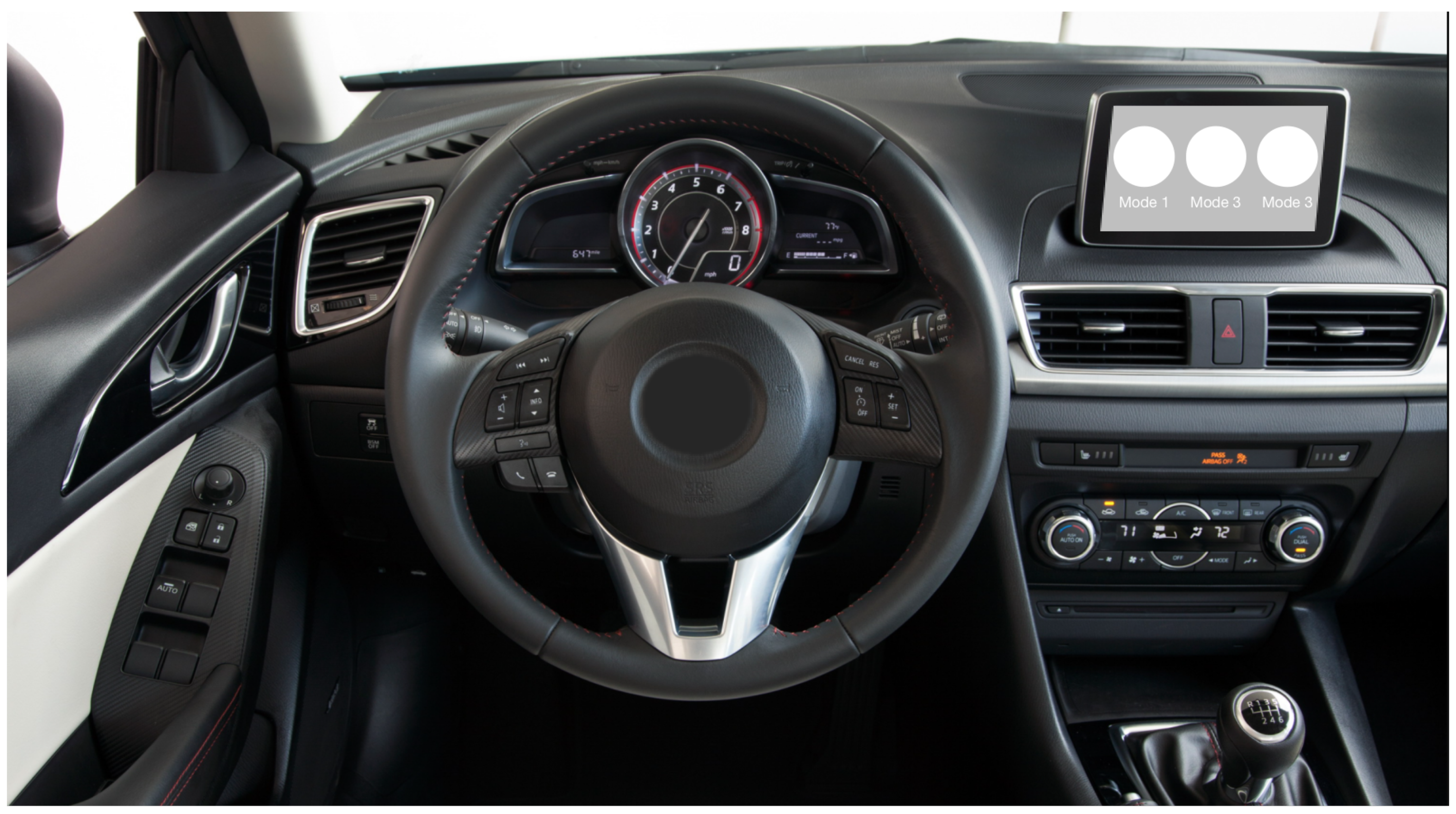
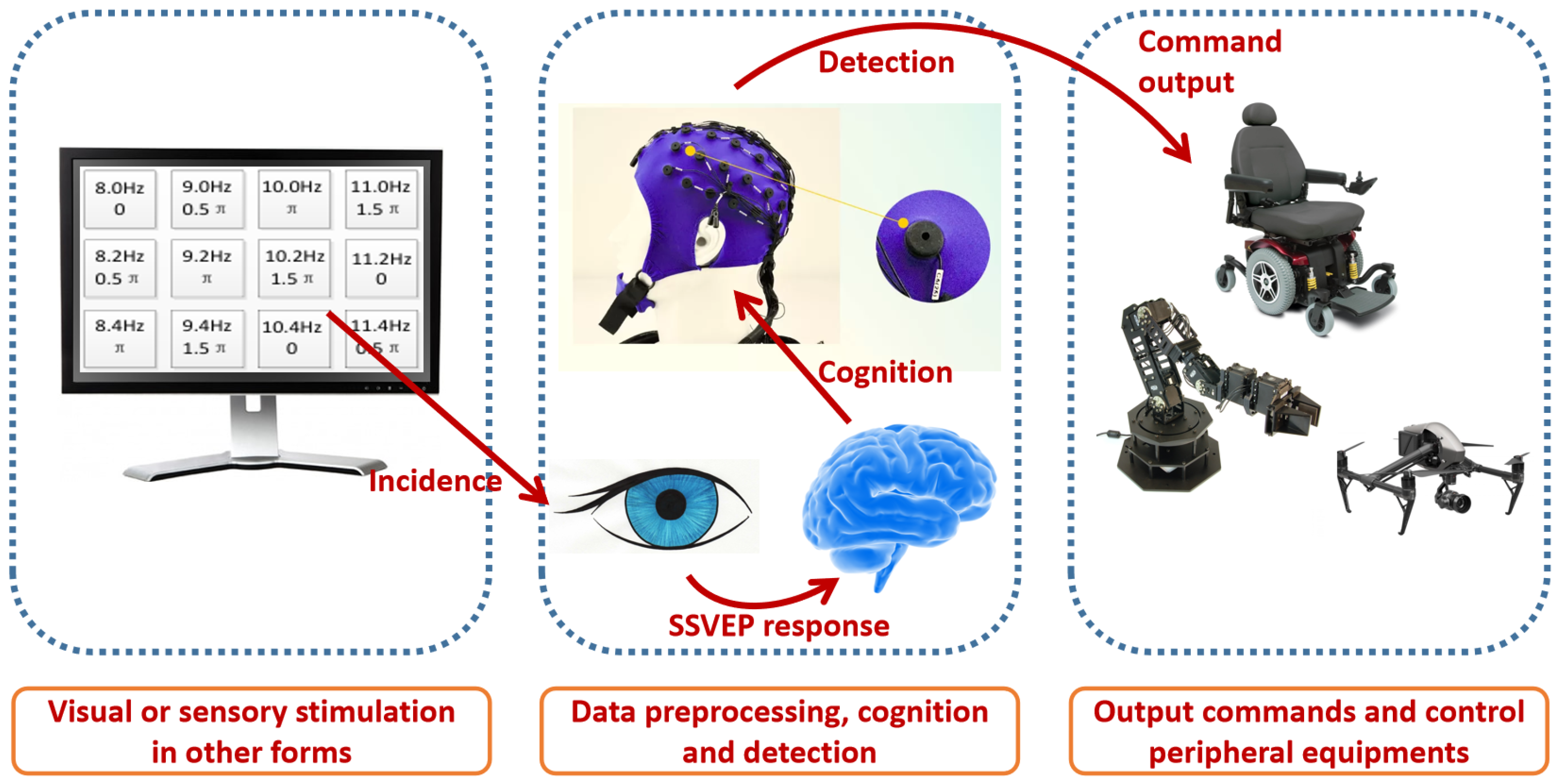
2.1. SSVEP-Based Driving Mode Selection
2.2. SSVEP Detection Algorithm
2.3. Energy Consumption Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Experiment Settings
3.1.1. SSVEP interface
3.1.2. Offline and Real-Time Driving Mode Selection
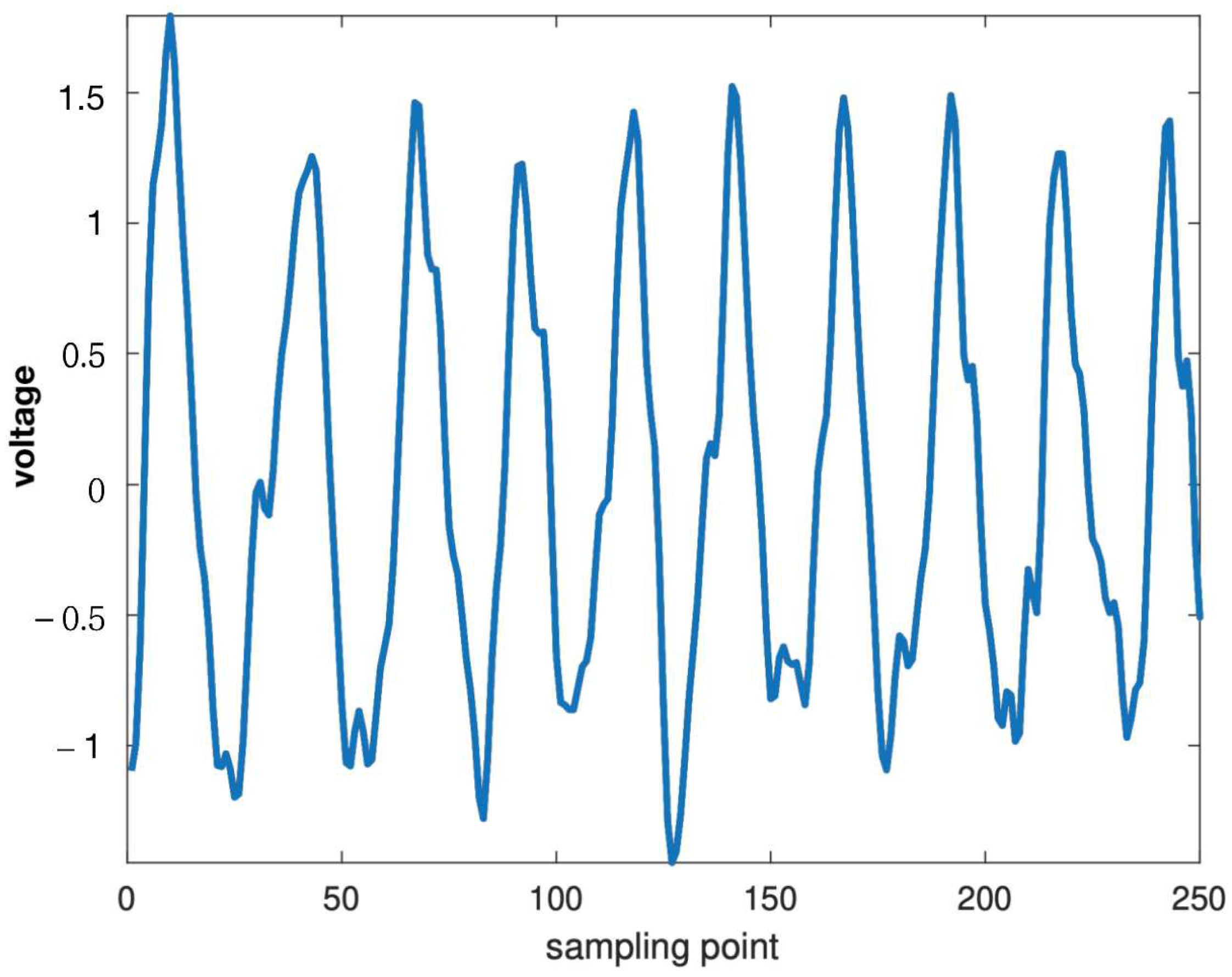
3.1.3. EEG Recording and Preprocessing
3.1.4. Subjects
3.2. SSVEP Detection Performance
3.2.1. SSVEP Detection Accuracy Versus Flickering Duration
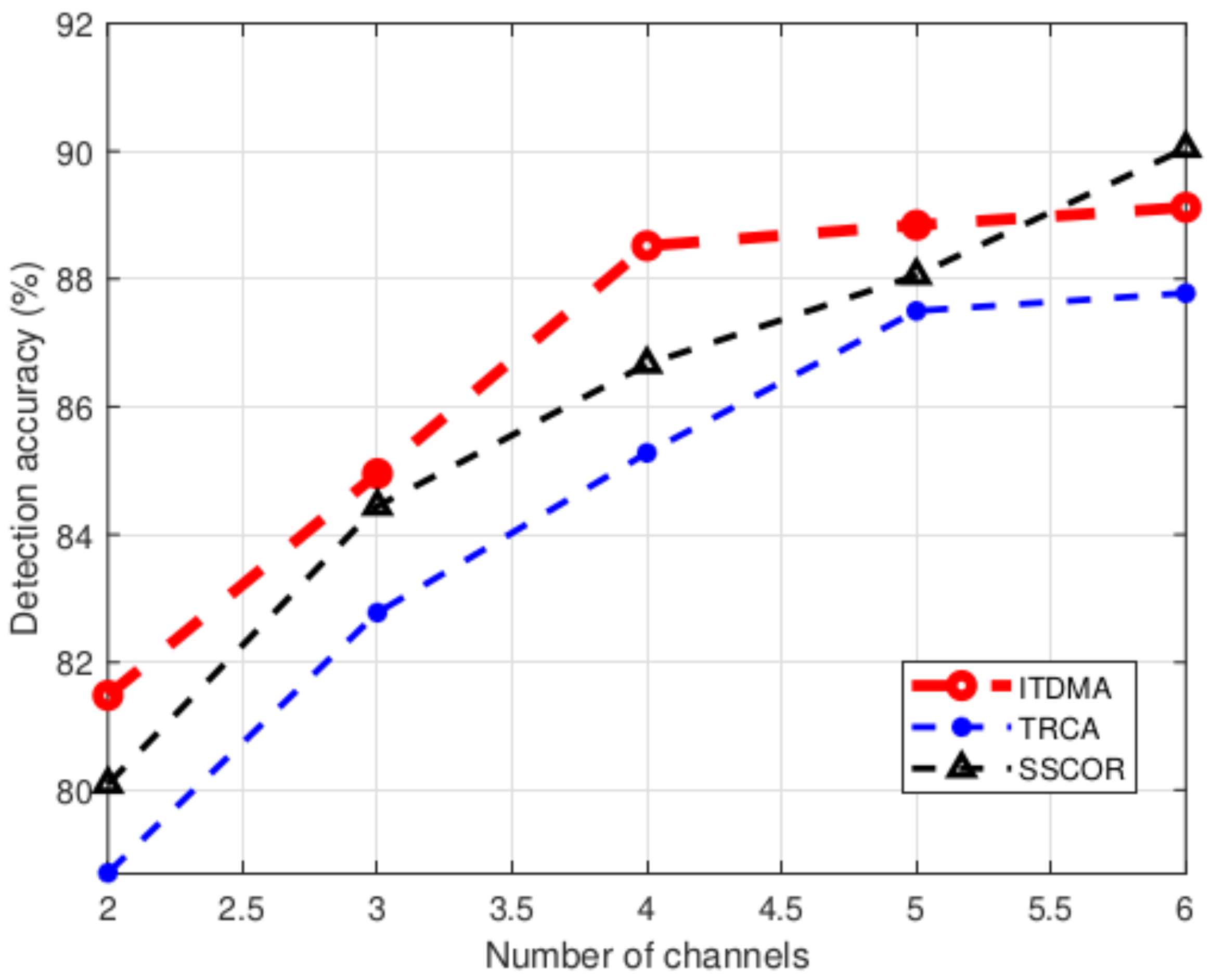
3.2.2. SSVEP Detection Accuracy Versus the Number of EEG Channels
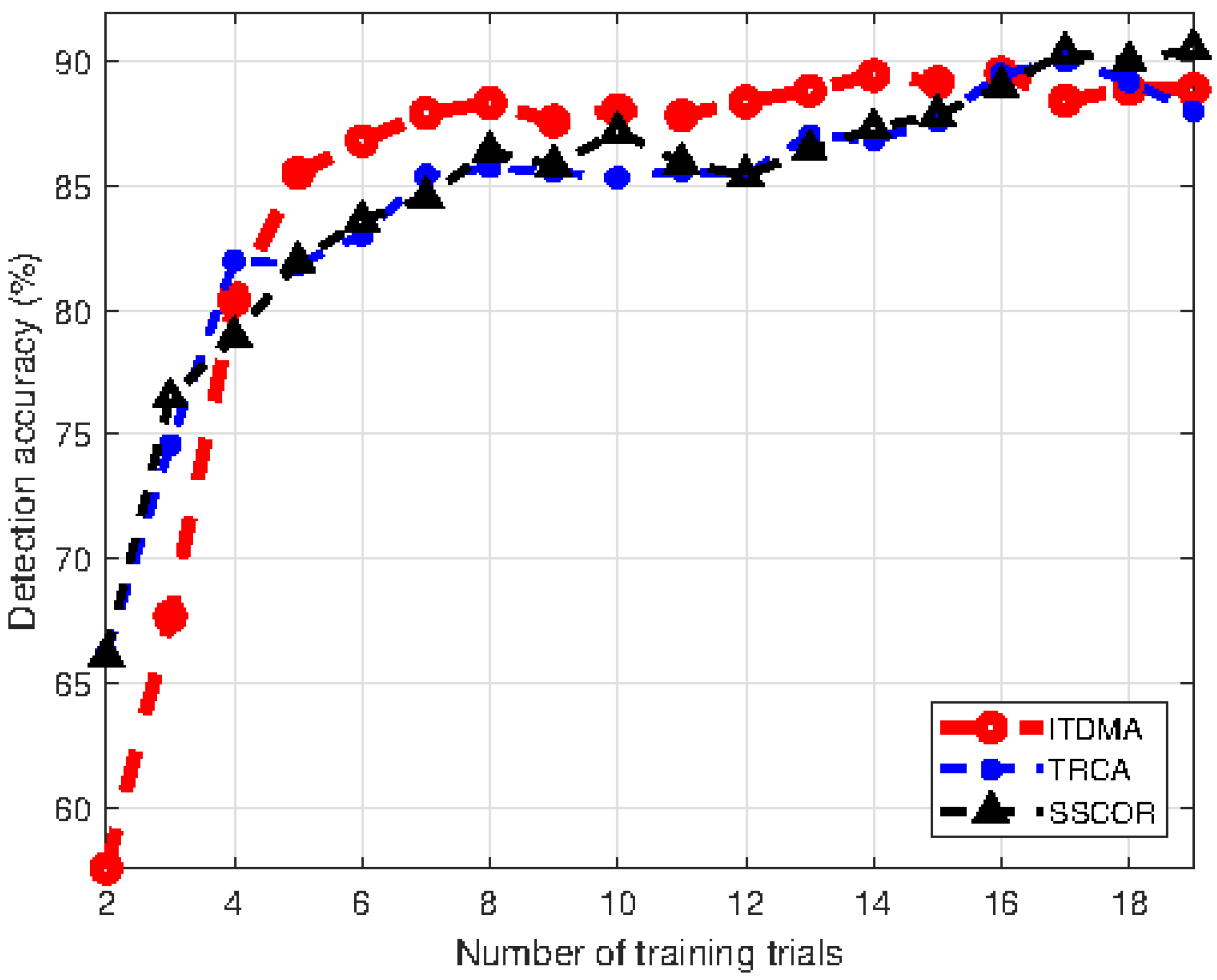
3.2.3. SSVEP Detection Accuracy Versus the Number of Training Trials
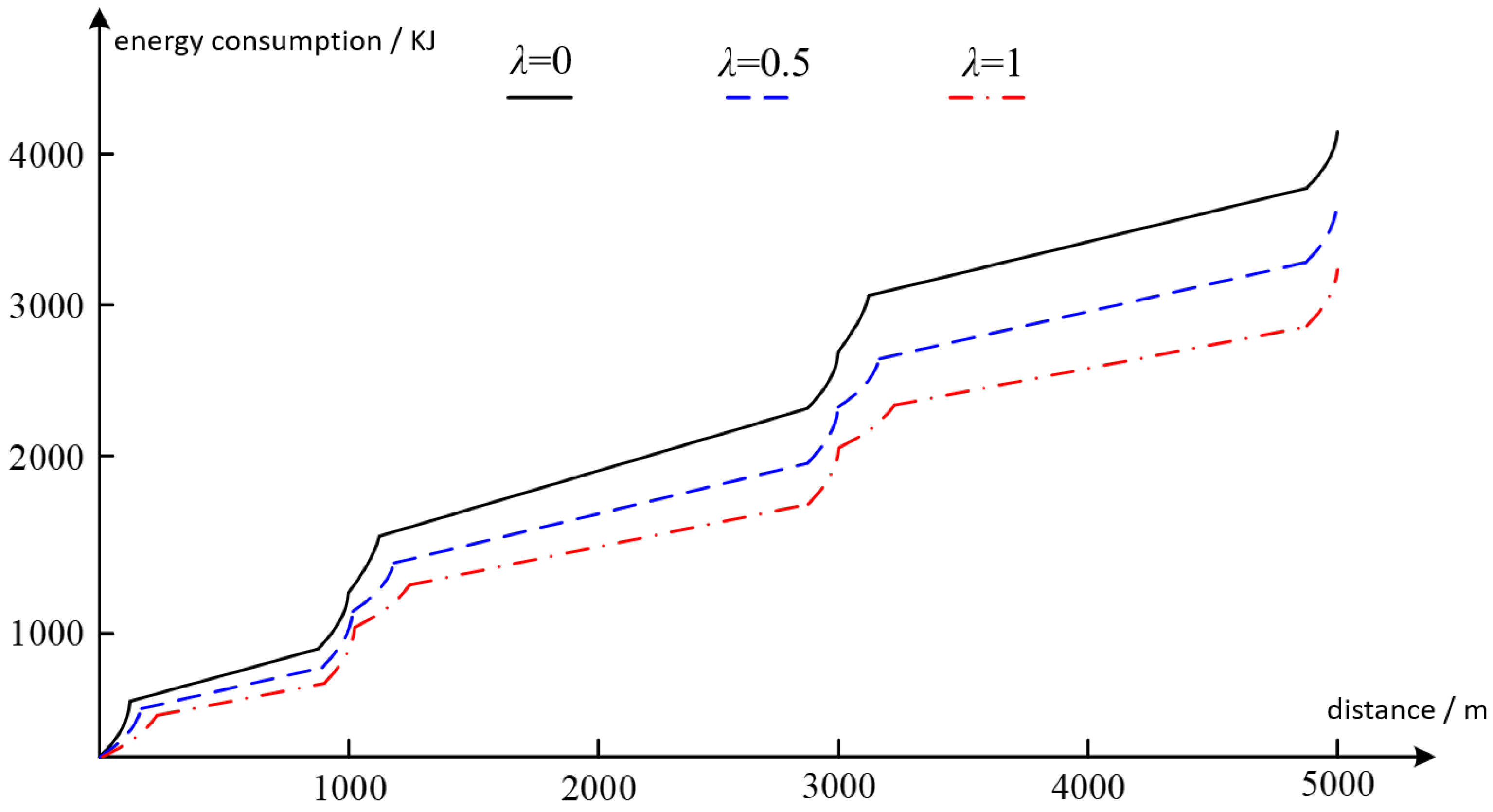
3.3. Energy Consumption
3.4. Challenges and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of Open Access Journals |
| TLA | Three-letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H. Paradigm Using Peripheral Vision. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 056021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Hu, H. A new SSVEP-based BCI utilizing frequency and space to encode visual targets. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 189301. [Google Scholar]
- Echtioui, A.; Zouch, W.; Ghorbel, M.; Mhiri, C.; Hamam, H. A novel ensemble learning approach for classification of EEG motor imagery signals. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, Harbin, China, 28 June–2 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Anumanchipalli, G.K.; Chartier, J.; Chang, E.F. Speech synthesis from neural decoding of spoken sentences. Nature 2019, 568, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, F.R.; Avansino, D.T.; Hochberg, L.R.; Henderson, J.M.; Shenoy, K.V. High-performance brain-to-text communication via handwriting. Nature 2021, 593, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, M.; Li, Y. An EOG-based wheelchair robotic arm system for assisting patients with severe spinal cord injuries. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 026021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qaysi, Z.T.; Zaidan, B.B.; Zaidan, A.A.; Suzani, M.S. A review of disability EEG based wheelchair control system: Coherent taxonomy, open challenges and recommendations. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 164, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouichka, O.; Echtioui, A.; Hamam, H. Deep Learning Models for Predicting Epileptic Seizures Using iEEG Signals. Electronics 2022, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podmore, J.J.; Breckon, T.P.; Aznan, N.K.; Connolly, J.D. On the Relative Contribution of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for SSVEP-Based Bio-Signal Decoding in BCI Speller Applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorbello, R.; Tramonte, S.; Giardina, M.E.; La Bella, V.; Spataro, R.; Allison, B.; Guger, C.; Chella, A. A Human–Humanoid Interaction Through the Use of BCI for Locked-In ALS Patients Using Neuro-Biological Feedback Fusion. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Cha, H.S.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H.; Im, C.H. Development of an Online Home Appliance Control System Using Augmented Reality and an SSVEP-Based Brain–Computer Interface. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 163604–163614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, S.W. Towards brain–computer interfaces for drone swarm control. In Proceedings of the 8th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwon, Korea, 26–28 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vernon, S.; Joshi, S.S. Brain–Muscle–Computer Interface: Mobile-Phone Prototype Development and Testing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2011, 15, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.K.; Chaurasiya, R.K.; Verma, S.; Sinha, G.R. A Thresholding-Free State Detection Approach for Home Appliance Control Using P300-Based BCI. IEEE Sensors J. 2021, 21, 16927–16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yu, Z.L.; Lin, C.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. A Bayesian Shared Control Approach for Wheelchair Robot With Brain Machine Interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiri, R.; Borhani, S.; Kilmarx, J.; Esterwood, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X. A Usability Study of Low-Cost Wireless Brain-Computer Interface for Cursor Control Using Online Linear Model. IEEE Trans.-Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2020, 50, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.; Gu, Z. Target Selection With Hybrid Feature for BCI-Based 2-D Cursor Control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, E.; Jiang, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, D. Toward brain-actuated car applications: Self-paced control with a motor imagery-base brain–computer interface. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 77, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stawicki, P.; Gembler, F.; Volosyak, I. Driving a Semiautonomous Mobile Robotic Car Controlled by an SSVEP-Based BCI. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 4909685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Chavarriaga, R.; Khaliliardali, Z.; Gheorghe, L.; Iturrate, I.; Millán, J.d.R. EEG-based decoding of error-related brain activity in a real-world driving task. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 066028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Bi, L.; Li, H. Model Predictive-Based Shared Control for Brain-Controlled Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliliardali, Z.; Chavarriaga, R.; Gheorghe, L.A.; Millán, J.d.R. Action prediction based on anticipatory brain potentials during simulated driving. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 066006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, S.W. Detection of braking intention during simulated driving based on EEG Analysis: Online study. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Hong Kong, China, 9–12 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Bi, L. Combined Lateral and Longitudinal Control of EEG Signals-Based Brain-Controlled Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1732–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hekmatmanesh, A.; Nardelli, P.H.; Handroos, H. Review of the state-of-the-art of brain-controlled vehicles. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 110173–110193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, D.; Li, C.; Qi, S. Brain–Computer Interface Speller Based on Steady-State Visual Evoked Potential: A Review Focusing on the Stimulus Paradigm and Performance. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gao, X. BETA: A Large Benchmark Database Toward SSVEP-BCI Application. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Jiang, L.; Dong, G.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y. An Open Dataset for Wearable SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 21, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, H. A Maximum Likelihood Perspective of Spatial Filter Design in SSVEP-Based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 2706–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Hu, H.; Zhou, T. Enhancing detection of SSVEPs through spatial filtering: An inter-trial distance minimization perspective. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Disaster Management (ICT-DM), Hangzhou, China, 3–5 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.T.; Gao, X.; Jung, T.P. Enhancing Detection of SSVEPs for a High-Speed Brain Speller Using Task-Related Component Analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, D.; Li, F.; Yin, E.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, Q.; Tanaka, T.; Yao, D.; Xu, P. Correlated Component Analysis for Enhancing the Performance of SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.K.; Reddy, M.R. Designing a Sum of Squared Correlations Framework for Enhancing SSVEP-Based BCIs. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Lv, C.; Cao, D.; Lu, C. Energy oriented driving behavior analysis and personalized prediction of vehicle states with joint time series modeling. Appl. Energy 2020, 261, 114471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.; Walsh, C.; Carroll, S. Impact of driving characteristics on electric vehicle energy consumption and range. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 6, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ming, W. Energy-saving driving mode for PHEV drivers based on energy cycle model. In Proceedings of the Hybrid and Electric Vehicles Conference 2013, London, UK, 6–7 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zhou, D.; Huang, J.; Du, R.; Zhang, X. Optimal Path Planning for Electric Vehicle with Consideration of Traffic Light and Energy Consumption. Automot. Eng. 2021, 43, 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbakhti, M.; Beiramvand, M.; Rejer, I.; Augustyniak, P.; Broniec-Wójcik, A.; Wierzchon, M.; Marozas, V. Simultaneous Eye Blink Characterization and Elimination From Low-Channel Prefrontal EEG Signals Enhances Driver Drowsiness Detection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, L.W.; Komarov, O.; Lai, W.K.; Liang, W.G.; Jung, T.P. Eyeblink recognition improves fatigue prediction from single-channel forehead EEG in a realistic sustained attention task. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 036015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| 2 m/s | |
| 0.5 m/s | |
| m | 1500 kg |
| f | 0.015 |
| 1.2 | |
| 0.3 | |
| A | 2 m |
| v | 15 m/s |
| The Damping Coefficient | 0 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Energy Consumption in the Real-Time Experiment (kJ) | 3916 | 3504 | 3452 |
| Energy Consumption in the Prior Experiment (kJ) | 4105 | 3618 | 3206 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; Sun, C. Driving Mode Selection through SSVEP-Based BCI and Energy Consumption Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155631
Wu J, Wang Z, Xu T, Sun C. Driving Mode Selection through SSVEP-Based BCI and Energy Consumption Analysis. Sensors. 2022; 22(15):5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155631
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Juai, Zhenyu Wang, Tianheng Xu, and Chengyang Sun. 2022. "Driving Mode Selection through SSVEP-Based BCI and Energy Consumption Analysis" Sensors 22, no. 15: 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155631
APA StyleWu, J., Wang, Z., Xu, T., & Sun, C. (2022). Driving Mode Selection through SSVEP-Based BCI and Energy Consumption Analysis. Sensors, 22(15), 5631. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155631







