Coupling Effects Analysis and Suppression in a Highly Integrated Ka-Band Receiver Front-End MMIC for a Passive Millimeter-Wave Imager System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The influence of various potential coupling effects in the integrated MMIC on IRR is quantitatively analyzed, and the design requirements are put forward accordingly;
- (2)
- Corresponding solutions are proposed for three coupling paths: By designing a double-balanced mixer (DBM) with high isolation characteristics, the mutual coupling in the RF-LO path is less than −34 dB; By tuning the distance between the main transmission path of LNA and LO chain, while adding isolation vias, the LO coupling from the space and dielectric is suppressed to −29 dB; By using differential lines to design the crossover structure, the coupling of the LO to the mixing unit is −25 dB, and the coupling of LO to the IF port is reduced to −40 dB by the 180° reverse superposition of balun;
- (3)
- Compared with the reported receiver MMICs based on similar processes, the MMIC proposed in this paper not only has a higher integration level, but also has advantages in its low noise characteristics (Noise figure 3~3.5 dB, IRR greater than 35 dB) and low power consumption (LO drive power −15 dBm, DC power consumption 330 mW). This receiver MMIC is very suitable for a high-sensitivity large-scale array PMMI system.
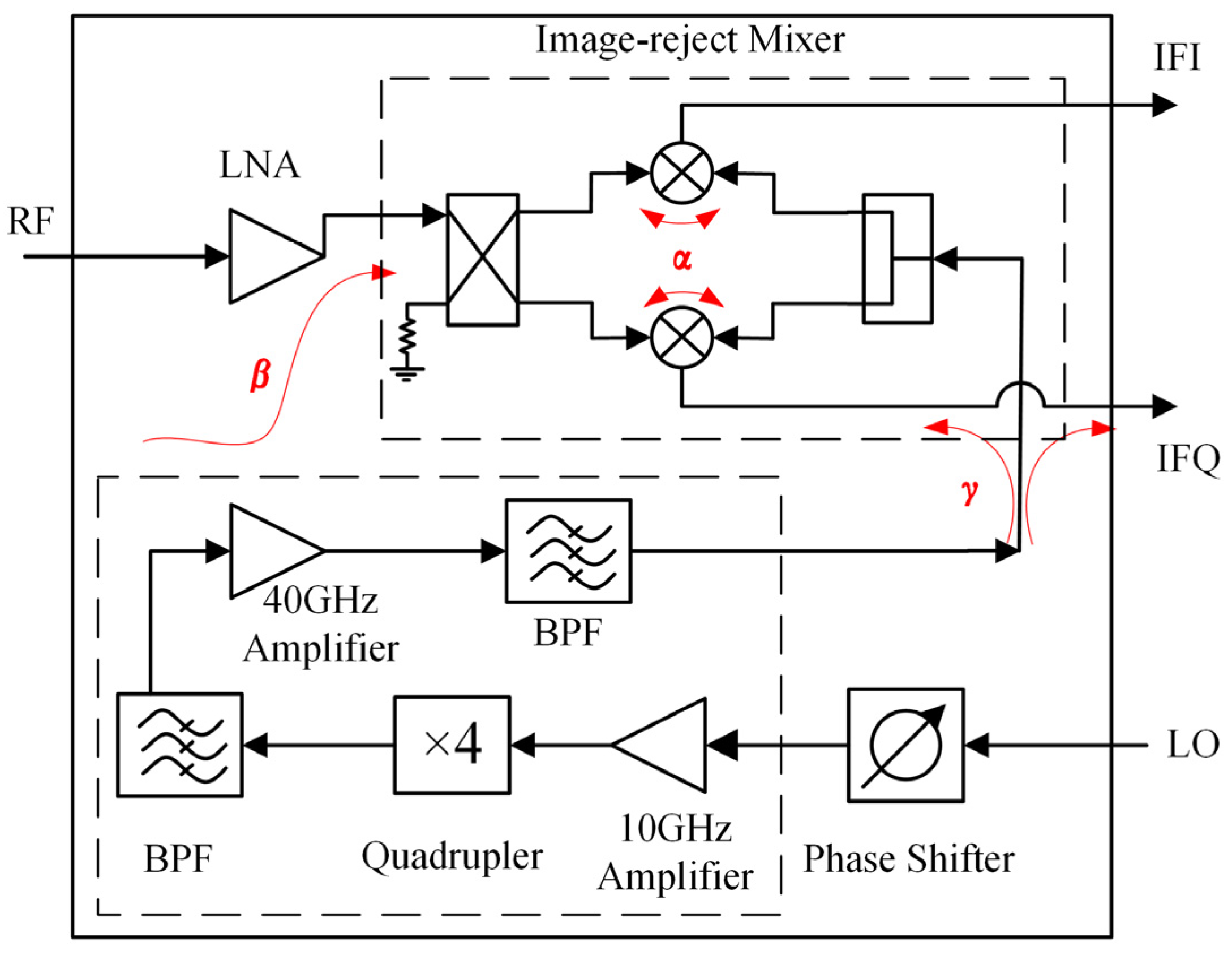
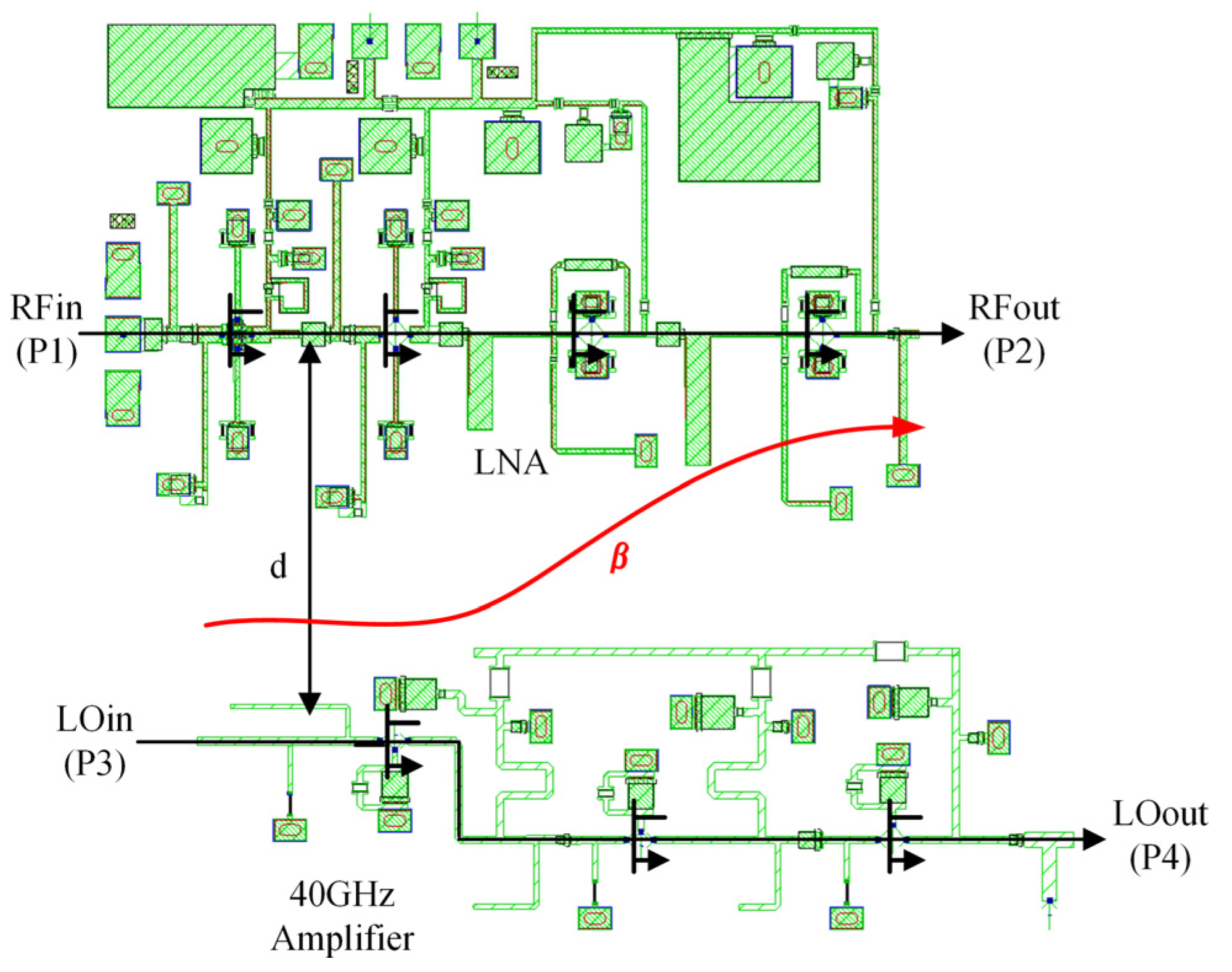
2. Integrated Receiver Front-End MMIC Overview and Coupling Analysis
2.1. Integrated Ka-Band Receiver Front-End MMIC Overview
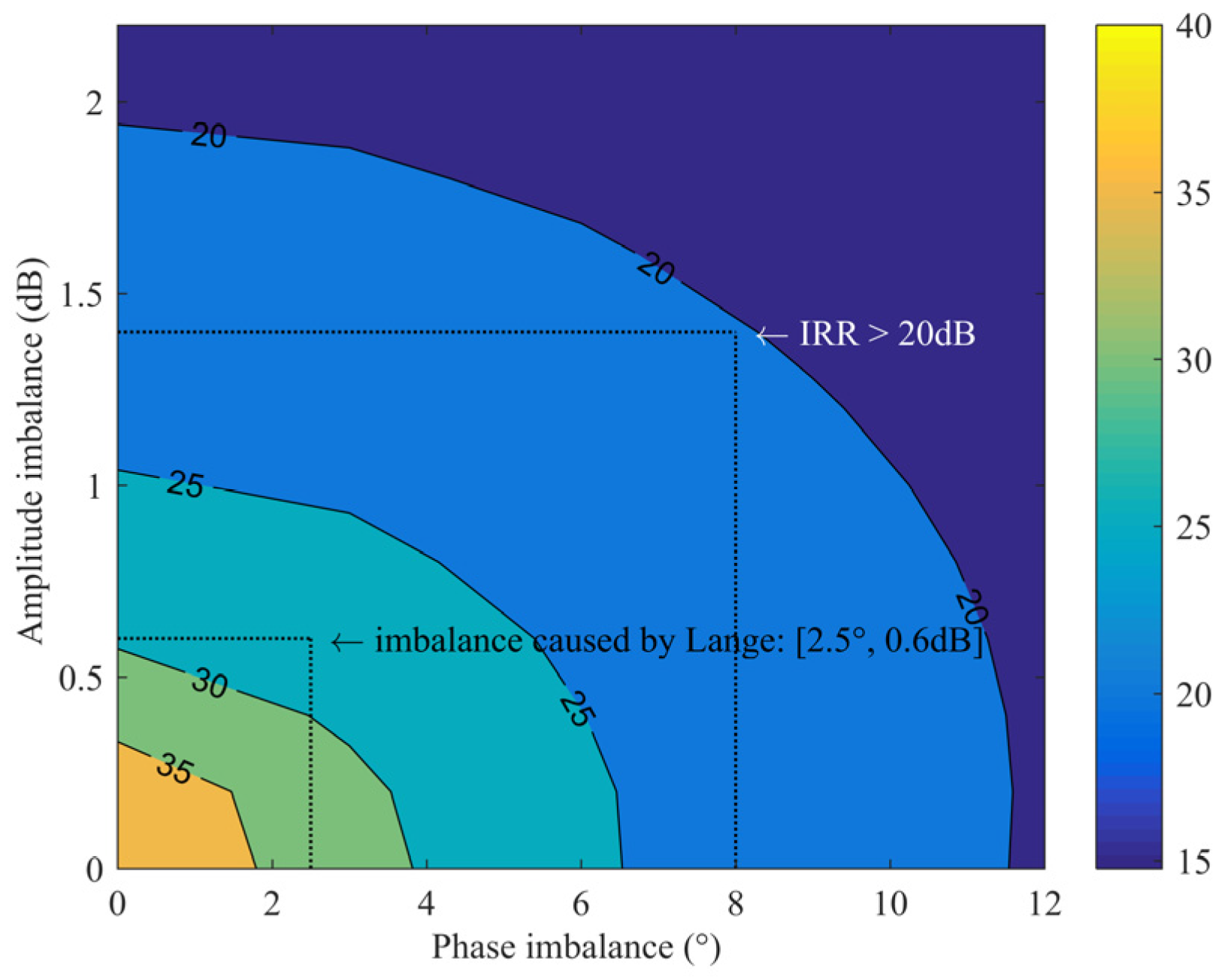
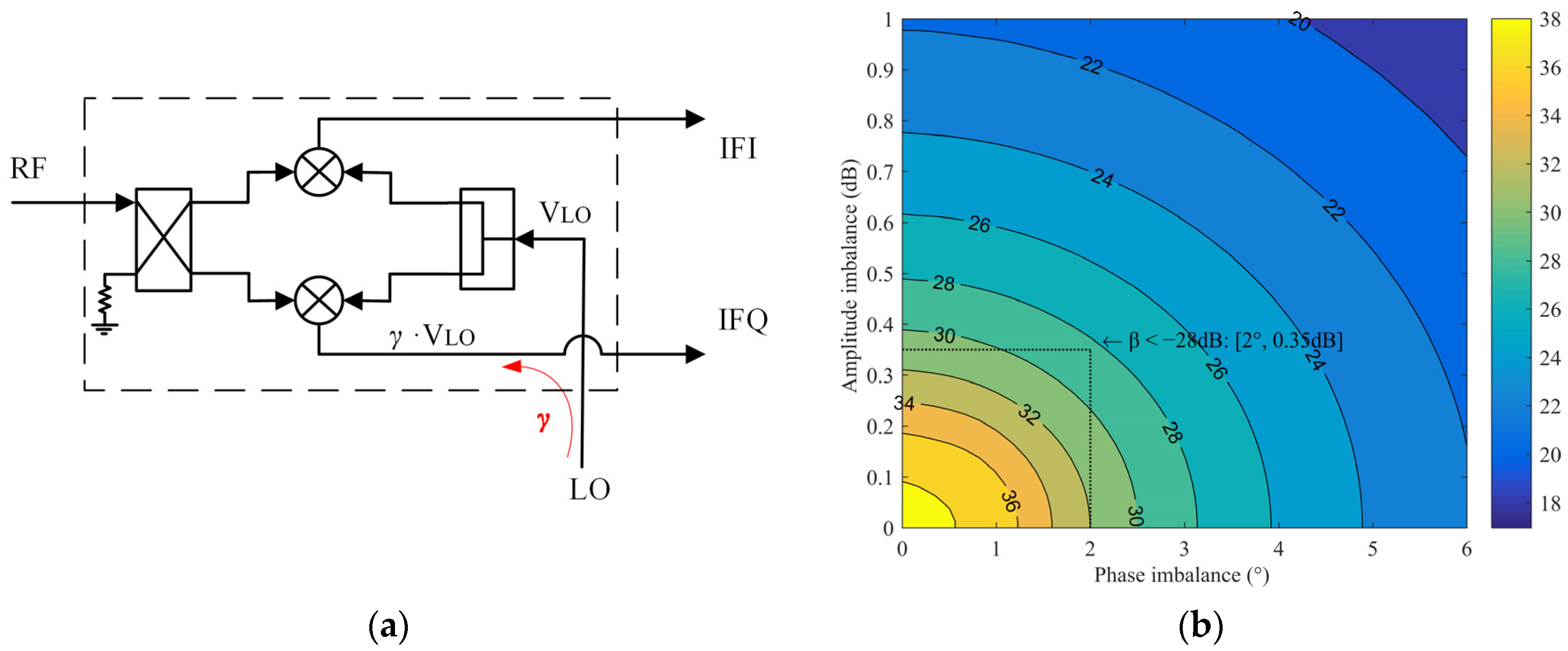
2.2. Analysis of Potential Coupling Paths and Coupling Effects on IRR
3. Coupling Effect Solution and Integrated Receiver MMIC Design
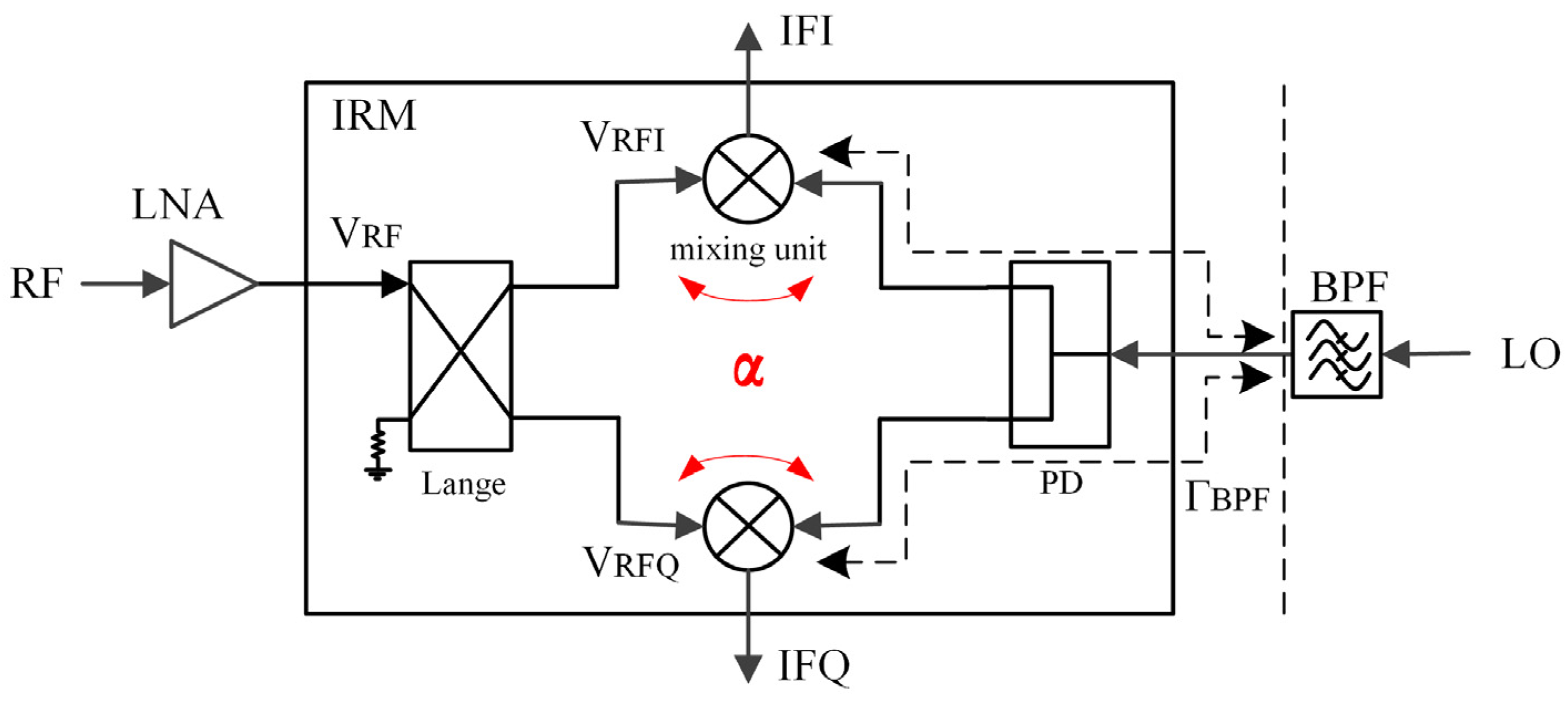
3.1. Solution to the Coupling in the Mixer RF-LO Path
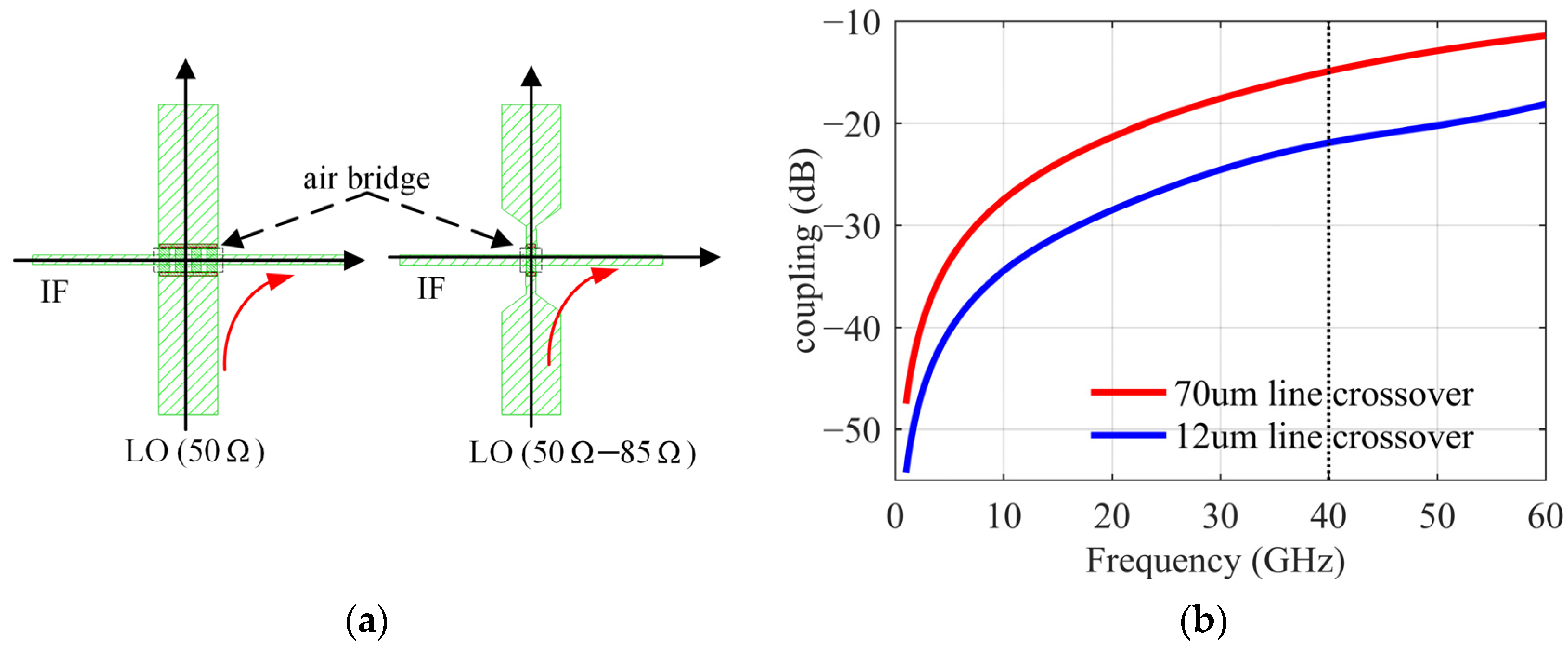
3.2. Solution to the Coupling from Space and Dielectric
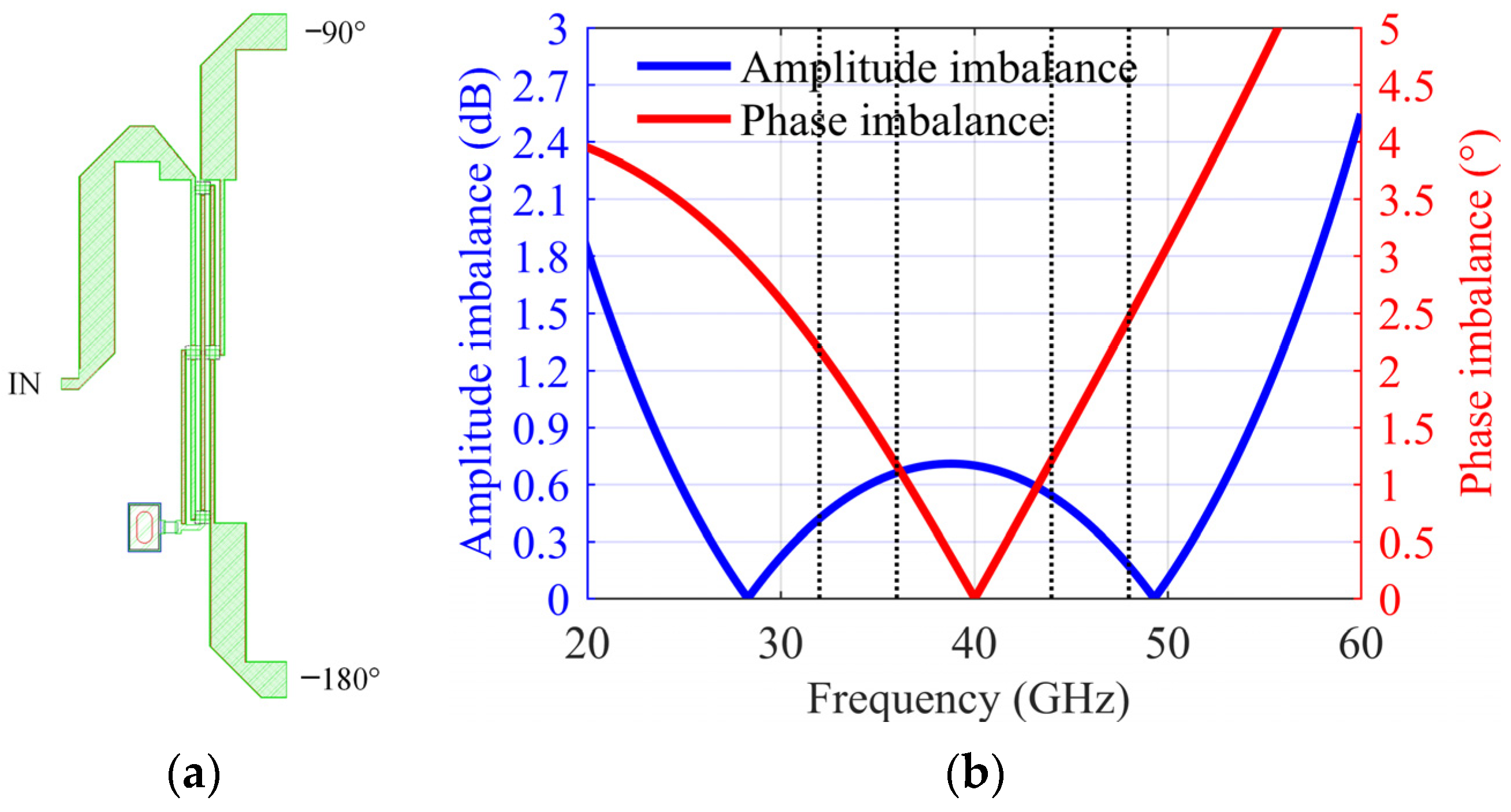
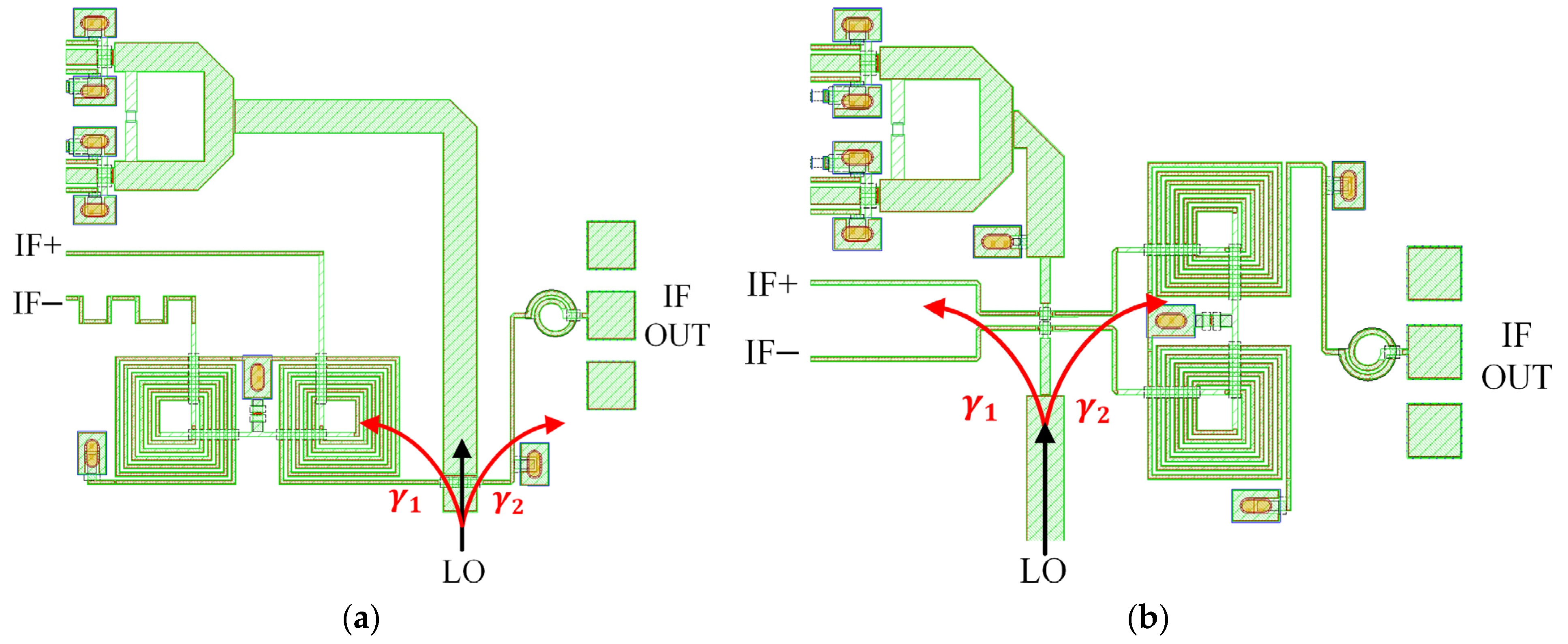
3.3. Solution to the Coupling Caused by the Line Intersection
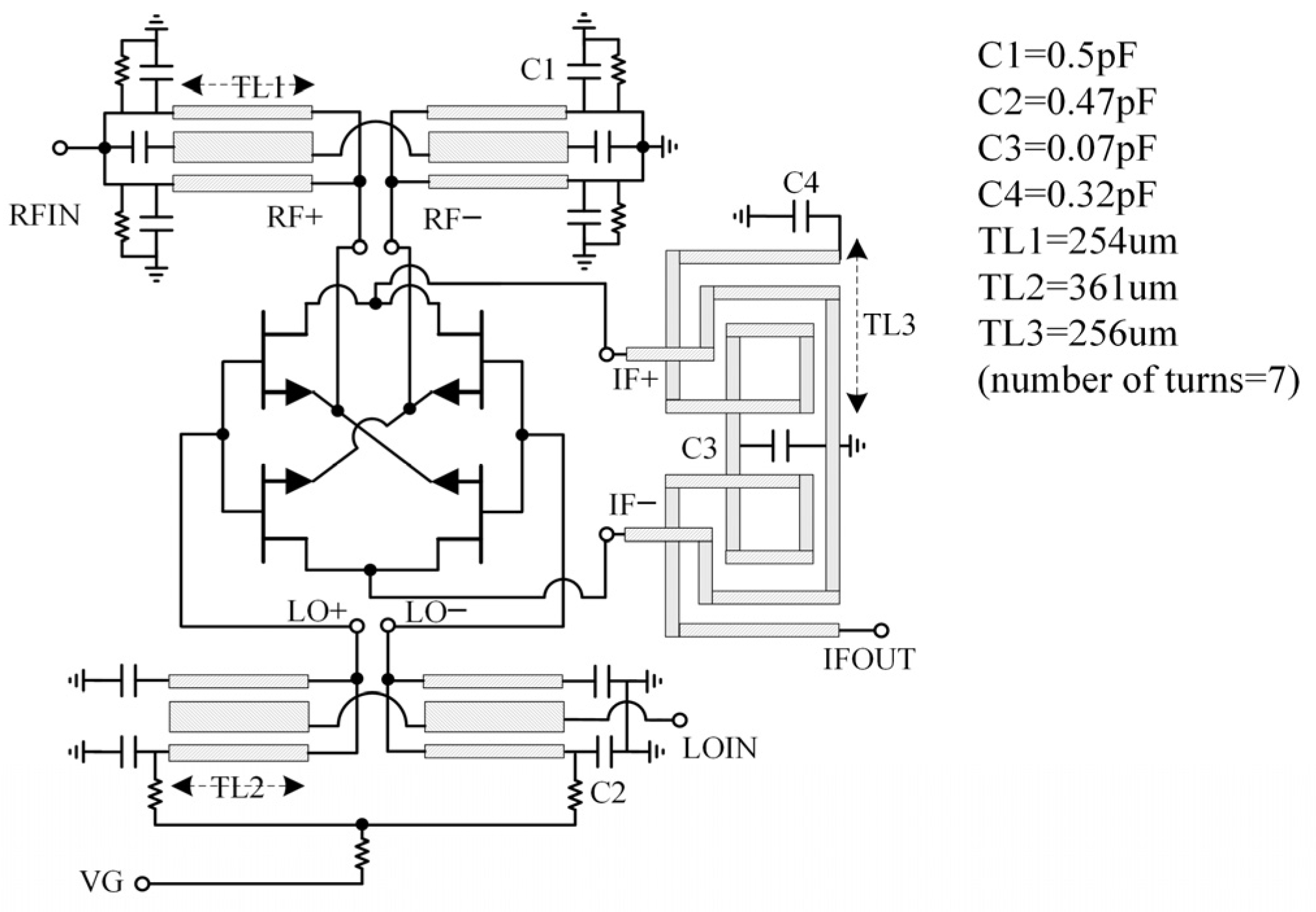
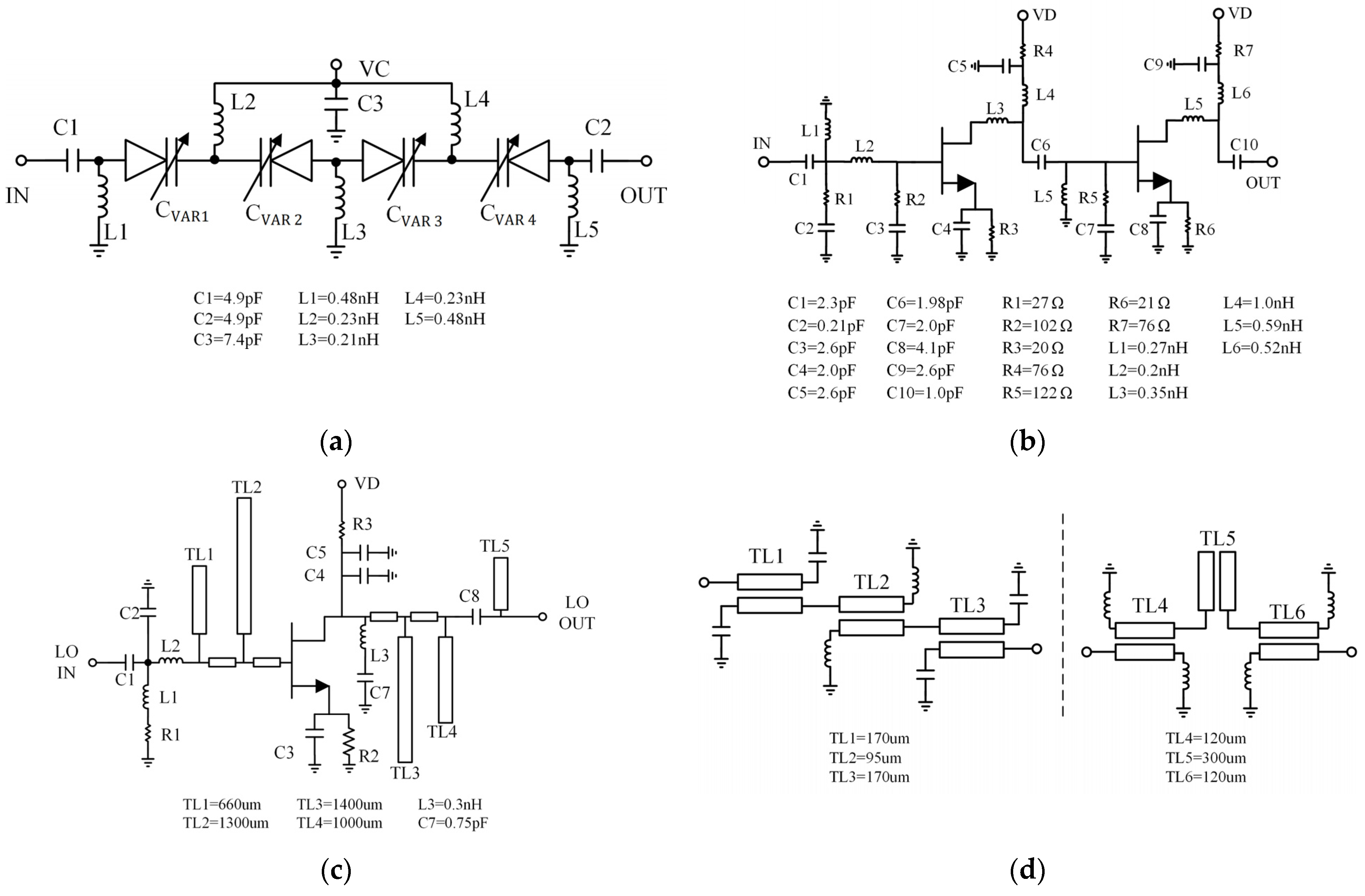
3.4. Implementation of the Integrated Receiver MMIC
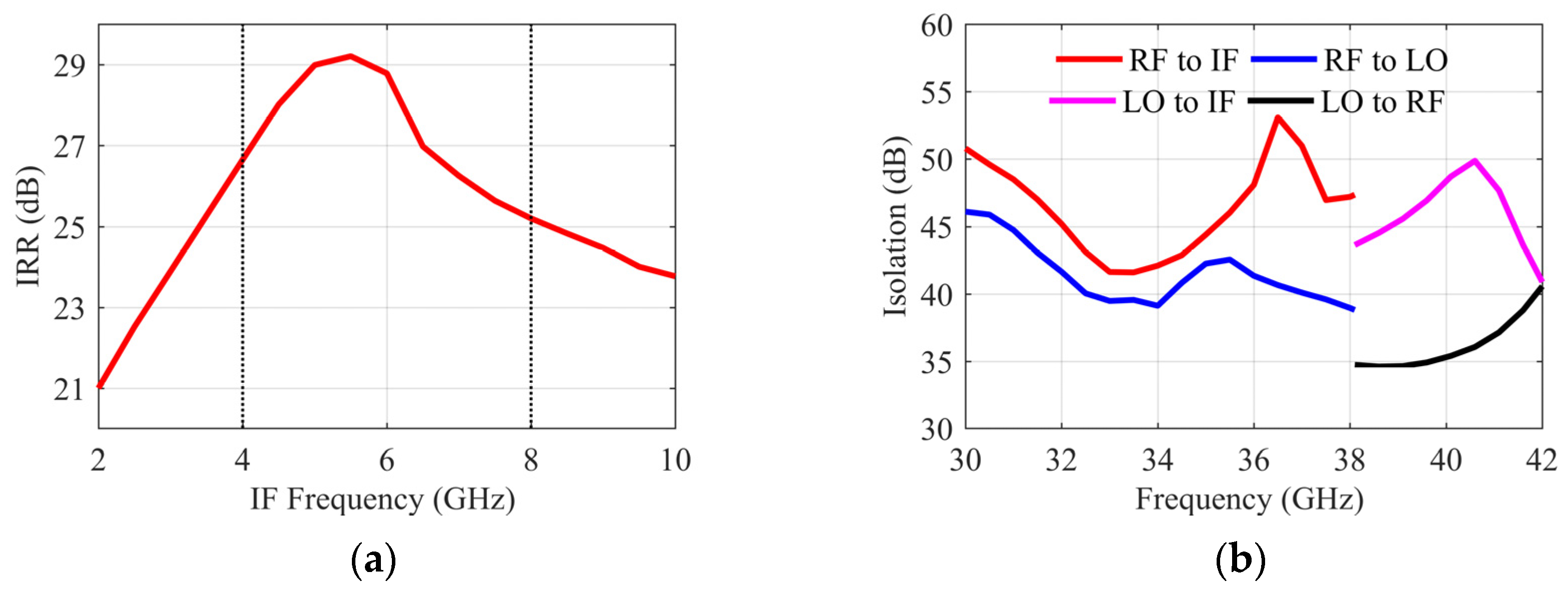
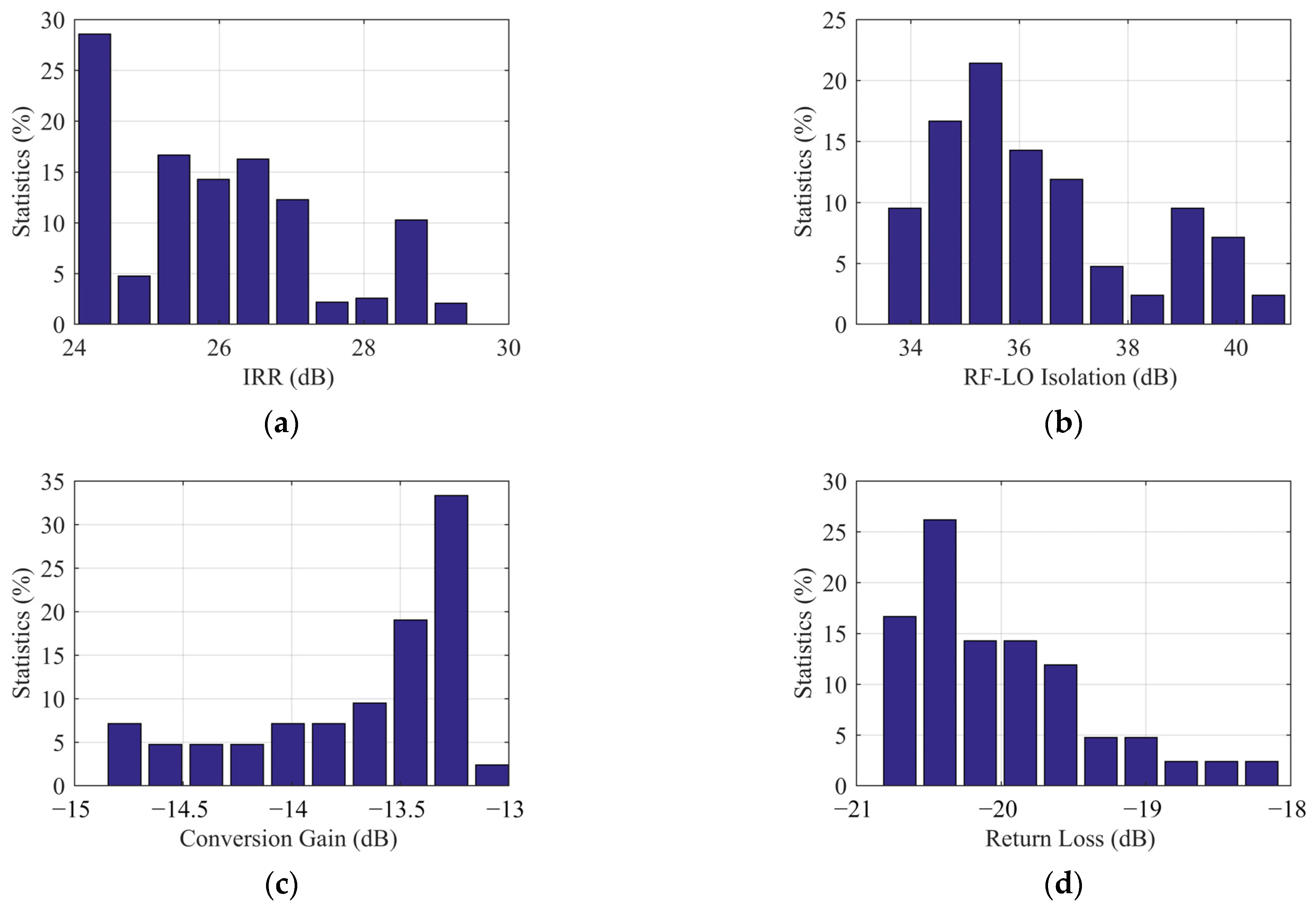
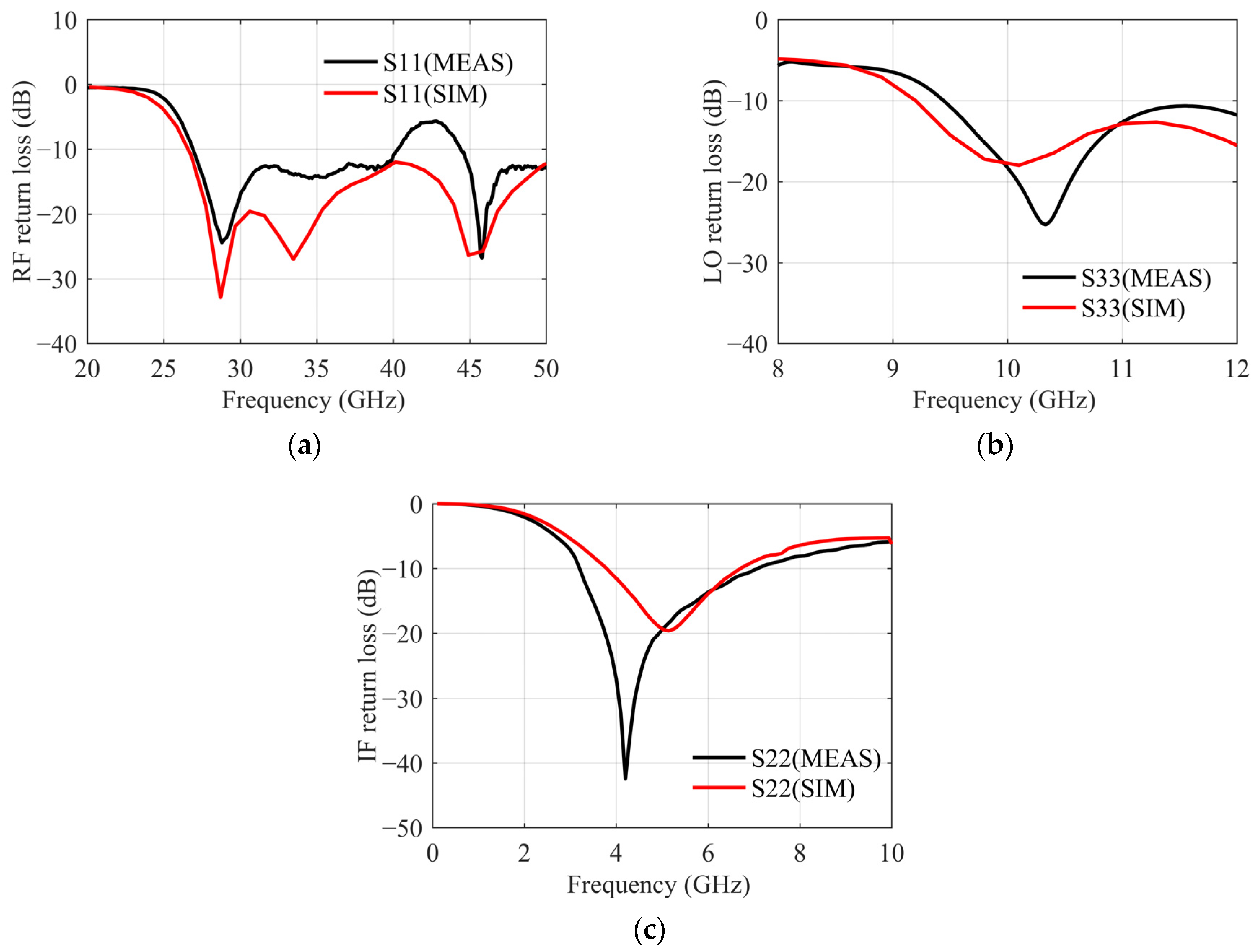
4. Measurement Results and Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinclair, G.; Appleby, R.; Coward, P.; Price, S. Passive millimeter-wave imaging in security scanning. In Proceedings of the AeroSense 2000, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, R.; Anderton, R. Millimeter-Wave and Submillimeter-Wave Imaging for Security and Surveillance. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, N. Indoor Full-Body Security Screening: Radiometric Microwave Imaging Phenomenology and Polarimetric Scene Simulation. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 144621–144637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S. Microwave Imaging in Security—Two Decades of Innovation. IEEE J. Microw. 2021, 1, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, A.; Si, W.; Guo, X.; Miao, J. Calibration of Visibility Samples for Real-Time Passive Millimeter Wave Imaging. IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 106441–106450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Utomo, D.; Shin, S.; Han, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, J. Ka-band RF Front-End with 5dB NF and 16dB conversion gain in 45nm CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Daegu, Korea, 12–15 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, N.; Gu, P.; You, X.; Zhao, D. A Ka-Band CMOS 4-Beam Phased-Array Receiver with Symmetrical Beam-Distribution Network. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 2020, 3, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Rebeiz, G. A High-Linearity X-Band Four-Element Phased-Array Receiver: CMOS Chip and Packaging. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cao, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z. A wideband Ka-band receiver front-end in 90-nm CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Microwave Integrated Circuit Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 6–8 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Basu, S.; Liao, K.; Wang, Y. Highly Integrated Ka-Band Sub-Harmonic Image-Reject Down-Converter MMIC. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2009, 19, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, S.; Convert, E.; Beasly, P.; Bessemoulin, A.; Dadello, A.; Costantini, A.; Fattorini, A.; McCulloch, M.; Lawrence, B. Broadband integrated millimeter-wave up- and down-converter GaAs MMICs. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2006, 54, 2050–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, S.; Karnfelt, C.; Zirath, H.; Kozhuharov, R.; Kuylenstierna, D.; Fager, C.; Ferndahl, M. 60 GHz Single-Chip Front-End MMICs and Systems for Multi-Gb/s Wireless Communication. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibpour, O.; He, Z.; Strupinski, W.; Rorsman, N.; Ciuk, T.; Ciepielewski, P.; Zirath, H. A W-band MMIC Resistive Mixer Based on Epitaxial Graphene FET. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2017, 27, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Hong, W.; Chen, J. Design of monolithic image rejection mixer. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Symposium on Signals, Systems and Electronics, Nanjing, China, 17–20 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwa, T.; Katoh, T.; Ishida, T.; Nakayama, Y. A V-band drain injected/resistive dual-mode monolithic mixer. In Proceedings of the GaAs IC Symposium—IEEE Gallium Arsenide Integrated Circuit Symposium—21st Annual Technical Digest 1999 (Cat. No.99CH36369), Monterey, CA, USA, 17–20 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwa, T.; Katoh, T.; Ishida, T.; Kojima, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Mitsui, Y. A V-band monolithic InP HEMT resistive mixer with low LO-power requirement. In Proceedings of the 1997 International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, Cape Cod, MA, USA, 11–15 May 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Wu, P.; Yeh, M.; Fu, J.; Chang, H.; Lin, K.; Wang, H. Analysis of Multiconductor Coupled-Line Marchand Baluns for Miniature MMIC Design. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.; Leong, Y.; Lee, C. Analysis and design of miniaturized lumped-distributed impedance-transforming baluns. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2003, 51, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Lin, C.; Chiu, J.; Wang, Y. An Ultra-Broadband Doubly Balanced Monolithic Ring Mixer for Ku- to Ka-band Applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2007, 17, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagra, A.; York, R. Distributed analog phase shifters with low insertion loss. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1999, 47, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, R.; Yan, B. A Ka-band GaAs MMIC quadrupler with high conversion gain and efficient rejection of undesired harmonics. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications (IMWS-AMP), Chengdu, China, 20–22 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Ohashi, Y.; Okubo, N. A 15/60 GHz one-stage MMIC frequency quadrupler. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1996 Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Monolithic Circuits Symposium, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–19 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Hsieh, Y.; Chiong, C.; Hwang, Y. Q-Band GaAs Bandpass Filter Designs for ALMA Band-1. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2009, 19, 353–355. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ma, K. Analysis and Design of a Broadband Receiver Front End for 0.1-to-40-GHz Application. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 2393–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chiang, C.; Huang, R.; Zhou, J.; Du, J.; Wen, K.; Chang, M.; Kuan, Y. A K/Ka/V Triband Single-Signal-Path Receiver with Variable-Gain Low-Noise Amplifier and Constant-Gain Phase Shifter in 28-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 2579–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Ref. | Technology | RF (GHz) | CG (dB) | NF (dB) | IRR (dB) | LO Power (dBm) | PDC (mW) | Phase Shift Range (°) | Integration Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | 0.15 µm GaAs pHEMT | 29~36 | 10~14 | 3.5~4.5 | 20 | 9 | 800 | - | LNA, sub-harmonic IRM |
| [11] | 0.15 µm GaAs pHEMT | 15~35 | 8 | 4.2 | 10 | 2 | 2000 | - | LNA, nonbalanced IRM, LO buffer, LO doubler |
| [11] | 0.15 µm GaAs pHEMT | 35~45 | 10~12 | 3.5 | 20 | 2 | 800 | - | LNA, IRM, LO buffer, LO doubler |
| [12] | 0.15 µm GaAs mHEMT | 56~64 | 10~15 | 7.2 | 13 | −1 | 450 | - | Amplifier, IRM, ×8 LO-chain |
| [24] | 0.15 µm GaAs E-mode pHEMT | 0.1~40 | 16 | 3.4~4.2 | - | 10 | 415 | - | LNA, symmetric distributed drain mixer |
| [6] | 45 nm CMOS | 30~40 | 15 | 5 | - | - | 87.6 | - | LNA, mixer, output buffer, LO buffer |
| [25] | 28 nm CMOS | 30–34.6 | 34.6 | 5.12 | - | - | 131 | 360 | LNA, mixer, IF amplifier, LO buffer, phase shifter |
| This work | 0.15 µm GaAs pHEMT | 32~36 | 6.1~8.7 | 3~3.5 | 35 | −15 | 330 | 500 | LNA, double balanced resistive IRM, quadrupler, Phase shifter |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Hu, A.; Gong, J.; Altaf, A.; Miao, J. Coupling Effects Analysis and Suppression in a Highly Integrated Ka-Band Receiver Front-End MMIC for a Passive Millimeter-Wave Imager System. Sensors 2022, 22, 5695. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155695
Chen X, Hu A, Gong J, Altaf A, Miao J. Coupling Effects Analysis and Suppression in a Highly Integrated Ka-Band Receiver Front-End MMIC for a Passive Millimeter-Wave Imager System. Sensors. 2022; 22(15):5695. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155695
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xi, Anyong Hu, Jianhao Gong, Amjad Altaf, and Jungang Miao. 2022. "Coupling Effects Analysis and Suppression in a Highly Integrated Ka-Band Receiver Front-End MMIC for a Passive Millimeter-Wave Imager System" Sensors 22, no. 15: 5695. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155695
APA StyleChen, X., Hu, A., Gong, J., Altaf, A., & Miao, J. (2022). Coupling Effects Analysis and Suppression in a Highly Integrated Ka-Band Receiver Front-End MMIC for a Passive Millimeter-Wave Imager System. Sensors, 22(15), 5695. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155695






