Characterization of Thermoluminescent Dosimeters for Neutron Dosimetry at High Altitudes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Thermoluminescent Dosimetric System: Dosimeters, Annealing, and Readout Signal
2.2. Ambient Dose Equivalent Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calibration of Thermoluminescent Dosimeters
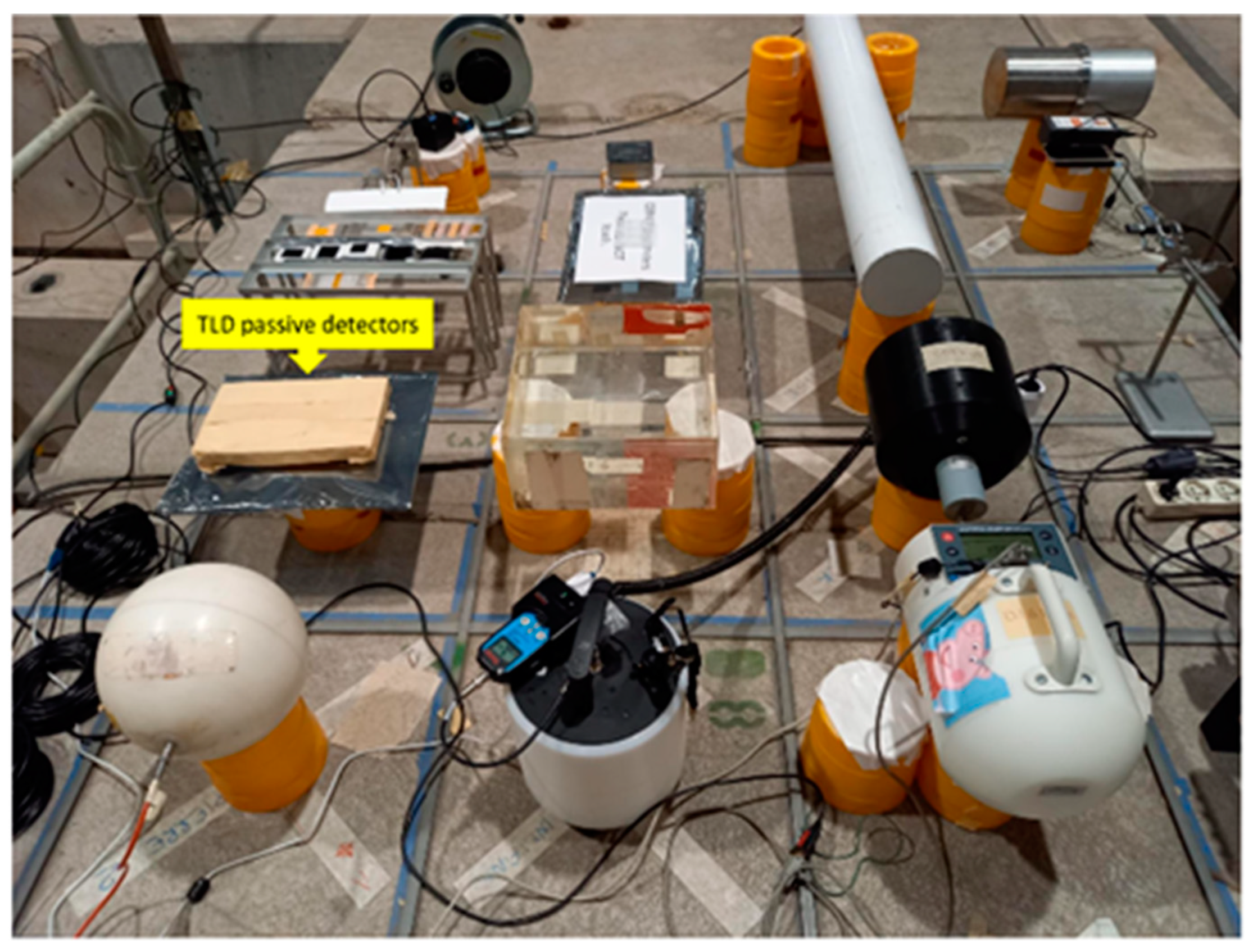
3.2. Irradiation Experiment: TLDs Exposure to the Neutron Field at the CERF Facility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation; Report to General Assembly, Annex B; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, M.; Aisa, D.; Alpat, B.; Alvino, A.; Ambrosi, G.; Andeen, K.; Arruda, L.; Attig, N.; Azzarello, P.; Bachlechner, A.; et al. Precision Measurement of the Proton Flux in Primary Cosmic Rays from Rigidity 1 GV to 1.8 TV with the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 171103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aab, A.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Albury, J.M.; Allekotte, I.; Almela, A.; Castillo, J.A.; Alvarez-Muñiz, J.; Batista, R.A.; Anastasi, G.A.; et al. Measurement of the cosmic-ray energy spectrum above 2.5 × 1018 eV using the Pierre Auger Observatory. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 062005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Pelliccioni, M.; Rancati, T. Calculation of the Radiation Environment Caused by Galactic Cosmic Rays for Determining Air Crew Exposure. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2001, 93, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, M.; Gialanella, G.; Grossi, G.; Pugliese, M.; Scampoli, P.; Kawata, T.; Yasuda, N.; Furusawa, Y. Influence of the shielding on the induction of chromosomal aberrations in human lymphocytes exposed to high-energy iron ions. J. Radiat. Res. 2002, 43, S107–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scampoli, P.; Durante, M.; Grossi, G.; Manti, L.; Pugliese, M.; Gialanella, G. Fragmentation studies of relativistic iron ions using plastic nuclear track detectors. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 35, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, J.W.; Chen, J.; Matthaeus, W.H.; Smith, C.W.; Pomerantz, M.A. Long-term variations of interplanetary magnetic field spectra with implications for cosmic ray modulation. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1993, 98, 3585–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, G.; Arun, T.; Dhar, A.; Patil, A. Rapid decrease in total magnetic field F at Antarctic stations—Its relationship to core-mantle features. Antarct. Sci. 2002, 14, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heller, R.; Merrill, R.T.; McFadden, P.L. The variation of intensity of earth’s magnetic field with time. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2002, 131, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepidi, S.; Cafarella, L.; Francia, P.; Meloni, A.; Palangio, P.; Schott, J.J. Low frequency geomagnetic field variations at Dome C (Antarctica). Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordaro, E.G.; Venegas-Aravena, P.; Laroze, D. Variations of geomagnetic cutoff rigidity in the southern hemisphere close to 70°W (South Atlantic Anomaly and Antarctic zones) in the period 1975 2010. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassinopoulos, E.G.; Xapsos, M.A.; Stauffer, C.A. Forty-Year “Drift” and Change of the SAA; NASA/TM 201521754; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015.
- Pavón-Carrasco, F.J.; De Santis, A. The South Atlantic Anomaly: The Key for a Possible Geomagnetic Reversal. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, A.D.; Kanekal, S.G.; Baker, D.N.; Klecker, B.; Looper, M.D.; Mazur, J.E.; Schiller, Q. SAMPEX observations of the South Atlantic anomaly secular drift during solar cycles 22–24. Space Weather 2017, 15, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zou, H.; Zong, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Shi, W. The Secular Variation of the Center of Geomagnetic South Atlantic Anomaly and Its Effect on the Distribution of Inner Radiation Belt Particles. Space Weather 2017, 15, 1548–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanini, A.; Ongaro, C.; Manfredotti, C.; Tommasino, L.; Losa, P.M. Neutron spectrometry at various altitudes in atmosphere by passive detector technique. Nuovo Cimento. C 2001, 24CS2, 691–697. [Google Scholar]
- Zanini, A.; Storini, M.; Visca, L.; Durisi, E.; Fasolo, F.; Perosino, M.; Borla, O.; Saavedra, O. Neutron spectrometry at high mountain observatories. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2005, 67, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, A.; Storini, M.; Saavedra, O. Cosmic rays at High Mountain Observatories. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 44, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, A.; Ciancio, V.; Laurenza, M.; Storini, M.; Esposito, A.; Terrazas, J.C.; Morfino, P.; Liberatore, A.; Di Giovan, G. Environmental radiation dosimetry at Argentine Antarctic Marambio Base (64°13′ S, 56°43′ W): Preliminary results. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 175–176, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanini, A.; Vernetto, S.; Ciancio, V.; Di Giovan, G.; Morfino, P.; Liberatore, A.; Giannini, G.; Hubert, G. Environmental radiation dosimetry at high southern latitudes with Liulin type instruments. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 208–209, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernetto, S.; Laurenza, M.; Storini, M.; Zanini, A.; Diego, P.; Massetti, S.; Liberatore, A.; Terrazas, J.; Vigorito, C.; Vallania, P.; et al. Long term measurements of neutron dose rates at Testa Grigia high altitude research station (3480 m. a.s.l.). Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 193, 109972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, D.; Zhou, D.; Flood, E. Investigation of cosmic rays and their secondaries at aircraft altitudes. Radiat. Meas. 2001, 34, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhwar, G.D.; Atwell, W.; Badavi, F.F.; Yang, T.C.; Cleghorn, T.F. Space Radiation Absorbed Dose Distribution in a Human Phantom. Radiat. Res. 2002, 157, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P. Overview of research on aircraft crew dosimetry during the last solar cycle. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2009, 136, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, M.; Loffredo, F.; Quarto, M.; Roca, V.; Mattone, C.; Borla, O.; Zanini, A. Results of nDOSE and HiDOSE Experiments for Dosimetric Evaluation During STS-134 Mission. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrožová, I.; Beck, P.; Benton, E.R.; Billnert, R.; Bottollier-Depois, J.-F.; Caresana, M.; Dinar, N.; Domański, S.; Gryziński, M.A.; Kákona, M.; et al. REFLECT—Research flight of EURADOS and CRREAT: Intercomparison of various radiation dosimeters onboard aircraft. Radiat. Meas. 2020, 137, 106433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukashev, K.; Argynova, A.; Zhukov, V.; Idrissova, T.; Iskakov, B.; Piskal, V.; Sadykov, T.; Sadykov, Z.; Stepanov, A.; Serikkanov, A. The Complex of Experimental Facilities for the Cosmic Ray Investigation at the Tien Shan Mountain Station. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Annual Limits on Intake of Radionuclides by Workers Based on the 1990 Recommendations; ICRP Publication 61; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1991; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosino, F.; Thinová, L.; Briestenský, M.; Sabbarese, C. Study of 222Rn continuous monitoring time series and dose assessment in six European caves. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2020, 191, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Radiological Protection from Cosmic Radiation in Aviation. Ann. ICRP 2016, 45, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhm, W.; Mares, V.; Pioch, C.; Simmer, G.; Weitzenegger, E. Continuous measurement of secondary neutrons from cosmic radiation at mountain altitudes and close to the north pole—A discussion in terms of H*(10). Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2009, 136, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioch, C.; Mares, V.; Vashenyuk, E.; Balabin, Y.; Rühm, W. Measurement of cosmic ray neutrons with Bonner sphere spectrometer and neutron monitor at 79°N. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2011, 626–627, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T. Evaluation of World Population-Weighted Effective Dose due to Cosmic Ray Exposure. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawn, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Chakrabarty, S.; Mufti, S.; Bakshi, A.; Sapra, B. Cosmic ray neutron spectrometry and dosimetry at High Altitude Research Laboratory, Gulmarg, Kashmir, India. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 185, 109523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements. Neutron Dosimetry for Biology and Medicine: ICRU Report 26; International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ing, H.; Piesch, E. Status on Neutron Dosimetry. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1985, 10, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, A.; Marrale, M.; Brai, M. Neutron–gamma mixed field measurements by means of MCP–TLD600 dosimeter pair. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2007, 264, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, F.; Silari, M. The CERN-EU high-energy Reference Field (CERF) facility: New FLUKA reference values of spectral fluences, present and newly proposed operational quantities. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2020, 979, 164477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbarese, C.; Ambrosino, F.; Roca, V. Analysis by scanner of tracks produced by Radon alpha particles in CR-39 detectors. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2020, 191, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, G.F. Radiation Detection and Measurement, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenopoulou, V.; Carinou, E.; Stamatelatos, I.E. Personal neutron dosimetry at a research reactor facility. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2001, 96, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, N.; Hassan, G.M.; El-Sersy, A.R.; Ezzat, M. Study of the improvement of TLD cards for personal neutron dosimetry. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2010, 165, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawiah, A.; Bauk, S.; Abdul-Rashid, H.; Gieszczyk, W.; Hashim, S.; Mahdiraji, G.; Tamchek, N.; Bradley, D. Potential application of pure silica optical flat fibers for radiation therapy dosimetry. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2014, 106, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Carrillo, H.R. TLD pairs, as thermal neutron detectors in neutron multisphere spectrometry. Radiat. Meas. 2002, 35, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I.; Pradhan, A.S.; Kim, J.L.; Kim, B.H.; Yim, K.S. Response of 6LiF: Mg, Cu, Si and 7LiF: Mg, Cu, Si TLD pairs to the neutrons and photon mixtures. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2008, 45, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Carrillo, H.R.; Guzman-Garcia, K.A.; Gallego, E.; Lorente, A. Passive neutron area monitor with pairs of TLDs as neutron detector. Radiat. Meas. 2014, 69, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Conversion Coefficients for Use in Radiological Protection against External Radiation; ICRP Publication 74; International Commission on Radiological Protection: Stockholm, Sweden, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Bedogni, R.; Angelone, M.; Pietropaolo, A.; Pillon, M.; Roberts, N.J.; Romano, M.; Salvador-Castiñeira, P.; Sans-Planell, O.; Thomas, D.J.; Treccani, M. Comparing Thermal Neutron Fluence Measurements in the Large Homogeneity Area HOTNES Facility. In Proceedings of the NEUDOS-13, Kraków, Poland, 14–19 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bedogni, R.; Sperduti, A.; Pietropaolo, A.; Pillon, M.; Pola, A.; Gómez-Ros, J.M. Experimental characterization of HOTNES: A new thermal neutron facility with large homogeneity area. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrom. Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2017, 843, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, R.; Pietropaolo, A.; Gomez-Ros, J. The thermal neutron facility HOTNES: Theoretical design. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 127, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
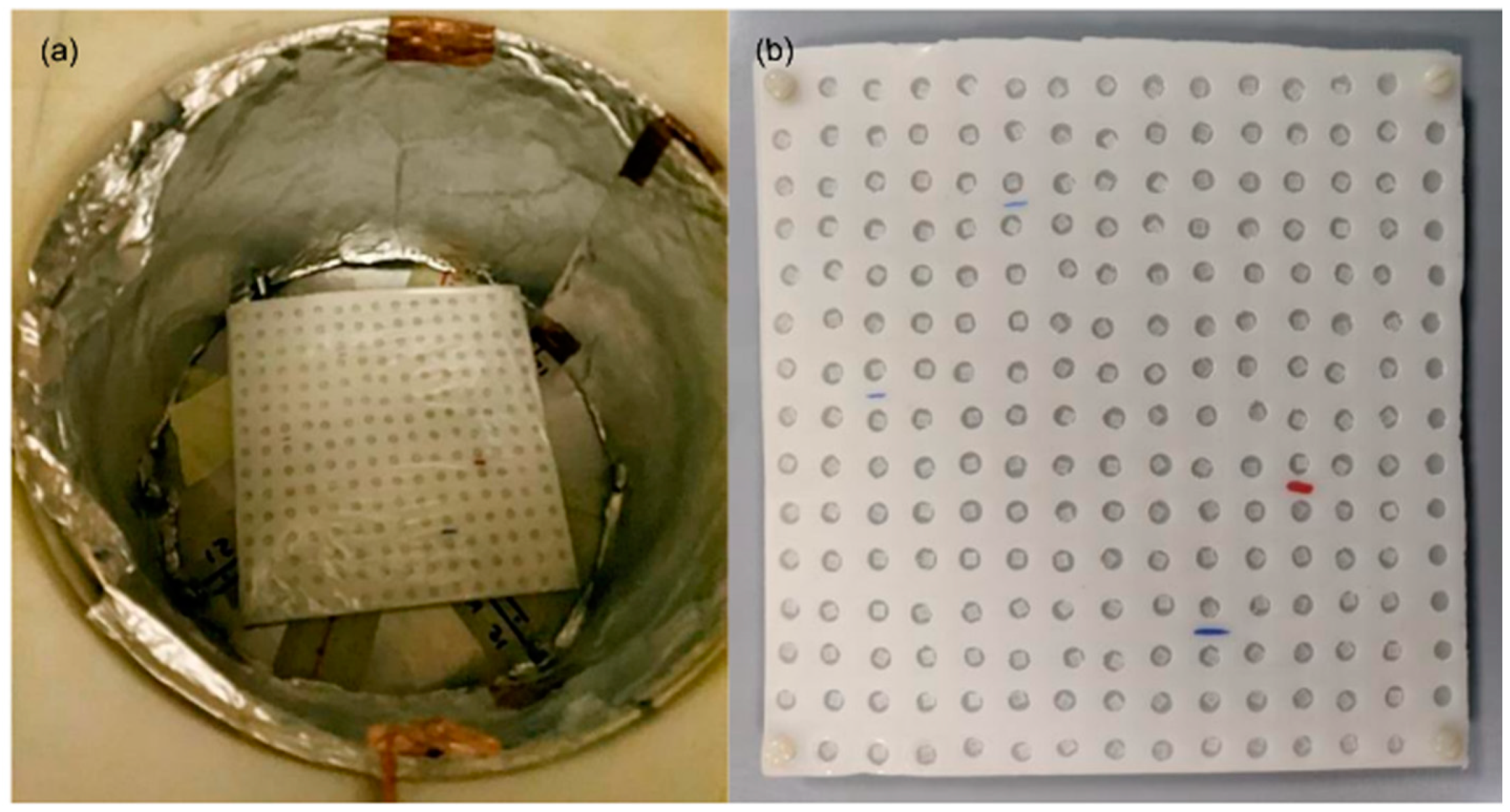

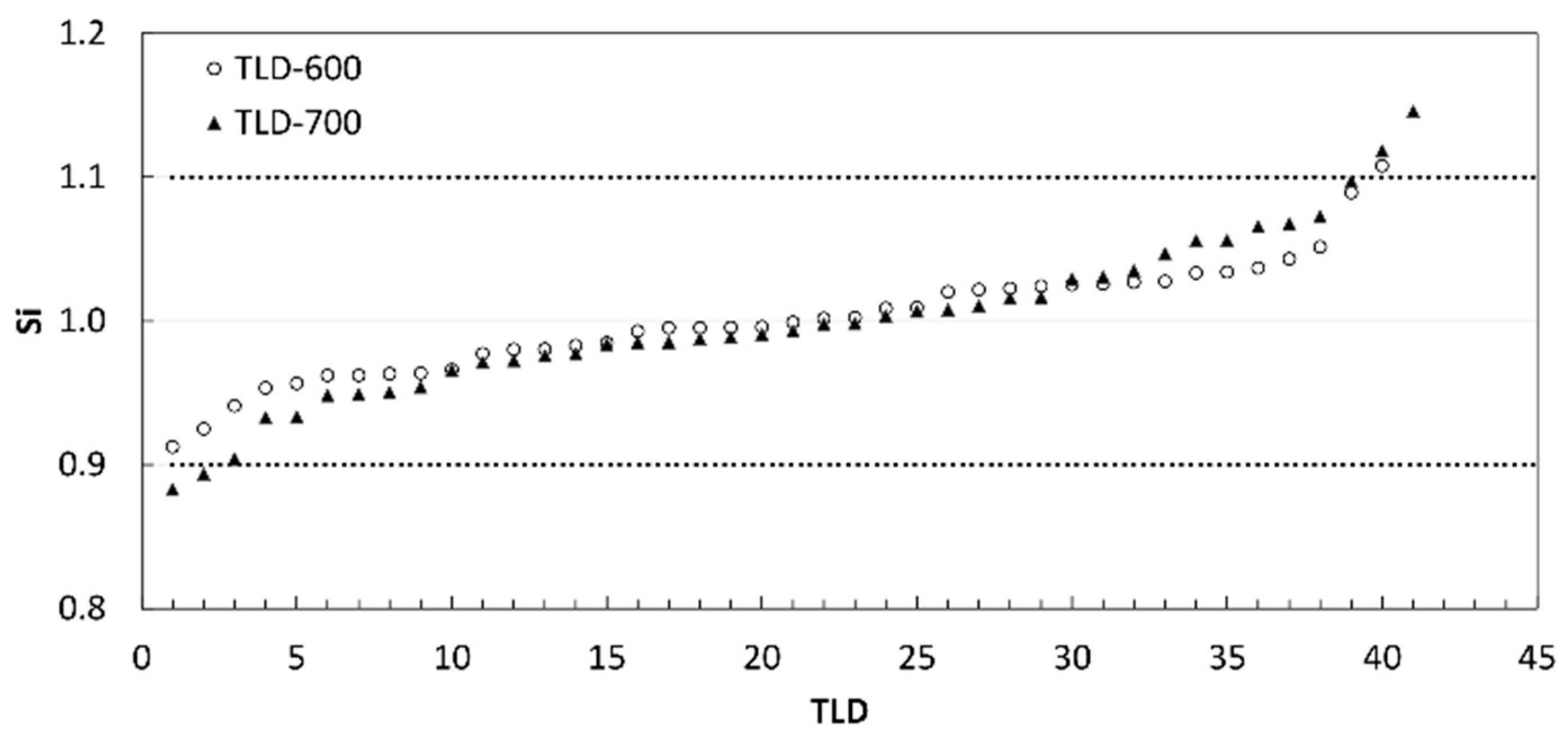
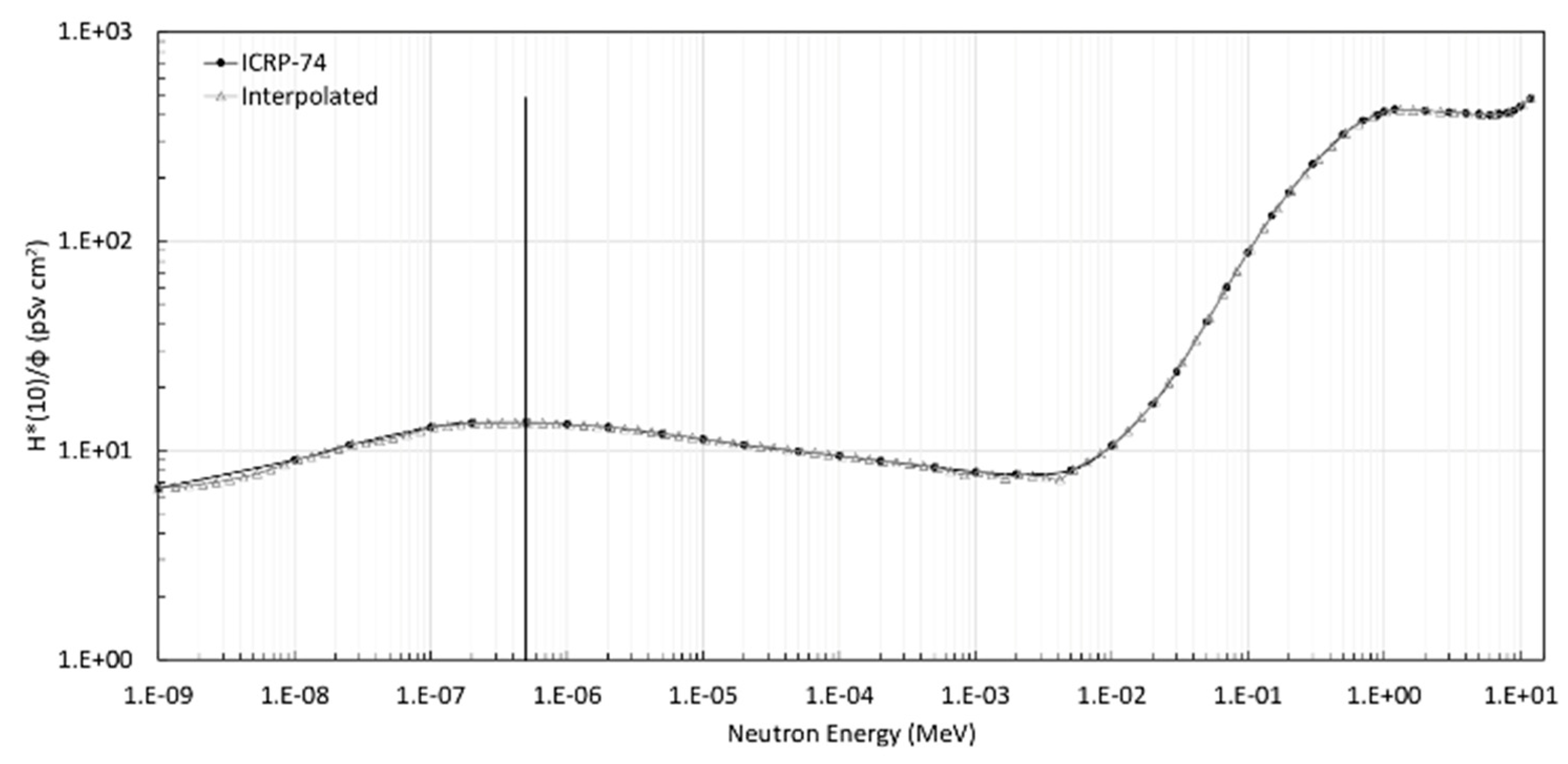
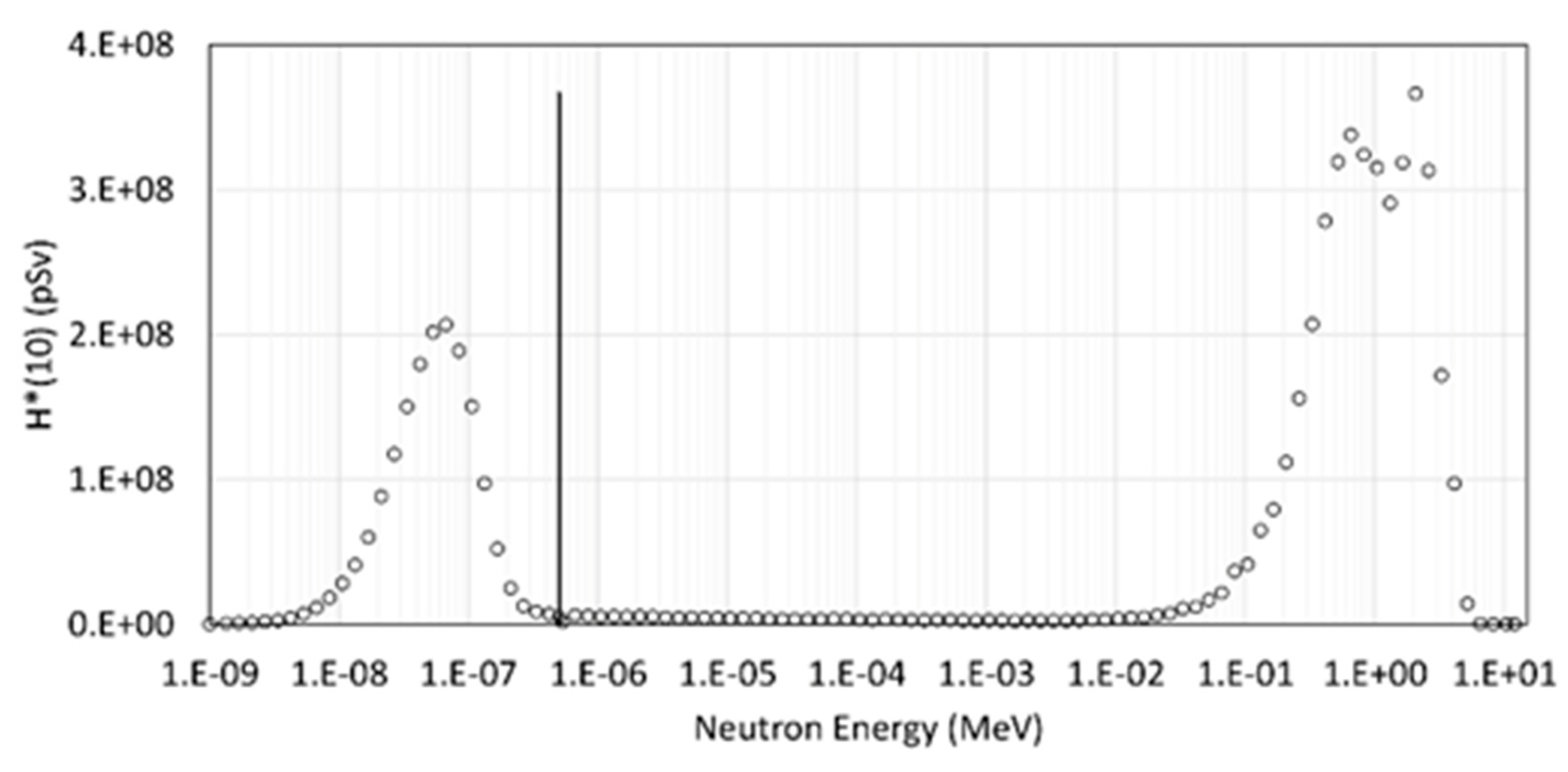

| TLD-600 | TLD-700 | |
|---|---|---|
| TL exposure (nC) | 520 ± 18 | 8.6 ± 0.4 |
| TL background (nC) | 3.6 ± 0.2 | 3.5 ± 0.1 |
| TL600,n(nC) | 511 ± 18 | |
| H*(10)0.5eV (mSv) | 1.67 ± 0.03 | |
| CF600,n (nC/mSv) | 306 ± 12 | |
| TLD-600 | TLD-700 | |
|---|---|---|
| TL exposure (nC) | 6.8 ± 0.4 | 4.7 ± 0.6 |
| TL background (nC) | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 2.67 ± 0.16 |
| TL600,n (nC) | 2.4 ± 0.8 | |
| H*(10)0.5eV (mSv) | 0.008 ± 0.003 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Avino, V.; Ambrosino, F.; Bedogni, R.; Campoy, A.I.C.; La Verde, G.; Vernetto, S.; Vigorito, C.F.; Pugliese, M. Characterization of Thermoluminescent Dosimeters for Neutron Dosimetry at High Altitudes. Sensors 2022, 22, 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155721
D’Avino V, Ambrosino F, Bedogni R, Campoy AIC, La Verde G, Vernetto S, Vigorito CF, Pugliese M. Characterization of Thermoluminescent Dosimeters for Neutron Dosimetry at High Altitudes. Sensors. 2022; 22(15):5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155721
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Avino, Vittoria, Fabrizio Ambrosino, Roberto Bedogni, Abner Ivan C. Campoy, Giuseppe La Verde, Silvia Vernetto, Carlo Francesco Vigorito, and Mariagabriella Pugliese. 2022. "Characterization of Thermoluminescent Dosimeters for Neutron Dosimetry at High Altitudes" Sensors 22, no. 15: 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155721
APA StyleD’Avino, V., Ambrosino, F., Bedogni, R., Campoy, A. I. C., La Verde, G., Vernetto, S., Vigorito, C. F., & Pugliese, M. (2022). Characterization of Thermoluminescent Dosimeters for Neutron Dosimetry at High Altitudes. Sensors, 22(15), 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155721










