Concurrent fNIRS and EEG for Brain Function Investigation: A Systematic, Methodology-Focused Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
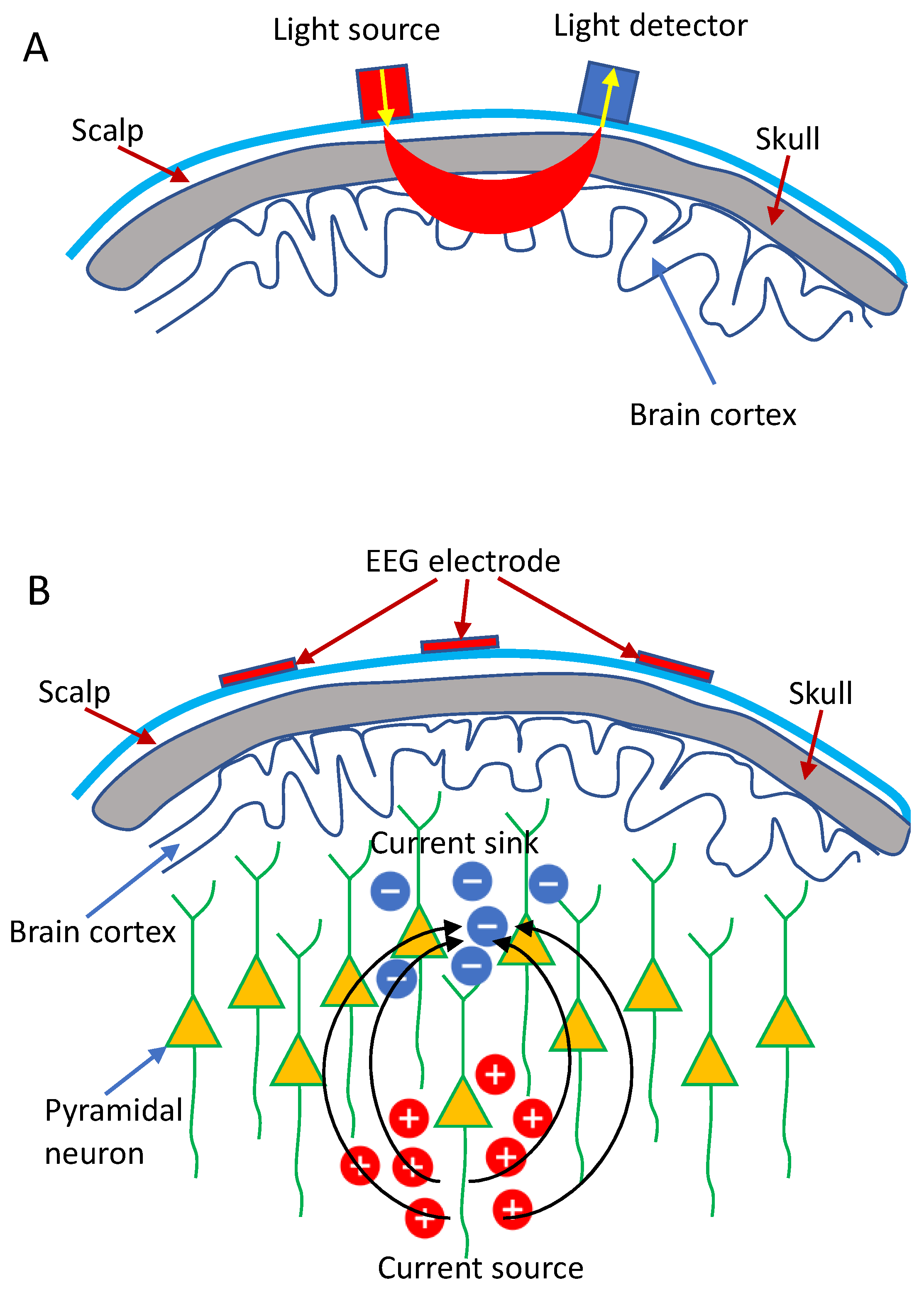
1.1. The Fundamental Basis of fNIRS
1.2. The Fundamental Basis of EEG
1.3. Integration of EEG and fNIRS: Rationale and Advantages
1.4. Motivation of the Present Review
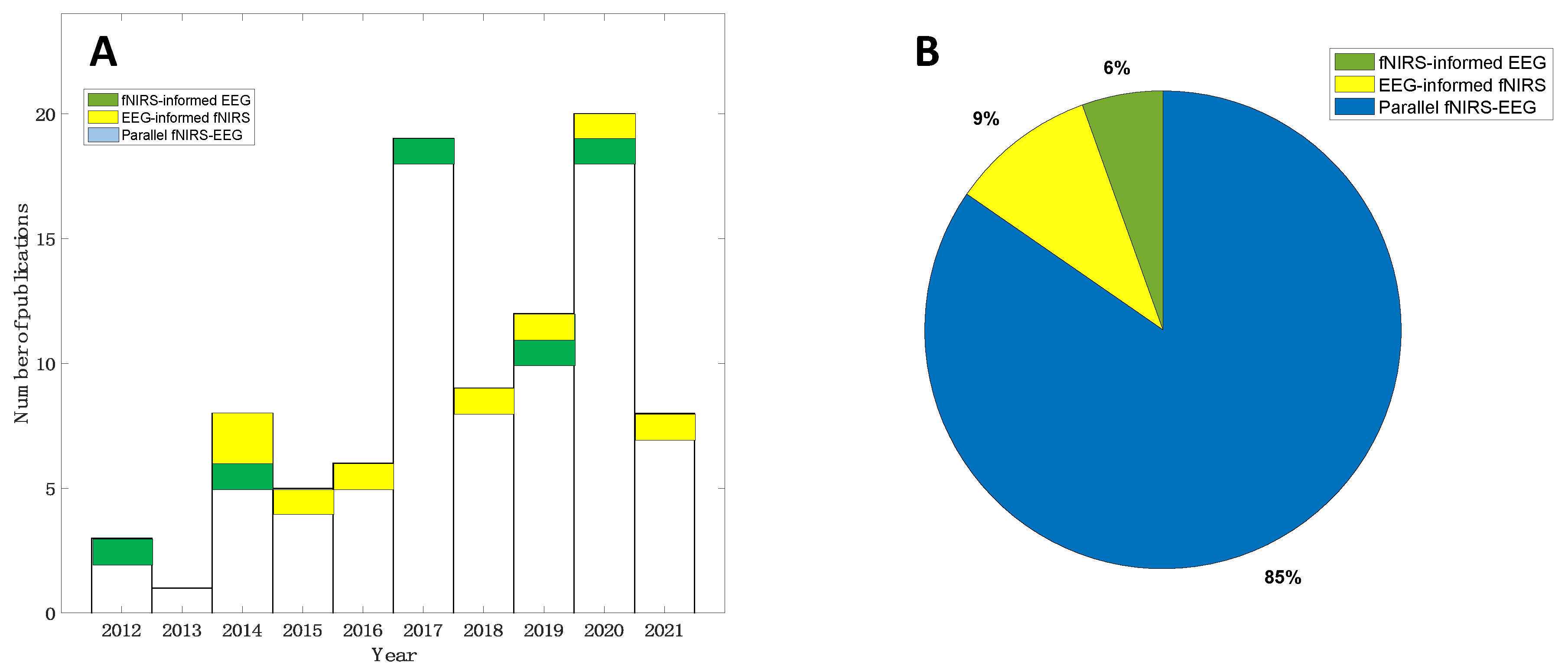
2. Methodology
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Prescreening and Qualifying Criteria
3. Results
3.1. Preprocessing of fNIRS and EEG Signal
3.1.1. Basic Preprocessing of fNIRS Signal
3.1.2. Basic Preprocessing of EEG Signal
3.2. EEG-Informed fNIRS Analyses
3.3. FNIRS-Informed EEG Analyses
3.3.1. FNIRS-Informed EEG Source Imaging Analysis
3.3.2. FNIRS-Informed EEG Channel Selection for BCI Studies
| Authors | Tasks | Brain Regions | Features | Analysis Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aihara et al., 2012 [67] | Motor (Simulation; Experiment) | fNIRS: Motor EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO peak EEG: Source current amplitude | EEG source imaging |
| Morioka et al., 2014 [68] | Mental | fNIRS: Parietal, occipital EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO t-statistic EEG: Source current amplitude | EEG source imaging |
| Li et al., 2017 [61] | Motor | fNIRS: Motor EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HBO/HbR concentrations and slope EEG: Wavelet transform coefficients | Binary classification |
| Li et al., 2019 [27] | Working memory | fNIRS: Frontal, central EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO t-statistic EEG: Functional connectivity | EEG source imaging, Brain network analysis |
| Li et al., 2020 [69] | Motor | fNIRS: Frontal, parietal EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO t-statistic EEG: Functional connectivity | EEG source imaging, Brain network analysis |
3.4. Parallel Analysis of EEG-fNIRS
3.4.1. Feature Fusion Based on fNIRS–EEG Signals for Classification
3.4.2. Correlational Analysis of Concurrent fNIRS–EEG Data
4. Integrated Analysis of Concurrent fNIRS-EEG: Current Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herculano-Houzel, S. The human brain in numbers: A linearly scaled-up primate brain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakkenberg, B.; Pelvig, D.; Marner, L.; Bundgaard, M.J.; Gundersen, H.J.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Regeur, L. Aging and the human neocortex. Exp. Gerontol. 2003, 38, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobsis, F.F. Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science 1977, 198, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. Neuroimage 2012, 63, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Kleiser, S.; Metz, A.J.; Zimmermann, R.; Pavia, J.M.; Wolf, U.; Wolf, M. A review on continuous wave functional near-infrared spectroscopy and imaging instrumentation and methodology. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, H. Über das elektroenkephalogramm des menschen. Arch. Für Psychiatr. Und Nervenkrankh. 1929, 87, 527–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsaki, G.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents—EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomer, D.L.; Da Silva, F.L. Niedermeyer’s Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzagalli, D.A. Electroencephalography and high-density electrophysiological source localization. Handb. Psychophysiol. 2007, 3, 56–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Quinlan, E.B.; Dodakian, L.; McKenzie, A.; Kathuria, N.; Zhou, R.J.; Augsburger, R.; See, J.; Le, V.H.; Srinivasan, R.; et al. Connectivity measures are robust biomarkers of cortical function and plasticity after stroke. Brain 2015, 138, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Potter, T.; Li, R.; Quach, M.; Zhang, Y. Establishing functional brain networks using a nonlinear partial directed coherence method to predict epileptic seizures. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 329, 108447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Deep convolutional neural network-based epileptic electroencephalogram (EEG) signal classification. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Potter, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Single-trial EEG Emotion recognition using granger causality/transfer entropy analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 346, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; She, Q.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Driving fatigue detection from EEG using a modified PCANet method. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 4721863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y. EEG-based driving fatigue detection using a two-level learning hierarchy radial basis function. Front. Neurorobotics 2021, 15, 618408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Rui, G.; Chen, W.; Li, S.; Schulz, P.E.; Zhang, Y. Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease using non-invasive near-infrared spectroscopy. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Zhou, T.; Potter, T.; Zou, L.; Zhang, Y. The cortical network of emotion regulation: Insights from advanced EEG-fMRI integration analysis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Potter, T.; Nguyen, T.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic reorganization of the cortical functional brain network in affective processing and cognitive reappraisal. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2020, 30, 2050051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Rui, G.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Fang, F.; Zhang, Y. Functional network alterations in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment characterized using functional near-infrared spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 28, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Bray, S.; Bryant, D.M.; Glover, G.H.; Reiss, A.L. A quantitative comparison of NIRS and fMRI across multiple cognitive tasks. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 2808–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C. Motor imagery and direct brain-computer communication. Proc. IEEE 2001, 89, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Yang, L.; Wilke, C.; Yuan, H. Electrophysiological imaging of brain activity and connectivity-challenges and opportunities. IEEE Trans. BioMed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1918–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Gomez-Gil, J. Brain computer interfaces, a review. Sensors 2012, 12, 1211–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldert, S.; Tushaus, L.; Kaller, C.P.; Aertsen, A.; Mehring, C. fNIRS exhibits weak tuning to hand movement direction. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Girouard, H.; Iadecola, C. Neurovascular coupling in the normal brain and in hypertension, stroke, and Alzheimer disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Esposito, M.; Deouell, L.Y.; Gazzaley, A. Alterations in the BOLD fMRI signal with ageing and disease: A challenge for neuroimaging. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Nguyen, T.; Potter, T.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic cortical connectivity alterations associated with Alzheimer’s disease: An EEG and fNIRS integration study. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 21, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli, S.; Mehnert, J.; Steinbrink, J.; Curio, G.; Villringer, A.; Muller, K.R.; Blankertz, B. Enhanced performance by a hybrid NIRS-EEG brain computer interface. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, A.P.; Keles, H.O.; Omurtag, A. Hybrid EEG-fNIRS Asynchronous Brain-Computer Interface for Multiple Motor Tasks. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, A.M.; Zappasodi, F.; Di Pompeo, F.; Merla, A. Simultaneous functional near-infrared spectroscopy and electroencephalography for monitoring of human brain activity and oxygenation: A review. Neurophotonics 2017, 4, 041411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.M.; Pollonini, L. NIRSplot: A tool for quality assessment of fNIRS scans. In Optics and the Brain; Optical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Obrig, H.; Neufang, M.; Wenzel, R.; Kohl, M.; Steinbrink, J.; Einhaupl, K.; Villringer, A. Spontaneous low frequency oscillations of cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism in human adults. Neuroimage 2000, 12, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucel, M.A.; Selb, J.; Aasted, C.M.; Lin, P.Y.; Borsook, D.; Becerra, L.; Boas, D.A. Mayer waves reduce the accuracy of estimated hemodynamic response functions in functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, J.W.; Aarabi, A.; Huppert, T.J. Autoregressive model based algorithm for correcting motion and serially correlated errors in fNIRS. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigadoi, S.; Ceccherini, L.; Cutini, S.; Scarpa, F.; Scatturin, P.; Selb, J.; Gagnon, L.; Boas, D.A.; Cooper, R.J. Motion artifacts in functional near-infrared spectroscopy: A comparison of motion correction techniques applied to real cognitive data. Neuroimage 2014, 85 Pt 1, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novi, S.L.; Roberts, E.; Spagnuolo, D.; Spilsbury, B.M.; Price, D.C.; Imbalzano, C.A.; Forero, E.; Yodh, A.G.; Tellis, G.M.; Tellis, C.M.; et al. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy for speech protocols: Characterization of motion artifacts and guidelines for improving data analysis. Neurophotonics 2020, 7, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholkmann, F.; Spichtig, S.; Muehlemann, T.; Wolf, M. How to detect and reduce movement artifacts in near-infrared imaging using moving standard deviation and spline interpolation. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, B.; Dumont, G.A. Wavelet-based motion artifact removal for functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, A.M.; Maclin, E.L.; Fabiani, M.; Gratton, G. A kurtosis-based wavelet algorithm for motion artifact correction of fNIRS data. Neuroimage 2015, 112, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Noah, J.A.; Hirsch, J. Separation of the global and local components in functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals using principal component spatial filtering. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, P.; Scholkmann, F.; Hamilton, A.; Burgess, P.; Tachtsidis, I. Current Status and Issues Regarding Pre-processing of fNIRS Neuroimaging Data: An Investigation of Diverse Signal Filtering Methods Within a General Linear Model Framework. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, M.A.; Luhmann, A.V.; Scholkmann, F.; Gervain, J.; Dan, I.; Ayaz, H.; Boas, D.; Cooper, R.J.; Culver, J.; Elwell, C.E.; et al. Best practices for fNIRS publications. Neurophotonics 2021, 8, 012101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.; Tsai, Y.T.; Meng, L.F.; Wu, T. The removal of ocular artifacts from EEG signals using adaptive filters based on ocular source components. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 3489–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.F.; Yang, Y.; Lin, P.; Wang, P.; Zheng, C.X. Automatic removal of eye-movement and blink artifacts from EEG signals. Brain Topogr. 2010, 23, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Teng, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, X. The Removal of EOG Artifacts From EEG Signals Using Independent Component Analysis and Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolich, L.; Dowding, I. Removal of muscular artifacts in EEG signals: A comparison of linear decomposition methods. Brain Inform. 2018, 5, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriguen, J.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. EEG artifact removal-state-of-the-art and guidelines. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Bian, G.B.; Tian, Z. Removal of Artifacts from EEG Signals: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yu, G. Automatic removal of various artifacts from EEG signals using combined methods. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 27, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Nguyen, D.K.; Tayah, T.; Vannasing, P.; Tremblay, J.; Sawan, M.; Lassonde, M.; Lesage, F.; Pouliot, P. fNIRS-EEG study of focal interictal epileptiform discharges. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 108, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliot, P.; Tran, T.P.Y.; Birca, V.; Vannasing, P.; Tremblay, J.; Lassonde, M.; Nguyen, D.K. Hemodynamic changes during posterior epilepsies: An EEG-fNIRS study. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 108, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, M.T.; Frost, H.R.; Diamond, S.G. Modeling Neurovascular Coupling from Clustered Parameter Sets for Multimodal EEG-NIRS. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 830849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Nguyen, D.K.; Vannasing, P.; Tremblay, J.; Lesage, F.; Pouliot, P. Using patient-specific hemodynamic response function in epileptic spike analysis of human epilepsy: A study based on EEG-fNIRS. Neuroimage 2016, 126, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.J.; Ghafoor, U.; Hong, K.S. Early Detection of Hemodynamic Responses Using EEG: A Hybrid EEG-fNIRS Study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Shimada, S. Simultaneous EEG-NIRS Measurement of the Inferior Parietal Lobule During a Reaching Task With Delayed Visual Feedback. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing fNIRS analysis using EEG rhythmic signatures: An EEG-informed fNIRS analysis study. IEEE Trans. BioMed. Eng. 2020, 67, 2789–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirpal, P.; Damseh, R.; Peng, K.; Nguyen, D.K.; Lesage, F. Multimodal Autoencoder Predicts fNIRS Resting State From EEG Signals. Neuroinformatics, 2021; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, S.; Ye, J.C. Statistical analysis of fNIRS data: A comprehensive review. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Pouliot, P.; Lesage, F.; Nguyen, D.K. Multichannel continuous electroencephalography-functional near-infrared spectroscopy recording of focal seizures and interictal epileptiform discharges in human epilepsy: A review. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 031402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Potter, T.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing Performance of a Hybrid EEG-fNIRS System Using Channel Selection and Early Temporal Features. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borich, M.R.; Brown, K.E.; Lakhani, B.; Boyd, L.A. Applications of Electroencephalography to characterize brain activity: Perspectives in stroke. J. Neurol. Phys. 2015, 39, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Sohrabpour, A.; Brown, E.; Liu, Z.M. Electrophysiological source imaging: A noninvasive window to brain dynamics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 20, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-Curve. Siam. Rev. 1992, 34, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Brunet, D. EEG source imaging: A practical review of the analysis steps. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, R.; Cassar, T.; Muscat, J.; Camilleri, K.P.; Fabri, S.G.; Zervakis, M.; Xanthopoulos, P.; Sakkalis, V.; Vanrumste, B. Review on solving the inverse problem in EEG source analysis. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2008, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, T.; Takeda, Y.; Takeda, K.; Yasuda, W.; Sato, T.; Otaka, Y.; Hanakawa, T.; Honda, M.; Liu, M.G.; Kawato, M.; et al. Cortical current source estimation from electroencephalography in combination with near-infrared spectroscopy as a hierarchical prior. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 4006–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, H.; Kanemura, A.; Morimoto, S.; Yoshioka, T.; Oba, S.; Kawanabe, M.; Ishii, S. Decoding spatial attention by using cortical currents estimated from electroencephalography with near-infrared spectroscopy prior information. Neuroimage 2014, 90, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, S.; Roh, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. Multimodal Neuroimaging Using Concurrent EEG/fNIRS for Poststroke Recovery Assessment: An Exploratory Study. Neurorehab. Neural Repair 2020, 34, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putze, F.; Hesslinger, S.; Tse, C.; Huang, Y.; Herff, C.; Guan, C.; Schultz, T. Hybrid fNIRS-EEG based classification of auditory and visual perception processes. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.X.; Xu, B.L.; Jiang, C.H.; Fu, Y.F.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, H.Y.; Shi, G. A hybrid BCI based on EEG and fNIRS signals improves the performance of decoding motor imagery of both force and speed of hand clenching. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 036004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, H.; Garbey, M.; Omurtag, A. Measuring mental workload with EEG+fNIRS. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Stress assessment based on decision fusion of EEG and fNIRS signals. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19889–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Kiguchi, M.; Badruddin, N.; Dass, S.C.; Hani, A.F.; Tang, T.B. Mental stress assessment using simultaneous measurement of EEG and fNIRS. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 3882–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omurtag, A.; Aghajani, H.; Keles, H.O. Decoding human mental states by whole-head EEG+fNIRS during category fluency task performance. J. Neural Eng. 2017, 14, 066003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ayaz, H.; Akansu, A.N. Multimodal Affective State Assessment Using fNIRS + EEG and Spontaneous Facial Expression. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firooz, S.; Setarehdan, S.K. IQ estimation by means of EEG-fNIRS recordings during a logical-mathematical intelligence test. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 110, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicalese, P.A.; Li, R.; Ahmadi, M.B.; Wang, C.; Francis, J.T.; Selvaraj, S.; Schulz, P.E.; Zhang, Y. An EEG-fNIRS hybridization technique in the four-class classification of alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 336, 108618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi, M.; Bahram Borgheai, S.; Jafari, R.; Constant, N.; Diouf, R.; Shahriari, Y.; Mankodiya, K. Merging fNIRS-EEG brain monitoring and body motion capture to distinguish Parkinson’s disease. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.S.; Khan, M.J.; Hong, M.J. Feature Extraction and Classification Methods for Hybrid fNIRS-EEG Brain-Computer Interfaces. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Hong, M.J.Y.; Hong, K.S. Decoding of four movement directions using hybrid NIRS-EEG brain-computer interface. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Hong, K.S. Hybrid EEG-fNIRS-based eight-command decoding for bci: Application to quadcopter control. Front. Neurorobotics 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.; Lee, H.G.; Nam, Y.; Kang, H.; Koh, C.S.; Shin, H.C.; Choi, S. A hybrid NIRS-EEG system for self-paced brain computer interface with online motor imagery. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 244, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Fazli, S.; Mehnert, J.; Lee, S.-W. Subject-dependent classification for robust idle state detection using multi-modal neuroimaging and data-fusion techniques in BCI. Pattern. Recogn. 2015, 48, 2725–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Ding, M.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, P.; Gao, J.-F.; Wang, R.-M.; Sun, G.-P.; Iramina, K.; Deng, H.-H.; Yang, Y.-K. Temporal-spatial features of intention understanding based on EEG-fNIRS bimodal measurement. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14245–14258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Shin, J.; Im, C.H. Toward a compact hybrid brain-computer interface (BCI): Performance evaluation of multi-class hybrid EEG-fNIRS BCIs with limited number of channels. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padfield, N.; Zabalza, J.; Zhao, H.; Masero, V.; Ren, J. EEG-based brain-computer interfaces using motor-imagery: Techniques and challenges. Sensors 2019, 19, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezazadeh Sereshkeh, A.; Yousefi, R.; Wong, A.T.; Rudzicz, F.; Chau, T. Development of a ternary hybrid fNIRS-EEG brain–computer interface based on imagined speech. Brain Comput. Interfaces 2019, 6, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Nguyen, T.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.G.; Jun, S.C. Exploring Neuro-Physiological Correlates of Drivers’ Mental Fatigue Caused by Sleep Deprivation Using Simultaneous EEG, ECG, and fNIRS Data. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ayaz, H.; Shewokis, P.A. Multisubject "Learning" for Mental Workload Classification Using Concurrent EEG, fNIRS, and Physiological Measures. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ayaz, H.; Shewokis, P.A. Mental workload classification with concurrent electroencephalography and functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Brain Comput. Interfaces 2017, 4, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhudhaif, A. An effective classification framework for brain-computer interface system design based on combining of fNIRS and EEG signals. PEER J. Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.H.; Khan, M.U.; Mishra, D. A Computationally Efficient Method for Hybrid EEG-fNIRS BCI Based on the Pearson Correlation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1838140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Hasan, M.A.H. Hybrid EEG-fNIRS BCI Fusion Using Multi-Resolution Singular Value Decomposition (MSVD). Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 599802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Kim, D.W.; Muller, K.R.; Hwang, H.J. Improvement of Information Transfer Rates Using a Hybrid EEG-NIRS Brain-Computer Interface with a Short Trial Length: Offline and Pseudo-Online Analyses. Sensors 2018, 18, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Kwon, J.; Im, C.H. A Ternary Hybrid EEG-NIRS Brain-Computer Interface for the Classification of Brain Activation Patterns during Mental Arithmetic, Motor Imagery, and Idle State. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Uddin, M.S.; Ahmad, M. Modeling and classification of voluntary and imagery movements for brain–computer interface from fNIR and EEG signals through convolutional neural network. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2019, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirpal, P.; Kassab, A.; Pouliot, P.; Nguyen, D.K.; Lesage, F. fNIRS improves seizure detection in multimodal EEG-fNIRS recordings. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.; van Ginneken, B.; Sanchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Naseer, N.; Yazidi, A.; Eide, P.K.; Hassan, H.W.; Mirtaheri, P. Analysis of Human Gait using Hybrid EEG-fNIRS-based BCI System: A review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Sandmann, P.; Thorne, J.D.; Herrmann, C.S.; Debener, S. Association of Concurrent fNIRS and EEG Signatures in Response to Auditory and Visual Stimuli. Brain Topogr. 2015, 28, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Farrand, J.; Craft, M.A.; Carlson, B.W.; Yuan, H. Amplitude of fNIRS Resting-State Global Signal Is Related to EEG Vigilance Measures: A Simultaneous fNIRS and EEG Study. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 560878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balconi, M.; Vanutelli, M.E. Hemodynamic (fNIRS) and EEG (N200) correlates of emotional inter-species interactions modulated by visual and auditory stimulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zich, C.; Debener, S.; Thoene, A.K.; Chen, L.C.; Kranczioch, C. Simultaneous EEG-fNIRS reveals how age and feedback affect motor imagery signatures. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgheai, S.B.; Deligani, R.J.; McLinden, J.; Zisk, A.; Hosni, S.I.; Abtahi, M.; Mankodiya, K.; Shahriari, Y. Multimodal exploration of non-motor neural functions in ALS patients using simultaneous EEG-fNIRS recording. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 066036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, E.; Brunetti, A.; Ricci, K.; Delussi, M.; Bevilacqua, V.; de Tommaso, M. Mutual interaction between motor cortex activation and pain in fibromyalgia: EEG-fNIRS study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C. Assessing brain networks by resting-state dynamic functional connectivity: An fNIRS-EEG Study. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.T.; King, J.T.; Chuang, C.H.; Ding, W.; Chuang, W.Y.; Liao, L.D.; Wang, Y.K. Exploring the brain responses to driving fatigue through simultaneous EEG and fNIRS measurements. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2020, 30, 1950018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaga, Y.; Ueda, R.; Tanaka, M.; Kita, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Okumura, Y.; Egashira, Y.; Shirakawa, Y.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Kitamura, Y.; et al. Executive dysfunction in medication-naive children with ADHD: A multi-modal fNIRS and EEG study. Brain Dev. 2020, 42, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Okumura, Y.; Kita, Y.; Oi, Y.; Shinoda, H.; Inagaki, M. The relationship between the superior frontal cortex and alpha oscillation in a flanker task: Simultaneous recording of electroencephalogram (EEG) and near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Neurosci. Res. 2018, 131, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, H.O.; Barbour, R.L.; Omurtag, A. Hemodynamic correlates of spontaneous neural activity measured by human whole-head resting state EEG plus fNIRS. Neuroimage 2016, 138, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, P.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Levy, A.D.; Jones, E.J.H.; Tachtsidis, I. An analysis framework for the integration of broadband NIRS and EEG to assess neurovascular and neurometabolic coupling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakrishnan Nair, V.; Kish, B.R.; Yang, H.S.; Yu, Z.; Guo, H.; Tong, Y.; Liang, Z. Monitoring anesthesia using simultaneous functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Electroencephalography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Assessment of mental stress effects on prefrontal cortical activities using canonical correlation analysis: An fNIRS-EEG study. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2583–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, R.B.; Massaro, A.; Chang, T.; Vezina, G.; du Plessis, A. A novel technique for quantitative bedside monitoring of neurovascular coupling. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 259, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalak, L.F.; Tian, F.; Adams-Huet, B.; Vasil, D.; Laptook, A.; Tarumi, T.; Zhang, R. Novel Wavelet Real Time Analysis of Neurovascular Coupling in Neonatal Encephalopathy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarelli, A.M.; Perpetuini, D.; Croce, P.; Filippini, C.; Cardone, D.; Rotunno, L.; Anzoletti, N.; Zito, M.; Zappasodi, F.; Merla, A. Evidence of Neurovascular Un-Coupling in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease through Multimodal EEG-fNIRS and Multivariate Analysis of Resting-State Data. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, D.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Filippini, C.; Cardone, D.; Croce, P.; Rotunno, L.; Anzoletti, N.; Zito, M.; Zappasodi, F.; Merla, A. Working Memory Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease Is Detected by Complexity Analysis of Multimodal EEG-fNIRS. Entropy 2020, 22, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Han, Y. Abnormal dynamic functional connectivity and brain states in Alzheimer’s diseases: Functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Mayseless, N.; Balters, S.; Reiss, A.L. Dynamic inter-brain synchrony in real-life inter-personal cooperation: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy hyperscanning study. Neuroimage 2021, 238, 118263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Pasqualetti, F.; Cieslak, M.; Telesford, Q.K.; Alfred, B.Y.; Kahn, A.E.; Medaglia, J.D.; Vettel, J.M.; Miller, M.B.; Grafton, S.T. Controllability of structural brain networks. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Gao, Y.; Schulz, P.E.; Selvaraj, S.; Zhang, Y. Brain controllability distinctiveness between depression and cognitive impairment. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 294, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheid, B.H.; Ashourvan, A.; Stiso, J.; Davis, K.A.; Mikhail, F.; Pasqualetti, F.; Litt, B.; Bassett, D.S. Time-evolving controllability of effective connectivity networks during seizure progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2006436118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Luhmann, A.; Ortega-Martinez, A.; Boas, D.A.; Yucel, M.A. Using the General Linear Model to Improve Performance in fNIRS Single Trial Analysis and Classification: A Perspective. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Martinez, A.; Von Luhmann, A.; Farzam, P.; Rogers, D.; Mugler, E.M.; Boas, D.A.; Yucel, M.A. Multivariate Kalman filter regression of confounding physiological signals for real-time classification of fNIRS data. Neurophotonics 2022, 9, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Bryant, D.M.; Reiss, A.L. NIRS-based hyperscanning reveals increased interpersonal coherence in superior frontal cortex during cooperation. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, H.Y.; Barrett, G.M.; Borisevich, A.; Chaturvedi, A.; Dahle, J.L.; Dehghani, H.; Dubois, J.; Field, R.M.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Gundran, A.; et al. Kernel Flow: A high channel count scalable time-domain functional near-infrared spectroscopy system. J Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 074710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Luhmann, A.; Wabnitz, H.; Sander, T.; Muller, K.R. M3BA: A Mobile, Modular, Multimodal Biosignal Acquisition Architecture for Miniaturized EEG-NIRS-Based Hybrid BCI and Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, L.; Cooper, R.J.; Yucel, M.A.; Perdue, K.L.; Greve, D.N.; Boas, D.A. Short separation channel location impacts the performance of short channel regression in NIRS. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, M.; Scholkmann, F.; Wolf, U.; Wolf, M.; Elwell, C.; Tachtsidis, I. Modelling confounding effects from extracerebral contamination and systemic factors on functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Neuroimage 2016, 143, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Luhmann, A.; Boukouvalas, Z.; Muller, K.R.; Adali, T. A new blind source separation framework for signal analysis and artifact rejection in functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Neuroimage 2019, 200, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Authors | Tasks | Brain Regions | Features | Analysis Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peng et al., 2014 [51] | Resting | fNIRS: Whole EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR/HbT concentration EEG: Amplitude | GLM |
| Pouliot et al., 2014 [52] | Resting | fNIRS: Whole EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR/HbT concentration EEG: Amplitude | GLM |
| Talukdar et al., 2015 [53] | Resting | fNIRS: Whole EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO concentration EEG: Power spectral envelopes | GLM |
| Peng et al., 2016 [54] | Simulation; Resting | fNIRS: Whole EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR/HbT concentration EEG: Amplitude | GLM |
| Khan et al., 2018 [55] | Motor | fNIRS: Left motor EEG: Left motor | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentration EEG: Power spectrum | Vector-phase analysis |
| Zama et al., 2019 [56] | Motor | fNIRS: Motor EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentration EEG: ERD/ERS | GLM |
| Li et al., 2020 [57] | Motor | fNIRS: Motor EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentration EEG: Absolute Power (amplitude) | GLM |
| Sirpal et al., 2021 [58] | Resting | fNIRS: Whole EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO concentration EEG: Amplitude | Autoencoder |
| Features | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Mean (µ) | |
| Slope (Sp) | |
| Standard deviation (Sd) | |
| Skewness (Skew) | |
| Kurtosis (Kurt) | |
| Median (Med) | |
| Power spectral density (PSD) | |
| Logarithmic band power (PLB) | |
| Common spatial pattern (CSP) | |
| Phase locking value (PLV) | |
| Pearson correlation coefficient (r) |
| Authors | Task | Brain Regions | Features | Correlation Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al., 2015 [101] | Visual and auditory | fNIRS: Temporal, occipital EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentrations EEG: ERP | Pearson correlation |
| Chen et al., 2020 [102] | Resting | Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR global amplitude EEG: Power Spectrum | Partial correlation |
| Balconi et al., 2016 [103] | Visual and auditory | fNIRS: Frontal EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO concentrations EEG: ERP | Pearson correlation |
| Zich et al., 2017 [104] | Motor execution | Central | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentrations EEG: ERD | Pearson correlation |
| Borgheai et al., 2019 [105] | Mental arithmetic | fNIRS: Frontal EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentrations EEG: Power spectrum and ERP | Pearson correlation |
| Gentile et al., 2020 [106] | Finger tapping | fNIRS: Motor EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentrations EEG: ERP | Linear regression |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [107] | Resting | Whole | fNIRS: dynamic functional connectivity EEG: Microstate (amplitude) | Pearson correlation |
| Lin et al., 2020 [108] | Mental | Occipital and parietal | fNIRS: HbO concentration EEG: Power spectrum and ERD | Pearson correlation |
| Kaga et al., 2020 [109] | Working memory | fNIRS: Frontal EEG: Pz, Cz, Pz, | fNIRS: HbO concentration EEG: ERP | Pearson correlation |
| Suzuki et al., 2018 [110] | Working memory | fNIRS: Frontal EEG: Fz, O1, O2, | fNIRS: HbO concentration EEG: Power spectrum | Pearson correlation |
| Keles et al., 2016 [111] | Resting | Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentrations EEG: Power spectrum | Cross-correlation |
| Pinti et al., 2021 [112] | Visual stimulation | Occipital | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentrations EEG: Power spectrum | Cross-correlation |
| Nair et al., 2021 [113] | Anesthesia | Frontal | fNIRS: HbO/HbR amplitude EEG: Amplitude | Cross-correlation and phase difference |
| Al-Shargie et al., 2017 [114] | Mental arithmetic | Frontal | fNIRS: HbO concentration EEG: Average power (amplitude) | Canonical correlation analysis |
| Govindan et al., 2016 [115] | Resting | Frontotemporal | fNIRS: difference between HbO and HbR EEG: Amplitude | Coherence and Phase Spectra |
| Chalak et al., 2017 [116] | Resting | Parietal | fNIRS: Cerebral tissue oxygen saturation EEG: Amplitude | Wavelet coherence |
| Chiarelli et al., 2021 [117] | Resting | Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR concentrations EEG: Power envelops | GLM-Standardized β-weight |
| Prepetuini et al., 2020 [118] | Working memory | fNIRS: Frontal EEG: Whole | fNIRS: HbO/HbR sample entropy EEG: Sample entropy | GLM-Standardized β-weight |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Yang, D.; Fang, F.; Hong, K.-S.; Reiss, A.L.; Zhang, Y. Concurrent fNIRS and EEG for Brain Function Investigation: A Systematic, Methodology-Focused Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155865
Li R, Yang D, Fang F, Hong K-S, Reiss AL, Zhang Y. Concurrent fNIRS and EEG for Brain Function Investigation: A Systematic, Methodology-Focused Review. Sensors. 2022; 22(15):5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155865
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rihui, Dalin Yang, Feng Fang, Keum-Shik Hong, Allan L. Reiss, and Yingchun Zhang. 2022. "Concurrent fNIRS and EEG for Brain Function Investigation: A Systematic, Methodology-Focused Review" Sensors 22, no. 15: 5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155865
APA StyleLi, R., Yang, D., Fang, F., Hong, K.-S., Reiss, A. L., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Concurrent fNIRS and EEG for Brain Function Investigation: A Systematic, Methodology-Focused Review. Sensors, 22(15), 5865. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155865






