A QoS Prediction Approach Based on Truncated Nuclear Norm Low-Rank Tensor Completion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
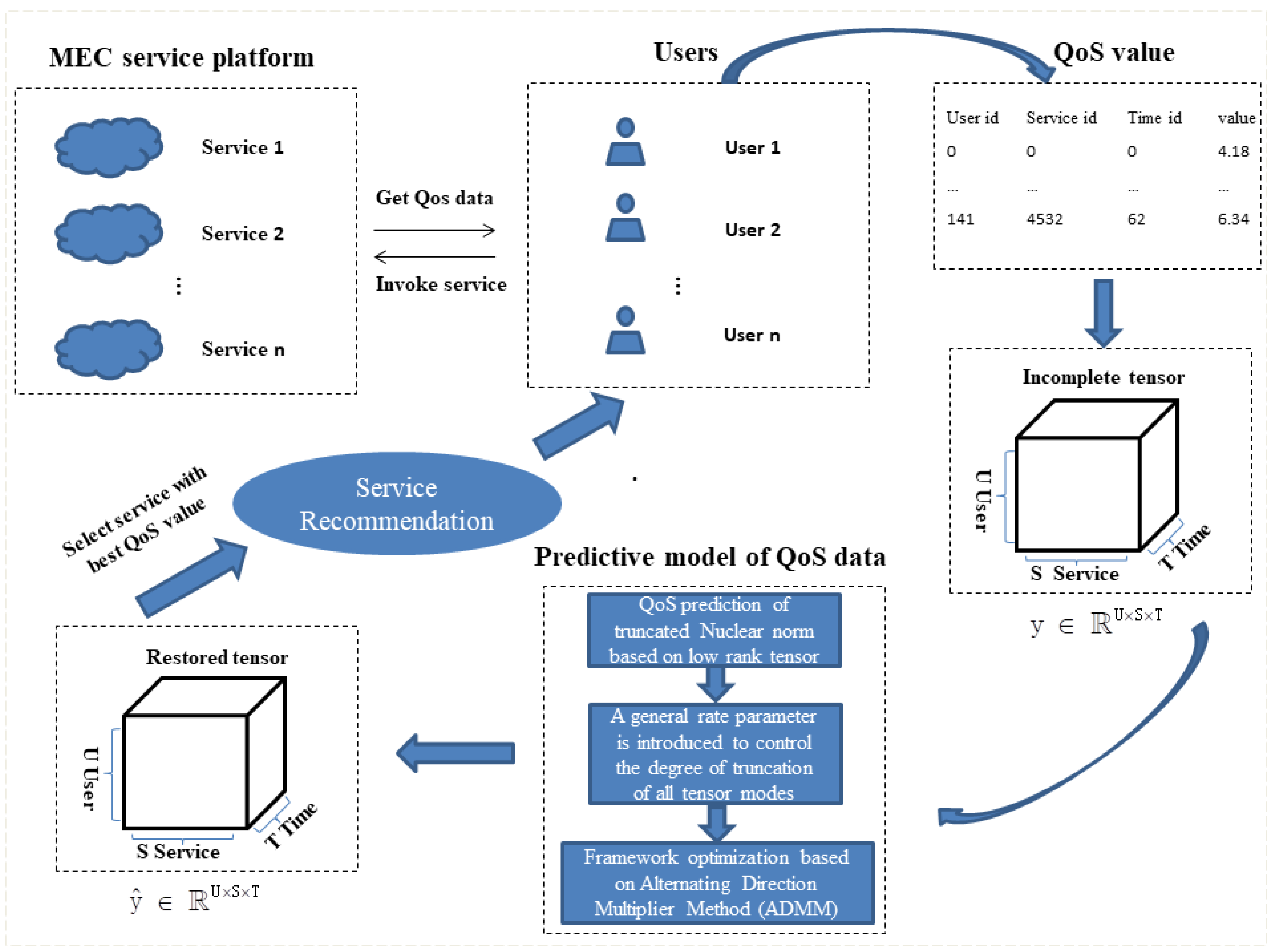
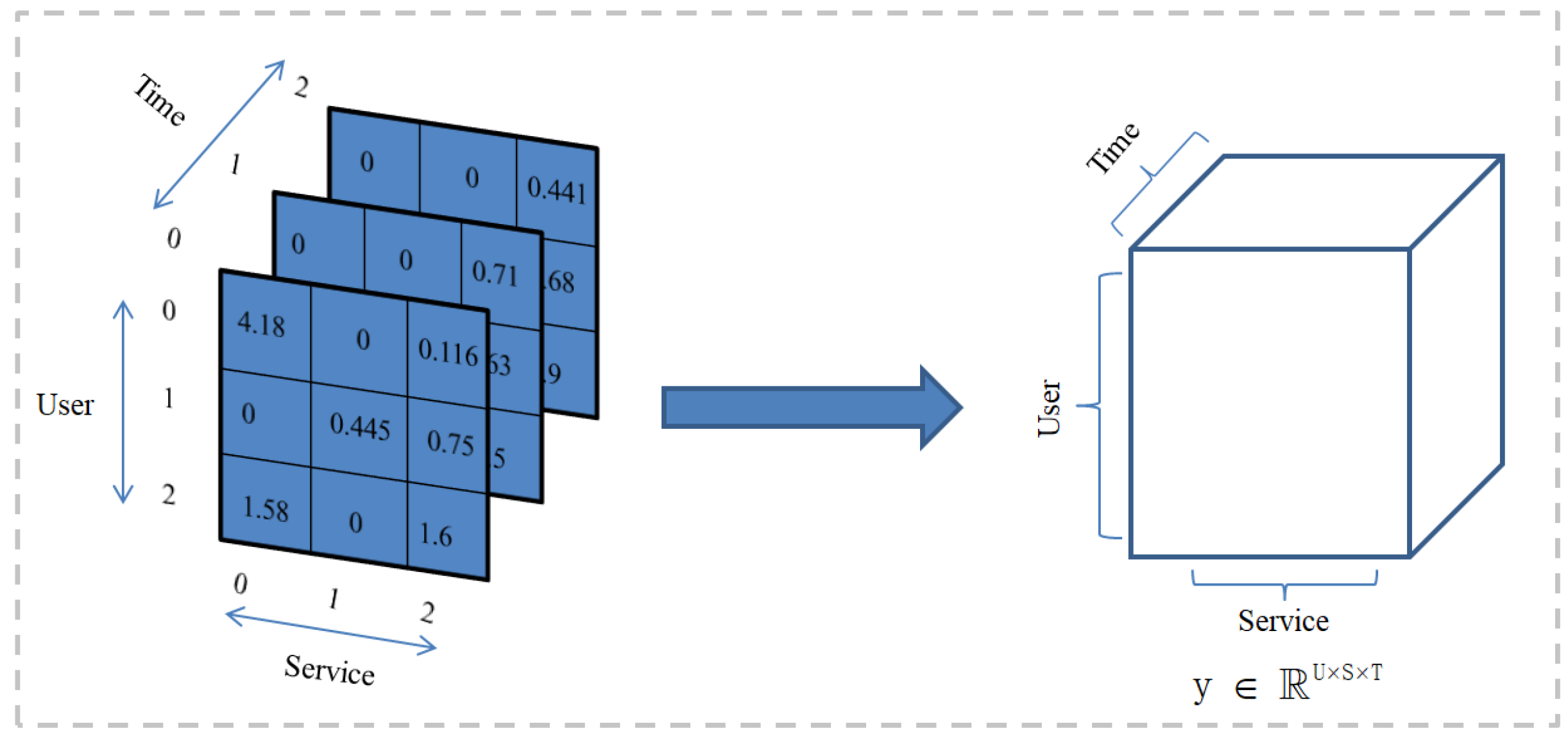
- In order to better express complex multivariate QoS data, we add the dimension of time based on the second-order “User-Service” to form a third-order tensor “User-Service-Time” to represent the QoS data. The QoS data tensor with the addition of time information can well express the complex ternary relationships between data;
- In order to greatly exploit the QoS data correlation between MEC services, we propose the TLTC (Truncated nuclear norm Low-rank Tensor Completion) method to predict the QoS data. As the constructed QoS third-order tensor has low-rank characteristics, the TCTL method approximates the rank of a tensor by the truncated nuclear norm. Meanwhile, a general truncation rate parameter is introduced to control the degree of truncation of the tensor model in order to better analyze the potential characteristics of the QoS data tensor. Finally, the Alternating Direction Method Multiplies (ADMM) method is used for iterative optimization;
- In order to prove the effectiveness of the QoS data prediction model based on the TLTC method proposed in this paper, we conducted an experimental evaluation on the public dataset WS-Dream. The metrics use Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) to evaluate the prediction accuracy. Experimental results show that our QoS data prediction model outperforms other prediction methods.
2. Related Work
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Expression of Tensors
3.2. Low-Rank Matrix Completion
3.3. Low-Rank Tensor Completion
4. Prediction Framework and Method
4.1. Prediction Framework
| Algorithm 1: Tensor Construction “User-Service-Time”. |
|
4.2. Method
| Algorithm 2: TLTC Optimization Imputation Algorithm. |
|
5. Experiment Description
5.1. Database and Baseline Models
5.2. Evaluation Metrics
5.3. Parameter Settings
5.4. Analysis of Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngu, A.H.; Gutierrez, M.; Metsis, V.; Nepal, S.; Sheng, Q.Z. IoT middleware: A survey on issues and enabling technologies. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Hosseini, M.; Pompili, D. Mobile edge computing: Recent efforts and five key research directions. IEEE Comsocmmtc Commun. 2017, 12, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T.F.; Zhou, M.T.; Yv, C.B.; Shen, F.; Li, J.; He, W. An Integrated Edge and Cloud Computing Platform for Multi-Industrial Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 1st International Conference on Digital Twins and Parallel Intelligence, Beijing, China, 15 July 2021; pp. 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shou, G.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Z. Mobile Edge Computing: Progress and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Cloud Computing, Services and Engineering (Mobile Cloud), Oxford, UK, 29 March 2016; pp. 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Xu, X.; Chu, D.; Zhang, W.E. Context-Aware and Adaptive QoS Prediction for Mobile Edge Computing Services. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2022, 15, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Qiu, P.; Zhai, J.; Fan, D.; Peng, H. Multi-objective service composition model based on cost-effective optimization. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xu, H.; Liang, T.; Chen, M.; Gao, H.; Longo, A. Leveraging Data Augmentation for Service QoS Prediction in Cyber-physical Systems. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2021, 21, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Hsu, C.H.; Yang, F. Collaboration reputation for trustworthy Web service selection in social networks. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2016, 82, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, J.; Hsu, C.H. QoS prediction for service recommendations in mobile edge computing. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2019, 127, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wen, J.; Wang, X. From reputation perspective: A hybrid matrix factorization for qos prediction in location-aware mobile service recommendation system. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2019, 2019, 8950508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Shen, L.; Li, F.; You, D.; Mapetu, J.P.B. Web service QoS prediction: When collaborative filtering meets data fluctuating in big-range. World Wide Web 2020, 23, 1715–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Li, C.J.; Yu, Z.L. Dynamic Web service selection group decision-making based on heterogeneous QoS models. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2012, 19, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, W. Predictive-trend-aware composition of web services with time-varying Quality-Of-Service. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1910–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, A.; Salakhutdinov, R. Probabilistic matrix factorization. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’07, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 December 2007; pp. 1257–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, G.; Chen, J.; He, Q.; Li, K.C.; Zhang, B.; Gan, Y. NDMF: Neighborhood-Integrated Deep Matrix Factorization for Service QoS Prediction. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2020, 17, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Jing, X.Y.; Wu, D.; He, Z.; Cao, J.; Yue, D.; Wang, L. Similarity-maintaining privacy preservation and location-aware low-rank matrix factorization for QoS prediction based web service recommendation. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2021, 14, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Shang, M.; Luo, X. A momentum-incorporated latent factorization of tensors model for temporal-aware QoS missing data prediction. Neurocomputing 2019, 367, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, X. Temporal QoS-aware web service recommendation via non-negative tensor factorization. In Proceedings of the WWW ’14: 23rd International World Wide Web Conference, Seoul, Korea, 7–11 April 2014; pp. 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Lyu, M.R. WSPred: A time-aware personalized QoS prediction framework for web services. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering, Washington, DC, USA, 29 November 2011; pp. 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xie, B.; Mei, H. Personalized QoS prediction for web services via collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Web Services, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 9 July 2007; pp. 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wenwu, Z.; Li, H. Improved Collaborative Filtering Algorithm Based on Network Site Users. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Big Data and Informatization Education, Hangzhou, China, 2–4 April 2021; pp. 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.J. Categorization for grouping associative items mining in Item-based collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Information Science and Applications, Jeju, Korea, 26 April 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Ma, H.; Lyu, M.R.; King, I. QoS-aware web service recommendation by collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2011, 4, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Peng, Q.; Hu, X.; Rong, Y. Web service recommendation based on time series forecasting and collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Web Services, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June 2015; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S. Time-aware cloud service recommendation using similarity enhanced collaborative filtering and ARIMA model. Decis. Support Syst. 2018, 107, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wu, L.; Guo, K.; Li, W.; Luo, X.; Zhu, Q. On dynamic performance estimation of fault-prone Infrastructure-as-a-Service clouds. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13, 1550147717718514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; He, P.; Zheng, Z.; Lyu, M.R. Online QoS prediction for runtime service adaptation via adaptive matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2017, 28, 2911–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Musialski, P.; Wonka, P.; Ye, J. Tensor completion for estimating missing values in visual data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Q.; Yang, K. An efficient tensor completion method via truncated nuclear norm. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2020, 70, 9p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Kwok, J.T.; Wang, T.; Liu, T.Y. Large-scale Low-rank matrix learning with non-convex regularizers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 2628–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Saunier, N.; Sun, L. Scalable Low-rank tensor learning for spatiotemporal traffic data imputation. Transp. Res. Part Emerg. Technol. 2021, 129, 14p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, L. Low-Rank Autoregressive Tensor Completion for Multivariate Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10436. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, L. A Nonconvex Low-Rank Tensor Completion Model for Spatiotemporal Traffic Data Imputation. Transp. Res. Part Emerg. Technol. 2020, 117, 12p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lei, M.; Saunier, N.; Sun, L. Low-Rank Autoregressive Tensor Completion for Spatiotemporal Traffic Data Imputation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 12301–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.R.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, W.X. Low-rank Tensor Completion by Sum of Tensor Nuclear Norm Minimization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 134943–134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silic, M.; Delac, G.; Srbljic, S. Prediction of atomic web services reliability for QoS-aware recommendation. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2015, 8, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, H.; Gao, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, G. A hybrid tensor factorization approach for QoS prediction in time-aware mobile edge computing. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 8056–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Statistics | Throughput | Response Time |
|---|---|---|
| Scale of QoS values | 0–1000 kbps | 0–20 s |
| Mean of QoS values | 9.609 kbps | 3.165 s |
| Standrad Deviation | 50.11 s | 6.12 s |
| Num. of Users | 142 | 142 |
| Num. of Services | 4532 | 4532 |
| Num. of Time Intervals | 64 | 64 |
| Interval of Time Slots | 15 min | 15 min |
| Num. of Records | 30,287,611 | 30,287,611 |
| No. | Train:Test | Training Data | Testing Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10%:90% | 3,028,761 | 27,258,850 |
| 2 | 15%:85% | 4,543,142 | 25,744,469 |
| 3 | 20%:80% | 6,057,522 | 24,230,089 |
| 4 | 25%:75% | 7,571,903 | 22,715,708 |
| 5 | 30%:70% | 9,086,283 | 21,201,328 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, H.; Dong, Q.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, Z. A QoS Prediction Approach Based on Truncated Nuclear Norm Low-Rank Tensor Completion. Sensors 2022, 22, 6266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22166266
Xia H, Dong Q, Zheng J, Chen Y, Gao C, Wang Z. A QoS Prediction Approach Based on Truncated Nuclear Norm Low-Rank Tensor Completion. Sensors. 2022; 22(16):6266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22166266
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Hong, Qingyi Dong, Jiahao Zheng, Yanping Chen, Cong Gao, and Zhongmin Wang. 2022. "A QoS Prediction Approach Based on Truncated Nuclear Norm Low-Rank Tensor Completion" Sensors 22, no. 16: 6266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22166266
APA StyleXia, H., Dong, Q., Zheng, J., Chen, Y., Gao, C., & Wang, Z. (2022). A QoS Prediction Approach Based on Truncated Nuclear Norm Low-Rank Tensor Completion. Sensors, 22(16), 6266. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22166266





