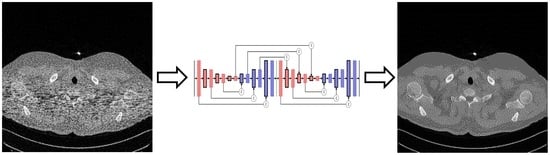
Image Recovery from Synthetic Noise Artifacts in CT Scans Using Modified U-Net
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Data Set
2.2. Noise Simulation
2.3. Selection of Denoising Technique
2.4. Performance Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Noise Synthesis
3.2. Observed Network Setting
3.3. Comparison between Denoising Techniques
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genevois, P.A.; Tack, D. Dose Reduction and Optimization in Computed Tomography of the Chest. In Radiation Dose from Adult and Pediatric Multidetector Computed Tomography, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume 10, pp. 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Naidich, D.P.; Marshall, C.H.; Gribbin, C.; Arams, R.S.; McCauley, D.I. Low-dose CT of the lungs: Preliminary observations. Radiology 1990, 175, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massoumzadeh, P.; Don, S.; Hildebolt, C.F.; Bae, K.T.; Whiting, B.R. Validation of CT dose-reduction simulation. Med. Phys. 2008, 36, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberle, D.R.; Abtin, F.; Brown, K. Computed Tomography Screening for Lung Cancer: Has It Finally Arrived? Implications of the National Lung Screening Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Wang, J.; Leng, S.; Schmidt, B.; Allmendinger, T.; Grant, K.; Flohr, T.; McCollough, C.H. Electronic noise in CT detectors: Impact on image noise and artifacts. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, W626–W632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhove, V.V.; Beenhouwer, J.D.; Schryver, T.D.; Hoorebeke, L.V.; Sijbers, J. Data-Driven Affine Deformation Estimation and Correction in Cone Beam Computed Tomography. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.R.; Wittram, C.; Shepard, J.; McLeaod, T.; Rhea, J. Standard-Dose and 50%—Reduced-Dose Chest CT: Comparing the Effect on Image Quality. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 179, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T.; Ohno, Y.; Takenaka, D.; Nishino, M.; Gautam, S.; Sugimura, K.; Kauczor, H.U.; Hatabu, H. Standard-dose vs. low-dose CT protocols in the evaluation of localized lung lesions: Capability for lesion characterization—iLEAD study. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2016, 3, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Gou, S.P.; Yao, Y.; Bai, J.; Jiao, L.; Sheng, K. Denoising of Low Dose CT Image with Context-Based BM3D. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Singapore, 22–25 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wolterink, J.M.; Leiner, T.; Viergever, M.A.; Isgum, I. Generative Adversarial Networks for Noise Reduction in Low-Dose CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2536–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rong, J.; Lu, H.; Xing, Y.; Meng, J. Low-Dose Lung CT Image Restoration Using Adaptive Prior Features From Full-Dose Training Database. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2510–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L. CT image denoising based on sparse representation using global dictionary. In Proceedings of the ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering, Beijing, China, 25–28 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alsamadony, K.L.; Yildirim, E.U.; Glatz, G.; Waheed, U.B.; Hanafy, S.M. Deep Learning Driven Noise Reduction for Reduced Flux Computed Tomography. Sensors 2021, 21, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrin, S.; Alom, M.Z.; Burada, R.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Medical Image Denoising with Recurrent Residual U-Net (R2U-Net) base Auto-Encoder. In Proceedings of the IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON), Dayton, OH, USA, 15–19 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.C.; Hoang, Q.V.; Le, T.H.; Peng, Y.T.; Huang, C.C.; Zhang, C.; Fung, B.C.M.; Cheng, K.H.; Huang, S.W. An Advanced Noise Reduction and Edge Enhancement Algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21, 5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Yin, X.; Chen, Y.; Shu, H.; Luo, L.; Coatrieux, G.; Gui, Z.; et al. Improving Low-Dose CT Image Using Residual Convolutional Network. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 24698–24705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Chen, B.; Holmes, D.R.I.; Duan, X.; Yu, Z.; Yu, L.; Leng, S.; Fletcher, J.G. Low Dose CT Image and Projection Data (LDCT-and-Projection-data) (Version 4) [Data set]. In The Cancer Imaging Archive; TCIA: Manchester, NH, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L. A Multifeature Extraction Method Using Deep Residual Network for MR Image Denoising. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 8823861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, F.; Fan, H.; Zhang, C. Brief review of image denoising techniques. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art 2019, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image Denoising by Sparse 3-D Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gurrola-Ramos, J.; Dalmau, O.; Alarcon, T.E. A Residual Dense U-Net Neural Network for Image Denoising. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 31742–31754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.P.; Stille, M.; Buzug, T.M. Residual U-Net Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Low-Dose CT Denoising. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 4, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Han, B. Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.J.; Shen, C.; Yang, T.B. Image Restoration Using Convolutional Auto-encoders with Symmetric Skip Connections. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.08921. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kalra, M.K.; Lin, F.; Chen, Y.; Liao, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Low-Dose CT With a Residual Encoder-Decoder Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2524–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Ehrlich, M.; Shah, S.; Davis, L.; Chellappa, R. Stacked U-Nets for Ground Material Segmentation in Remote Sensing Imagery. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake CIty, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sevastopolsky, A.; Drapak, S.; Kiselev, K.; Snyder, B.; Keenan, J.; Georgievskaya, A. Stack-U-Net: Refinement network for improved optic disc and cup image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–21 February 2019; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa, S.; Sei, Y.; Orihara, R.; Ohsuga, A. Computed tomography image reconstruction using stacked U-Net. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 90, 101920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayachi, R.; Afif, M.; Said, Y.; Atri, M. Strided Convolution Instead of Max Pooling for Memory Efficiency of Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the SETIT 2018, Maghreb, Tunisia, 18–20 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. ADAM: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L. FFDNet: Toward a Fast and Flexible Solution for CNN based Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4608–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Soundararajan, R.; Bovik, A.C. Making a “Completely Blind” Image Quality Analyzer. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, S.; Wang, Z. A Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of Image Quality Assessment Algorithms. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 140030–140070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K. Data from the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) [Data set]. In The Cancer Imaging Archive; TCIA: Manchester, NH, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


















| Network | Filter | NIQEAV | PSNRAV | SSIMAV | Training Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | 2 × [3 × 3] | 7.672 | 10.377 | 0.00890 | 544 |
| Stacked | 1 × [3 × 3] | 7.695 | 10.432 | 0.00892 | 816 |
| Stacked | 2 × [3 × 3] | 7.667 | 10.557 | 0.00895 | 1229 |
| Stacked | 3 × [3 × 3] | 7.727 | 10.570 | 0.00895 | 2191 |
| Stacked | 1 × [5 × 5] | 7.886 | 10.549 | 0.00895 | 1564 |
| Stacked | 1 × [7 × 7] | 7.928 | 10.582 | 0.00896 | 3528 |
| S-Dual [3 × 3] | SegNet | DeConvNet | RedNet | UNet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 1229 | 644 | 576 | 764 | 406 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunawan, R.; Tran, Y.; Zheng, J.; Nguyen, H.; Chai, R. Image Recovery from Synthetic Noise Artifacts in CT Scans Using Modified U-Net. Sensors 2022, 22, 7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22187031
Gunawan R, Tran Y, Zheng J, Nguyen H, Chai R. Image Recovery from Synthetic Noise Artifacts in CT Scans Using Modified U-Net. Sensors. 2022; 22(18):7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22187031
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunawan, Rudy, Yvonne Tran, Jinchuan Zheng, Hung Nguyen, and Rifai Chai. 2022. "Image Recovery from Synthetic Noise Artifacts in CT Scans Using Modified U-Net" Sensors 22, no. 18: 7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22187031
APA StyleGunawan, R., Tran, Y., Zheng, J., Nguyen, H., & Chai, R. (2022). Image Recovery from Synthetic Noise Artifacts in CT Scans Using Modified U-Net. Sensors, 22(18), 7031. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22187031