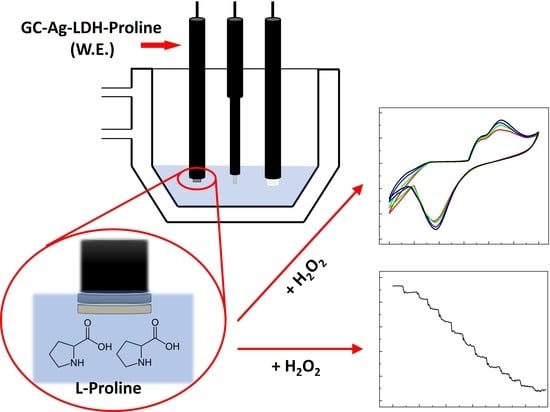
Novel Electrochemical Sensors Based on L-Proline Assisted LDH for H2O2 Determination in Healthy and Diabetic Urine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. LDH Preparation and Characterization
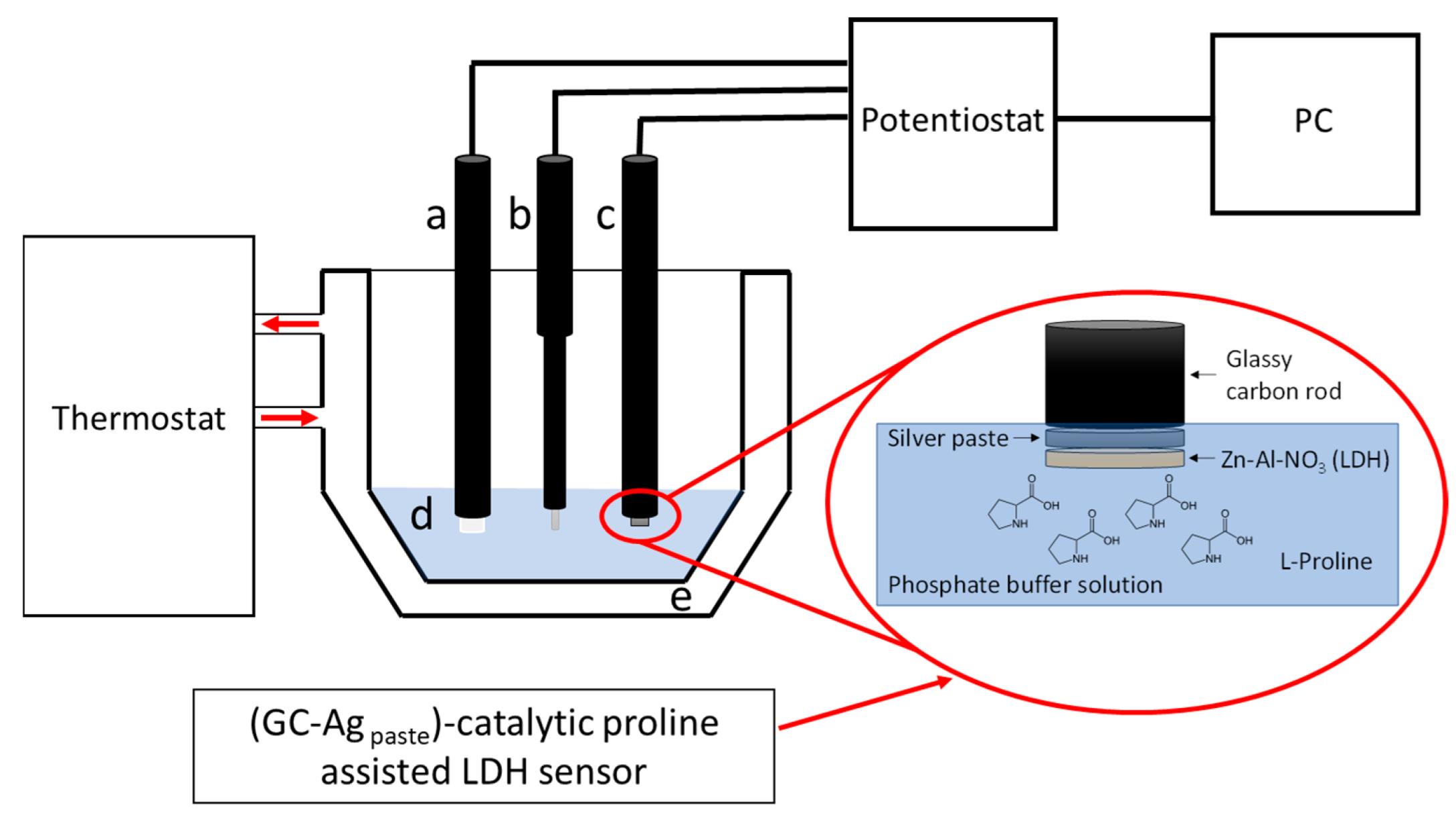
2.3. Sensor Preparation
2.4. Electrochemical Apparatus and Experimental Measurements
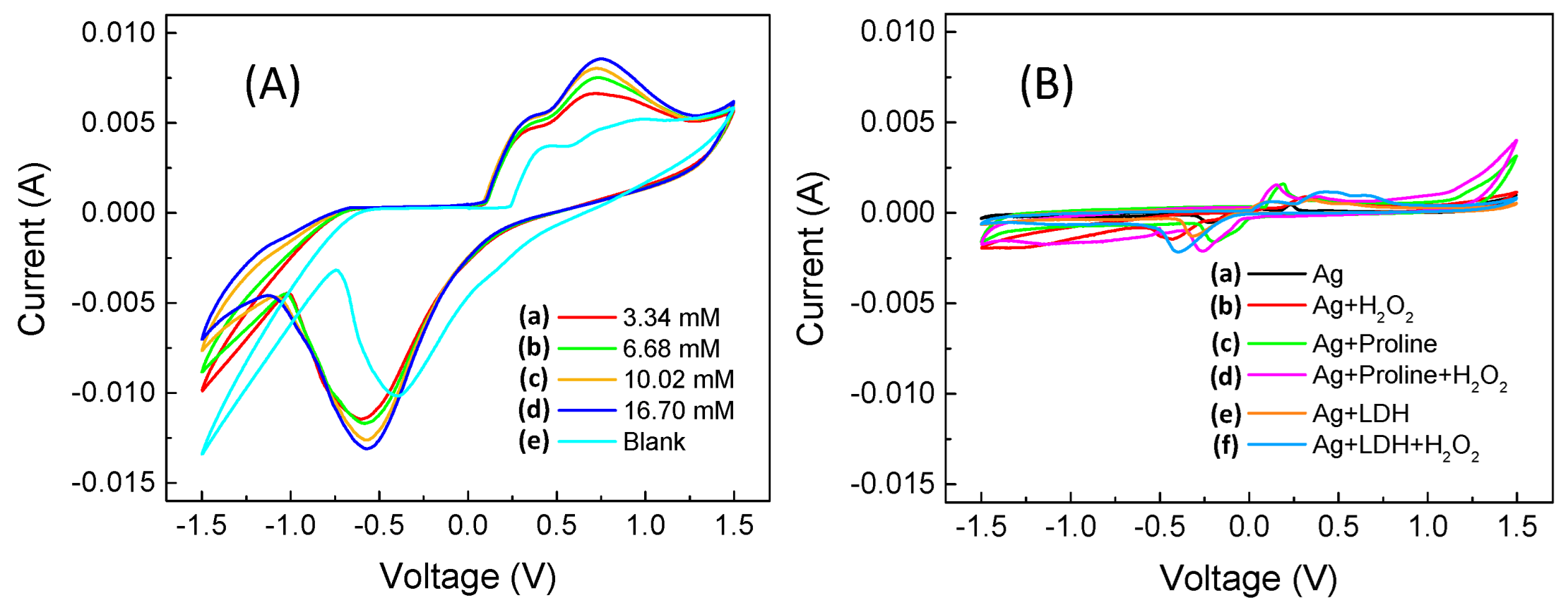
2.4.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
2.4.2. Amperometric Measurements
2.4.3. Real Sample Analysis
2.4.4. Clark Catalytic LDH Amperometric Sensor ·Preparation and Measurements·
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Pharmacopeia. Hydrogen Peroxide Concentrate; USP Monographs; United States Pharmacopeia (USP-NF): Rockville, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perathoner, S.; Centi, G. Wet Hydrogen Peroxide Catalytic Oxidation (WHPCO) of Organic Waste in Agro-Food and Industrial Streams. Top. Catal. 2005, 33, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.E.; Luo, W.; Zhu, L.; Zou, J.; Tang, H. Fluorometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide in Milk by Using a Fenton Reaction System. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.D.S.; de Oliveira, G.C.M.; Santos, F.A.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Janegitz, B.C. Use of Zein Microspheres to Anchor Carbon Black and Hemoglobin in Electrochemical Biosensors to Detect Hydrogen Peroxide in Cosmetic Products, Food and Biological Fluids. Talanta 2019, 194, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, F.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.-H.; Liu, S.-Y.; Wei, F.; Dong, X.-Y.; Cheng, J.-K.; Huang, W.-H. Real-Time Monitoring of Oxidative Burst from Single Plant Protoplasts Using Microelectrochemical Sensors Modified by Platinum Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8453–8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, S.K.; Sreejith, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y. Immobilizing Gold Nanoparticles in Mesoporous Silica Covered Reduced Graphene Oxide: A Hybrid Material for Cancer Cell Detection through Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13648–13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Zhu, C.; Bao, N.; Gu, H. Detection of Cellular H2O2 in Living Cells Based on Horseradish Peroxidase at the Interface of Au Nanoparticles Decorated Graphene Oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 211, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, J.; Duan, X.; Ren, J.; Xiao, F.; Wang, S. Pd Nanoparticles Decorated N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Nanospheres with High Electrochemical Sensing Performance in Cancer Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22563–22573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C.Y.; Pralle, A.; Isacoff, E.Y.; Chang, C.J. A Selective, Cell-Permeable Optical Probe for Hydrogen Peroxide in Living Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15392–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üzer, A.; Durmazel, S.; Erçağ, E.; Apak, R. Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide and Triacetone Triperoxide (TATP) with a Silver Nanoparticles—Based Turn-on Colorimetric Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitinaivinij, K.; Parnklang, T.; Thammacharoen, C.; Ekgasit, S.; Wongravee, K. Colorimetric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide by Morphological Decomposition of Silver Nanoprisms Coupled with Chromaticity Analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9816–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Lo, Y.-R.; Lin, Y.-C.; Shi, Y.-C.; Li, P.-L. A Spectrometric Method for Hydrogen Peroxide Concentration Measurement with a Reusable and Cost-Efficient Sensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 25716–25729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K. Stopped-Flow Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide with Hemoglobin as Catalyst. Talanta 2000, 51, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, M.; Kamino, S.; Doi, M.; Takada, S.; Mitani, S.; Yanagihara, R.; Asano, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Fujita, Y. Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide with Osmium(VIII) and m-Carboxyphenylfluorone. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 814–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, J.E.; Jones, P.; Scholes, G. Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide and Organic Hydropheroxides at Low Concentrations in Aqueous Solution. Anal. Chim. Acta 1983, 155, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Shen, H. Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide by Using the Cleavage of Eriochrome Black T in the Presence of Peroxidase. Talanta 1997, 44, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, A. Silver Nanoclusters-Catalyzed Luminol Chemiluminescence for Hydrogen Peroxide and Uric Acid Detection. Talanta 2017, 166, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cai, S.; Ren, Q.-Q.; Wen, W.; Zhao, Y.-D. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensing for Hydrogen Peroxide: A Review. Analyst 2012, 137, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulaboski, R.; Mirčeski, V.; Kappl, R.; Hoth, M.; Bozem, M. Review—Quantification of Hydrogen Peroxide by Electrochemical Methods and Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, G82–G101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, W.; Sunarso, J.; Xu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H. 3D Ordered Macroporous SmCoO3 Perovskite for Highly Active and Selective Hydrogen Peroxide Detection. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 260, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, P.; Gong, Z.; Xu, G.; Cai, C. Electrochemical Detection of Extracellular Hydrogen Peroxide Released from RAW 264.7 Murine Macrophage Cells Based on Horseradish Peroxidase–Hydroxyapatite Nanohybrids. Analyst 2011, 136, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Cai, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C. Electrochemical Measurement of the Flux of Hydrogen Peroxide Releasing from RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells Based on Enzyme-Attapulgite Clay Nanohybrids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4012–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.K.; Sukumaran Nair, K.M.; Thomas, S.; Rouxel, D.; Alwarappan, S.; Kalarikkal, N. In Situ Synthesis of Silver Nanospheres, Nanocubes, and Nanowires over Boron-Doped Graphene Sheets for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Application and Enzyme-Free Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13603–13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, J.S.; Gonzaga, V.A.M.; Poli, A.L.; Schmitt, C.C. Photochemical Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles on Chitosans/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite Films and Antibacterial Activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Layani, M.; Cai, X.; Zhao, H.; Magdassi, S.; Lan, M. An Inkjet Printed Ag Electrode Fabricated on Plastic Substrate with a Chemical Sintering Approach for the Electrochemical Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.-C.; Dong, X.-Z.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Zhao, Z.-S. Investigate the Electrical and Thermal Properties of the Low Temperature Resistant Silver Nanowire Fabricated by Two-Beam Laser Technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 439, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Wu, F.; Hu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wu, Z. Size Controllable Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles Loading on Graphene Sheets@cerium Oxide Nanocomposites Modified Gold Electrode for Nonenzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; He, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, A.; Duan, H. Real-Time Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide Secretion in Live Cells by Pt Nanoparticles Decorated Graphene–Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Paper Electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, R.; Lee, J.S. Tungsten Carbide Microspheres as a Noble-Metal-Economic Electrocatalyst for Methanol Oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 6557–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Li, F.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Catalytic Applications of Layered Double Hydroxides: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7040–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, D. Supported Catalysts Based on Layered Double Hydroxides for Catalytic Oxidation and Hydrogenation: General Functionality and Promising Application Prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5291–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Aziz, A.; Dao, A.Q.; Hakeem, A.; Wang, H.; Dong, S.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, F.; Liu, H. Real-Time Tracking of Hydrogen Peroxide Secreted by Live Cells Using MnO2 Nanoparticles Intercalated Layered Doubled Hydroxide Nanohybrids. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 898, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrabito, G.; Pezzilli, R.; Prestopino, G.; Medaglia, P.G. Layered Double Hydroxides in Bioinspired Nanotechnology. Crystals 2020, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, M.; Pezzilli, R.; Prestopino, G.; Di Natale, C.; Medaglia, P.G. Fabrication and Characterization of a Layered Double Hydroxide Based Catalase Biosensor and a Catalytic Sensor for Hydrogen Peroxide Determination. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassetti, M.; Pezzilli, R.; Prestopino, G.; Di Biagio, F.; Di Natale, C.; Medaglia, P.G. A New Clark-Type Layered Double Hydroxides-Enzyme Biosensor for H2O2 Determination in Highly Diluted Real Matrices: Milk and Cosmetics. Processes 2021, 9, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heli, H.; Pishahang, J.; Amiri, H.B. Synthesis of Hexagonal CoAl-Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoshales/Carbon Nanotubes Composite for the Non-Enzymatic Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 768, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Liu, H.; Aziz, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Ajmal, M.; Xiao, F.; Liu, H. Core-Shell Iron Oxide-Layered Double Hydroxide: High Electrochemical Sensing Performance of H 2 O 2 Biomarker in Live Cancer Cells with Plasma Therapeutics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Chu, Y. One-Step Voltammetric Deposition of l-Proline Assisted Silver Nanoparticles Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 833, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charithra, M.M.; Manjunatha, J.G. Poly (l-Proline) Modified Carbon Paste Electrode as the Voltammetric Sensor for the Detection of Estriol and Its Simultaneous Determination with Folic and Ascorbic Acid. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lian, M.; Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, W. Amperometric Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide via an ITO Electrode Modified with Gold Nanoparticles Electrodeposited on a CoMn-Layered Double Hydroxide. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3989–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, F.; Zhu, L.; Ding, Y.; Deng, D. Electrochemical Sensing Platform of Natural Estrogens Based on the Poly(l-Proline)-Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Composite Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 187, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, F.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Layered Double Hydroxide Films: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boclair, J.W.; Braterman, P.S. Layered Double Hydroxide Stability. 1. Relative Stabilities of Layered Double Hydroxides and Their Simple Counterparts. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, T.; Bosch, P.; Ramos, E.; Gomez, R.; Novaro, O.; Acosta, D.; Figueras, F. Synthesis and Characterization of Sol−Gel Hydrotalcites. Structure and Texture. Langmuir 1996, 12, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laipan, M.; Xiang, L.; Yu, J.; Martin, B.R.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, J.; He, H.; Clearfield, A.; Sun, L. Layered Intercalation Compounds: Mechanisms, New Methodologies, and Advanced Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forano, C.; Hibino, T.; Leroux, F.; Taviot-Guého, C. Layered Double Hydroxides. In Handbook of Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Theng, B.K.G., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Chapter 13.1; Volume 1, pp. 1021–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Prestopino, G.; Arrabito, G.; Generosi, A.; Mattoccia, A.; Paci, B.; Perez, G.; Verona-Rinati, G.; Medaglia, P.G. Emerging Switchable Ultraviolet Photoluminescence in Dehydrated Zn/Al Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoplatelets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polese, D.; Mattoccia, A.; Giorgi, F.; Pazzini, L.; Di Giamberardino, L.; Fortunato, G.; Medaglia, P.G. A Phenomenological Investigation on Chlorine Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxides Used as Room Temperature Gas Sensors. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 692, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G.J.; Thomas, J.D.R. Selective Ion-Sensitive Electrodes. Sel. Annu. Rev. Anal. Sci. 1973, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascini, M. Uses of Known Addition, Gran’s Plots and the Related Methods with Ion-Selective Electrodes. In Ion-Selective Electrode Reviews; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; Volume 2, pp. 17–71. ISBN 978-0-08-028434-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Yang, Z.; Wen, R.; Yang, B.; Long, W. The Application of Zn–Al-Hydrotalcite as a Novel Anodic Material for Ni–Zn Secondary Cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 224, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, S.; Zeng, H.-Y.; Cao, X.; Dan Pan, A.; Xiao, G.-F.; Ding, P.-X. Hydrogen Peroxide Biosensor Based on Chitosan/2D Layered Double Hydroxide Composite for the Determination of H2O2. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 123, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Wada, N.; Tsuhako, M. Intercalation of Amino Acids and Peptides into Mg–Al Layered Double Hydroxide by Reconstruction Method. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 269, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, A.; Mohammadi, H. Amperometry. In Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; p. B9780124095472142000. ISBN 978-0-12-409547-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Xia, B.; Zhang, Y. Direct Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis of Hemoglobin in a Multilayer {nanogold/PDDA}n Inorganic–Organic Hybrid Film. Microchim. Acta 2008, 160, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, C.-C. Eliminating the Interference of Oxygen for Sensing Hydrogen Peroxide with the Polyaniline Modified Electrode. Sensors 2008, 8, 8237–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tjiu, W.W.; Fan, W.; Liu, T. Electrodepositing Ag Nanodendrites on Layered Double Hydroxides Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode: Novel Hierarchical Structure for Hydrogen Peroxide Detection. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 90, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, J. Electrodeposition of Silver Nanoparticles on a Zinc Oxide Film: Improvement of Amperometric Sensing Sensitivity and Stability for Hydrogen Peroxide Determination. Microchim. Acta 2010, 169, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Zheng, J. Novel Nonenzymatic Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on Fe3O4/PPy/Ag Nanocomposites. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 747, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbakhshi, M.; Habibi, B. A Novel and Facile Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots via Salep Hydrothermal Treatment as the Silver Nanoparticles Support: Application to Electroanalytical Determination of H2O2 in Fetal Bovine Serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-H.; Ogino, K.; Sato, Y.; Sakano, N.; Kubo, M.; Takemoto, K.; Masatomi, C. Urinary Hydrogen Peroxide as Biomarker. In General Methods in Biomarker Research and their Applications; Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-94-007-7740-8. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, D.; Jacob, J.; Kunjamma, G.; Madhusoodanan, U.K.; Ghosh, S. Measurement of Urinary Hydrogen Peroxide by FOX-1 Method in Conjunction with Catalase in Diabetes Mellitus—A Sensitive and Specific Approach. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 350, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

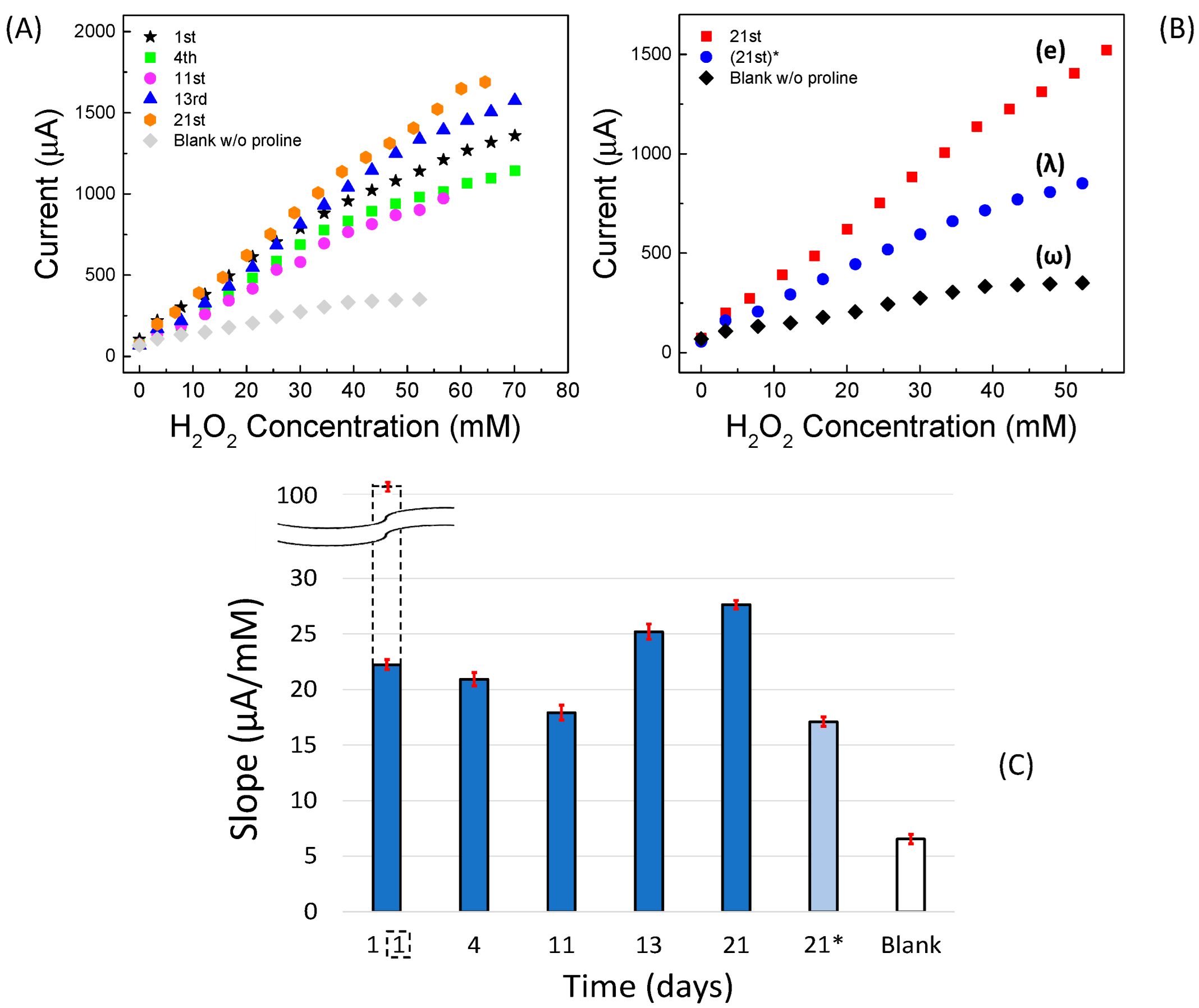
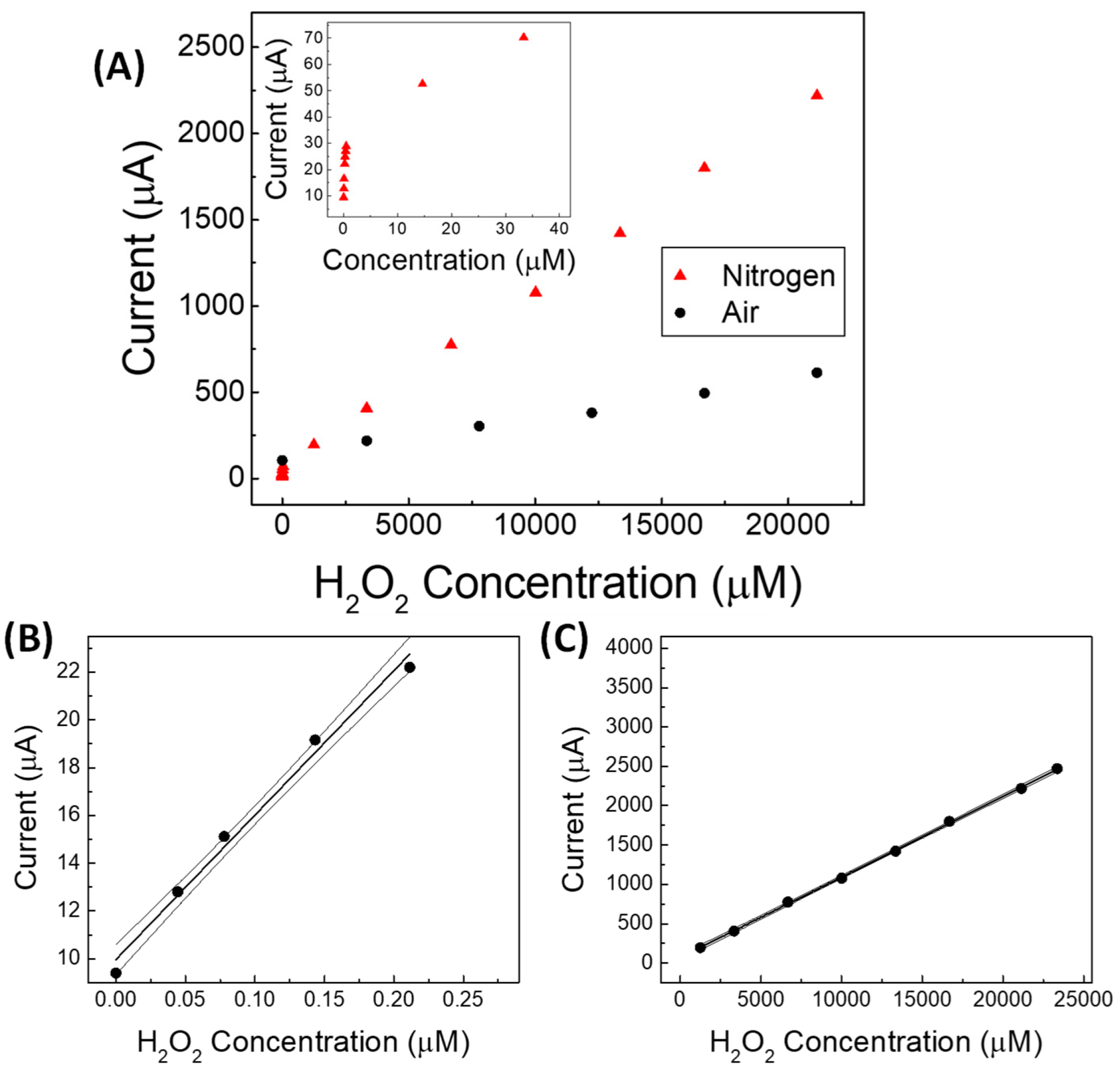
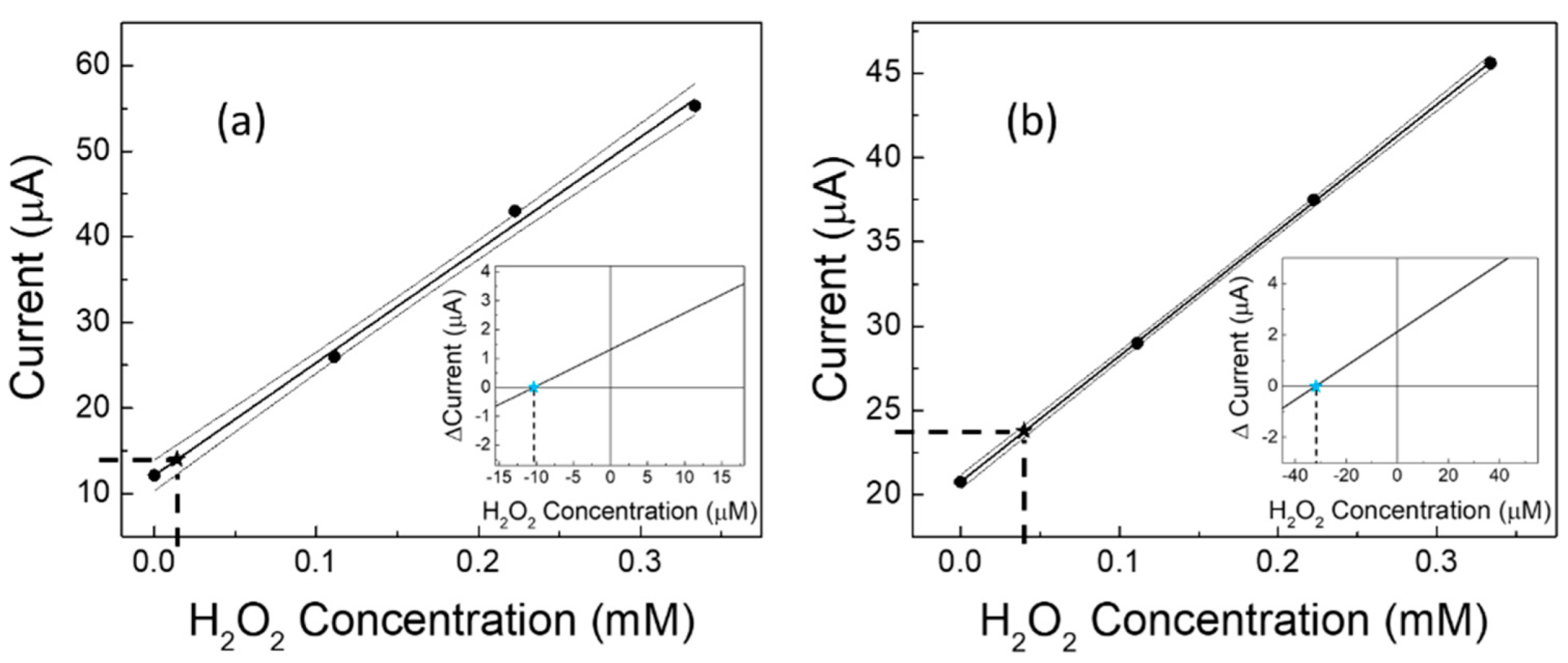
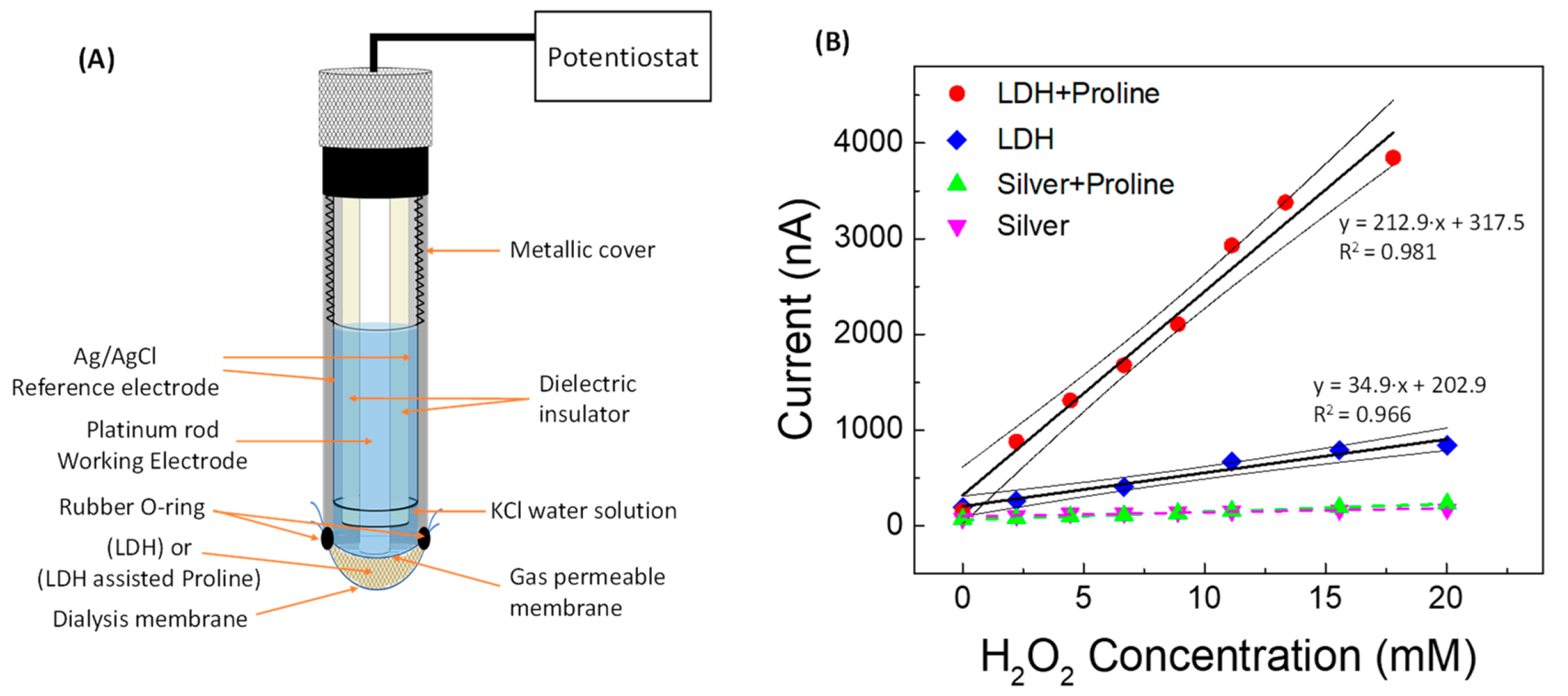
| Linear Regression (y = mA; x = mM) | Linearity Range (mM) | R2 | LOD (mM) | RSD % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st day | y = (0.256 ± 0.0130)∙x + (9.819 ± 0.1110) | 0–17 | 0.9899 | 0.5 | 2.25 |
| blank | y = (0.0676 ± 0.00460)∙x + (8.597 ± 0.0680) | 0–30 | 0.9822 | 0.5 | 2.25 |
| Non Enzymatic Catalytic (GC-Agpaste)-Proline Assisted LDH Sensor | Enzymatic or Catalytic (GC-Agpaste)-LDH Sensors (Not Proline Assisted) [34] | |
|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 0% | - |
| Uric acid | 0% | - |
| Ascorbic acid | ≈0% | −5.6% |
| Sodium nitrite | 0% | −1% |
| Sodium nitrate | +1% | +3% |
| Fe3+ | ≈+30% | +32% |
| Potassium permanganate | +440% | +1300% |
| Best Analytical data of GC-LDH-Catalase Enzymatic biosensor studied in previous work and method validation | ||||||||
| Linear Regression | Linearity Range (mM) | R2 | LOD (mM) | LOQ (mM) | RSD% | Response time (s) | Lifetime (days) | Ref |
| y = (10.09 ± 0.29) x + (115.1 ± 29.1) | 0.25–158 | 0.9976 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 8.5 | 75 | [34] |
| (y = μA; x = mM) | ||||||||
| Best Analytical data of non-enzymatic catalytic LDH sensor studied in previous work and method validation | ||||||||
| Linear Regression | Linearity Range (mM) | R2 | LOD (mM) | LOQ (mM) | RSD% | Response time (s) | Lifetime (days) | Ref |
| y = (0.9662 ± 0.0109) x + (−102.6 ± 8.85) | 144.5–1195.2 | 0.9986 | 1 | 3 | 1.8 | 17.5 | 68 | [34] |
| (y = μA; x = mM) | ||||||||
| Best Analytical data of non-enzymatic catalytic proline assisted LDH sensor studied in this work and method validation | ||||||||
| (operating under static air) | ||||||||
| Linear Regression | Linearity Range (mM) | R2 | LOD (mM) | LOQ (mM) | RSD% | Response time (s) | Lifetime (days) | Ref |
| y = (27.407 ± 0.450) x + (83.466 ± 8.713) | 0.3–33.4 | 0.9981 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 5 | 7 | ≥21 | This work |
| (y = μA; x = mM) | ||||||||
| Best Analytical data of non-enzymatic catalytic proline assisted LDH sensor studied in this work and method validation | ||||||||
| (operating under nitrogen—low concentration range) | ||||||||
| Linear Regression | Linearity Range (mM) | R2 | LOD (mM) | LOQ (mM) | RSD% | Response time (s) | Lifetime (days) | Ref |
| y = (30874.1 ± 3685.7) x + (15.12 ± 1.17) | 0.00005–0.00022 | 0.9561 | 0.00005 | 0.0001 | 5 | 10 | >3 | This work |
| (y = μA; x = mM) | 0.05–0.22 (µM) | 0.05 (µM) | 0.1 (µM) | |||||
| Best Analytical data of non-enzymatic catalytic proline assisted LDH sensor studied in this work and method validation | ||||||||
| (operating under nitrogen—high concentration range) | ||||||||
| Linear Regression | Linearity Range (mM) | R2 | LOD (mM) | LOQ (mM) | RSD% | Response time (s) | Lifetime (days) | Ref |
| y = (102.9 ± 1.2) x + (66.9 ± 16.3) | 0.012–23.3 | 0.9995 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 2.5 | 10 | >3 | This work |
| (y = μA; x = mM) | ||||||||
| Exp. Values [µM] Found by Regression Equation Method (This Work) | Exp. Values [µM] Found by Gran’s plot Method (This Work) | Exp. Values [µM] Reported in Literature [61,62] | Exp. Values [µM] Reported in Literature [37] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy subject | 30.0 ± 1.00 | 21.0 ± 1.30 | 20 ± 1.4 | 35.4 |
| Diabetic subject | 80.0 ± 4.00 | 64.0 ± 4.20 | 42 ± 0.72 | “higher than healthy” |
| Sample | Found Concentration in Urine Sample (µM) | H2O2 Additions (µM) | Found + Added Nominal Value (µM) | Experimental Value (µM) | Δ (%) (RSD% = 0.7) | Percent Recovery (RSD% = 0.7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | 15.0 | 96.0 | 111.0 | 105.6 | −4.9 | 95.1 |
| Healthy | 15.0 | 318.0 | 333.0 | 328.0 | −1.5 | 98.5 |
| Diabetic | 40.0 | 71.0 | 111.0 | 110.2 | −0.7 | 99.3 |
| Diabetic | 40.0 | 293.5 | 333.5 | 332.8 | −0.2 | 99.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomassetti, M.; Pezzilli, R.; Prestopino, G.; Di Natale, C.; Medaglia, P.G. Novel Electrochemical Sensors Based on L-Proline Assisted LDH for H2O2 Determination in Healthy and Diabetic Urine. Sensors 2022, 22, 7159. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197159
Tomassetti M, Pezzilli R, Prestopino G, Di Natale C, Medaglia PG. Novel Electrochemical Sensors Based on L-Proline Assisted LDH for H2O2 Determination in Healthy and Diabetic Urine. Sensors. 2022; 22(19):7159. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197159
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomassetti, Mauro, Riccardo Pezzilli, Giuseppe Prestopino, Corrado Di Natale, and Pier Gianni Medaglia. 2022. "Novel Electrochemical Sensors Based on L-Proline Assisted LDH for H2O2 Determination in Healthy and Diabetic Urine" Sensors 22, no. 19: 7159. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197159
APA StyleTomassetti, M., Pezzilli, R., Prestopino, G., Di Natale, C., & Medaglia, P. G. (2022). Novel Electrochemical Sensors Based on L-Proline Assisted LDH for H2O2 Determination in Healthy and Diabetic Urine. Sensors, 22(19), 7159. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197159