A Red-Emitting Fluorescence Sensor for Detecting Boronic Acid-Containing Agents in Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
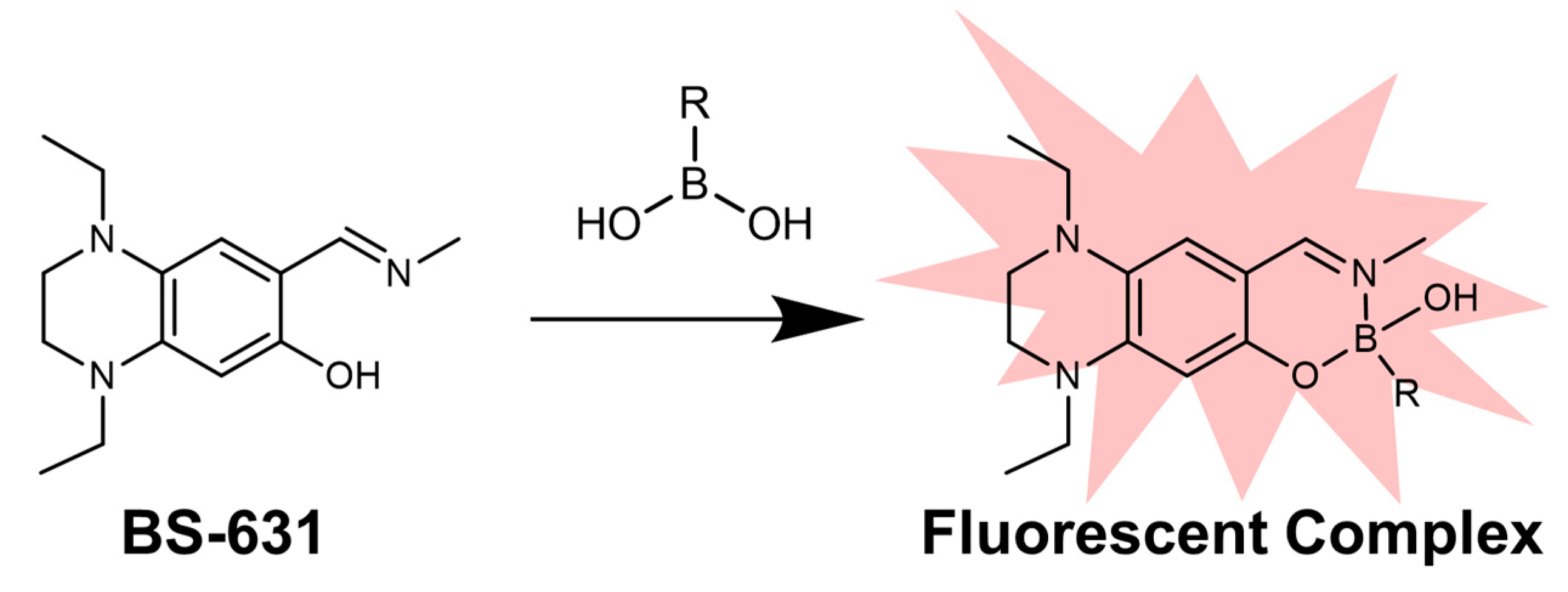
2.1. Preparation of BS-631
2.2. Fluorescence Property
2.3. Selectivity Assay
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy Study
2.5. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
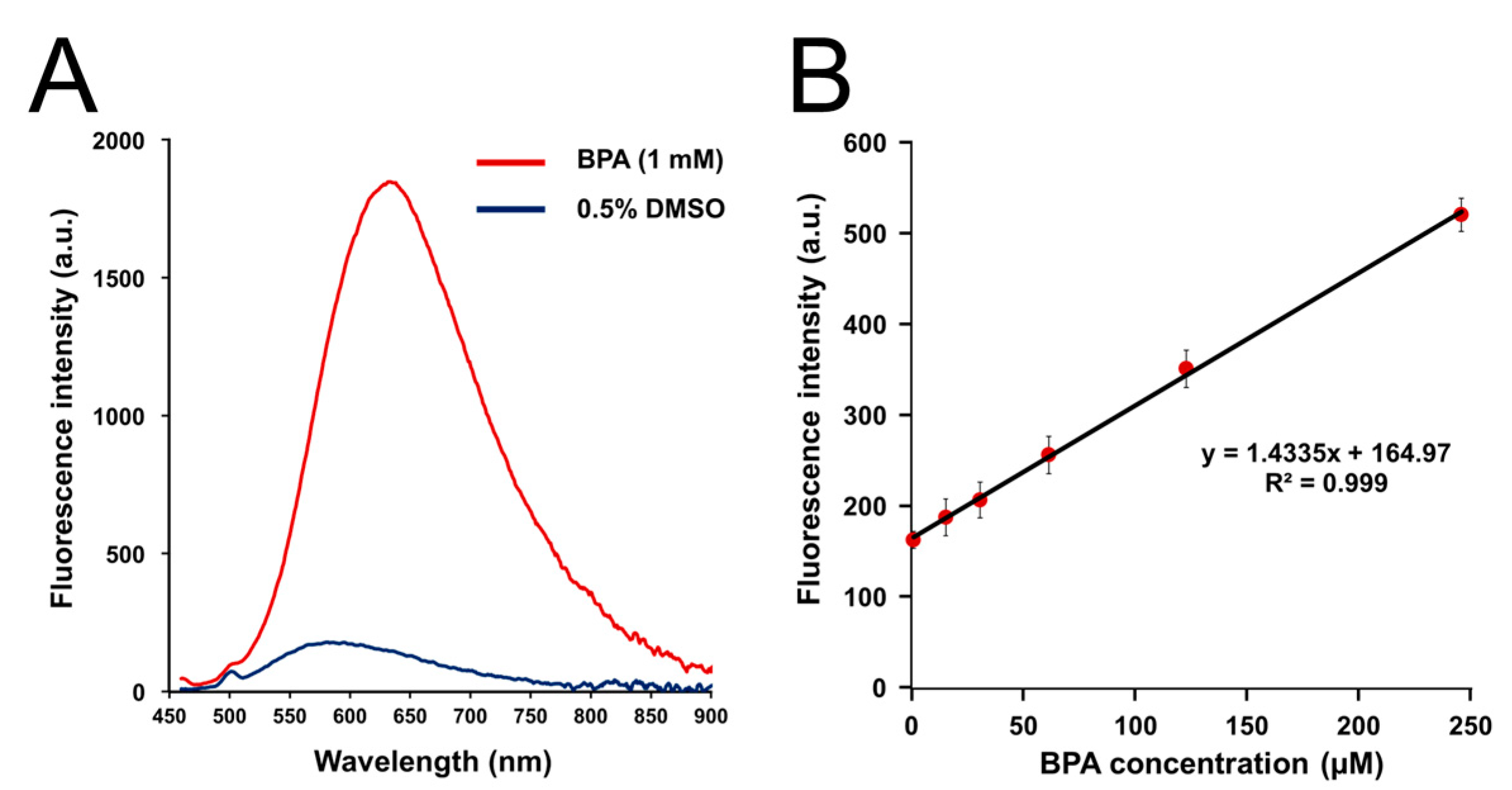
3.1. Fluorescence Properties of BS-631
3.2. Selectivity Assay
3.3. Fluorescence Microscopy Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fyfe, J.W.B.; Watson, A.J.B. Recent Developments in Organoboron Chemistry: Old Dogs, New Tricks. Chem 2017, 3, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, B.C.; Nandwana, N.K.; Das, S.; Nandwana, V.; Shareef, M.A.; Das, Y.; Saito, M.; Weiss, L.M.; Almaguel, F.; Hosmane, N.S.; et al. Boron Chemicals in Drug Discovery and Development: Synthesis and Medicinal Perspective. Molecules 2022, 27, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.F.S.; Denny, W.A.; Dos Santos, J.L. Boron in drug design: Recent advances in the development of new therapeutic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinna, S.; Finch, J. Spotlight on tavaborole for the treatment of onychomycosis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 6185–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J.; Kauffman, M. Development of the proteasome inhibitor Velcade (Bortezomib). Cancer Investig. 2004, 22, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.L. Critical review, with an optimistic outlook, on Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 88, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, R.F.; Coderre, J.A.; Vicente, M.G.; Blue, T.E. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: Current status and future prospects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3987–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snyder, H.R.; Reedy, A.J.; Lennarz, W.J. Synthesis of Aromatic Boronic Acids. Aldehydo Boronic Acids and a Boronic Acid Analog of Tyrosine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, R.F.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T. A realistic appraisal of boron neutron capture therapy as a cancer treatment modality. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanno, H.; Nagata, H.; Ishiguro, A.; Tsuzuranuki, S.; Nakano, S.; Nonaka, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Kimura, T.; Sugawara, A.; Okazaki, Y.; et al. Designation Products: Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Head and Neck Carcinoma. Oncologist 2021, 26, e1250–e1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Hirano, F.; Temma, T. Evaluation of 3-Borono-l-Phenylalanine as a Water-Soluble Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Agent. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomoto, T.; Inoue, Y.; Yao, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kanamori, K.; Takemoto, H.; Matsui, M.; Tomoda, K.; Nishiyama, N. Poly(vinyl alcohol) boosting therapeutic potential of p-boronophenylalanine in neutron capture therapy by modulating metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skwierawska, D.; Lopez-Valverde, J.A.; Balcerzyk, M.; Leal, A. Clinical Viability of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Personalized Radiation Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.; Lorey, D.R. SIMS ion microscopy imaging of boronophenylalanine (BPA) and 13C15N-labeled phenylalanine in human glioblastoma cells: Relevance of subcellular scale observations to BPA-mediated boron neutron capture therapy of cancer. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 260, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldossari, S.; McMahon, G.; Lockyer, N.P.; Moore, K.L. Microdistribution and quantification of the boron neutron capture therapy drug BPA in primary cell cultures of human glioblastoma tumour by NanoSIMS. Analyst 2019, 144, 6214–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Ishimura, M.; Ohta, Y.; Takenaka, H.; Watanabe, T.; Tanaka, H.; Ono, K.; Kirihata, M. Detection of boronic acid derivatives in cells using a fluorescent sensor. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 6927–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Ishimura, M.; Ohta, Y.; Takenaka, H.; Kirihata, M. Visualization of Boronic Acid Containing Pharmaceuticals in Live Tumor Cells Using a Fluorescent Boronic Acid Sensor. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, S.; Kondo, N.; Hagimori, M.; Temma, T. Development of a switching-type fluorescence sensor for the detection of boronic acid-containing agents. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska-Olejniczak, K.; Kaniowski, D.; Araszkiewicz, M.; Tyminska, K.; Korgul, A. Molecular Mechanisms of Specific Cellular DNA Damage Response and Repair Induced by the Mixed Radiation Field During Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 676575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronoff, M.R.; VanVeller, B.; Raines, R.T. Detection of boronic acids through excited-state intramolecular proton-transfer fluorescence. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5382–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frath, D.; Azizi, S.; Ulrich, G.; Retailleau, P.; Ziessel, R. Facile synthesis of highly fluorescent Boranil complexes. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 3414–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xiang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.B. A General Method To Increase Stokes Shift by Introducing Alternating Vibronic Structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7716–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, F.; Luo, H.; Liao, L.; Song, X.; Chen, W. Red-emitting boron difluoride complexes with a mega-large Stokes shift and unexpectedly high fluorescence quantum yield. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2159–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Voitchovsky, K.; Song, X. An aqueous red emitting fluorescent fluoride sensing probe exhibiting a large Stokes shift and its application in cell imaging. Chem Commun. 2014, 50, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Fang, Q.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Song, X.; Foley, J. Selective, highly sensitive fluorescent probe for the detection of sulfur dioxide derivatives in aqueous and biological environments. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watabe, T.; Ikeda, H.; Nagamori, S.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Naka, S.; Kanai, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Aoki, M.; Shimosegawa, E.; et al. (18)F-FBPA as a tumor-specific probe of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): A comparison study with (18)F-FDG and (11)C-Methionine PET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondo, N.; Aoki, E.; Takada, S.; Temma, T. A Red-Emitting Fluorescence Sensor for Detecting Boronic Acid-Containing Agents in Cells. Sensors 2022, 22, 7671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197671
Kondo N, Aoki E, Takada S, Temma T. A Red-Emitting Fluorescence Sensor for Detecting Boronic Acid-Containing Agents in Cells. Sensors. 2022; 22(19):7671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197671
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondo, Naoya, Erika Aoki, Shinya Takada, and Takashi Temma. 2022. "A Red-Emitting Fluorescence Sensor for Detecting Boronic Acid-Containing Agents in Cells" Sensors 22, no. 19: 7671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197671
APA StyleKondo, N., Aoki, E., Takada, S., & Temma, T. (2022). A Red-Emitting Fluorescence Sensor for Detecting Boronic Acid-Containing Agents in Cells. Sensors, 22(19), 7671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197671







