Adaptive Multi-ROI Agricultural Robot Navigation Line Extraction Based on Image Semantic Segmentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Acquisition and Dataset Construction
2.1.1. Data Sources and Labeling
2.1.2. Data Enhancement
2.1.3. Evaluation Basis for Ridge Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Path Recognition Model between Crop Ridges
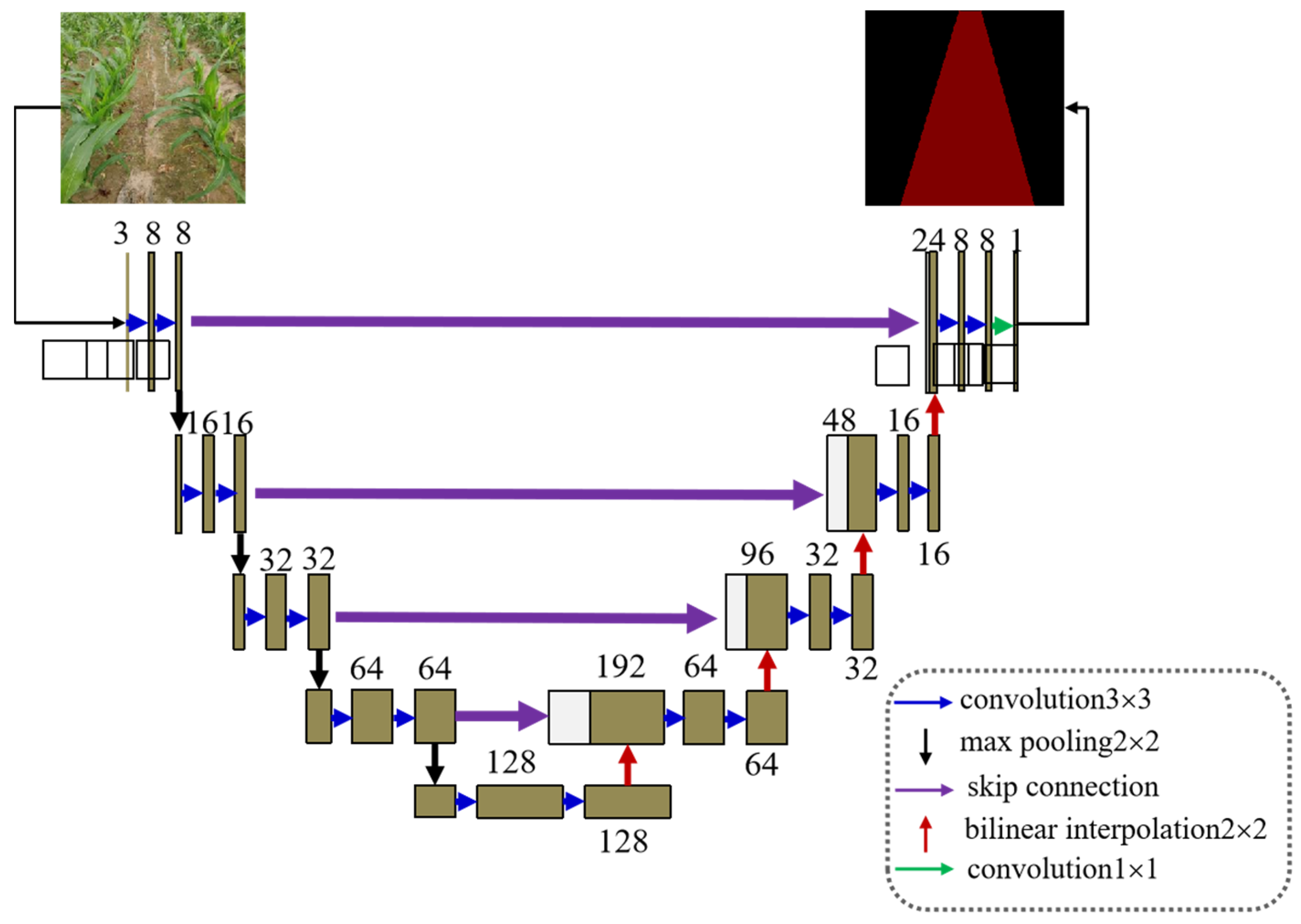
2.2.1. Construction of Semantic Segmentation Model between Crop Ridges
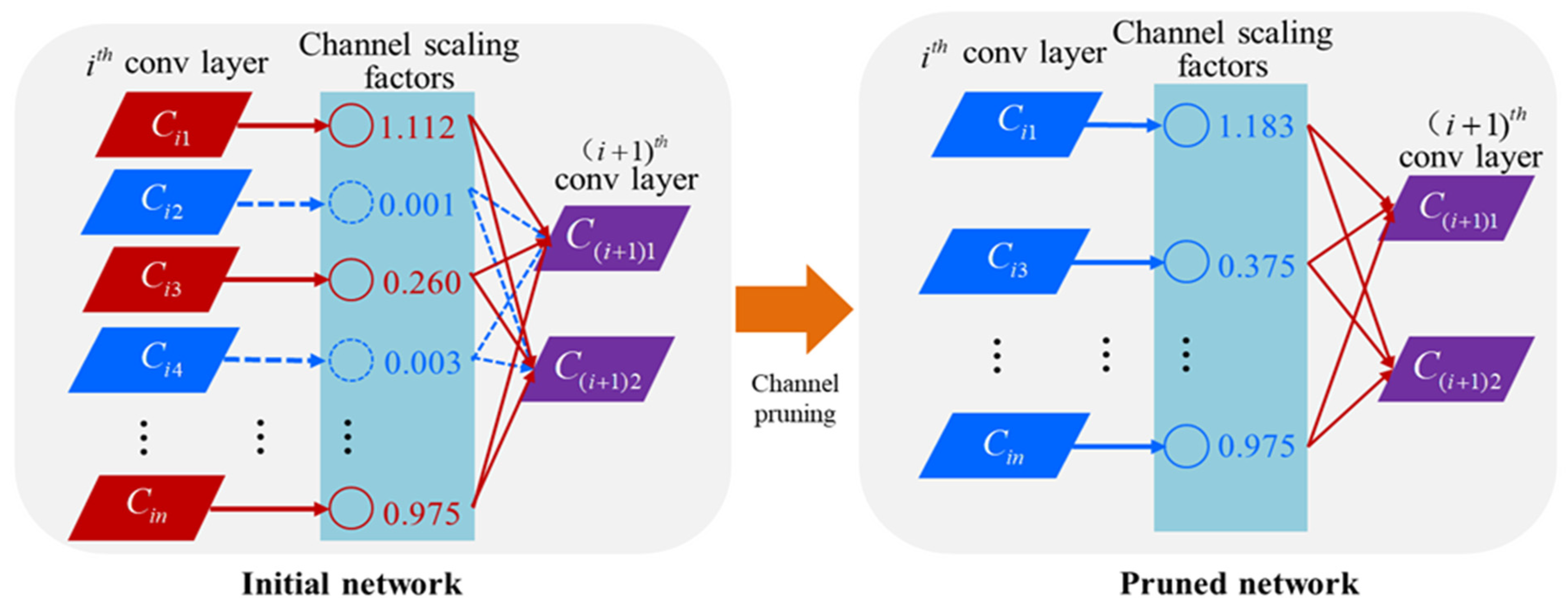
- (1)
- Sparse training by applying the L1 rule constraint to the batch normalization layer coefficients of the U-net corn ridge row segmentation model so that the model was adjusted in the direction of structural sparseness.
- (2)
- Channel pruning. After the sparse training was completed, channel pruning was performed at a certain pruning rate to generate a simplified model with less storage space.
- (3)
- Local adjustment of the pruned network model to solve the problem of excessive model accuracy loss after channel pruning to effectively restore the lost accuracy.
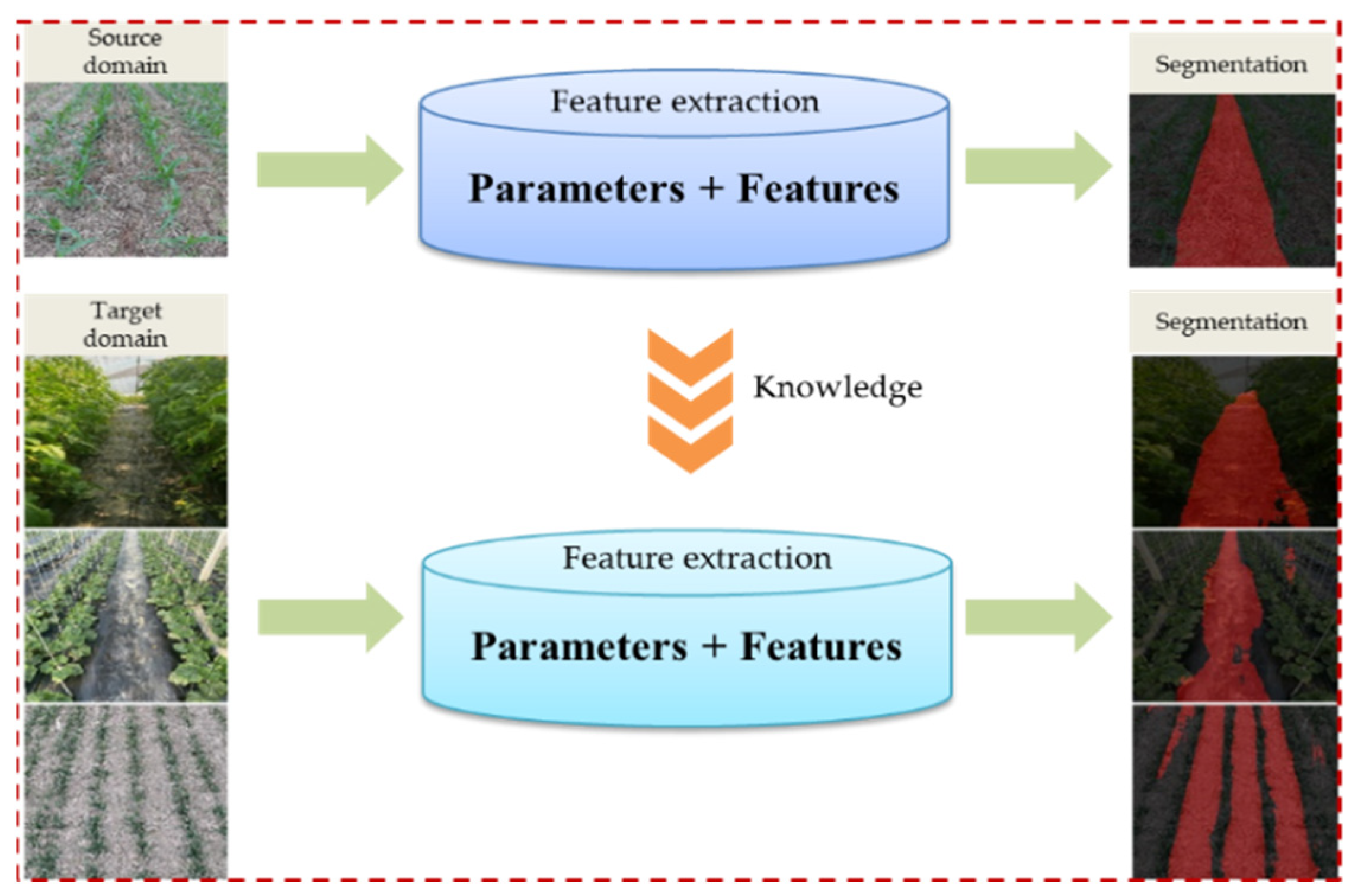
2.2.2. Transfer Learning
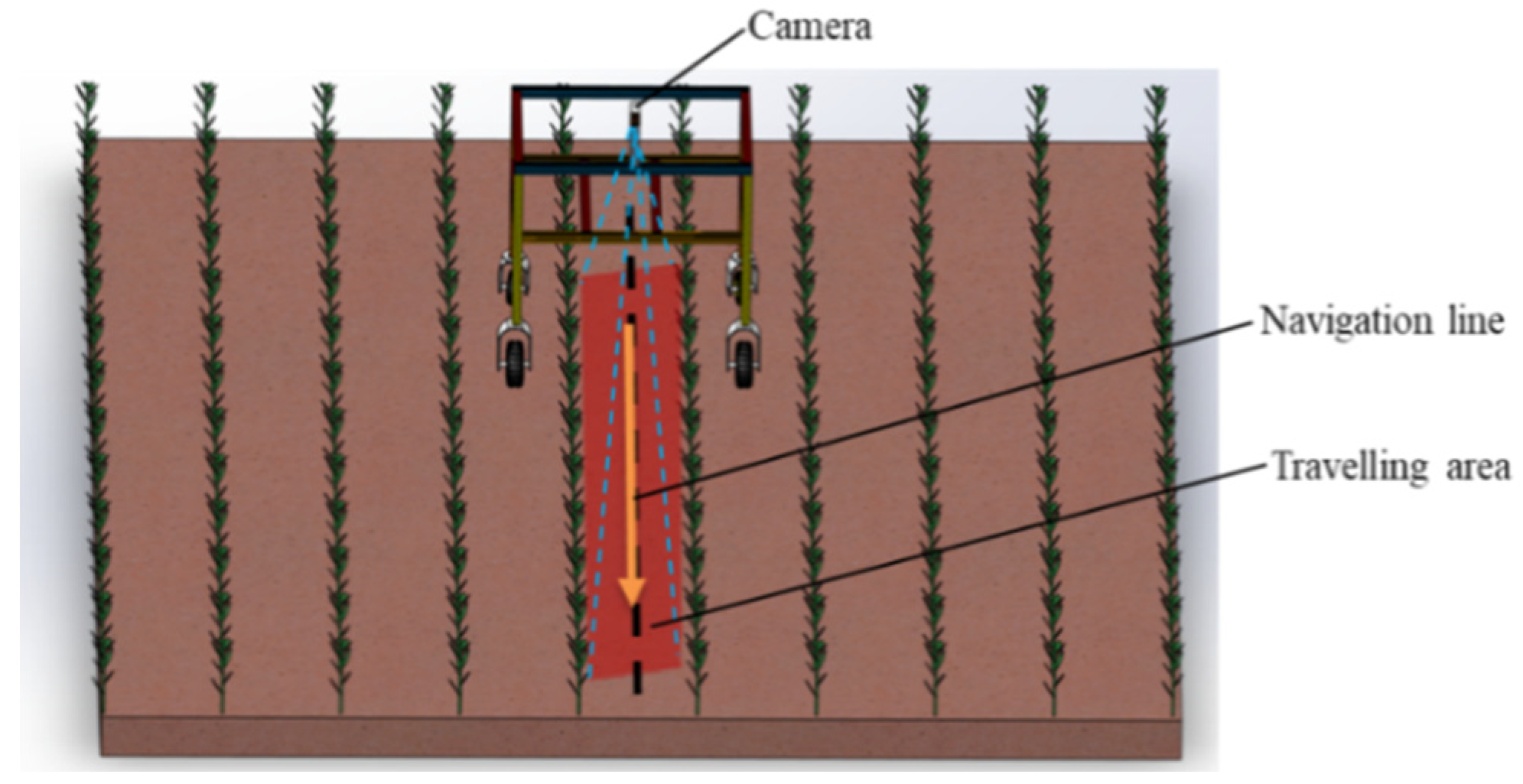
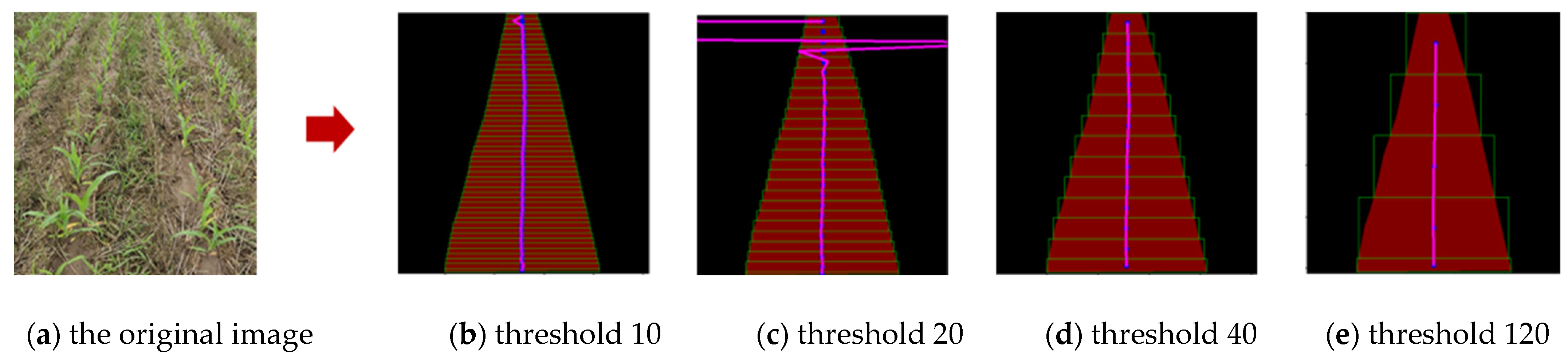
2.2.3. Navigation Line Extraction
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Test Platform
3.2. Image Semantic Segmentation between Crop Ridges
3.2.1. Path Segmentation Evaluation Index
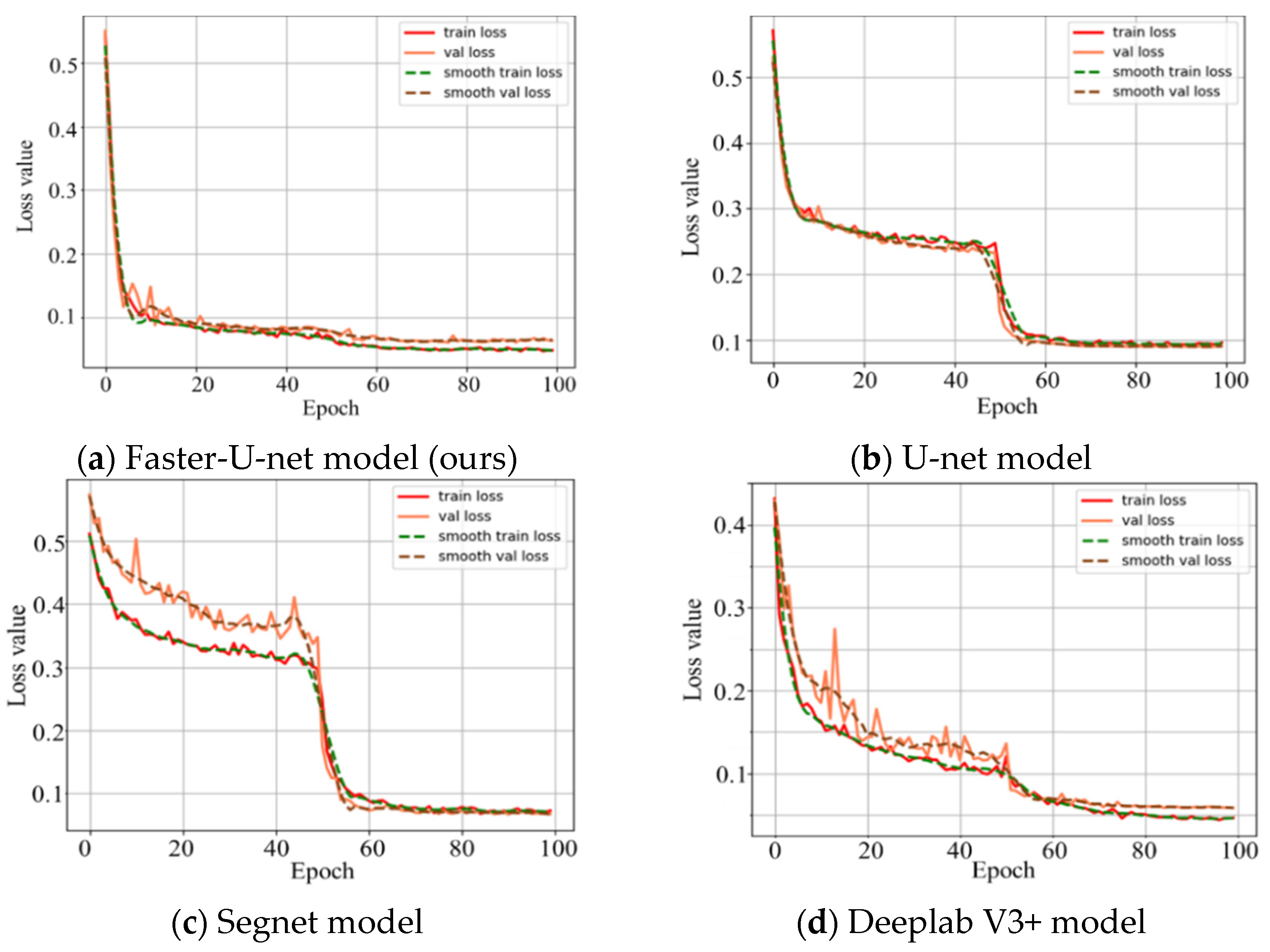
3.2.2. Network Model Training
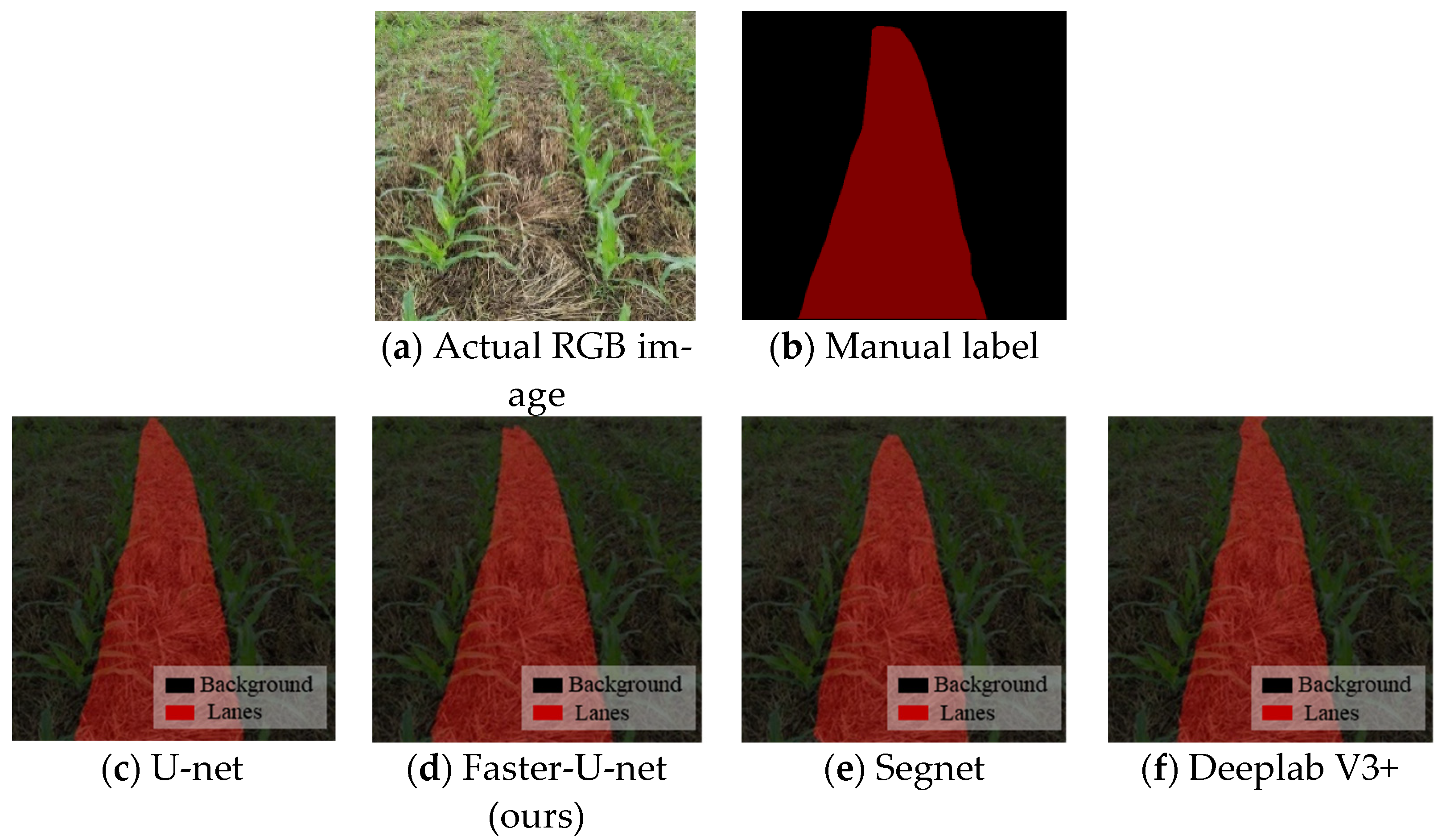
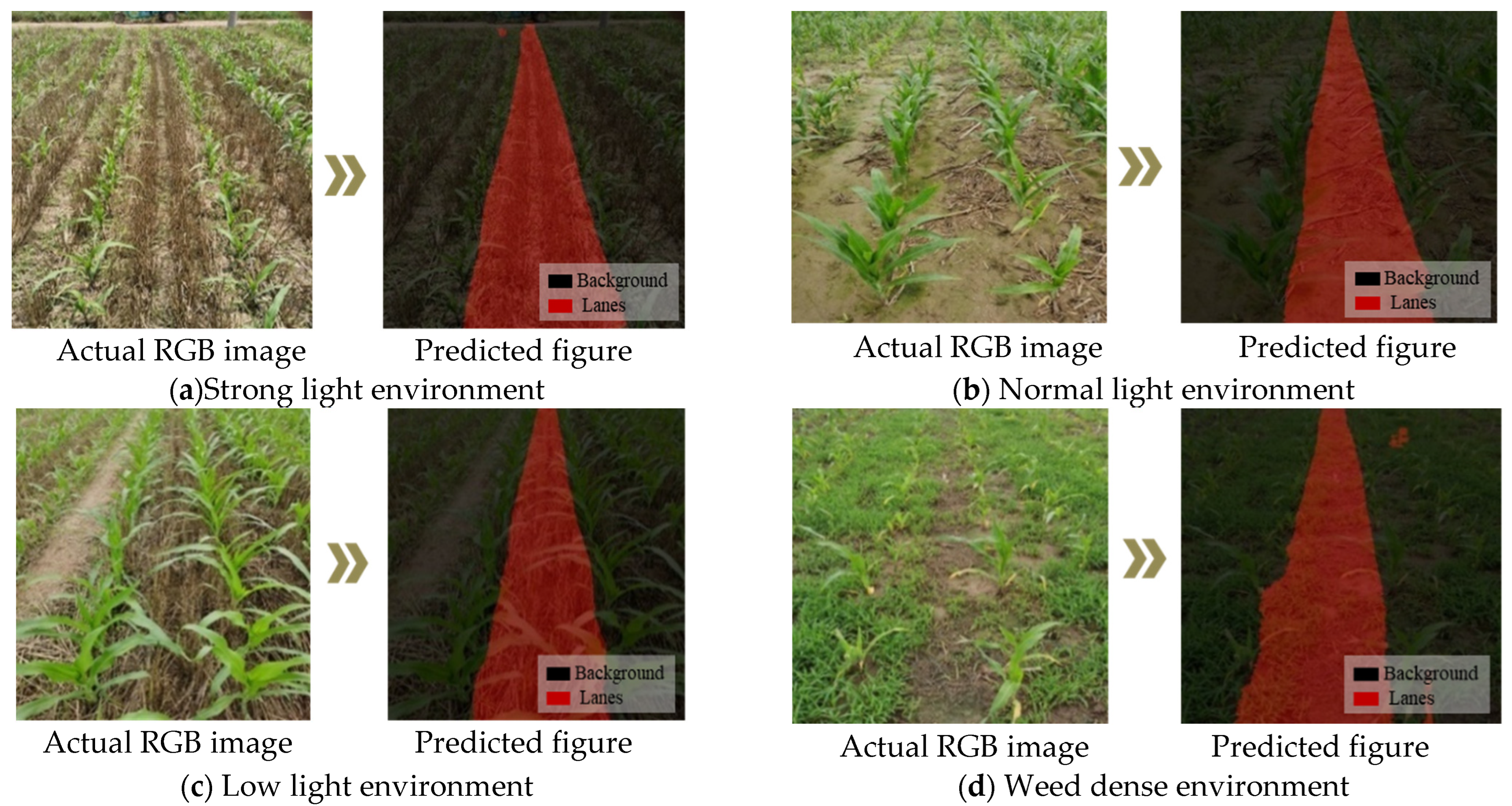
3.2.3. Segmentation Accuracy Test
3.3. Navigation Line Extraction Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Ji, Y.; Li, S.; Cao, R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. Research Progress of Agricultural Machinery Navigation Technology. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, J.; Fan, L.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, K.; Wang, J.; Song, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z. Review of wheeled mobile robots’ navigation problems and application prospects in agriculture. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49248–49268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Geng, J.; Ying, Y. Navigation path recognition between crop ridges based on semantic segmentation. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zha, J.; Wen, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, T.; Dong, X.; Yang, X. Real-time extraction of navigation line between corn rows. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Q.; Qiang, H.; Wu, J.H.; Xu, G.W.; Wang, Z.K. Navigation path extraction for greenhouse cucumber-picking robots using the prediction-point Hough transform. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasingham, S.; Ekpanyapong, M.; Chaihan, R. Integrating machine vision-based row guidance with GPS and compass-based routing to achieve autonomous navigation for a rice field weeding robot. Precis. Agric. 2020, 21, 831–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Li, X.N.; Zhang, B.H.; Zhou, J.; Tian, G.Z.; Xiong, Y.J.; Gu, B.X. Automated robust crop-row detection in maize fields based on position clustering algorithm and shortest path method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 154, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. A review of the use of convolutional neural networks in agriculture. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 156, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saleem, M.H.; Potgieter, J.; Arif, K.M. Automation in agriculture by machine and deep learning techniques: A review of recent developments. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 2053–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, F. Real-time semantic segmentation model for crop disease leaves using group attention module. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, M. Overview of deep learning intelligent driving methods. Qinghua Daxue Xuebao/J. Tsinghua Univ. 2018, 58, 438–444. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Ye, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, J. Path Recognition Method of Robot Vision Navigation in Unstructured Environments. Guangxue Xuebao/Acta Opt. Sin. 2018, 38, 0815028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, W.-J.; Huang, S.-K.; Chen, H.-C. Learning based semantic segmentation for robot navigation in outdoor environment. In Proceedings of the 2017 Joint 17th World Congress of International Fuzzy Systems Association and 9th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems (IFSA-SCIS), Otsu, Japan, 27–30 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Yu, Y. Field road scene recognition in hilly regions based on improved dilated convolutional networks. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Baheti, B.; Innani, S.; Gajre, S.; Talbar, S. Semantic scene segmentation in unstructured environment with modified DeepLabV3+. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, L. Path Recognition of Orchard Visual Navigation Based on U-Net. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ponnambalam, V.R.; Bakken, M.; Moore, R.J.; Glenn Omholt Gjevestad, J.; Johan From, P. Autonomous crop row guidance using adaptive multi-roi in strawberry fields. Sensors 2020, 20, 5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, P.V. Method and Means for Recognizing Complex Patterns. U.S. Patent 3069654, 18 December 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Wheat rows detection at the early growth stage based on Hough transform and vanishing point. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiang, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X. Extracting the navigation path of a tomato-cucumber greenhouse robot based on a median point Hough transform. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, J.; Yue, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H. Extracting navigation line to detect the maize seedling line using median-point Hough transform. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhu, D.; Jiao, J.; Chen, L. Extraction Method of Navigation Baseline of Corn Roots Based on Machine Vision. Nongye Jixie Xuebao/Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2017, 48, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wen, X.; Yue, X.; Chen, L. Autonomous detection of crop rows based on adaptive multi-ROI in maize fields. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Lv, S.; Jiang, M.; Song, H. Using channel pruning-based YOLO v4 deep learning algorithm for the real-time and accurate detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Shen, Z.; Huang, G.; Yan, S.; Zhang, C. Learning efficient convolutional networks through network slimming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2736–2744. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Sun, J. Convolutional neural networks at constrained time cost. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2015, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5353–5360. [Google Scholar]
- Bosilj, P.; Aptoula, E.; Duckett, T.; Cielniak, G. Transfer learning between crop types for semantic segmentation of crops versus weeds in precision agriculture. J. Field Robot. 2020, 37, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.-Z.; Luo, P.; He, Q.; Shi, Z.-Z. Survey on transfer learning research. Ruan Jian Xue Bao/J. Softw. 2015, 26, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Automatic detection of crop rows based on multi-ROIs. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 2429–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
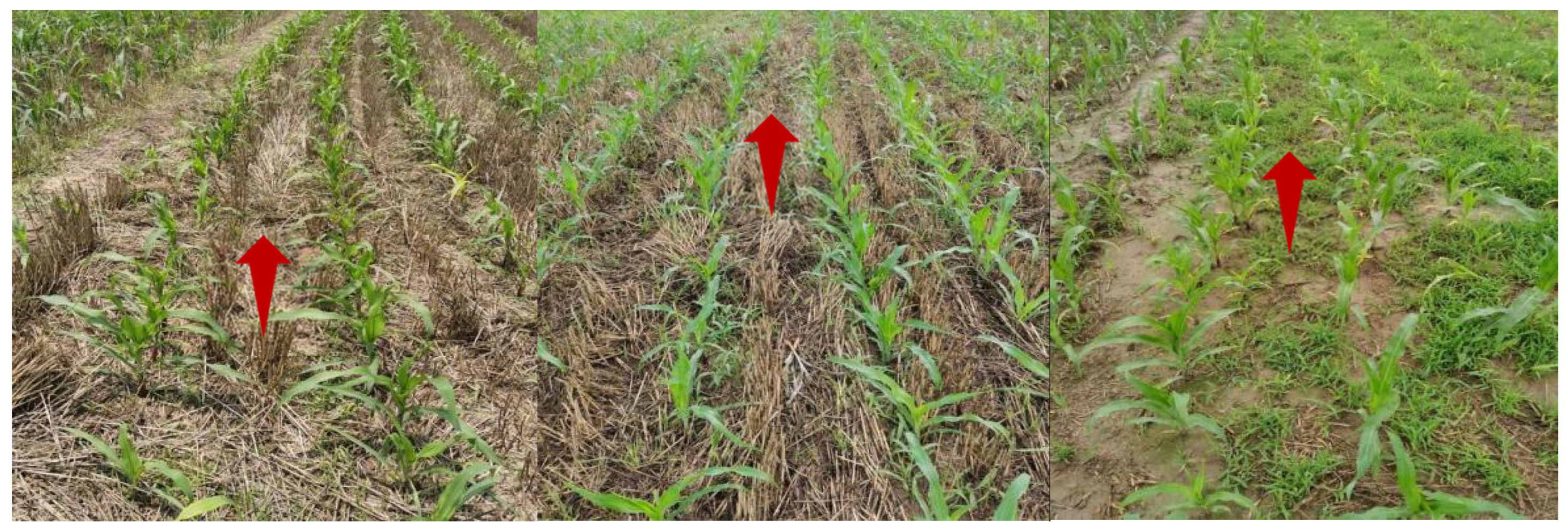

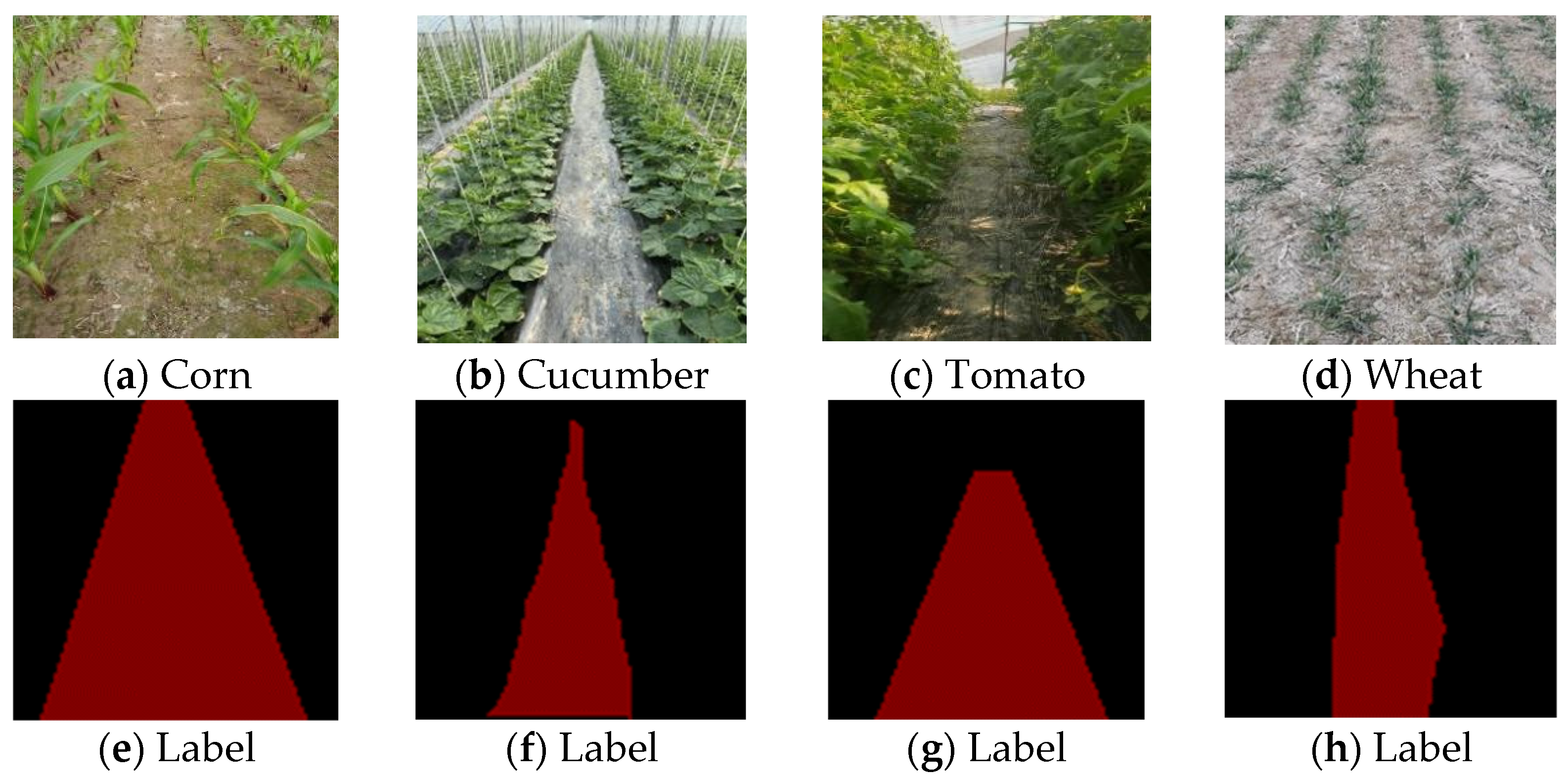




| Kind of Dataset | Number of Images | Original Image Resolution | Resized Image Resolution | Training Set | Validation Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 2000 | 1900 × 1180 | 512 × 512 | 1600 | 400 |
| Cucumber | 1000 | 1900 × 1180 | 512 × 512 | 800 | 200 |
| Tomato | 1000 | 1900 × 1180 | 512 × 512 | 800 | 200 |
| Wheat | 1000 | 1900 × 1180 | 512 × 512 | 800 | 200 |
| Network Model | Average Pixel Accuracy/% | MIoU/% | Detection Speed/fps·s−1 | Parameter Quantity/ × 106 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-net | 93.98 | 92.58 | 14.45 | 7.85 |
| Faster-U-net (ours) | 97.39 | 93.86 | 22.32 | 2.68 |
| Segnet | 94.43 | 91.75 | 16.68 | 29.94 |
| Deeplab V3+ | 96.16 | 93.60 | 12.67 | 34.67 |
| Experimental Conditions | Crop Category | mPA/% | MIoU/% | mP/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low light intensity | Corn | 97.35 | 94.30 | 96.76 |
| Normal light intensity | Corn | 97.68 | 94.92 | 97.10 |
| Strong light intensity | Corn | 97.17 | 93.70 | 96.32 |
| Crop Category | U-net | Faster-U-net | Segnet | Deeplab V3+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomato (transfer learning) | 0.9362 | 0.9401 | 0.9361 | 0.9368 |
| Tomato (no transfer learning) | 0.6095 | 0.8996 | 0.4683 | 0.2795 |
| Cucumber (transfer learning) | 0.8897 | 0.9314 | 0.8897 | 0.8876 |
| Cucumber (no transfer learning) | 0.8056 | 0.8187 | 0.5673 | 0.7614 |
| Wheat (transfer learning) | 0.8824 | 0.8910 | 0.8612 | 0.8873 |
| Wheat (no transfer learning) | 0.6947 | 0.7675 | 0.5034 | 0.6441 |
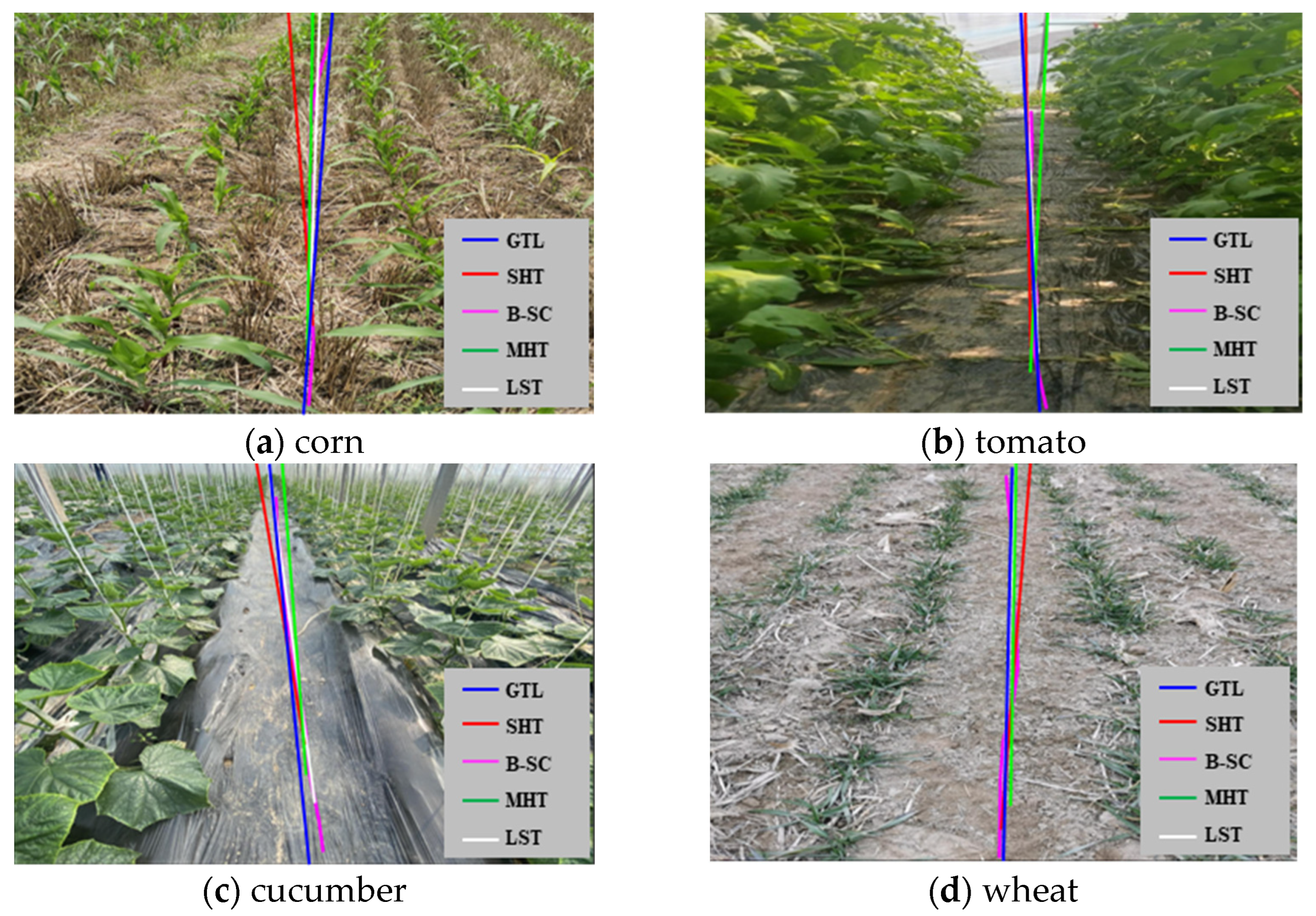
| Method | Average Difference in Corn Yaw Angle (°) | Average Difference in Cucumber Yaw Angle (°) | Average Difference in Tomato Yaw Angle (°) | Average Difference in Wheat Yaw Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LST | 0.638 | 0.572 | 0.541 | 0.996 |
| B-SC | 0.624 | 0.556 | 0.526 | 0.999 |
| SHT | 7.891 | 5.709 | 2.948 | 1.066 |
| MHT | 0.605 | 0.537 | 0.546 | 1.032 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Su, J.; Yue, Z.; Duan, F. Adaptive Multi-ROI Agricultural Robot Navigation Line Extraction Based on Image Semantic Segmentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207707
Li X, Su J, Yue Z, Duan F. Adaptive Multi-ROI Agricultural Robot Navigation Line Extraction Based on Image Semantic Segmentation. Sensors. 2022; 22(20):7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207707
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xia, Junhao Su, Zhenchao Yue, and Fangtao Duan. 2022. "Adaptive Multi-ROI Agricultural Robot Navigation Line Extraction Based on Image Semantic Segmentation" Sensors 22, no. 20: 7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207707
APA StyleLi, X., Su, J., Yue, Z., & Duan, F. (2022). Adaptive Multi-ROI Agricultural Robot Navigation Line Extraction Based on Image Semantic Segmentation. Sensors, 22(20), 7707. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207707






