Green and Integrated Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for Chloride Detection in Sweat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Device Fabrication
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Sensor Performance
3. Results and Discussion
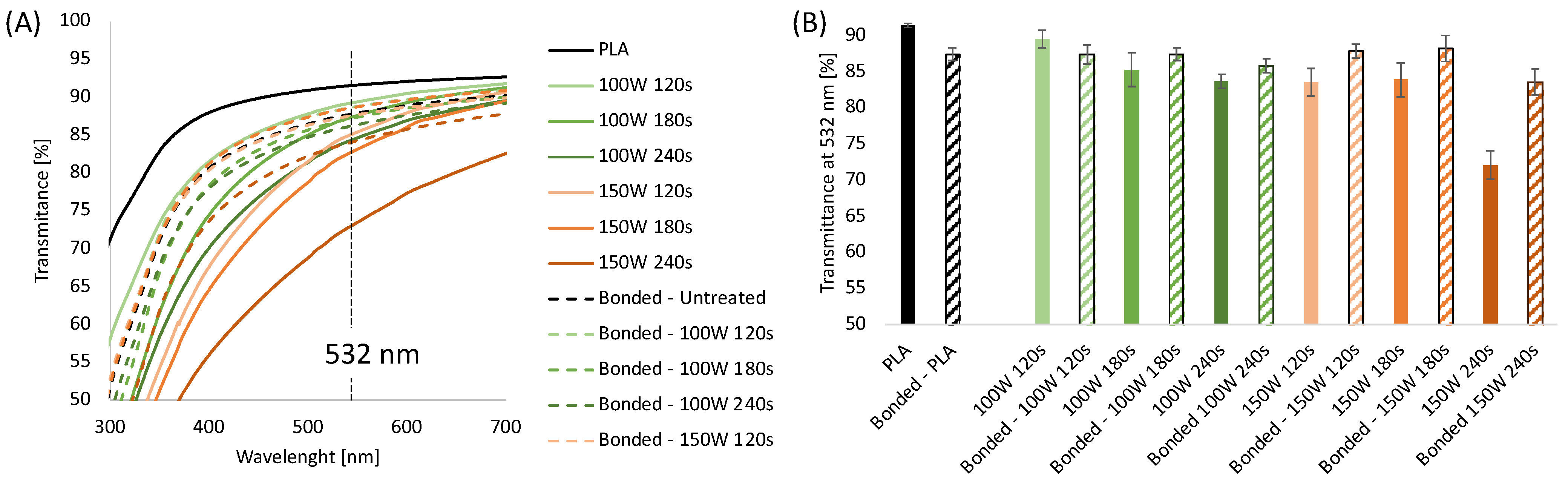
3.1. Influence of Plasma Treatment on Transparency and Wettability of PLA Sheets
3.2. Mechanical Tests on Bonded PLA Sheets
3.3. Wearable Sweat Sensors Platform Design and Fabrication
3.4. PLA Electrospun Membrane Characterization
3.5. Electrochemical Chloride Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, M.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. Wearable flexible sweat sensors for healthcare monitoring: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. The role of sampling in wearable sweat sensors. Talanta 2020, 212, 120801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazra, R.S.; Hasan Khan, M.R.; Kale, N.; Tanha, T.; Khandare, J.; Ganai, S.; Quadir, M. Bioinspired Materials for Wearable Devices and Point-of-Care Testing of Cancer. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Su, R.; Teng, L.; Tian, Q.; Han, F.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, R.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Recent advances in flexible and wearable sensors for monitoring chemical molecules. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1653–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Kamaroddin, M.F.; Sabli, N.; Tuan Abdullah, T.A.; Siajam, S.I.; Abdullah, L.C.; Abdul Jalil, A.; Ahmad, A. Membrane-based electrolysis for hydrogen production: A review. Membranes 2021, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasum, H.; Gill, N.; Mishra, R.; Lone, S. Wearable microfluidic-based e-skin sweat sensors. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 8691–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambate, P.K.; Rao, Z.; Dhanjai; Wu, J.; Shen, Y.; Boddula, R.; Huang, Y. Electrochemical (bio) sensors go green. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ji, H.; Huang, H.; Yi, N.; Shi, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, Z.; Feng, P.; Lin, T.; et al. Wearable circuits sintered at room temperature directly on the skin surface for health monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 45504–45515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Abu-Raya, Y.S.; Haick, H. Advanced materials for health monitoring with skin-based wearable devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, L.; Luo, M.; Fu, L.; Lin, B.; Xu, C. A High-Performance, Sensitive, Wearable Multifunctional Sensor Based on Rubber/CNT for Human Motion and Skin Temperature Detection. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.R.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Campos, A.M.; Wilson, D.; Otoni, C.G.; Barud, H.S.; Costa, C.A.R.; Domeneguetti, R.R.; Balogh, D.T.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; et al. Microbial nanocellulose adherent to human skin used in electrochemical sensors to detect metal ions and biomarkers in sweat. Talanta 2020, 218, 121153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaqat, S.; Dashtipour, K.; Rizwan, A.; Usman, M.; Shah, S.A.; Arshad, K.; Assaleh, K.; Ramzan, N. Personalized wearable electrodermal sensing-based human skin hydration level detection for sports, health and wellbeing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Park, W.; Lee, C.H. Electrochemically active materials and wearable biosensors for the in situ analysis of body fluids for human healthcare. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhai, Q.; An, T.; Gong, S.; Cheng, W. Stretchable gold fiber-based wearable textile electrochemical biosensor for lactate monitoring in sweat. Talanta 2021, 222, 121484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, D.; Orozco, J. Wearable electrochemical biosensors to measure biomarkers with complex blood-to-sweat partition such as proteins and hormones. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Bian, F.; Cai, L.; Zhao, Y. Encoded microneedle arrays for detection of skin interstitial fluid biomarkers. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luan, J.; Seth, A.; Liu, L.; You, M.; Gupta, P.; Rathi, P.; Wang, Y.; Cao, S.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Microneedle patch for the ultrasensitive quantification of protein biomarkers in interstitial fluid. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Soni, I.; Jayaprakash, G.K.; Flores-Moreno, R. Studies of Monoamine Neurotransmitters at Nanomolar Levels Using Carbon Material Electrodes: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xue, M.; Deng, M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Guo, Z. Recent advances in skin-like wearable sensors: Sensor design, health monitoring, and intelligent auxiliary. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 686–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; Zhong, F. Materials, Preparation Strategies, and Wearable Sensor Applications of Conductive Fibers: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Kuang, M.; Yan, J.; Wang, B.; Ma, H.; Cui, M.; Zhang, X. Cross-Links-Entanglements Integrated Networks Contributing to Highly Resilient, Soft, and Self-Adhesive Elastomers with Low Hysteresis for Green Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16631–16640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Chen, X.; Kang, Q.; Yan, X. Biomedical Application of Functional Materials in Organ-on-a-Chip. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongaro, A.E.; Di Giuseppe, D.; Kermanizadeh, A.; Miguelez Crespo, A.; Mencattini, A.; Ghibelli, L.; Mancini, V.; Wlodarczyk, K.L.; Hand, D.P.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Polylactic is a sustainable, low absorption, low autofluorescence alternative to other plastics for microfluidic and organ-on-chip applications. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6693–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, H.R.; Kang, T.; Shin, K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-L.; Chien, T.-F.; Luo, C.-H. Flexible PDMS electrode for one-point wearable wireless bio-potential acquisition. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 203, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H.M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D.; et al. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Windmiller, J.R.; Yang, Z.; Ramírez, J.; Chan, G.; Wang, J. Electrochemical tattoo biosensors for real-time noninvasive lactate monitoring in human perspiration. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6553–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Molinnus, D.; Mirza, O.; Guinovart, T.; Windmiller, J.R.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Andrade, F.J.; Schoening, M.J.; Wang, J. Epidermal tattoo potentiometric sodium sensors with wireless signal transduction for continuous non-invasive sweat monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Nakagawa, T.; Pavinatto, A.; Mensah, S.T.; Imani, S.; Mercier, P.; Wang, J. Eyeglasses based wireless electrolyte and metabolite sensor platform. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasova, S.; Crewther, B.; Bembnowicz, P.; Curto, V.; Ip, H.M.D.; Rosa, B.; Yang, G.-Z. A wearable multisensing patch for continuous sweat monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelsen, M.; Janssen, M.; Hamm, U. Consumers’ response to environmentally-friendly food packaging-a systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongaro, A.E.; Keraite, I.; Liga, A.; Conoscenti, G.; Coles, S.; Schulze, H.; Bachmann, T.T.; Parvez, K.; Casiraghi, C.; Howarth, N.; et al. Laser Ablation of Poly(lactic acid) Sheets for the Rapid Prototyping of Sustainable, Single-Use, Disposable Medical Microcomponents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4899–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, F.; Pavia, F.C.; Vitrano, I.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M.; Brucato, V.; Carrubba, V. La Effect of hydroxyapatite concentration and size on morpho-mechanical properties of PLA-based randomly oriented and aligned electrospun nanofibrous mats. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 101, 103449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, F.; Keraite, I.; Ongaro, A.E.; Howarth, N.M.; La Carrubba, V.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. Engineered Membranes for Residual Cell Trapping on Microfluidic Blood Plasma Separation Systems: A Comparison between Porous and Nanofibrous Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Tian, Y. Study of PMMA thermal bonding. Microsyst. Technol. 2007, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chong, Z.Z.; Tor, S.B.; Liu, E.; Loh, N.H. Low temperature and deformation-free bonding of PMMA microfluidic devices with stable hydrophilicity via oxygen plasma treatment and PVA coating. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 8377–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Agudo, V.; Hierro-Oliva, M.; Gallardo-Moreno, A.M.; González-Martín, M.L. Effect of plasma treatment on the surface properties of polylactic acid films. Polym. Test. 2021, 96, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, F.; Campora, S.; Tirri, G.; Capuana, E.; Carfì Pavia, F.; Brucato, V.; Ghersi, G.; La Carrubba, V. Core-shell PLA/Kef hybrid scaffolds for skin tissue engineering applications prepared by direct kefiran coating on PLA electrospun fibers optimized via air-plasma treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 127, 112248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Bourham, M.; Barrett, D.G.; Pal, L.; McCord, M. Sustainable atmospheric-pressure plasma treatment of cellulose triacetate (CTA) films for electronics. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 75302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Koerner, T.; Horton, J.H.; Oleschuk, R.D. Fabrication and characterization of poly (methylmethacrylate) microfluidic devices bonded using surface modifications and solvents. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abgrall, P.; Low, L.-N.; Nguyen, N.-T. Fabrication of planar nanofluidic channels in a thermoplastic by hot-embossing and thermal bonding. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.-L.; Larsson, A.; Ocklind, A.; Öhrlund, A. Characterization of air plasma-treated polymer surfaces by ESCA and contact angle measurements for optimization of surface stability and cell growth. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-B.; Lin, C.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Lin, Y.-F. On the surface modification of microchannels for microcapillary electrophoresis chips. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 4616–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P’pin, A.; Youinou, P.; Studer, V.; Lebib, A.; Chen, Y. Nanoimprint lithography for the fabrication of DNA electrophoresis chips. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 61, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Zhou, Y.; Balgley, B.M.; Cooper, J.W.; Lee, C.S.; DeVoe, D.L. Electrospray interfacing of polymer microfluidics to MALDI-MS. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 3631–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintberg, L.; Svedberg, M.; Nikolajeff, F.; Thornell, G. Fabrication of a paraffin actuator using hot embossing of polycarbonate. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2003, 103, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Klapperich, C.M. Thermoplastic microfluidic device for on-chip purification of nucleic acids for disposable diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xanthopoulos, N.; Reymond, F.; Rossier, J.S.; Girault, H.H. Polymer microchips bonded by O2-plasma activation. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.M.; Rosenstein, B.J.; White, T.B.; Accurso, F.J.; Castellani, C.; Cutting, G.R.; Durie, P.R.; LeGrys, V.A.; Massie, J.; Parad, R.B.; et al. Guidelines for diagnosis of cystic fibrosis in newborns through older adults: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation consensus report. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, S4–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodin, J.L.; Verbrugge, F.H.; Ellis, S.G.; Mullens, W.; Testani, J.M.; Tang, W.H.W. Importance of abnormal chloride homeostasis in stable chronic heart failure. Circ. Hear. Fail. 2016, 9, e002453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruta, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamakoshi, E.; Nishiwaki, H.; Koiwa, F.; Imai, E.; Hishida, A. Association between serum Na-Cl level and renal function decline in chronic kidney disease: Results from the chronic kidney disease Japan cohort (CKD-JAC) study. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napier, C.; Pearce, S.H.S. Autoimmune Addison’s disease. Presse Med. 2012, 41, e626–e635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Shirreffs, S.M. Muscle cramping during exercise: Causes, solutions, and questions remaining. Sport. Med. 2019, 49, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, M.F. Muscle cramps during exercise-is it fatigue or electrolyte deficit? Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2008, 7, S50–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokdemir, Y.; Karadag, B.T. Sweat Testing and Recent Advances. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvelli, A.; Campi, B.; Mergni, G.; Di Cicco, M.E.; Turini, P.; Scardina, P.; Zucchi, R.; Pifferi, M.; Taccetti, G.; Paolicchi, A.; et al. Sweat chloride assay by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: A confirmation test for cystic fibrosis diagnosis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6909–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Jung, M.; Lee, H.; Han, M.S. Development of a fluorescent chemosensor for chloride ion detection in sweat using Ag+-benzimidazole complexes. Dye Pigment. 2020, 177, 108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.B. Determination of nine components in Bayer liquors by high performance ion chromatography with conductivity detector. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2006, 51, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.P.; Ratterman, M.E.; Griffin, D.K.; Hou, L.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Naik, R.R.; Hagen, J.A.; Papautsky, I.; Heikenfeld, J.C. Adhesive RFID Sensor Patch for Monitoring of Sweat Electrolytes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzara, F.; Patella, B.; D’Agostino, C.; Bruno, M.G.; Carbone, S.; Lopresti, F.; Aiello, G.; Torino, C.; Vilasi, A.; O’Riordan, A.; et al. PANI-Based Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for pH Sweat Monitoring. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, B.; Sortino, A.; Mazzara, F.; Aiello, G.; Drago, G.; Torino, C.; Vilasi, A.; O’Riordan, A.; Inguanta, R. Electrochemical detection of dopamine with negligible interference from ascorbic and uric acid by means of reduced graphene oxide and metals-NPs based electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1187, 339124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzara, F.; Patella, B.; Aiello, G.; Sunseri, C.; Inguanta, R. Ascorbic Acid determination using linear sweep voltammetry on flexible electrode modified with gold nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 20th Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference (MELECON), Palermo, Italy, 16–18 June 2020; pp. 406–410. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Qiao, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Gao, L.; Zhang, L. Wearable Sensor for Continuous Sweat Biomarker Monitoring. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Channa, A.; Jeoti, V.; Stojanović, G.M. Comprehensive Review on Wearable Sweat-Glucose Sensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueck, A.; Iftekhar, T.; Stannard, A.B.; Yelamarthi, K.; Kaya, T. A Real-Time Wireless Sweat Rate Measurement System for Physical Activity Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patella, B.; Aiello, G.; Drago, G.; Torino, C.; Vilasi, A.; O’Riordan, A.; Inguanta, R. Electrochemical detection of chloride ions using Ag-based electrodes obtained from compact disc. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1190, 339215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, B.; Aiello, G.; Torino, C.; Vilasi, A.; O’Riordan, A.; Inguanta, R. Silver based sensors from CD for chloride ions detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 20–23 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, S.; Park, S.M.; Han, S.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, D.S. One-step fabrication of a tunable nanofibrous well insert via electrolyte-assisted electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 38300–38306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotaling, N.A.; Bharti, K.; Kriel, H.; Simon, C.G. DiameterJ: A validated open source nanofiber diameter measurement tool. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, K.S.; Kalyanam, S.; Palaniappan, J.; Insana, M.F. Indentation analysis of biphasic viscoelastic hydrogels. Mech. Mater. 2016, 92, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, D. Determination of Chloride Ion Concentration by Titration (Mohr’s Method). 2011. Available online: https://www.canterbury.ac.nz/media/documents/science-outreach/chloride_volhard.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- De Geyter, N.; Morent, R.; Desmet, T.; Trentesaux, M.; Gengembre, L.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C.; Payen, E. Plasma modification of polylactic acid in a medium pressure DBD. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morent, R.; De Geyter, N.; Trentesaux, M.; Gengembre, L.; Dubruel, P.; Leys, C.; Payen, E. Influence of discharge atmosphere on the ageing behaviour of plasma-treated polylactic acid. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2010, 30, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Thouless, M.D.; Waas, A.M.; Schroeder, J.A.; Zavattieri, P.D. Mixed-mode cohesive-zone models for fracture of an adhesively bonded polymer–matrix composite. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2006, 73, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-W.; DeVoe, D.L. Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, E.M.; Martinu, L.; Wertheimer, M.R. Plasma surface modification of polymers for improved adhesion: A critical review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1993, 7, 1091–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebska-Podsiadły, J.; Dörsam, E. Effects of argon low temperature plasma on PLA film surface and aging behaviors. Vacuum 2017, 145, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, F.; Carfì Pavia, F.; Ceraulo, M.; Capuana, E.; Brucato, V.; Ghersi, G.; Botta, L.; La Carrubba, V. Physical and biological properties of electrospun poly(d,l-lactide)/nanoclay and poly(d,l-lactide)/nanosilica nanofibrous scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 2120–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasiewska, L.A.; Seymour, I.; Patella, B.; Inguanta, R.; Burgess, C.M.; Duffy, G.; O’Riordan, A. Reagent free electrochemical-based detection of silver ions at interdigitated microelectrodes using in-situ pH control. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 333, 129531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnkova, L.; Adam, V.; Hubalek, J.; Babula, P.; Kizek, R. Amperometric sensor for detection of chloride ions. Sensors 2008, 8, 5619–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, H.S.; Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Tschulik, K.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical detection of chloride levels in sweat using silver nanoparticles: A basis for the preliminary screening for cystic fibrosis. Analyst 2013, 138, 4292–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopresti, F.; Patella, B.; Divita, V.; Zanca, C.; Botta, L.; Radacsi, N.; O’Riordan, A.; Aiello, G.; Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M.; Inguanta, R.; et al. Green and Integrated Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for Chloride Detection in Sweat. Sensors 2022, 22, 8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218223
Lopresti F, Patella B, Divita V, Zanca C, Botta L, Radacsi N, O’Riordan A, Aiello G, Kersaudy-Kerhoas M, Inguanta R, et al. Green and Integrated Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for Chloride Detection in Sweat. Sensors. 2022; 22(21):8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218223
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopresti, Francesco, Bernardo Patella, Vito Divita, Claudio Zanca, Luigi Botta, Norbert Radacsi, Alan O’Riordan, Giuseppe Aiello, Maïwenn Kersaudy-Kerhoas, Rosalinda Inguanta, and et al. 2022. "Green and Integrated Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for Chloride Detection in Sweat" Sensors 22, no. 21: 8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218223
APA StyleLopresti, F., Patella, B., Divita, V., Zanca, C., Botta, L., Radacsi, N., O’Riordan, A., Aiello, G., Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M., Inguanta, R., & La Carrubba, V. (2022). Green and Integrated Wearable Electrochemical Sensor for Chloride Detection in Sweat. Sensors, 22(21), 8223. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218223












