Development of Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer System for Coin Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Design and Working Principle
2.1. Experimental Coin Identification System
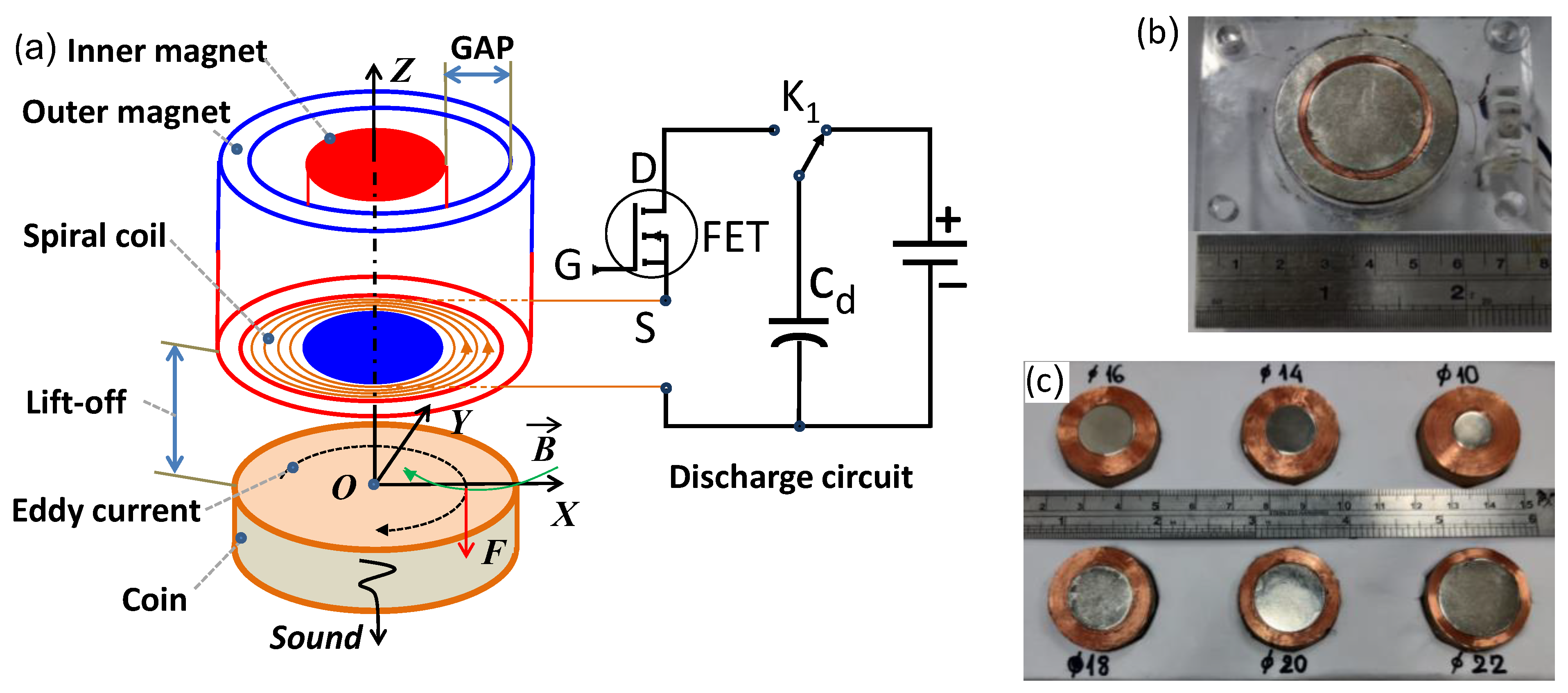
2.2. Design of the EMAT for Coin Identification
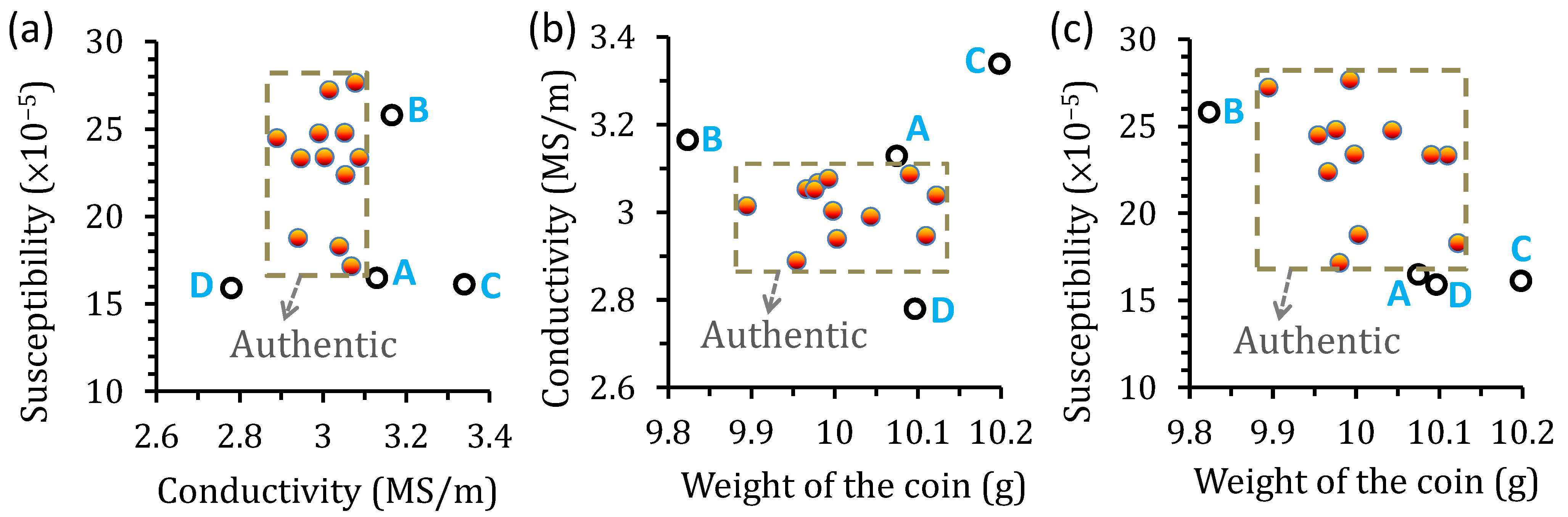
2.3. Properties of the Coin
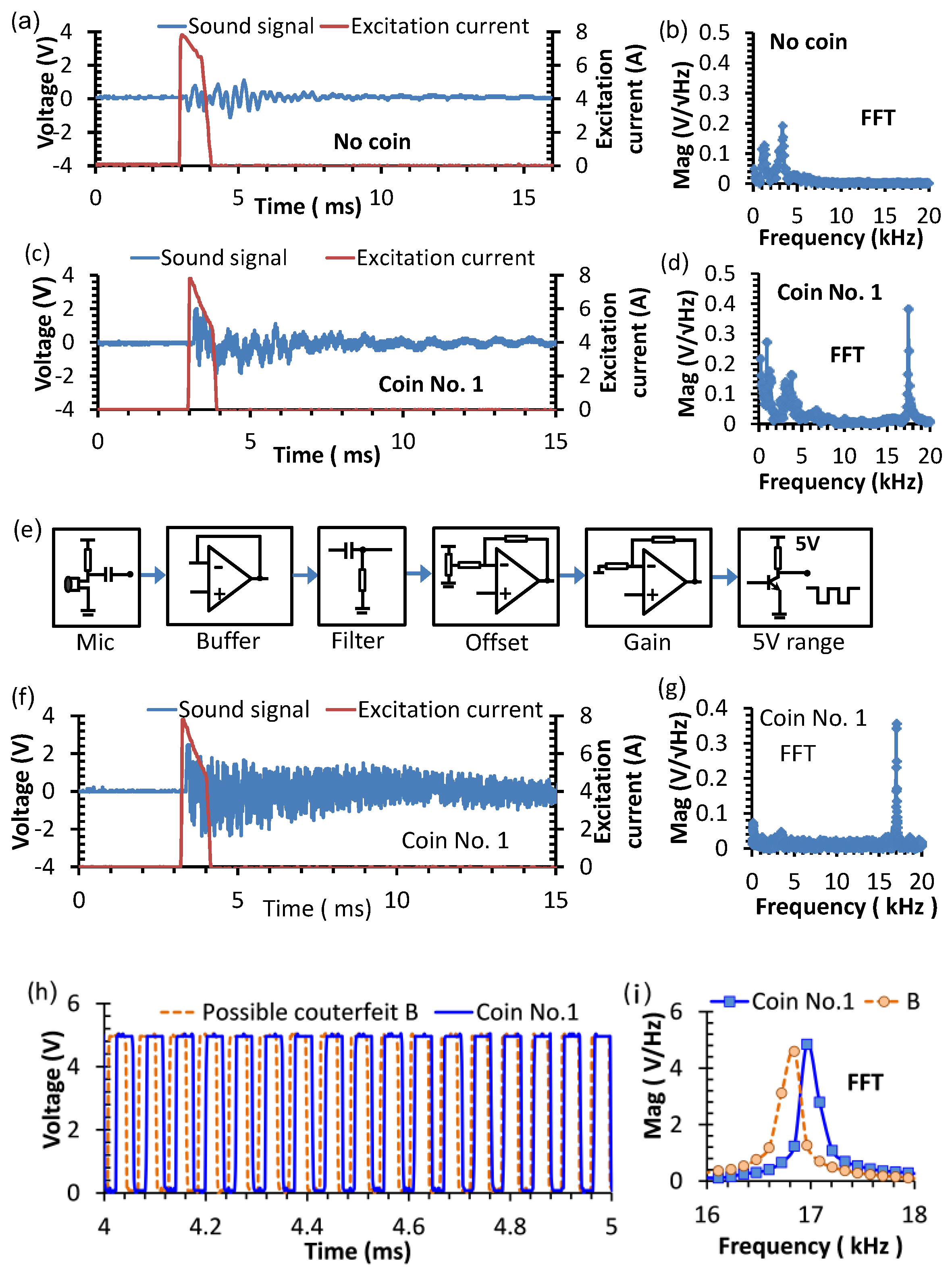
2.4. Optimal Excitation Pulse
2.5. Transforming Circuit for Sound Signal
3. Results and Discussion
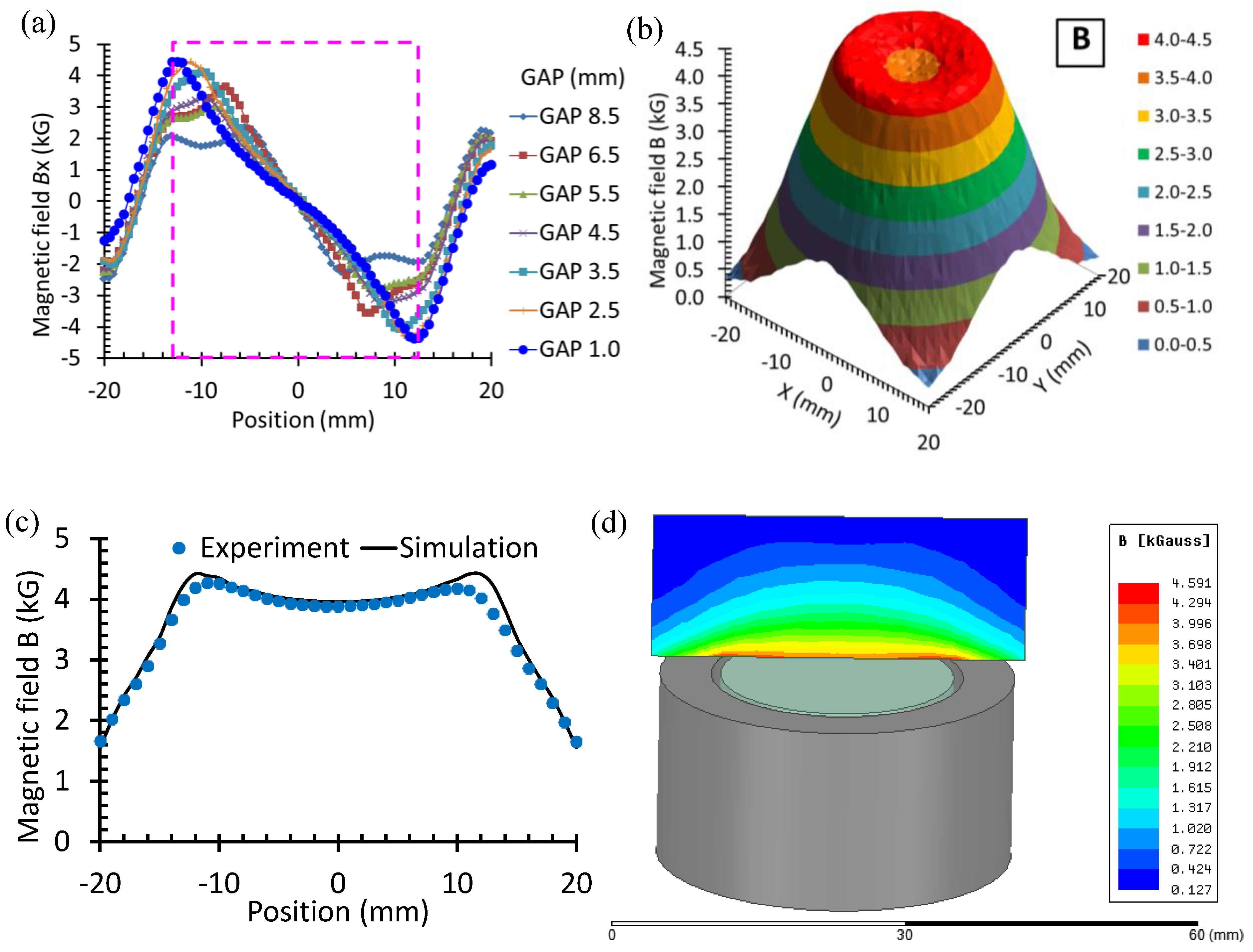
3.1. Optimal Diameters for Coil and Magnets of EMAT Probe
3.2. Optimal Liftoff Distance
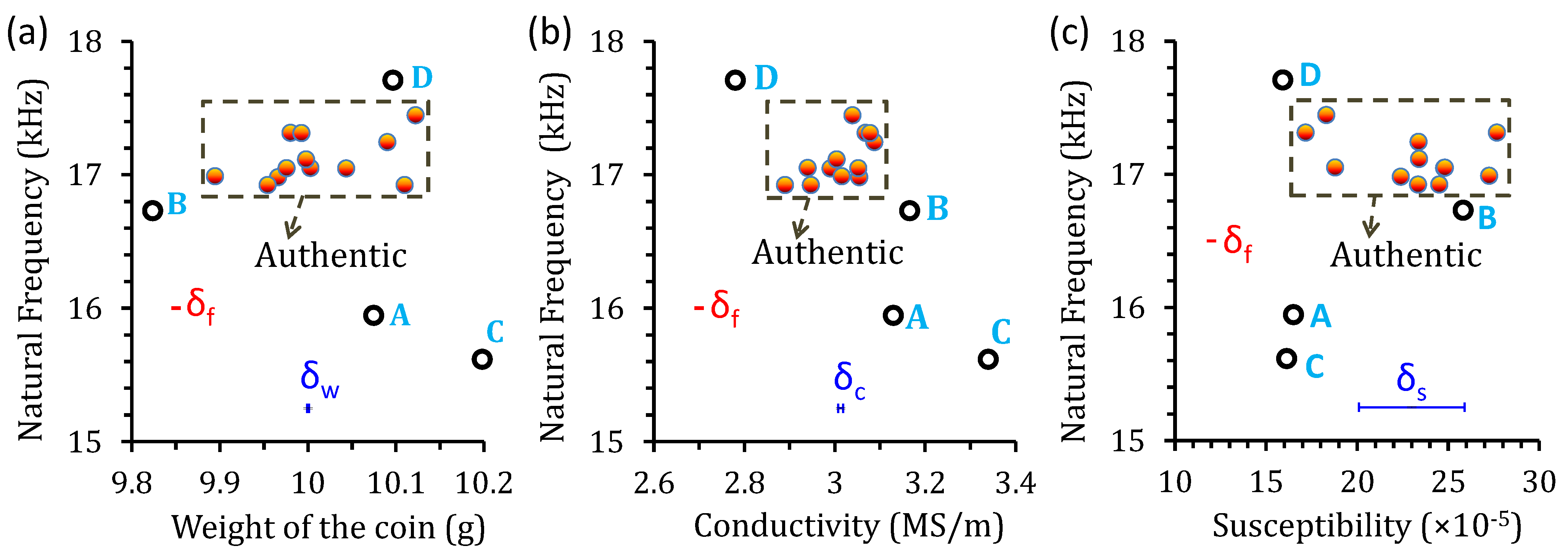
3.3. Coin Classification Using a Microcontroller-Based EMAT System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, H.H.; Cheng, K.C.; Chen, H.S. A systematic procedure for the forensic examination of questioned coins with a face value of fifty New Taiwan Dollars. Forensic Sci. J. 2002, 1, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hida, M.; Sato, H.; Sugawara, H.; Mitsui, T. Classification of counterfeit coins using multivariate analysis with X-ray diffraction and X-ray fluorescence methods. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 115, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, L.; Agresti, J.; Mascalchi, M.; Mencaglia, A.; Cacciari, I.; Siano, S. Combined elemental and microstructural analysis of genuine and fake copper-alloy coins. Quantum Electron. 2011, 41, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Suen, C.Y. An image-based approach to detection of fake coins. IEEE Trans. Inf. Secur. 2017, 12, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaee, S.; Rad, M.S.; Suen, C.Y. Detection of counterfeit coins based on 3D height-map image analysis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 174, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumi, M.; Omatu, S.; Takeda, F.; Kosaka, T. Rotation-invariant neural pattern recognition system with application to coin recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1992, 3, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.C.; Chang, W.L.; Wang, C.C.; Yu, S.F.; Jeng, J.T. A statistical pattern analysis approach for rapid coin identification based on Eddy-current sensors. Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 5579–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlosena, A.; Alfonso, A.J.; Arizti, F.; Martinez-de-Guerenu, A. Sensing in coin discriminators. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–8 February 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrijaseva, A.; Martens, O.; Land, R. Acoustic spectrum analysis of genuine and counterfeit euro coins. Elektron. Ir Elektrotechnika 2015, 21, 59-57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, M. Development of a simple and non-destructive examination for counterfeit coins using acoustic characteristics. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 177, e5–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Shi, W.; Lu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Dong, D.; Zeng, G. Application of pulse compression technique in metal materials cracks detection with LF-EMATs. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isla, J.; Cegla, F. Optimization of the bias magnetic field of shear wave EMATs. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 1148–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, P.; Li, J. Enhancement of the excitation efficiency of a torsional wave PPM EMAT array for pipe inspection by optimizing the element number of the array based on 3-D FEM. Sensors 2015, 15, 3471–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Chen, W.; Lu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W. Optimal Design of Spiral Coil EMATs for Improving Their Pulse Compression Effect. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2021, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, N.; Qian, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Li, X. Design of a new type of omnidirectional shear-horizontal EMAT by the use of half-ring magnets and PCB technology. Ultrasonics 2021, 115, 106465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.X.; Meng, X.Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, L. The Design of the Ultrasonic Nondestructive Testing System Based on the EMAT. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Hong Kong, China, 26–27 April 2016; Volume 44, p. 206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, G.; Tian, G.Y.; Meng, J.S.; Gao, B. Excitation power design base on series resonant electromagnetic ultrasonic sensor for pipeline NDT. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Far East NDT New Technology & Application Forum (FENDT), Nanchang, China, 22–24 June 2016; pp. 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, L. An exciting source for EMATs base on DDS technology. In Proceedings of the 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Qingdao, China, 23–25 May 2015; pp. 4284–4287. [Google Scholar]
- Bowler, N.; Huang, Y. Model-based characterization of homogeneous metal plates by four-point alternating current potential drop measurements. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, V.D.; Jeng, J.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Dinh, C.H.; Dao, D.V.; Pham, T.T. Magnetization measurement system with giant magnetoresistance zero-field detector. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 58, 6000405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rober, D. Blevins. Formulas for Natural Frequency and Mode Shape; Reprint Edition; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wong, K.W.; Xu, X.S.; Leung, A.Y.T. Natural vibration of circular and annular thin plates by Hamiltonian approach. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




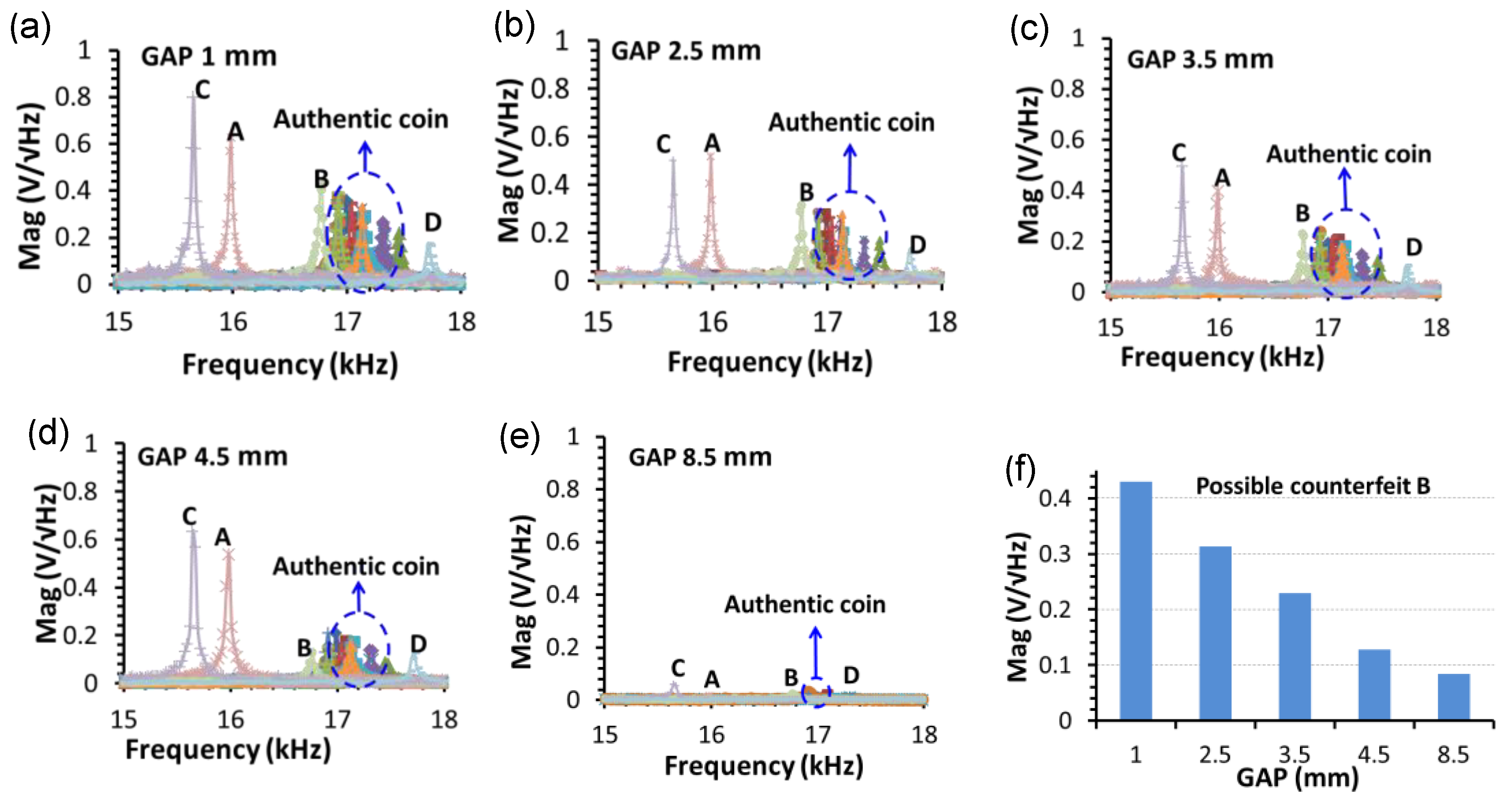
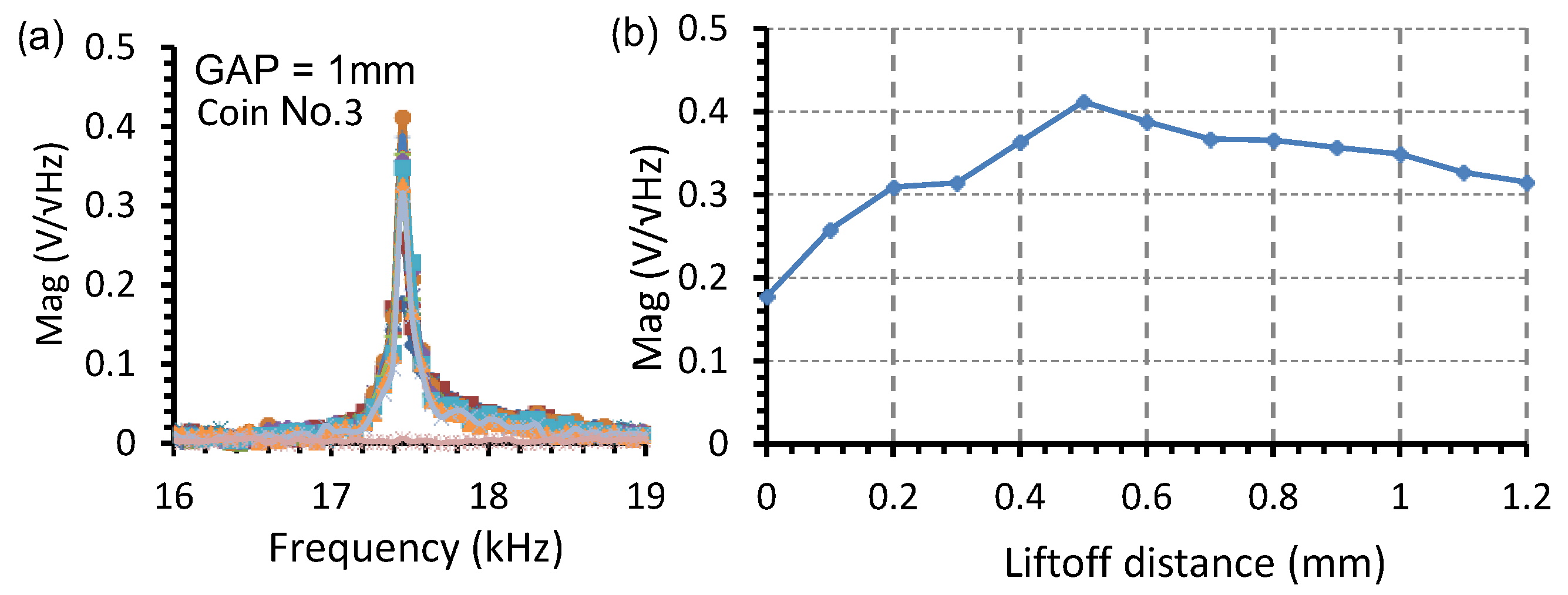
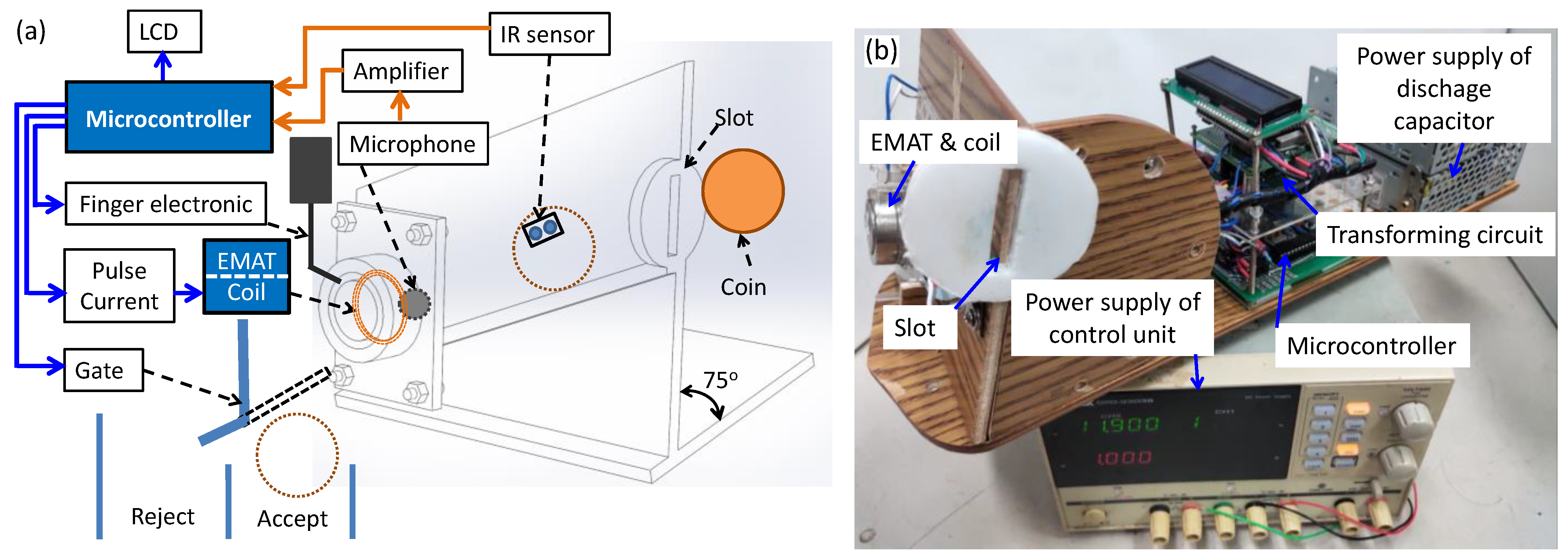

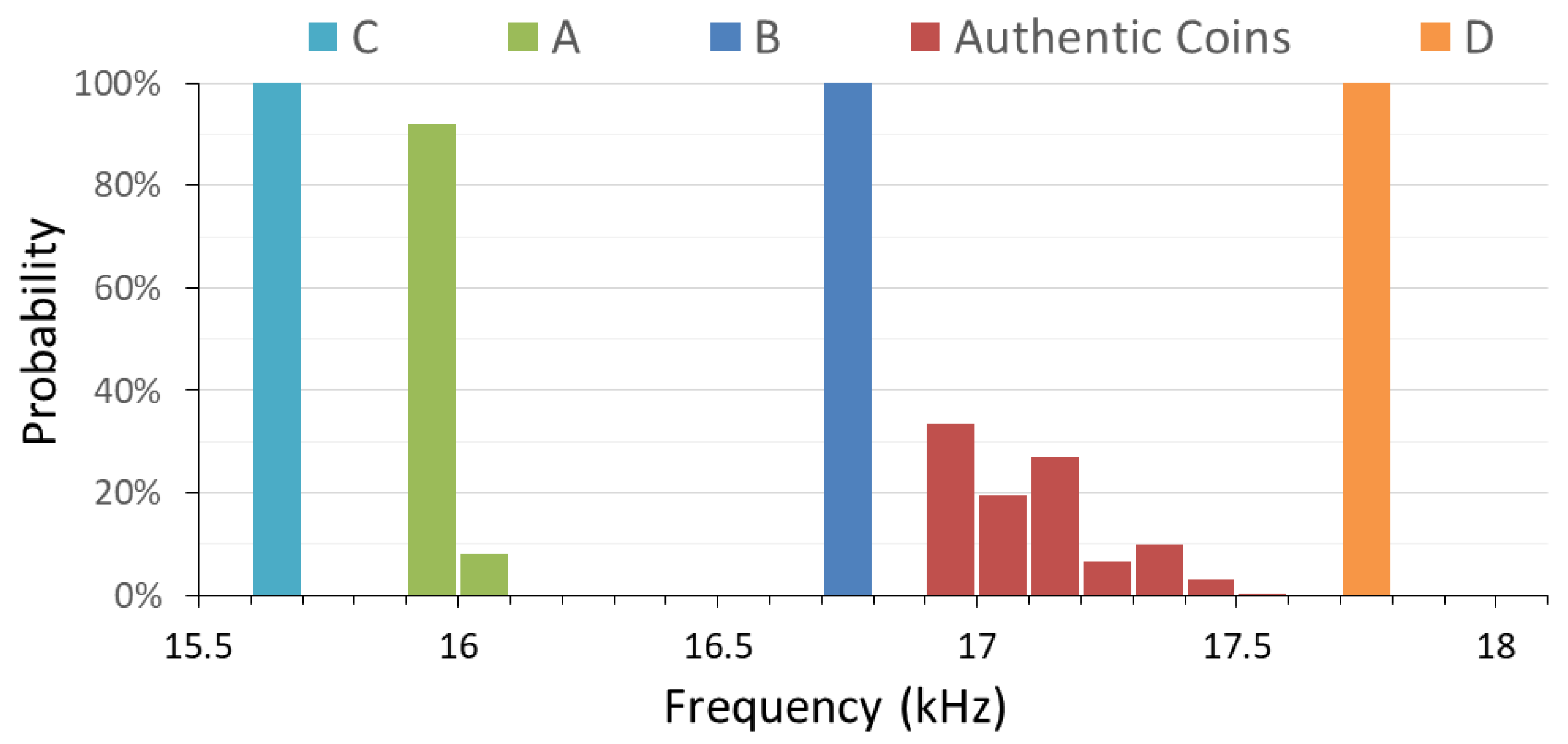
| Gap (mm) | Diameter of Inner Magnet (mm) | Spiral Coil (Turn) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 7 |
| 2.5 | 22 | 13 |
| 3.5 | 20 | 17 |
| 4.5 | 18 | 21 |
| 5.5 | 16 | 25 |
| 8.5 | 10 | 35 |
| Symbol | Material/Property | Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Copper alloy | Cu 92%, Al 6%, Ni 2% | |
| E | Young’s modulus | 110 GPa |
| ρ | Density | 7.865 g/cm3 |
| h | Thickness | 2.07 mm |
| r | Radius | 14 mm |
| ν | Poisson’s ratio | 0.3 |
| Properties | Variation | Δf0,1/f0,1 | Δf0,1/f0,1 for 1% Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radius, r | Δr | −2Δr/r | −2% |
| Thickness, h | Δh | Δh/h | 1% |
| Elastic modulus, E | ΔE | 0.5ΔE/E | 0.5% |
| Density, ρ | Δρ | −0.5Δρ/ρ | −0.5% |
| Poisson’s ratio, ν | Δν | νΔν/(1 – ν2) | 0.099% (ν = 0.3) |
| Features | ASD for All Coins | MD/ASD for Counterfeit Coins | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||
| Magnetic Susceptibility | δs = 5.79 × 10−5 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
| Electrical Conductivity | δc = 0.0109 MS/m | 3.8 | 7.1 | 23.1 | 10 |
| Weight | δw = 0.00215 g | 0 | 33 | 35 | 0 |
| Natural Frequency * | δf = 0.012 kHz | 81 | 16 | 109 | 22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dao, D.-V.; Jeng, J.-T.; Doan, V.-D.; Nguyen, H.-T.; Liang, B.-Y. Development of Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer System for Coin Classification. Sensors 2022, 22, 9055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239055
Dao D-V, Jeng J-T, Doan V-D, Nguyen H-T, Liang B-Y. Development of Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer System for Coin Classification. Sensors. 2022; 22(23):9055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239055
Chicago/Turabian StyleDao, Duy-Vinh, Jen-Tzong Jeng, Van-Dong Doan, Huu-Thang Nguyen, and Bo-Yao Liang. 2022. "Development of Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer System for Coin Classification" Sensors 22, no. 23: 9055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239055
APA StyleDao, D.-V., Jeng, J.-T., Doan, V.-D., Nguyen, H.-T., & Liang, B.-Y. (2022). Development of Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer System for Coin Classification. Sensors, 22(23), 9055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239055







