Influence of Insufficient Dataset Augmentation on IoU and Detection Threshold in CNN Training for Object Detection on Aerial Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Research Motivation
1.2. Paper Organisation
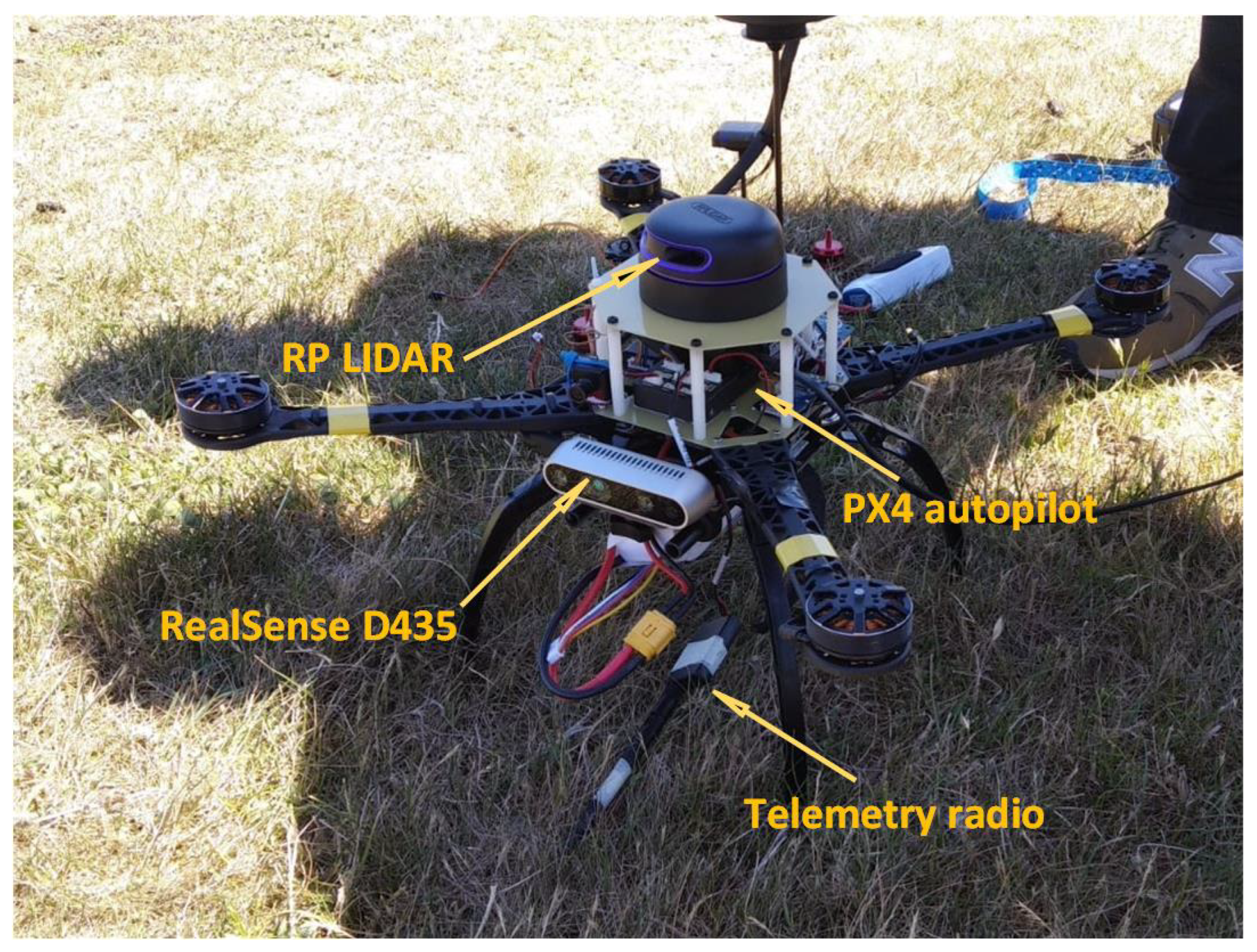
2. System Architecture
3. Image Modifications
4. Network Architecture
5. DNN Training
6. Evaluation of the Augmentation Influence
7. Results
7.1. Detection Confidence
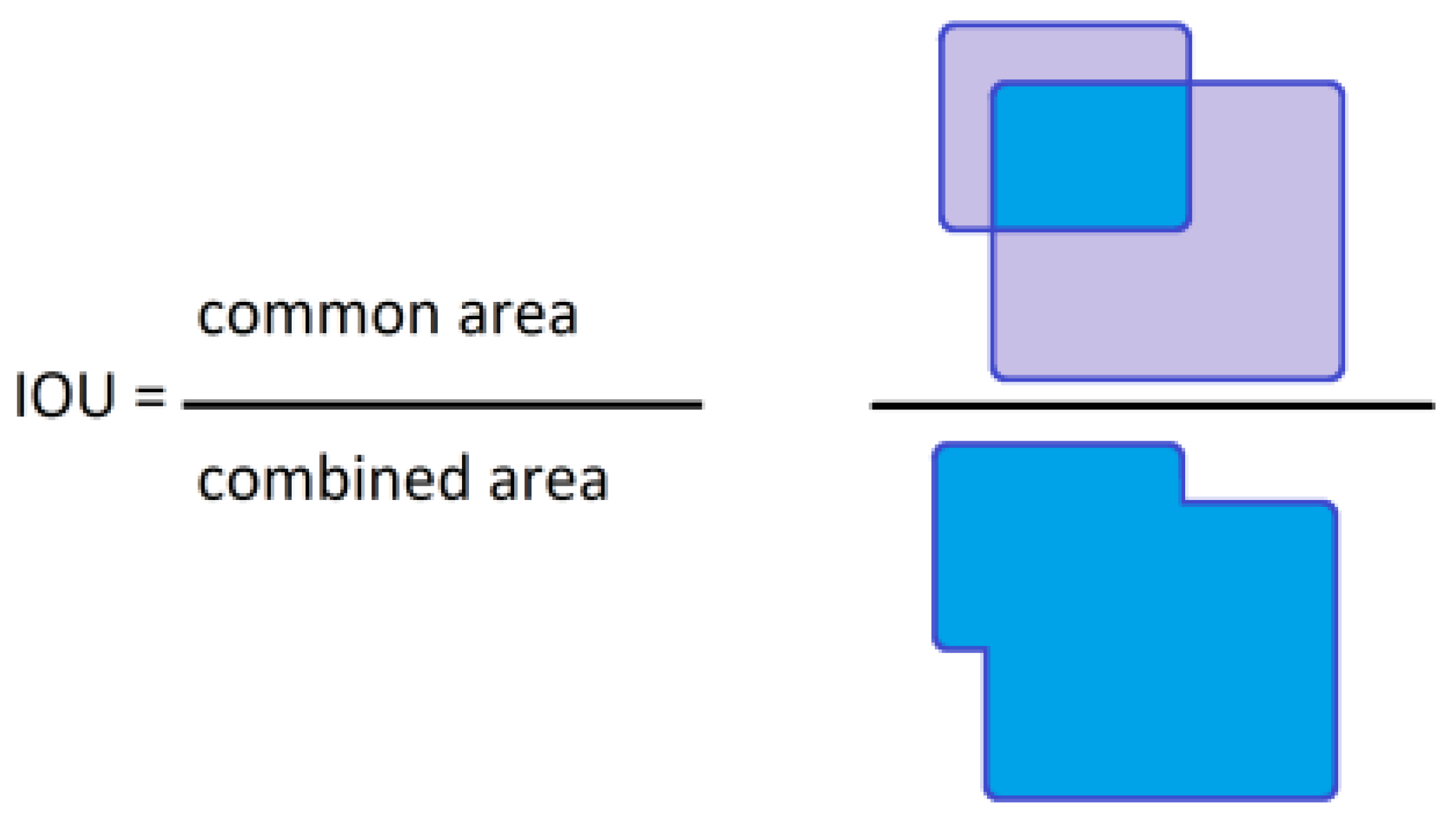
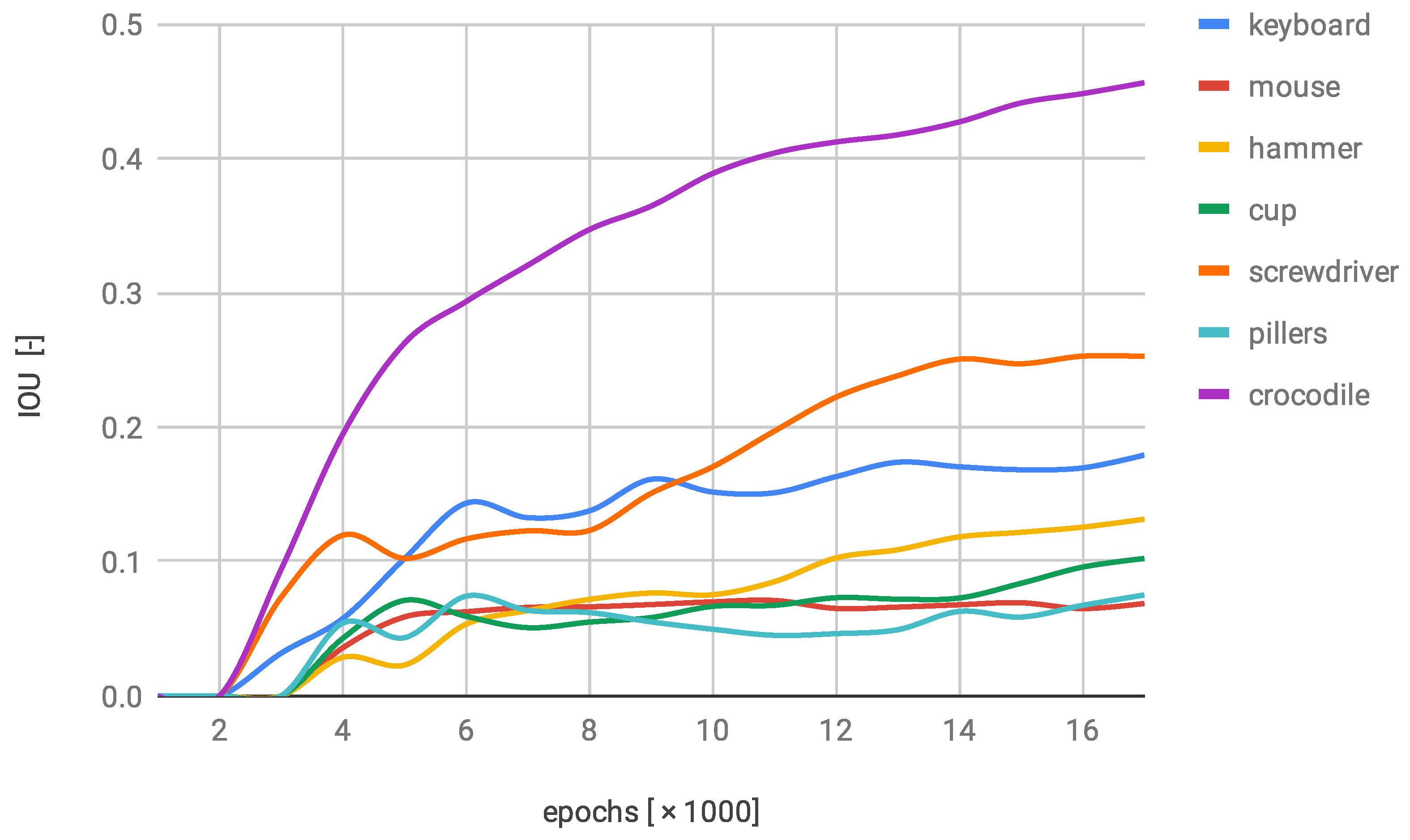
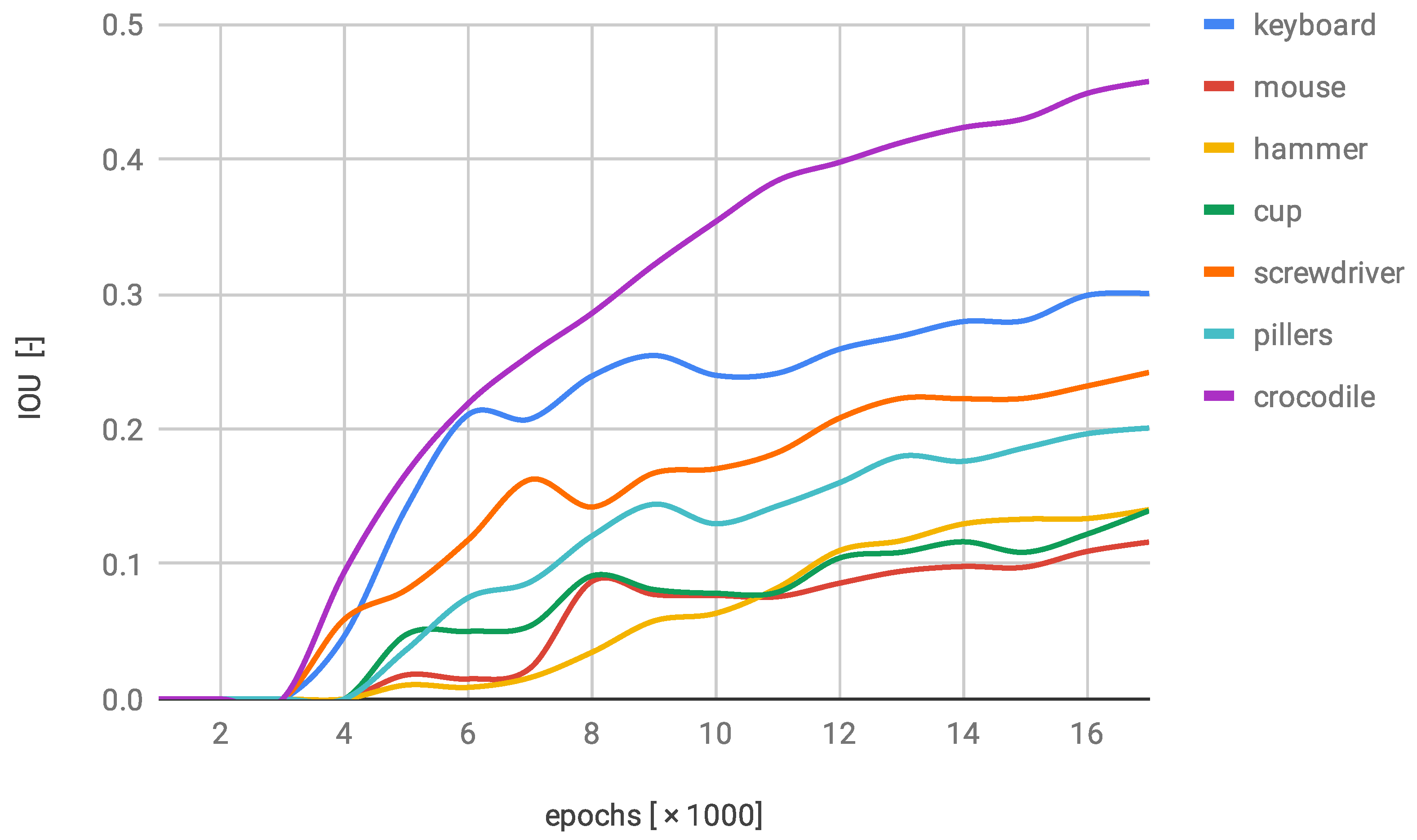
7.2. Bounding Rectangle Accuracy
7.3. Detection Examples
7.4. Trained Models Comparison
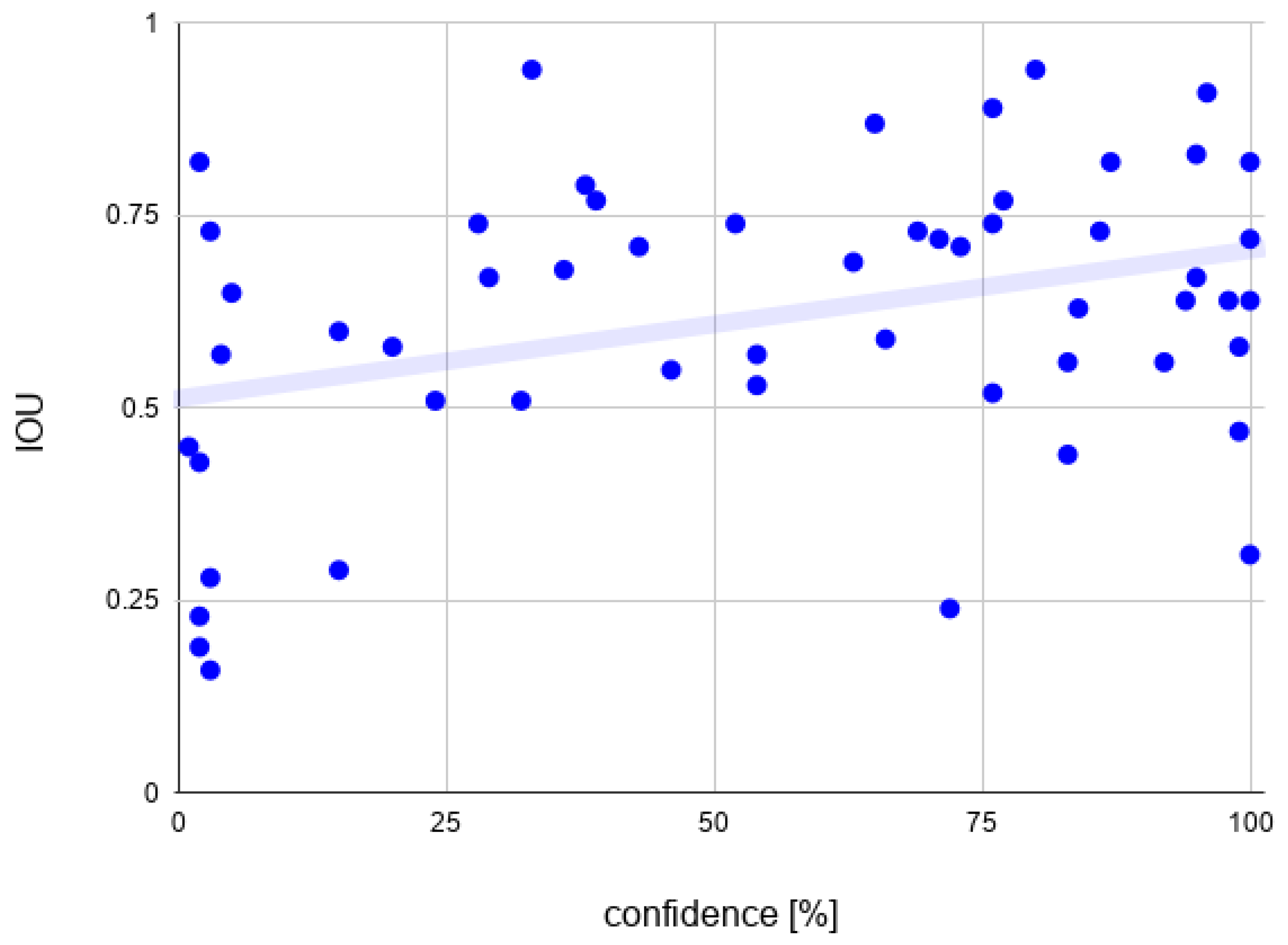
7.5. The Detection Confidence and IOU Correlation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razavian, A.S.; Azizpour, H.; Sullivan, J.; Carlsson, S. CNN Features off-the-shelf: An Astounding Baseline for Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 806–813. [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, K.; Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Return of the Devil in the Details: Delving Deep into Convolutional Nets. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, 1–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Derlatka, M.; Bogdan, M. Recognition of a Person Wearing Sport Shoes or High Heels through Gait Using Two Types of Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ang, L.M.; Seng, K.P. GPU-Based Embedded Intelligence Architectures and Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.K.; Caicedo, J.C.; Camargo, J.E. Fine-tuning Deep Convolutional Networks for Plant Recognition. In Proceedings of the Working Notes of CLEF 2015—Conference and Labs of the Evaluation forum, Toulouse, France, 8–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yosinski, J.; Clune, J.; Bengio, Y.; Lipson, H. How transferable are features in deep neural networks? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, W.; Dong, W.; Dong, L. The Effect of Training Dataset Size on SAR Automatic Target Recognition Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Beijing, China, 15–17 July 2022; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Simard, P.Y.; Steinkraus, D.; Platt, J.C. Best practices for convolutional neural networks applied to visual document analysis. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Edinburgh, UK, 6 August 2003; Volume 2, pp. 958–962. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Perez, L. The effectiveness of data augmentation in image classification using deep learning. Convolutional Neural Netw. Vis. Recognit. 2017, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Huang, M. Convolutional Neural Network With Data Augmentation for SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, J.; Bello, J.P. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Data Augmentation for Environmental Sound Classification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, S.F.; Karam, L.J. Understanding How Image Quality Affects Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eighth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Lisbon, Portugal, 6–8 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Song, S.; Cheung, N. On classification of distorted images with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 May 2017; pp. 1213–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Dodge, S.; Karam, L. A Study and Comparison of Human and Deep Learning Recognition Performance under Visual Distortions. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 31 July–3August 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, P.; Zou, W. Very Low Resolution Face Recognition Problem. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 327–340. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, U.; Chawla, P.; Tiwari, R. EnsembleNet: A hybrid approach for vehicle detection and estimation of traffic density based on faster R-CNN and YOLO models. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Harnal, S.; Tiwari, R.; Upadhyay, S.; Bhatia, S.; Mashat, A.; Alabdali, A.M. Recognition of Leaf Disease Using Hybrid Convolutional Neural Network by Applying Feature Reduction. Sensors 2022, 22, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Tang, H.; Sun, H.; Yang, X. Dropband: A convolutional neural network with data augmentation for scene classification of VHR satellite images. In Proceedings of the GEOBIA 2016: Solutions and Synergies Proceedings, Enschede, The Netherlands, 14–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Muhammad, K.; Hong, J.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Zhang, Y.D. Alcoholism identification via convolutional neural network based on parametric ReLU, dropout, and batch normalization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Harnal, S.; Tiwari, R.; Alharithi, F.S.; Almulihi, A.H.; Noya, I.D.; Goyal, N. A Hybrid Convolutional Neural Network Model for Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using Chest X-ray Images. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkar, T.S.; Karam, L.J. DeepCorrect: Correcting DNN Models Against Image Distortions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 6022–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemley, J.; Bazrafkan, S.; Corcoran, P. Smart Augmentation Learning an Optimal Data Augmentation Strategy. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5858–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.C.; Gatt, A.; Stamatescu, V.; McDonnellM, D. Understanding Data Augmentation for Classification: When to Warp? In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Gold Coast, Australia, 30 November–2 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, G.; Müller, S.; Von Bernuth, A.; Hospach, D.; Bringmann, O. Towards robust CNN-based object detection through augmentation with synthetic rain variations. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, NZ, USA, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuse, P.; Singh, B.; Raut, P. Effect of Data Augmentation on the Accuracy of Convolutional Neural Networks. In Information and Communication Technology for Competitive Strategies (ICTCS 2020); Joshi, A., Mahmud, M., Ragel, R.G., Thakur, N.V., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 191. [Google Scholar]
- Qingqing, L.; Taipalmaa, J.; Queralta, J.P.; Gia, T.N.; Gabbouj, M.; Tenhunen, H.; Raitoharju, J.; Westerlund, T. Towards Active Vision with UAVs in Marine Search and Rescue: Analyzing Human Detection at Variable Altitudes. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 4–6 November 2020; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Cao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lai, X.; Pan, Z. Drowning Detection Algorithm For Intelligent Lifebuoy. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems (ICUS), Beijing, China, 15–17 October 2021; pp. 512–519. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.; Damas, B.; Bernardino, A. Real-Time Ship Segmentation in Maritime Surveillance Videos Using Automatically Annotated Synthetic Datasets. Sensors 2022, 22, 8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. Yolact: Real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9157–9166. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. Yolact++: Better real-time instance segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Zhu, H.; Tang, F.; Wang, X. Drowning behavior detection in swimming pool based on deep learning. Signal Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Granmo, O.C.; Goodwin, M.; Fidje, J.T. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Fire Detection in Images. In Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference, EANN 2017, Athens, Greece, 25–27 August 2017; Boracchi, G., Iliadis, L., Jayne, C., Likas, A., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 744. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, K.; Ahmad, J.; Mehmood, I.; Rho, S.; Baik, S.W. Convolutional neural networks based fire detection in surveillance videos. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 18174–18183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, W. Image fire detection algorithms based on convolutional neural networks. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 19, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jintasuttisak, T.; Edirisinghe, E.; Elbattay, A. Deep neural network based date palm tree detection in drone imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadtare, M.; Choudhari, V.; Pedram, R.; Vartak, S. Comparison between YOLO and SSD Mobile Net for Object Detection in a Surveillance Drone. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Manag. 2021, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, O.; Ozer, S. YOLODrone: Improved YOLO Architecture for Object Detection in Drone Images. In Proceedings of the 44th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Virtual, 26–28 July 2021; pp. 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Spatio-Temporal Fish-Eye Image Processing Based on Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Shanghai, China, 15–18 May 2020; pp. 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Mikołajczyk, A.; Grochowski, M. Data augmentation for improving deep learning in image classification problem. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Interdisciplinary PhD Workshop (IIPhDW), Swinoujscie, Poland, 9–12 May 2018; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Szeliski, R. Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Available online: http://szeliski.org/Book/ (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Weng, J.; Cohen, P.; Herniou, M. Camera calibration with distortion models and accuracy evaluation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Nepal, U.; Eslamiat, H. Comparing YOLOv3, YOLOv4 and YOLOv5 for Autonomous Landing Spot Detection in Faulty UAVs. Sensors 2022, 22, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, P.; Rathi, P.; Kumar, M. YOLO v3-Tiny: Object Detection and Recognition using one stage improved model. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 6–7 March 2020; pp. 687–694. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Jilani, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Nikiforova, A. Improved YOLOv3-tiny Object Detector with Dilated CNN for Drone-Captured Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Data Science Technologies and Applications (IDSTA), San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–7 September 2022; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Divekar, A.V.; Anilkumar, C.; Naik, I.; Kulkarni, V.; Pattabiraman, V. Comparative analysis of deep learning image detection algorithms. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Sung, J.Y.; Park, S.H. Comparison of Faster-RCNN, YOLO, and SSD for real-time vehicle type recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), Seoul, Korea, 1–3 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.; Huangfu, T.; Wu, L.; Chen, W. Comparison of RetinaNet, SSD, and YOLO v3 for real-time pill identification. Bmc Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Lyu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. TPH-YOLOv5: Improved YOLOv5 based on transformer prediction head for object detection on drone-captured scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2778–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, R.; Netto, S.L.; da Silva, E.A.B. A Survey on Performance Metrics for Object-Detection Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), Niteroi, Brazil, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wenkel, S.; Alhazmi, K.; Liiv, T.; Alrshoud, S.; Simon, M. Confidence Score: The Forgotten Dimension of Object Detection Performance Evaluation. Sensors 2021, 21, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelazo, T. Own Work. CC BY-SA 2.5. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=5385852 (accessed on 29 October 2022).
- Fidenci, P. Own Work. CC BY-SA 2.5. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=6081116 (accessed on 29 October 2022).
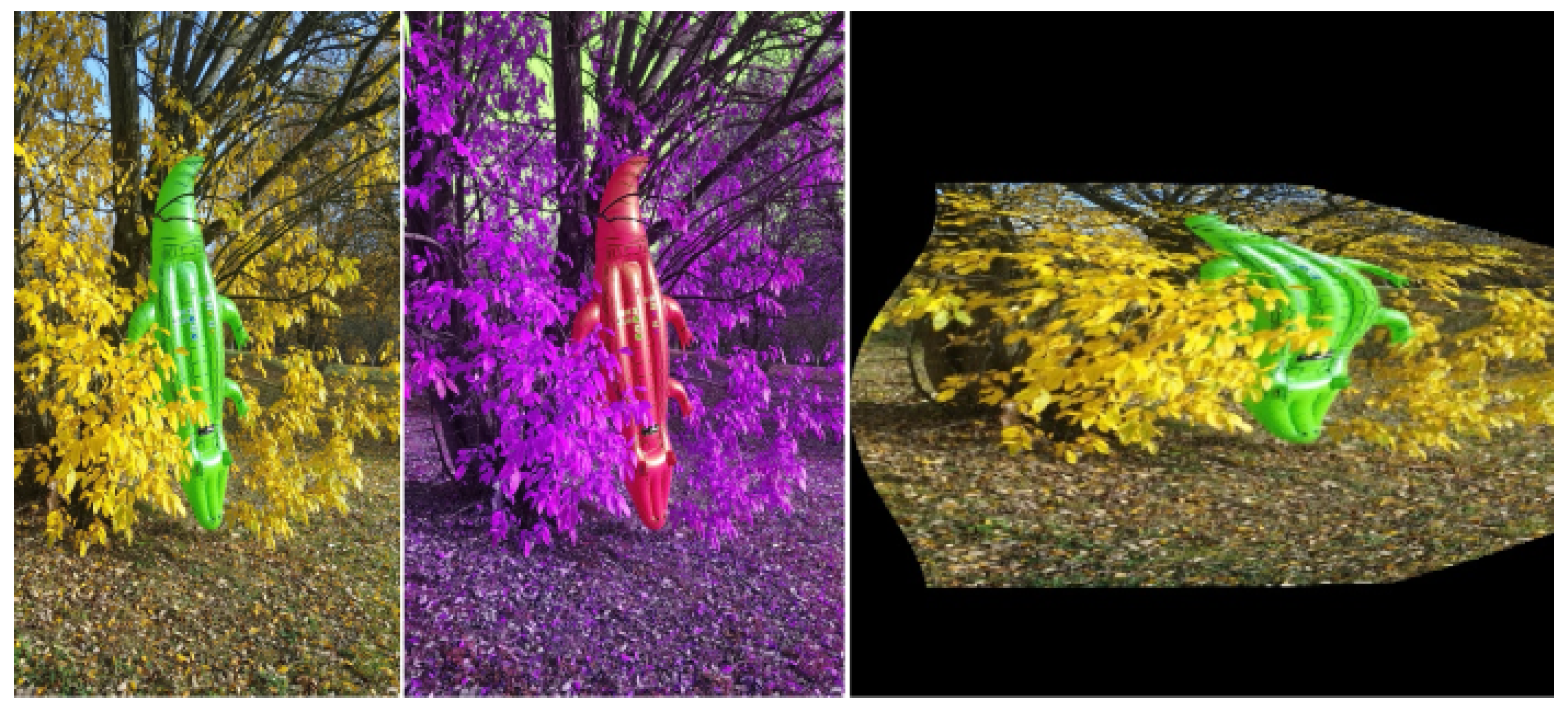









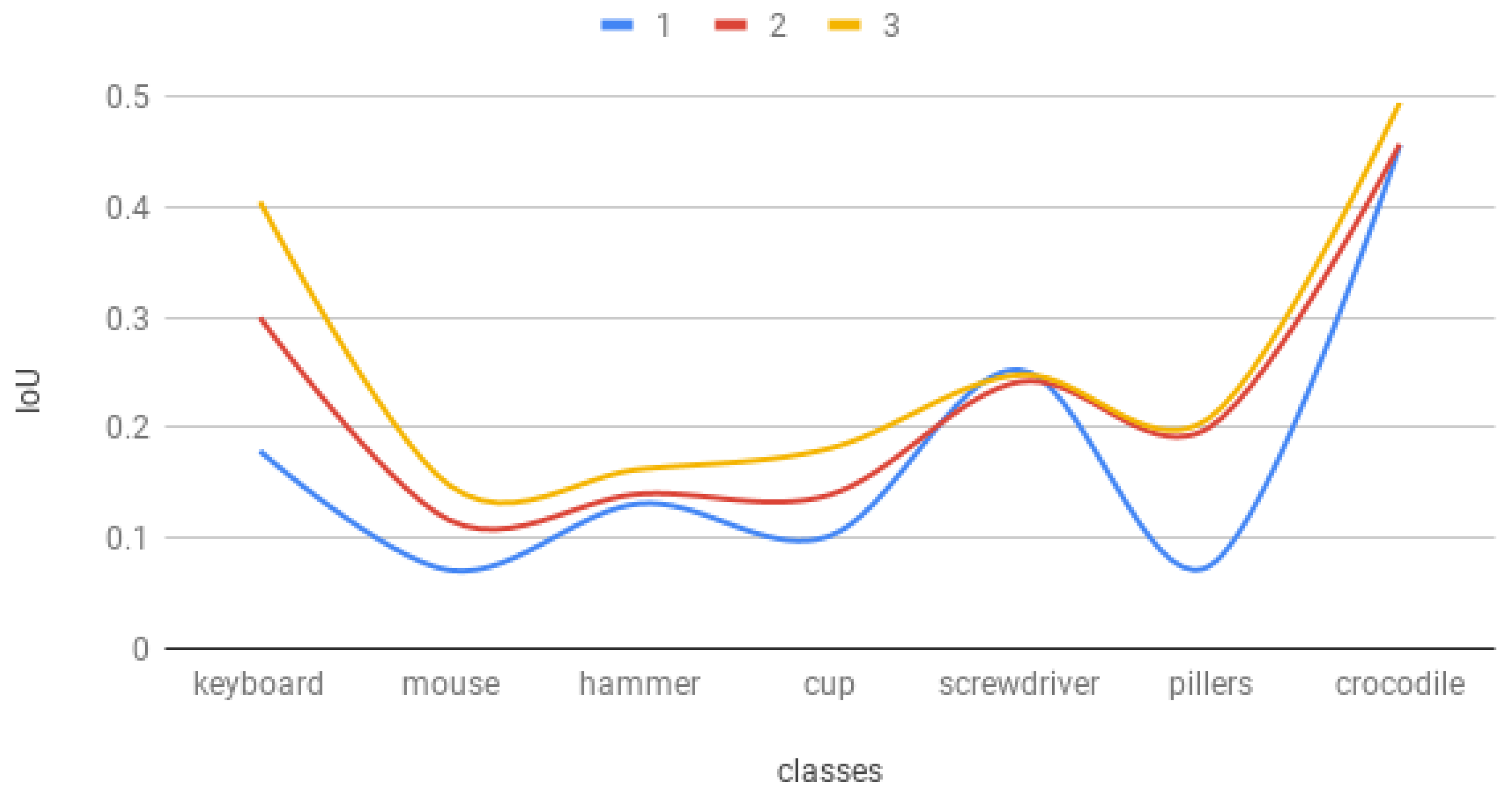
| Classes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gain | Modification | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | Average |
| absolute | DNN2 | 12.1 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 3.7 | −1.0 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 4.6 |
| DNN3 | 22.6 | 7.6 | 3.1 | 7.9 | −0.4 | 13.4 | 2.5 | 8.1 | |
| relative | DNN2 | 67.5 | 63.7 | 6.6 | 36.4 | −4.3 | 167 | 0.2 | 48.2 |
| DNN3 | 126 | 108 | 23.7 | 77.6 | −1.7 | 178 | 5.6 | 74.0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bożko, A.; Ambroziak, L. Influence of Insufficient Dataset Augmentation on IoU and Detection Threshold in CNN Training for Object Detection on Aerial Images. Sensors 2022, 22, 9080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239080
Bożko A, Ambroziak L. Influence of Insufficient Dataset Augmentation on IoU and Detection Threshold in CNN Training for Object Detection on Aerial Images. Sensors. 2022; 22(23):9080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239080
Chicago/Turabian StyleBożko, Arkadiusz, and Leszek Ambroziak. 2022. "Influence of Insufficient Dataset Augmentation on IoU and Detection Threshold in CNN Training for Object Detection on Aerial Images" Sensors 22, no. 23: 9080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239080
APA StyleBożko, A., & Ambroziak, L. (2022). Influence of Insufficient Dataset Augmentation on IoU and Detection Threshold in CNN Training for Object Detection on Aerial Images. Sensors, 22(23), 9080. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239080







