Discriminating between Absorption and Scattering Effects in Complex Turbid Media by Coupling Polarized Light Spectroscopy with the Mueller Matrix Concept
Abstract
:1. Introduction
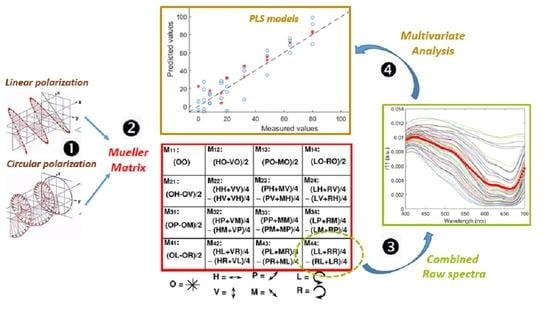
2. The Mueller Matrix
3. Materials and Methods
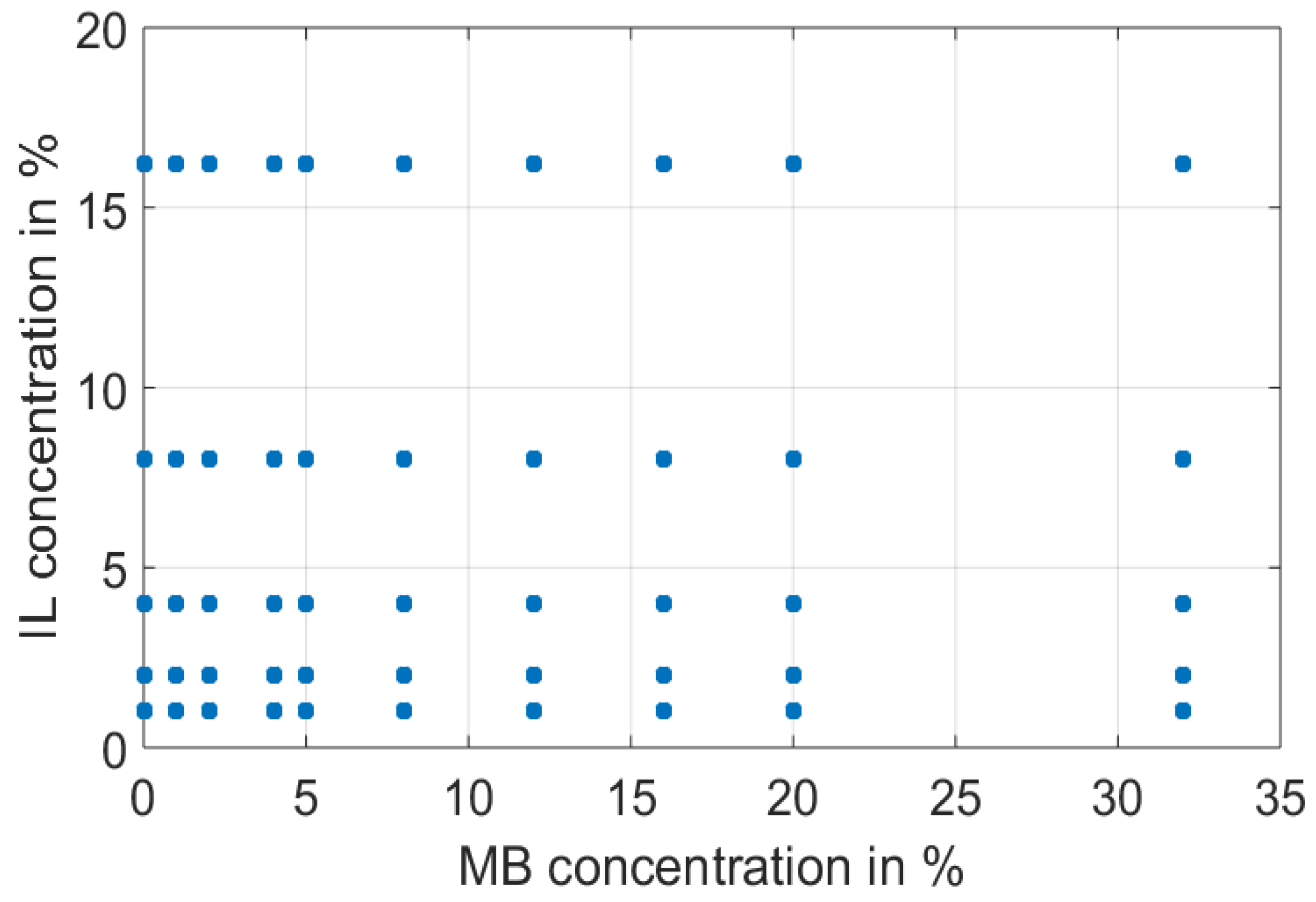
3.1. Liquid Optical Phantoms
3.1.1. Mixture Composition
3.1.2. Sample Preparation
3.2. Polarization Spectroscopy System
3.2.1. Experimental Setup
3.2.2. Spectral Acquisition
3.2.3. Determination of Mueller Matrix Elements
3.3. PLS Models
4. Results and Discussion
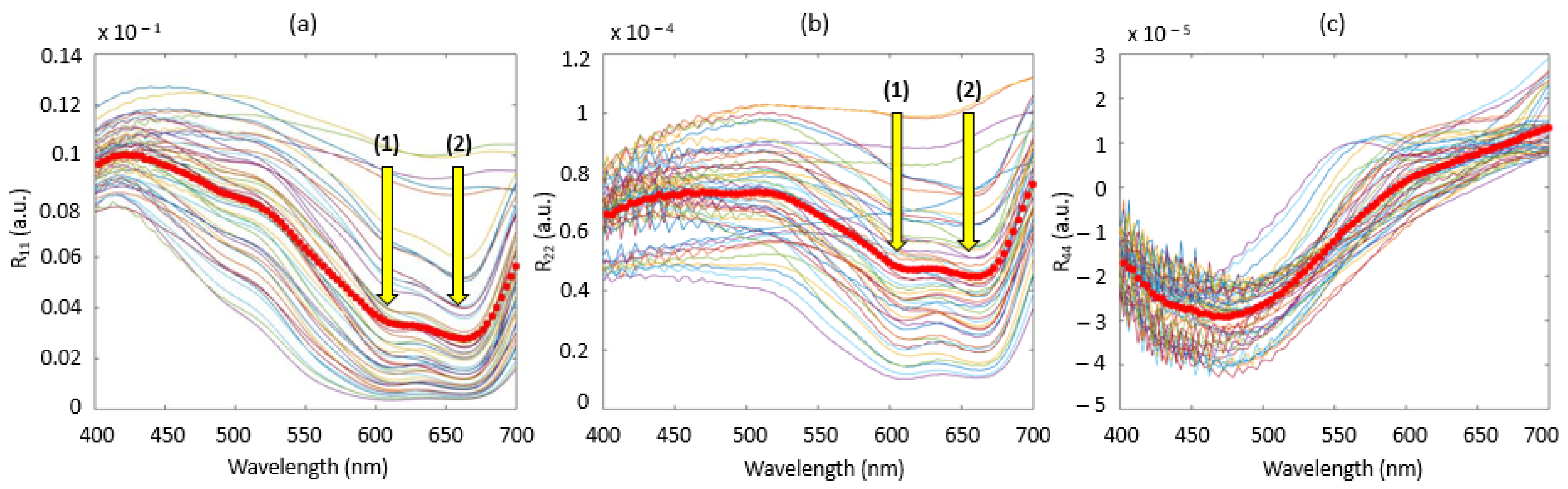
4.1. Raw Spectra Analysis
4.2. Cabs and Cdif Prediction Models
4.2.1. Absorber Concentration Models
4.2.2. Scatterer Concentration Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heesang, A.; Hyerin, S.; Dong-Myeong, S.; Kyujung, K.; Jong-ryul, C. Emerging optical spectroscopy techniques for biomedical applications—A brief review of recent progress. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2018, 53, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Jin, T.M.; Hu, X.N.; Zhong, J.E.; Wu, Q.T. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy to agriculture and food analysis. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi Guang Pu 2004, 24, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, A.; Kameoka, T. Applications of Infrared Spectroscopy to Biochemical, Food, and Agricultural Processes. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2008, 43, 416–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, P.A. Application of Spectroscopic Methods to Environmental Problems. Spectrosc. Lett. 2005, 38, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-P.; Morris, J.; Martin, E. Extracting Chemical Information from Spectral Data with Multiplicative Light Scattering Effects by Optical Path-Length Estimation and Correction. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7674–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquerre, C.; Gowen, A.A.; Burger, J.; Downey, G.; O’Donnell, C.P. Suppressing sample morphology effects in near infrared spectral imaging using chemometric data pre-treatments. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2012, 117, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnan, A.; Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.J.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard Normal Variate Transformation and De-Trending of Near-Infrared Diffuse Reflectance Spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; MacDougall, D.; Martens, H. Linearization and Scatter-Correction for Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectra of Meat. Appl. Spectrosc. 1985, 39, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, T.W. Scale-based normalization of spectral data. Cancer Biomark. 2006, 2, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Star, W.M.; Marijnissen, J.P.A.; Gemert, M.J.C. Light dosimetry in optical phantoms and in tissues: 1. Multiple flux and transport-theory. Phys. Med. Biol. 1988, 33, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thennadil, S.N.; Dzhongova, E. NIR Spectroscopy of Turbid Media: Maximising Extractable Information Using Light Propagation Theory. NIR News 2013, 24, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steponavicius, R.; Thennadil, S.N. Extraction of chemical information of suspensions using radiative transfer theory to remove multiple scattering effects: Application to a model multicomponent system. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steponavicius, R.; Thennadil, S.N. Extraction of chemical information of suspensions using radiative transfer theory to remove multiple scattering effects: Application to a model two-component System. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7713–7723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farrell, T.; Patterson, M.; Wilson, B. A diffusion theory model of spatially resolved, steady-state diffuse reflectance for the noninvasive determination of tissue optical properties in vivo. Med. Phys. 1992, 19, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsson, C.; Johansson, J.; Andersson-Engels, S.; Svanberg, S.; Folestad, S. Time-resolved NIR spectroscopy for quantitative analysis of intact pharmaceutical tablets. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrance, S.; Sun, Z.; Sevick-Muraca, E.M. Impact of excipient particle size on measurement of active pharmaceutical ingredient absorbance in mixtures using frequency domain photon migration. J. Med. Sci. 2004, 93, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartling, J.; Dam, J.; Andersson-Engels, S. Comparison of spatially and temporally resolved diffuse-reflectance measurement systems for determination of biomedical optical properties. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 4612–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Héran, D.; Ryckewaert, M.; Abautret, Y.; Zerrad, M.; Amra, C.; Bendoula, R. Combining light polarization and speckle measurements with multivariate analysis to predict bulk optical properties of turbid media. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 8247–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobrecht, A.; Bendoula, R.; Roger, J.-M.; Bellon-Maurel, V. Combining linear polarization spectroscopy and the representative layer theory to measure the Beer-Lambert law absorbance of highly scattering materials. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchin, V. Polarized light interaction with tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 071114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bendoula, R.; Gobrecht, A.; Moulin, B.; Roger, J.-M.; Bellon-Maurel, V. Improvement of the Chemical Content Prediction of a Model Powder System by Reducing Multiple Scattering Using Polarized Light Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2015, 69, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, A.; Deumié, C.; Vanzetta, I. Elliptically polarized light for depth resolved optical Imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bickel, W.S.; Bailey, W.M. Stokes vectors, Mueller matrices, and polarized light scattering. Am. J. Phys. 1985, 53, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hielscher, A.; Eick, A.; Mourant, J.; Shen, D.; Freyer, J.; Bigio, I. Diffuse backscattering Mueller matrices of highly scattering media. Opt. Express 1997, 1, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, B.D.; Li, Y.; Nezhuvingal, A.A. Determination of optical scattering properties in turbid media using Mueller matrix imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 054031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducanchez, A.; Bendoula, R.; Héran, D. Data on near infrared polarization spectroscopy measurements to evaluate the potential of the Muller matrix elements in characterization of turbid liquid samples. Data Brief 2019, 23, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, H. Memorandum on the Polarization Optics of the Photoelastic Shutter; Technical Report (Report No. 2 of the OSRD project OEMsr-576); OSRD: Washington, DC, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Freudenthal, J. Intuitive Interpretation of Mueller Matrices of Transmission; Hinds Instruments, Inc.: Hillsboro, OR, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.hindsinstruments.com (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- Chipman, R.A. Chapter 22: Polarimetry. In Handbook of Optics, 2nd ed.; Bass, M., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 2, pp. 22.1–22.37. [Google Scholar]
- Aernouts, B.; Zamora-Rojas, E.; Van Beers, R.; Watté, R.; Wang, L.; Tsuta, M.; Lammertyn, J.; Saeys, W. Supercontinuum laser based optical characterization of Intralipid phantoms in the 500–2250 nm range. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 32450–32467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninni, P.D.; Martelli, F.; Zaccanti, G. Intralipid: Towards a diffusive reference standard for optical tissue phantoms. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, N21–N28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flock, S.T.; Jacques, S.L.; Wilson, B.C.; Star, W.M.; Van Gemert, M.J. Optical properties of Intralipid: A phantom medium for light propagation studies. Lasers Surg. Med. 1992, 12, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, R.; Foschum, F.; Kienle, A. Optical properties of fat emulsions. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 5907–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- New Zealand Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.fresenius-kabi.com/nz/documents/Intralipid_Datasheet.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- Whateley, T.L.; Steele, G.; Urwin, J.; Smail, G.A. Particle size stability of intralipid and mixed total parenteral nutrition mixtures. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1984, 9, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genina, E.; Bashkatov, A.; Tuchin, V. Methylene blue diffusion in skin tissue. In Proceedings of the SPIE 5486, ALT’03 International Conference on Advanced Laser Technologies: Biomedical Optics, Silsoe, UK, 29 July 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMLC Website for Methylene Blue Spectral Data. Available online: https://omlc.org/spectra/mb/ (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Usacheva, M.N.; Teichert, M.C.; Biel, M.A. The role of the methylene blue and toluidine blue monomers and dimers in the photoinactivation of bacteria. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2003, B71, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, S. Cross-Validatory Estimation of the Number of Components in Factor and Principal Components Models. Technometrics 1978, 20, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Laan, J.; Wright, J.; Scrymgeour, D.; Kemme, S.; Dereniak, E. Evolution of circular and linear polarization in scattering environments. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 31874–31888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, B.; Guo, K.; Yin, Z.; Guo, Z. The Depolarization Performances of the Polarized Light in Different Scattering Media Systems. IEEE Photonics J. 2018, 10, 3900212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartazayeva, S.; Ni, X.; Alfano, R. Backscattering target detection in a turbid medium by use of circularly and linearly polarized light. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 1168–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awhangbo, L.; Bendoula, R.; Roger, J.-M.; Béline, F. Multi-block SO-PLS approach based on infrared spectroscopy for anaerobic digestion process monitoring. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 196, 103905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancolillo, A.; Måge, I.; Næs, T. Combining SO-PLS and linear discriminant analysis for multi-block classification. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 141, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| I | Total light intensity corresponding to addition of any two orthogonal components |
| Q | Portion of the intensity corresponding to the difference between vertical and horizontal polarization state |
| U | Portion of the intensity corresponding to the difference between intensities of linear +45° and −45° |
| V | Portion of the intensity corresponding to the difference between right circular and left circular polarization states |
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| IH | Linearly polarized along the horizontal axis (0°) |
| IV | Linearly polarized along the vertical axis (90°) |
| IP | Linearly polarized with a +45° offset |
| IM | Linearly polarized with a −45° offset |
| IR | Right-handed circularly polarized |
| IL | Left-handed circularly polarized |
| (a) | ||||
| Cabs | ||||
| LV | R2_pred | Bias_pred | RMSEp | |
| r11 | 5 | 0.81 | −1.64 | 16.8 |
| r22 | 5 | 0.92 | 0.05 | 11.2 |
| r33 | 6 | 0.75 | −2.47 | 19.9 |
| r44 | 6 | 0.72 | −1.33 | 21 |
| (b) | ||||
| Cdif | ||||
| LV | R2_pred | Bias_pred | RMSEp | |
| r11 | 5 | 0.75 | 0.014 | 0.647 |
| r22 | 6 | 0.47 | 0.040 | 0.933 |
| r33 | 6 | 0.61 | −0.083 | 0.871 |
| r44 | 5 | 0.80 | 0.040 | 0.564 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ducanchez, A.; Ryckewaert, M.; Heran, D.; Bendoula, R. Discriminating between Absorption and Scattering Effects in Complex Turbid Media by Coupling Polarized Light Spectroscopy with the Mueller Matrix Concept. Sensors 2022, 22, 9355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239355
Ducanchez A, Ryckewaert M, Heran D, Bendoula R. Discriminating between Absorption and Scattering Effects in Complex Turbid Media by Coupling Polarized Light Spectroscopy with the Mueller Matrix Concept. Sensors. 2022; 22(23):9355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239355
Chicago/Turabian StyleDucanchez, Arnaud, Maxime Ryckewaert, Daphne Heran, and Ryad Bendoula. 2022. "Discriminating between Absorption and Scattering Effects in Complex Turbid Media by Coupling Polarized Light Spectroscopy with the Mueller Matrix Concept" Sensors 22, no. 23: 9355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239355
APA StyleDucanchez, A., Ryckewaert, M., Heran, D., & Bendoula, R. (2022). Discriminating between Absorption and Scattering Effects in Complex Turbid Media by Coupling Polarized Light Spectroscopy with the Mueller Matrix Concept. Sensors, 22(23), 9355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239355