Strain Transfer Mechanisms and Mechanical Properties of Optical Fiber Cables
Abstract
1. Introduction
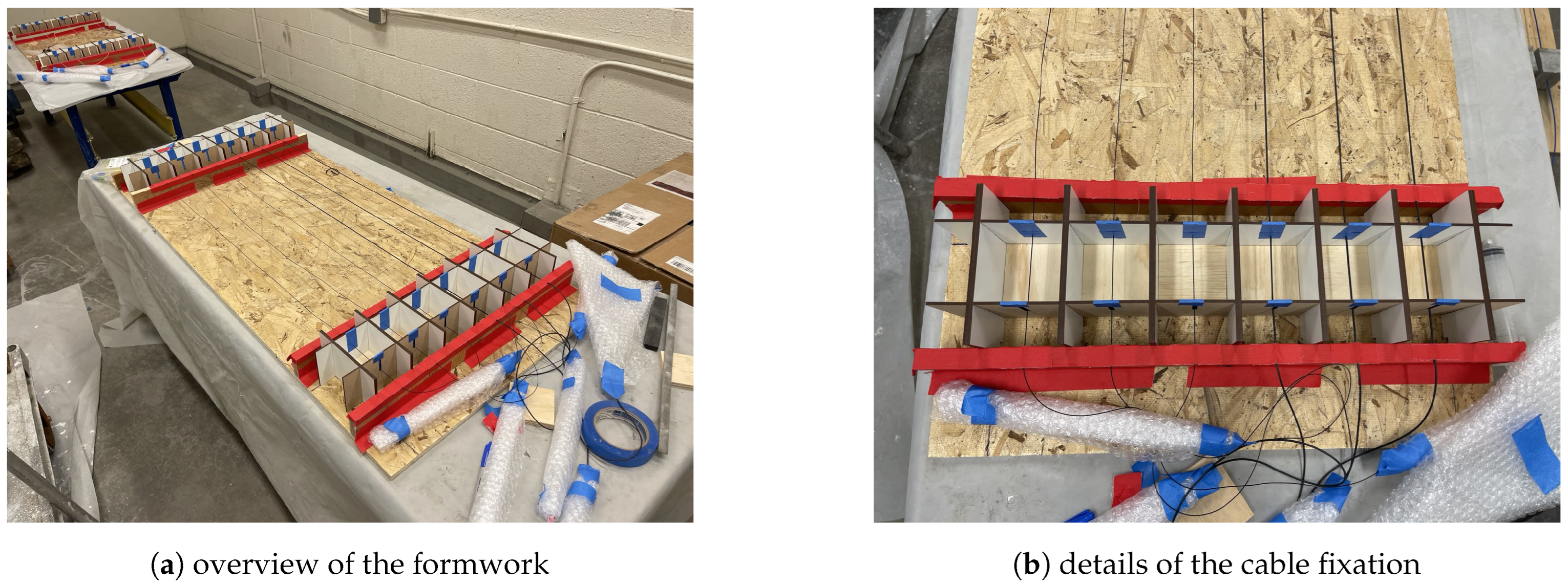
2. Specimen Preparation and Test Setup
3. Results and Discussion on Testing Results
3.1. Testing Protocol
3.2. Material and Calibration Parameters
3.3. PAI 0.9 mm and PUR-PAI 2.0 mm
3.4. PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm
3.5. PVC 0.9 mm
3.6. Stranded Steel 5.0 mm and PA-Steel 3.2 mm
4. Comparison of Different Types of Cable
4.1. Linear Distribution and Comparison with Mechanical Model
4.2. Strain Transfer Length l
4.3. Shear Stress Distribution along the Fiber Optic Core
4.4. Discussion of Visco-Elastic Behavior
5. Conclusions
- Under the tested strain levels (up to ~8000 nominal strain), the force–displacement relations varied significantly for the considered cables. For PAI 0.9 mm and PUR-PAI 2.0 mm, the results indicated linear behavior. For PVC 0.9 mm cables, large variations and nonlinear behavior was observed at early stages of testing (~3000 ). For PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm, PA-Steel 3.2 mm, and Stranded Steel 5.0 mm cable, varying levels of residual strain are observed under cyclic loading.
- With the increase of displacement demand, fiber optic cables sustained either interface damage or cable failure. Under the current embedding condition (~76 mm of embedding length with ~40 MPa concrete strength), interface damage between the cable and concrete is observed for PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm, PUR-PAI 2.0 mm, PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm and Stranded Steel 5.0 mm. The interface cohesion for Stranded Steel 5.0 mm is ~0.5 MPa, while the cohesion for the other other three cables is estimated to be ~0.05 MPa. For PA-Steel 3.2 mm, cable failure is observed with the estimation of cable strength to be ~60 MPa.
- The strain transfer length l is proposed to quantify the smoothing effect of different fiber optic cables under displacement discontinuity. For PAI 0.9 mm, l was the shortest and stayed constant at ~25 mm. For PVC 0.9 mm, the median value of l stays constant at ~35 mm while the variation increases with displacement. For PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm, PUR-PAI 2.0 mm, and PA-Steel 3.2 mm, l started between 30–50 mm and then significantly increased at higher strain levels due to nonlinear behavior. For Stranded Steel 5.0 mm, the median of l increases from 60 to 80 mm when the nominal displacement reaches 3 mm, after which l remains constant due to interface damage. In general, l provides a useful quantification of the strain transfer length that should be expected when interpreting fiber optic strain measurements.
- A more accurate method for cable calibration, i.e., calibrating the coefficient transforming the measured spectral shift to a strain level, is proposed. The new calibration method considers the influence of the strain transfer region near the cable fixations through integrating the strain along the whole cable length, instead of relying on a single strain value. Calibration coefficients are provided for different types of fiber optic cable.
- A modified mechanical model was able to reproduce the linear strain transfer mechanism of all six fiber optic cables. This model was used to infer the mechanical properties of the different cable coatings, which ranged from 70 MPa to 10 GPa. From the experiments, the relaxation time and viscosity for different fiber optic cables were also evaluated. For all cables other than PVC 0.9 mm, the total force drop (from viscous effects) is estimated to be less than 10%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soga, K.; Luo, L. Distributed fiber optics sensors for civil engineering infrastructure sensing. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2018, 3, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Kooi, K.; Hoult, N.A. Assessment of a steel model truss using distributed fibre optic strain sensing. Eng. Struct. 2018, 171, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Zhang, S.; Soga, K.; Luo, L.; Freifeld, B.; Kitayama, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Sugiyama, H. Distributed fiber optic strain sensing of bending deformation of a well mockup in the laboratory. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 96, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bado, M.F.; Casas, J.R.; Gómez, J. Post-processing algorithms for distributed optical fiber sensing in structural health monitoring applications. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bado, M.F.; Casas, J.R. A review of recent distributed optical fiber sensors applications for civil engineering structural health monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, D.K.; Soller, B.J.; Wolfe, M.S.; Froggatt, M.E. Distributed fiber-optic temperature sensing using Rayleigh backscatter. IET Conf. Publ. 2005, 2005, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broth, Z.; Hoult, N.A. Dynamic distributed strain sensing to assess reinforced concrete behaviour. Eng. Struct. 2020, 204, 110036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsberger, C.M.; Lienhart, W. Distributed fiber optic shape sensing along shotcrete tunnel linings: Methodology, field applications, and monitoring results. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 11, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandel, O.; Soliman, M.; Floyd, R.W.; Murray, C.D. Performance assessment of prestressed concrete bridge girders using fiber optic sensors and artificial neural networks. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 17, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkovski, T.; Lemcherreq, Y.; Mata-Falcón, J.; Kaufmann, W. Fundamental studies on the use of distributed fibre optical sensing on concrete and reinforcing bars. Sensors 2021, 21, 7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocal, C.G.; Fernandez, I.; Bado, M.F.; Casas, J.R.; Rempling, R. Assessment and visualization of performance indicators of reinforced concrete beams by distributed optical fibre sensing. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 3309–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Darwish, E.; Mosalam, K.M.; DeJong, M.J. Distributed fiber-optic strain sensing of an innovative reinforced concrete beam–column connection. Sensors 2022, 22, 3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poldon, J.J.; Bentz, E.C.; Hoult, N.A. Assessing beam shear behavior with distributed longitudinal strains. Struct. Concr. 2022, 23, 1555–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Coulibaly, A.A.; Cheng, J.; DeJong, M.J. Monitoring Reinforced Concrete Cracking Behavior under Uniaxial Tension Using Distributed Fiber-Optic Sensing Technology. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Libo, Y. Mechanics of bond and interface shear transfer in optical fiber sensors. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D. Strain transferring analysis of Fiber Bragg Grating sensors. Opt. Eng. 2006, 45, 024402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.T.; Leung, C.K.Y.; Olson, N.G. Investigation of the strain transfer for surface-attached optical fiber strain sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 035037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duck, G.; LeBlanc, M. Arbitrary strain transfer from a host to an embedded fiber-optic sensor. Smart Mater. Struct. 2000, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Feng, M. Sensing optical fiber installation study for crack identification using a stimulated Brillouin-based strain sensor. Struct. Health Monit. Int. J. 2012, 11, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Ansari, F.; Asce, M. Theoretical and Experimental Investigations into Crack Detection with BOTDR-Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors. J. Eng. Mech. 2013, 139, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, F.; Li, H.N.; Ansari, F. Characterization of OFDR distributed optical fiber for crack monitoring considering fiber-coating interfacial slip. Struct. Health Monit. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, A.; Chapeleau, X.; Leduc, D.; Abraham, O. Concrete crack monitoring using a novel strain transfer model for distributed fiber optics sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Cheng, J.; DeJong, M.J. A mechanical model to interpret distributed fiber optic strain measurement at displacement discontinuities. Struct. Health Monit. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcetelli, F.; Rossi, L.; Di Sante, R.; Bolognini, G. Strain transfer in surface-bonded optical fiber sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Shi, B.; Zhang, C.C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, H. Strain transfer mechanism in surface-bonded distributed fiber-optic sensors subjected to linear strain gradients: Theoretical modeling and experimental validation. Measurement 2021, 179, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Coulibaly, A.A.S.; DeJong, M. Fiber optic sensing of concrete cracking and rebar deformation using several types of cable. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Park, J.; Soga, K.; Momoki, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Imasato, Y.; Balagopal, A.; Fontenot, J.; Hall, T. Distributed fibre optic strain sensing of an axially deformed well model in the laboratory. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 72, 103028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















| Cable Type | Elastic Modulus | Strength | Calibration Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (GPa) | CV | Cohesion (MPa) | Cable (N) | Nominal Failure Strain | (/GHz) | Scale Factor | CV | |
| PVC 0.9 mm | 1.7 | 0.021 | >0.019 | 4 | 0.0038 | 6.74 | 1.01 | 0.006 |
| PAI 0.9 mm | 1.7 | 0.004 | 0.056 | >12 | >0.017 | 6.66 | 1.00 | 0.001 |
| PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm | 1.6 | 0.020 | 0.056 | >12 | >0.012 | 5.79 | 0.87 | 0.022 |
| PUR-PAI 2.0 mm | 0.35 | 0.003 | 0.059 | >28 | >0.031 | 6.57 | 0.99 | 0.015 |
| Stranded Steel 5.0 mm | 10.8 | 0.15 | 0.50 | >600 | >0.0036 | 6.28 | 0.94 | 0.103 |
| PA-Steel 3.2 mm | 7.6 | – | >0.63 | 480 | 0.024 | 6.48 | 0.97 | – |
| Cable Type | Mechanical Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | |||
| PVC 0.9 mm | 391 | 0.0020 | 0.0012 |
| PAI 0.9 mm | 348 | 0.0050 | 0.0030 |
| PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm | 241 | 0.0005 | 0.0048 |
| PUR-PAI 2.0 mm | 73 | 0.0120 | 0.0350 |
| Stranded Steel 5.0 mm | 10,769 | 0.0005 | 0.0025 |
| PA-Steel 3.2 mm | 7486 | 0.0002 | 0.0200 |
| Cable Type | Initial l (mm) | Final l (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CV | Mean | CV | |
| PVC 0.9 mm | 30 | 0.08 | 37 | 0.52 |
| PAI 0.9 mm | 26 | 0.12 | 24 | 0.42 |
| PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm | 47 | 0.04 | 79 | 0.15 |
| PUR-PAI 2.0 mm | 29 | 0.13 | 54 | 0.33 |
| Stranded Steel 5.0 mm | 78 | 0.59 | 80 | 0.37 |
| PA-Steel 3.2 mm | 47 | 0.06 | 129 | 0.06 |
| Cable Type | Relaxation Time (s) | Force Drop in 10 min | Final Force Drop (Estimated) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | CV | Mean | CV | Mean | CV | |
| PVC 0.9 mm | 536 | 0.61 | 11% | 0.30 | 13% | 0.29 |
| PAI 0.9 mm | 331 | 0.68 | 2% | 0.29 | 2% | 0.25 |
| PFA-Silicone 0.9 mm | 557 | 0.29 | 4% | 0.31 | 6% | 0.29 |
| PUR-PAI 2.0 mm | 273 | 0.24 | 4% | 0.22 | 4% | 0.31 |
| Stranded Steel 5.0 mm | 241 | 0.66 | 7% | 0.36 | 7% | 0.36 |
| PA-Steel 3.2 mm | 278 | 0.38 | 4% | 0.26 | 4% | 0.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Govindjee, S.; DeJong, M.J. Strain Transfer Mechanisms and Mechanical Properties of Optical Fiber Cables. Sensors 2022, 22, 9966. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249966
Zhang S, Liu H, Govindjee S, DeJong MJ. Strain Transfer Mechanisms and Mechanical Properties of Optical Fiber Cables. Sensors. 2022; 22(24):9966. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249966
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shenghan, Han Liu, Sanjay Govindjee, and Matthew J. DeJong. 2022. "Strain Transfer Mechanisms and Mechanical Properties of Optical Fiber Cables" Sensors 22, no. 24: 9966. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249966
APA StyleZhang, S., Liu, H., Govindjee, S., & DeJong, M. J. (2022). Strain Transfer Mechanisms and Mechanical Properties of Optical Fiber Cables. Sensors, 22(24), 9966. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249966






