New Label-Free Biosensing for the Evaluation of the AX-024 Inhibitor: Case Study for the Development of New Drugs in Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. BICELLs Fabrication and Materials
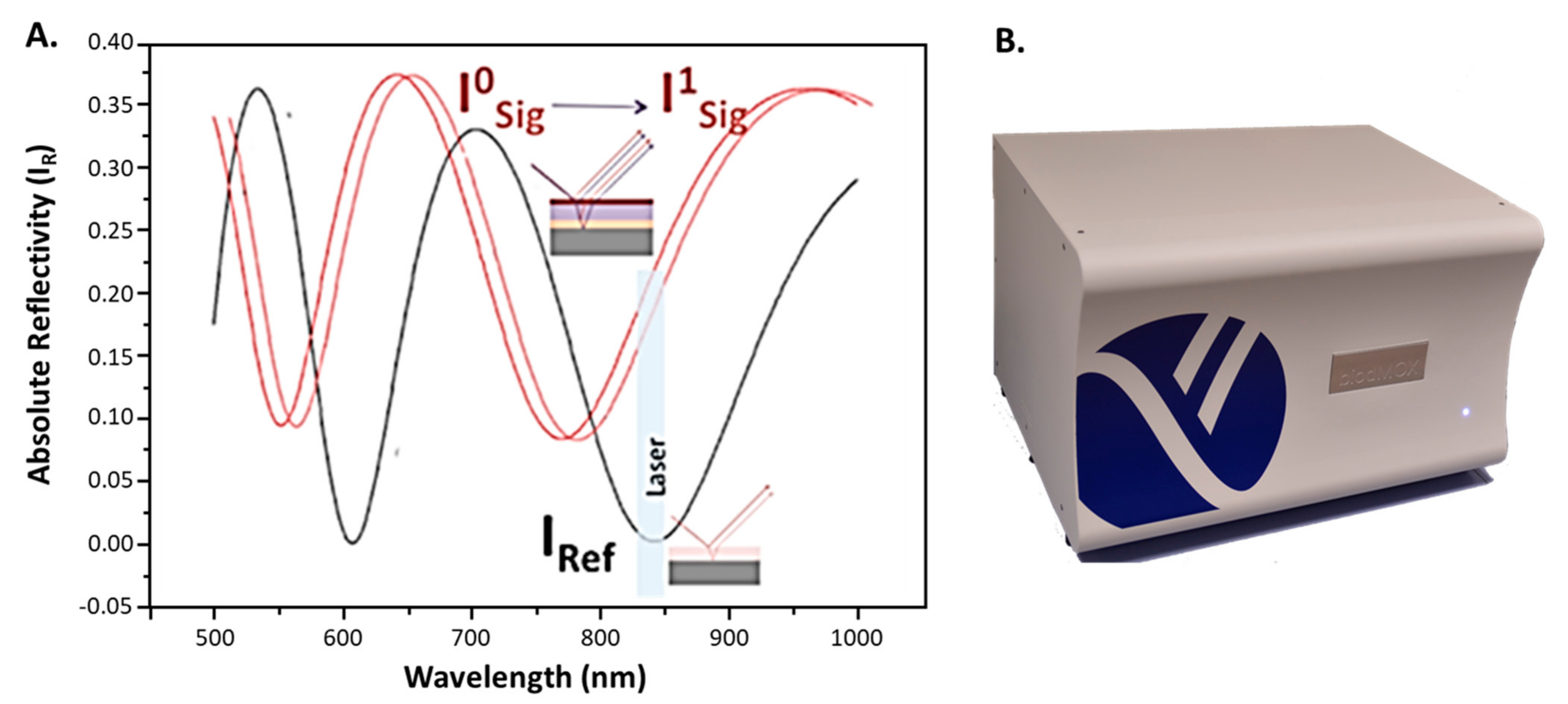
2.2. Point-of-Care Device
Label-Free Assay Protocol
2.3. Confocal Microscopy
Confocal Microscopy Assay Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Sensing Surface
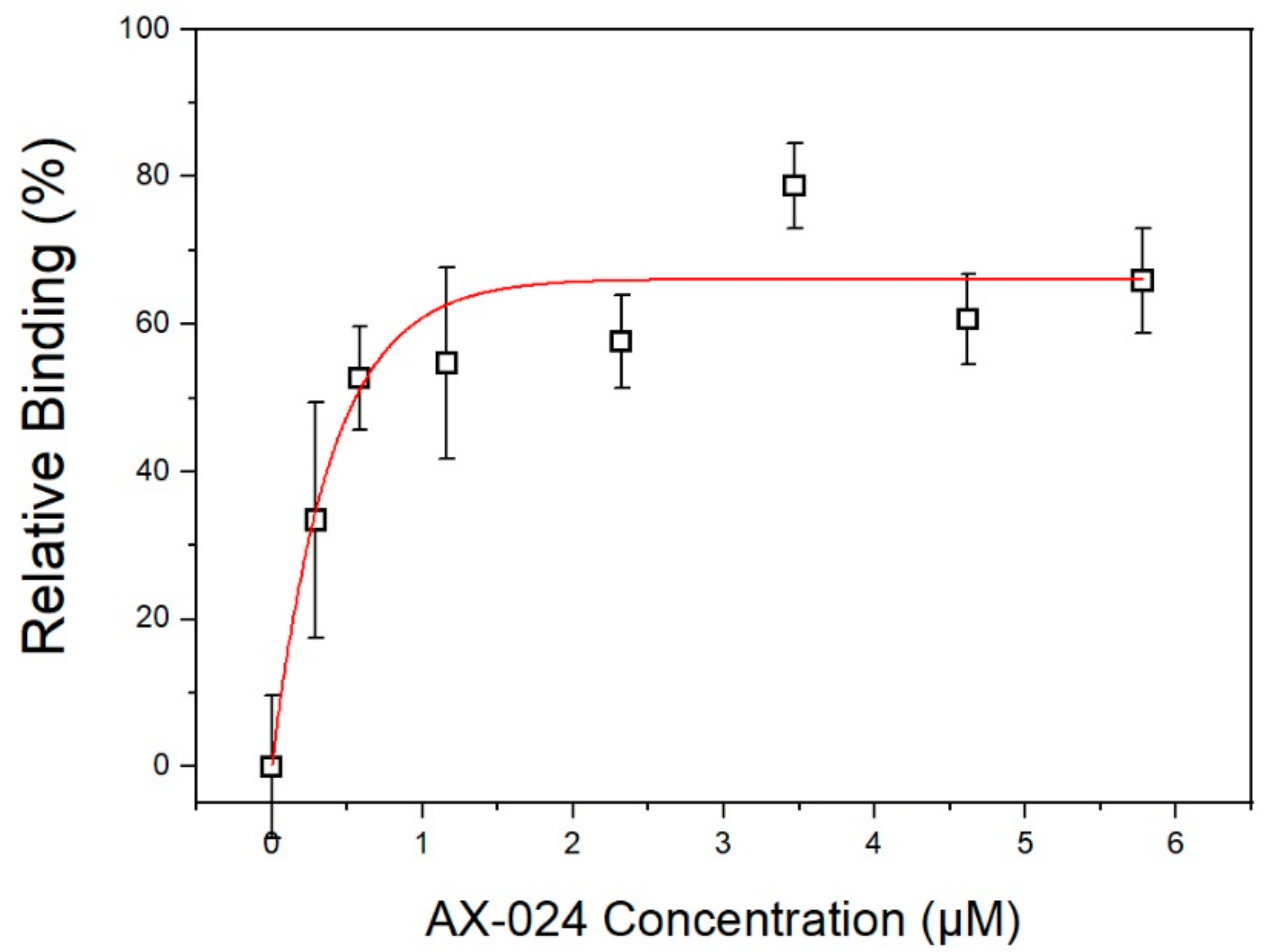
3.2. Evaluation of AX-024 Inhinitor with Point-of-Care Device
3.3. Evaluation of AX-024 Inhibitor with Confocal Microscopy
3.4. Comparison between Methods; Point-of-Care Device and Confocal Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balagué, C.; Kunkel, S.L.; Godessart, N. Understanding autoimmune disease: New targets for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrack, P.; Kappler, J.W.; Kotzin, B.L. Autoimmune disease: Why and where it occurs. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanos, D.P.; Smyk, D.S.; Rigopoulou, E.I.; Mytilinaiou, M.G.; Heneghan, M.A.; Selmi, C.; Gershwin, M.E. Twin studies in autoimmune disease: Genetics, gender and environment. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 38, J156–J169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, M.M.A.; Stevens, C.R.; Walsh, E.C.; De Jager, P.L.; Goyette, P.; Plenge, R.M.; Vyse, T.J.; Rioux, J.D. Defining the Role of the MHC in Autoimmunity: A Review and Pooled Analysis. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto, A.; Reyes-Garau, D.; Jiménez, M.A.; Carrasco, E.; Moreno, B.; Martínez-Pasamar, S.; Cortés, J.R.; Perona, A.; Abia, D.; Blanco, S.; et al. First-in-class inhibitor of the T cell receptor for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 370ra184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, E.; Togbe, D.; Holdorf, A.D.; Trubetskoy, D.; Nabti, S.; Küblbeck, G.; Klevenz, A.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Leithäuser, F.; Möller, P.; et al. Nck adaptors are positive regulators of the size and sensitivity of the T-cell repertoire. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15529–15534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, E.; Togbe, D.; Holdorf, A.; Trubetskoy, D.; Nabti, S.; Küblbeck, G.; Schmitt, S.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Leithäuser, F.; Möller, P.; et al. Fine Tuning of the Threshold of T Cell Selection by the Nck Adapters. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7518–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, K.; Rufer, A.C.; Muller, M.; Burger, D.; Casagrande, F.; Grossenbacher, T.; Huber, S.; Hug, M.N.; Koldewey, P.; D’Osualdo, A.; et al. Small molecule AX-024 reduces T cell proliferation independently of CD3ϵ/Nck1 interaction, which is governed by a domain swap in the Nck1-SH3.1 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7849–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehrotra, P. Biosensors and their applications—A review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial. Res. 2016, 6, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascual-Leone, A.M.; Medina, J.M. Herramientas Para el Diagnóstico y la Terapéutica; Instituto de España Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia Biosensores y Biochips: Madrid, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Florea, A.; Melinte, G.; Simon, I.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical Biosensors as Potential Diagnostic Devices for Autoimmune Diseases. Biosensors 2019, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skládal, P.; Jílková, Z.; Svoboda, I.; Kolář, V. Investigation of osteoprotegerin interactions with ligands and antibodies using piezoelectric biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, H.K.; Armani, A.M. Label-free biological and chemical sensors. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1544–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgado, M.; Sanza, F.J.; López, A.; Lavín, Á.; Casquel, R.; Laguna, M.F. Description of an Advantageous Optical Label-Free Biosensing Interferometric Read-Out Method to Measure Biological Species. Sensors 2014, 14, 3675–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgado, M.; Maigler, M.; Santamaria, B.; Hernandez, A.; Lavín, A.; Laguna, M.; Sanza, F.; Granados, D.; Casquel, R.; Portilla, J.; et al. Towards reliable optical label-free point-of-care (PoC) biosensing devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maigler, M.V.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.F.; Sanza, F.J.; Santamaria, B.; Lavin, A.; Espinosa, R.L. A New Device Based on Interferometric Optical Detection Method for Label-Free Screening of C-Reactive Protein. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 68, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santiveri, C.M.; Borroto, A.; Simón, L.; Rico, M.; Alarcón, B.; Jiménez, M.A. Interaction between the N-terminal SH3 domain of Nckα and CD3ɛ-derived peptides: Non-canonical and canonical recognition motifs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta–Proteins Proteom. 2008, 1794, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettau, M.; Pieper, J.; Gerneth, A.; Lengl-Janßen, B.; Voss, M.; Linkermann, A.; Schmidt, H.; Gelhaus, C.; Leippe, M.; Kabelitz, D.; et al. The adapter protein Nck: Role of individual SH3 and SH2 binding modules for protein interactions in T lymphocytes. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamaría, B.; Laguna, M.F.; López-Romero, D.; Hernandez, A.L.; Sanza, F.J.; Lavín, Á.; Casquel, R.; Maigler, M.V.; Espinosa, R.L.; Holgado, M. Development towards Compact Nitrocellulose-Based Interferometric Biochips for Dry Eye MMP9 Label-Free In-Situ Diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Romero, D.; Barrios, C.A.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.; Casquel, R. High aspect-ratio SU-8 resist nano-pillar lattice by e-beam direct writing and its application for liquid trapping. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, F.; Hintsche, R.; Pfeiffer, D.; Schubert, F.; Riedel, K.; Kindervater, R. Biosensors: Fundamentals, applications and trends. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 4, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras, M.F.L.; Ramirez, Y.; Martín, C.F.; Espinosa, R.L.; Lavín, A.; Holgado, M. A Point-of-Care Based on Label-Free Interferometric Optical Detection Method to Evaluate Interferon Gamma (IFN-γ): A Correlation with the ELISA Technique. Sensors 2020, 20, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, A.; Tomé-Amat, J.; Ramírez, Y.; Garrido-Arandia, M.; Valle, L.; Hernández-Ramírez, G.; Tramarin, L.; Herreros, P.; Santamaría, B.; Díaz-Perales, A.; et al. Developing an Optical Interferometric Detection Method based biosensor for detecting specific SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulins in Serum and Saliva, and their corresponding ELISA correlation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 345, 130394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundas, C.M.; Demonte, D.; Park, S. Streptavidin–biotin technology: Improvements and innovations in chemical and biological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9343–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincet, F.; Husson, J. The Solution to the Streptavidin-Biotin Paradox: The Influence of History on the Strength of Single Molecular Bonds. Biophys. J. 2005, 89, 4374–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blankenburg, R.; Meller, P.; Ringsdorf, H.; Salesse, C. Interaction between biotin lipids and streptavidin in monolayers: Formation of oriented two-dimensional protein domains induced by surface recognition. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 8214–8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaneshiudu, A.; Kuschal, C.; Sakamoto, F.H.; Anderson, R.R.; Schwarzenberger, K.; Young, R.C. Introduction to Confocal Microscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, K.; Nakano, H.; Wilson, T.; Fercher, A.F.; Drexler, W.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Reports on Progress in Physics Related content Confocal optical microscopy Confocal optical microscopy. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1995, 59, 427–471. [Google Scholar]
- Fries, J.R.; Brand, L.; Eggeling, C.; Köllner, A.M.; Seidel, C.A.M. Quantitative Identification of Different Single Molecules by Selective Time-Resolved Confocal Fluorescence Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 6601–6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavín, Á.; De Vicente, J.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.F.; Casquel, R.; Santamaría, B.; Maigler, M.V.; Hernández, A.L.; Ramírez, Y. On the Determination of Uncertainty and Limit of Detection in Label-Free Biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramírez, Y.; Laguna, M.F.; Holgado, M. New Label-Free Biosensing for the Evaluation of the AX-024 Inhibitor: Case Study for the Development of New Drugs in Autoimmune Diseases. Sensors 2022, 22, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031218
Ramírez Y, Laguna MF, Holgado M. New Label-Free Biosensing for the Evaluation of the AX-024 Inhibitor: Case Study for the Development of New Drugs in Autoimmune Diseases. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031218
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamírez, Yolanda, María Fe Laguna, and Miguel Holgado. 2022. "New Label-Free Biosensing for the Evaluation of the AX-024 Inhibitor: Case Study for the Development of New Drugs in Autoimmune Diseases" Sensors 22, no. 3: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031218
APA StyleRamírez, Y., Laguna, M. F., & Holgado, M. (2022). New Label-Free Biosensing for the Evaluation of the AX-024 Inhibitor: Case Study for the Development of New Drugs in Autoimmune Diseases. Sensors, 22(3), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031218







