A Comprehensive Survey on the Internet of Things with the Industrial Marketplace
Abstract
:1. Introduction
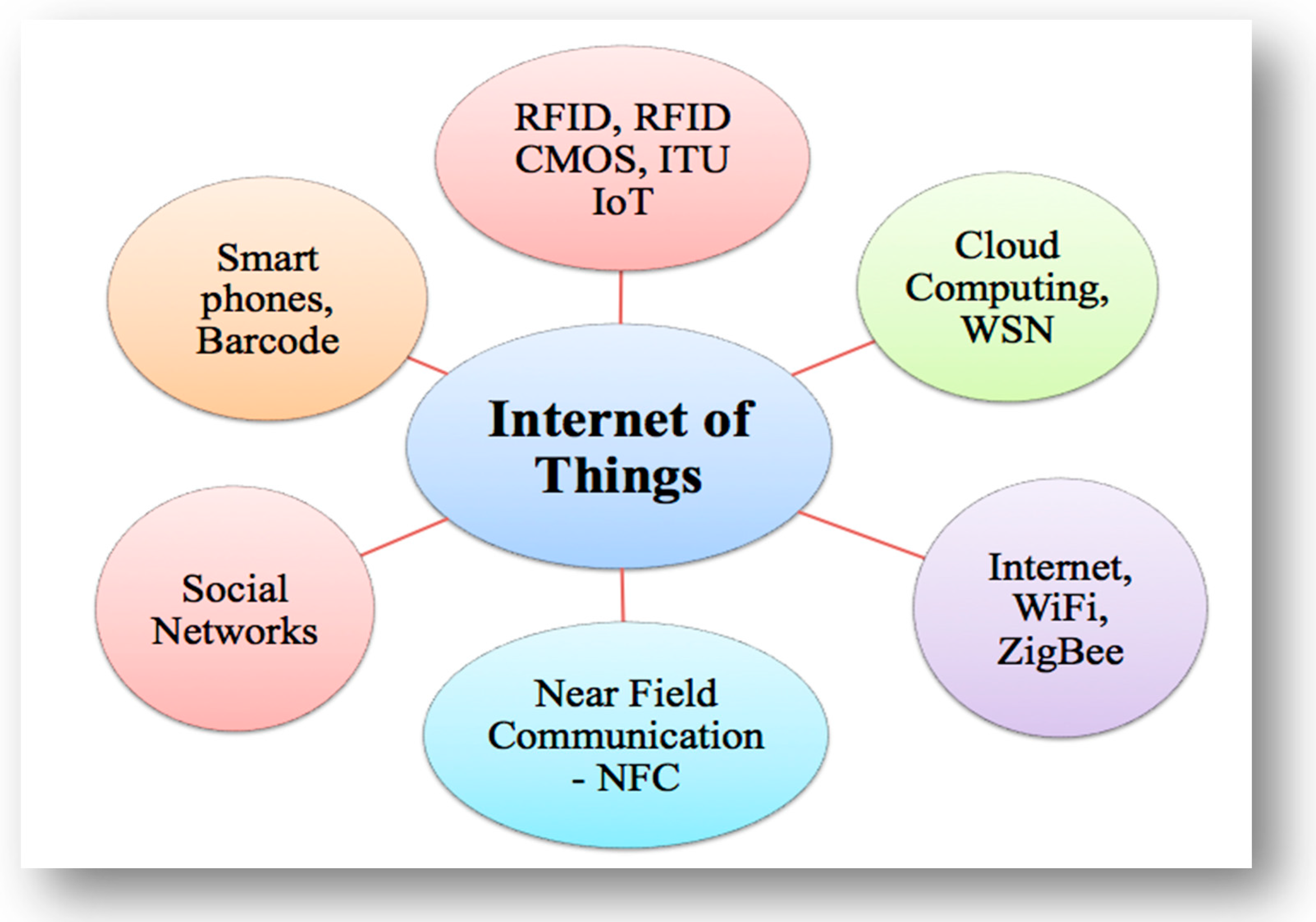
2. Internet of Things
- Connect
- 2.
- Collect
- 3.
- Compute
3. Background and Present Research on the IoT
- Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID)Primarily, the term “IoT” was introduced to indicate the particularly recognizable interoperable associated objects with radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology [2]. RFID makes the most of electromagnetic fields to pass data to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects [28,29]. RFID innovation is one of numerous IoT “empowering identification” technologies, and not essentially the major one [30]. It is one of the approaches used to link everyday items into networks [16,31]. The RFID system contains two main parts, which are:
- 1.1.
- RFID tags: Enclosed items that consist of information regarding the items. RFID tags, which are sometimes called transponders (transmitters/responders), are attached to objects to count or identify them [32]. RFID tags, either passive or active, contain an antenna and microchip as well.
- 1.2.
- Readers: Then, readers can receive and process the information without needing a line of sight, and then create a report about the system [29]. Readers, also known as transceivers (transmitters/receivers), are devices designed for use with a radio frequency interface (RFI) module and control unit [32]. The main function of readers is to activate tags, interact with tags, and also exchange information between tags and software applications.
- 2.
- Cloud Computing (CC)
- 3.
- Wireless Sensor NetworkThe wireless sensor network (WSN) platform has been applied to the industry and built into IoT technologies. Using WSNs, wireless sensor and actuator networks (WSANs), virtual network sensors (VSNs), robots, machines, and gadgets, huge data can continuously be generated [35]. Recently, the technology for wireless communication and WSN systems has been dramatically researched, and many uses of WSNs have been identified, such as in industry, farming, healthcare, and many other fields. Industrial control, health monitoring, traffic control, and environmental monitoring are among the applications of WSNs [33,36,37]. In addition, some of the developed technologies such as ZigBee, LoRA, and LoRaWAN can be included in the WSN:
- 3.1.
The LoRaWAN is LPWAN (low-power wide-network technology) that recently gained a lot of attention because of its use in IoT network systems [39]. A large amount of data is transferred over long distances using this method. It is ideal for the WSN due to its high levels of sturdiness and coverage. The LoRa is a physical layer created by Semtech [38]. In the 250 bps to 5.5 kbps range, LoRaWAN data transfer rates are found. It employs bandwidths and frequencies between 125 and 500 kHz. Two types of devices exist in the technology: nodes and gateways. A node communicates with the gateway by sending and receiving data. Thousands of nodes can be connected to a gateway at once [38].- 3.2.
- ZigBee: This is promoted by the ZigBee Alliance, which consists of hundreds of ZigBee member companies from semiconductors and software developers to original equipment manufacturers: Ember, Freescale, Chipcon, Invensys, Mitsubishi, CompXs, AMI AMI Semiconductors, ENQ Semiconductors. ZigBee and 802.15.4 are not the same [40].
- 4.
- Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
- 5.
- Smartphones
- 6.
- Near Field Communication (NFC)NFC guarantees that IoT technologies in a smart home are effectively implemented. The customer faces several tedious measures in linking devices without NFC in a smart home [47].NFC is similar to RFID, but it provides improved protection and functionality [48]. An article published on the NFC Forum discusses four primary topics for which NFC is required in the IoT. These are presented as follows:
- 6.1.
- NFC can link any unpowered computer to the network. Useful information about an item can be obtained by tapping an NFC tag.
- 6.2.
- The user will pick their link using NFC, which offers the easiest and most convenient way for the user to proceed.
- 6.3.
- By adopting NFC, you can simplify the handshake process to connect devices with a simple tap.
- 6.4.
- The possibility of eavesdropping with NFC is greatly reduced.
4. Advantages and Problems of the IoT
4.1. IoT Advantages
- Technical enhancement:
- 2.
- Enhanced consumer engagement:
- 3.
- Advanced information compilation:
- 4.
- Decreased waste:
- Improving technology:
- 2.
- Improved data collection:
4.2. IoT Problems
- Security and privacy:
- 2.
- Complexity:
- 3.
- Flexibility:
- 4.
- Marketing and content delivery:
5. IoT Technologies’ Architectural Design
- Sensing layer:
- 2.
- Networking layer:
- 3.
- Service layer:
- Tiny, illegible to humans, binary-based data.
- Text-based, legible to humans, larger-format data.
- 4.
- Interface layer:
6. Trends, Characteristics, and Application of the IoT
6.1. Trends and Characteristics of the IoT
- Architecture:
- 2.
- Intelligence:
- 3.
- Time considerations:
- 4.
- Size considerations:
6.2. Applications of the IoT
- Systems of intelligent transportation and logistics
- 2.
- Smart monitoring and conducting (home, office)
- 3.
- Healthcare
- 4.
- Personal and social
- 5.
- Security and anti-theft systems
- 6.
- Monitoring system for pollution
- 7.
- Environment monitoring systems
7. The IoT and Pandemic Control
- Using the IoT to examine a pandemic
- 2.
- Remote health monitoring
- 3.
- Temperature sensor
- 4.
- Using the IoT to ensure adherence to quarantine
- Wearable Devices
- 2.
- However, the global system for mobile communications (GSM) is lagging behind the new era of 5G technology, which combines the GSM module with unique mobile apps and transmits information to and views all details in the mobile apps [98]. This is the only way to effectively monitor users. Using powerful digital signal processing methods, Fyntanidou’s team developed a wrist-worn wearable device that continuously extracts vital signs such as the heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature [98,103].
- 3.
- Kinsa, a smart thermometer, is another excellent home health monitoring solution. Fever and illness can be mapped by the gadget, allowing users to respond quickly to their current condition. In addition, it keeps track of a family’s health and medical history, manages prescriptions, and sets up reminders, all while being child-friendly [92].
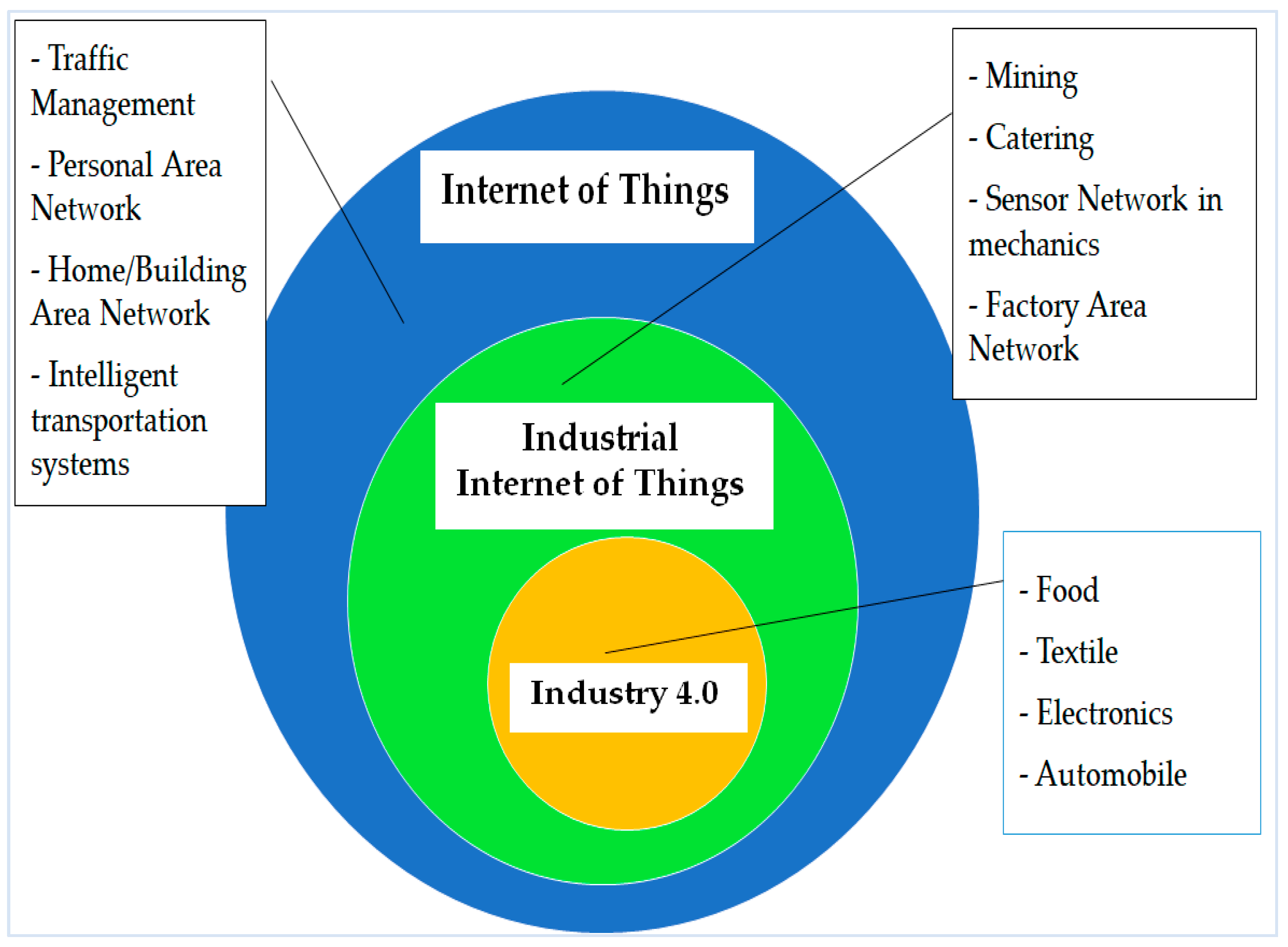
8. Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things
8.1. Industry 4.0
- Traffic management and toll collection system
- 2.
- Real-time vehicle navigation
8.2. Industrial Internet of Things
- Automated Production
- 2.
- Maintenance and Safety
- 3.
- Real-Time Efficiencies
- 4.
- Workforce-Equipment Connectivity
9. IoT Marketplace
IoT Development Market: Exports of Connected Devices
- Commercial & Industrial Electronics
- Good growth is projected for sales: 2013–2030 compound annual growth rate (CAGR) = 20%.
- The next decade (2021–2030) adds the highest amount of devices deployed.
- Consumers
- In the long term, revenue would see moderated growth: 2013–2030 = 13.8% (CAGR).
- The user base increased from 2015 to 2020 for connectable devices.
- New shipping for total compatibility will rise by 12.5% from 2013–2030.
- The dealers post their accessible sensor-flowing information and actuators admit items alongside some hint of their worth and states of utilization.
- Application designers and data/actuators admit purchasers to peruse or be suggested pertinent sensor data streams/device proprietors just as data intermediaries to interface with. This can be an index or potentially an endorsement instrument.
- Motivating mechanisms for vendors to afford valuable data and actuators, for example, adaptation per unit amount of data for the actuator to acquire.
- Directing ongoing data from sensor data sources to all purchasers that are approved dependent on the established understandings (counting installments, procedure arrangements).
- Steering continuous activation and control signals from approved clients (purchasers) to actuators. Assurance and prestige evaluating and determining components for clients to rate each other. Metering and charging instruments to uphold advertising agreements being steered through the commerce.
- APIs and SDKs for methodical admittance to different functionalities of the platform data naming and organizing capacities, just as security instruments to channel data.
- For the Internet of Vehicles (IoVs) to function, monetary transactions must be made between vehicle-to-vehicle networks, vehicle-to-roadside networks, and vehicle-to-infrastructure and pedestrian networks.
- Smart Agriculture—Real-time crop information is available to farmers and other agricultural supply chain participants using this technology.
- Smart Health—Data monetization is possible thanks to the wearable IoT (WIoT) devices used by patients, medical imaging, test results, social media, and external patient data that are collected by healthcare systems and patients alike.
10. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, L.; Wang, N. Future Internet: The Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and Engineering, ICACTE 2010, Chengdu, China, 20–22 August 2010; pp. V5-376–V5-380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, K. Internet of Things. Page 1—RFID Journal. Available online: https://www.rfidjournal.com/articles/view?4986 (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Okano, M.T. IOT and industry 4.0: The Industrial new revolution. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Management and Information Systems, ICMIS 2017, Bangkok, Thailand, 25–26 September 2017; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319881057_IOT_and_Industry_40_The_Industrial_New_Revolution (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Rahim, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Asyhari, A.T.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.; Ramasamy, D. Evolution of IOT-enabled connectivity and applications in Automotive Industry: A Review. Veh. Commun. 2021, 27, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kaushik, B. A survey on Internet of vehicles: Applications, security issues and solutions. Veh. Commun. 2019, 20, 100182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Silva, F.; Sarubbi, J.; Oliveira, T.; Meira, W.; Nogueira, J. Designing mobile content delivery networks for the Internet of vehicles. Veh. Commun. 2017, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, F. A cooperative route choice approach via virtual vehicle in iov. Veh. Commun. 2017, 9, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, R.; Rao, M.; Agrawal, H. Internet of things (iot) in the smart automotive sector: A review. IOSR J. Comput. Eng. 2018, 9, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fantian, Z.; Chunxiao, L.; Anran, Z.; Xuelong, H. Review of the key technologies and applications in internet of vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments (ICEMI), Yangzhou, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Adil, M.; Khan, M.K. Emerging IOT applications in Sustainable Smart Cities for COVID-19: Network security and data preservation challenges with future directions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbunge, E. Integrating emerging technologies into COVID-19 contact tracing: Opportunities, challenges and Pitfalls. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otoom, M.; Otoum, N.; Alzubaidi, M.A.; Etoom, Y.; Banihani, R. An IOT-based framework for early identification and monitoring of COVID-19 cases. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedaei, S.S.; Fotovvat, A.; Mohebbian, M.R.; Rahman, G.M.; Wahid, K.A.; Babyn, P.; Marateb, H.R.; Mansourian, M.; Sami, R. COVID-safe: An IOT-based system for Automated Health Monitoring and surveillance in post-pandemic life. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 188538–188551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, S.A. What Is Internet of Things (IoT)? Available online: https://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com/definition/Internet-of-Things-IoT (accessed on 28 December 2021).
- Sundmaeker, H.; Guillemin, P.; Friess, P.; Woelfflé, S. Vision and Challenges for Realising the Internet of Things; European Commission Information Society and Media: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; Available online: http://www.internet-of-things-research.eu/pdf/IoT_Clusterbook_March_2010.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Perera, C.; Liu, C.H.; Jayawardena, S.; Chen, A.M. A Survey on Internet of Things from Industrial Market Perspective. IEEE Access 2014, 2, 1660–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Siakas, K.V.; Anastasiadis, T. Internet of Things (IoT) in Industry: Contemporary Application Domains, Innovative Technologies and Intelligent Manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Res. Eng. 2018, 4, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU Internet Reports 2005: The Internet of Things. Available online: https://www.itu.int/osg/spu/publications/internetofthings/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Weber, R.H. Internet of Things–New security and privacy challenges. Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 2020, 26, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, J.; Joshi, S.; Barshikar, S. A Survey on Internet of Things. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Liu, D.; Hu, B.; Wang, H. A Vision of IoT: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities with China Perspective. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. Understanding the Internet of Things: Definition, potentials, and societal role of a fast evolving paradigm. Ad Hoc Netw. 2017, 56, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoglou Grammatikis, P.I.; Sarigiannidis, P.G.; Moscholios, I.D. Securing the Internet of Things: Challenges, threats and solutions. Internet Things 2019, 5, 41–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, B. IoT Market Overview. 2018. Available online: https://www.gsaglobal.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Bill-Morelli-GSA-Silicon-Summit-IoT-Market-Overview-IHS-Markit-4.9.18.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Li, Y.; Hou, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Towards a theoretical framework of strategic decision, supporting capability and information sharing under the context of Internet of Things. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2012, 13, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldikar, A.; Lalwani, P.; Pandey, S.; Chitari, A. IOT Based Industrial Management. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 2945–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juels, A. RFID security and privacy: A research survey. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2006, 24, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Applications of Internet of Things in manufacturing. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, CSCWD 2016, Nanchang, China, 4–6 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg, R.V.; Anzelmo, E.; Bassi, A.; Caprio, D.; Dodson, S.; Ratto, M. The Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 1st Berlin Symposium on Internet and Society, Berlin, Germany, 25–27 October 2011; Available online: http://www.pyfn.com/PDF/iot_pdfs/the_iot_paper_2011.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Welbourne, E.; Battle, L.; Cole, G.; Gould, K.; Rector, K.; Raymer, S.; Balazinska, M.; Borriello, G. Building the Internet of Things Using RFID: The RFID Ecosystem Experience. IEEE Internet Comput. 2009, 13, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Feng, Q.; Fan, T.; Lei, Q. RFID technology and its applications in Internet of Things (IoT). In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Communications and Networks, CECNet 2012, Yichang, China, 21–23 April 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, U.; Chaudhary, J.; Ahmad, M.; Naz, A.A. Survey on Internet of Things (IoT) for Different Industry Environments. Ann. Emerg. Technol. Comput. 2019, 3, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.D.; He, W.; Li, S. Internet of Things in Industries: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazam, M.; Zeadally, S.; Harras, K.A. Deploying Fog Computing in Industrial Internet of Things and Industry 4.0. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4674–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, L.D.; Wang, X. Compressed Sensing Signal and Data Acquisition in Wireless Sensor Networks and Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Xu, L.D. Integration of Distributed Enterprise Applications: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdiwar, S.D.; Akshith, R.; Shakruwala, Z.; Chadha, U.; Srinivasan, K.; Chang, C.Y. Recent advances on IOT-Assisted Wearable Sensor Systems for healthcare monitoring. Biosensors 2021, 11, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, W.D.; Pandya, S.; Koyuncu, B.; Ramani, B.; Bhaskar, S.; Ghayvat, H. NXTGeUH: LoRaWAN based NEXT generation ubiquitous healthcare system for vital signs Monitoring falls detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Punecon, Pune, India, 30 November–2 December 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ramya, C.M.; Shanmugaraj, M.; Prabakaran, R. Study on ZigBee technology. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Electronics Computer Technology, Kanyakumari, India, 8–10 April 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, B.; Sharipuddin; Kurniabudi; Budiarto, R.; Stiawan, D.; Hanapi, D. Monitoring Connectivity of Internet of Things Device on Zigbee Protocol. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, ICECOS 2018, Pangkal, Indonesia, 2–4 October 2018; pp. 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Wang, K.; Jones, J. E-business system integration: A systems perspective. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2012, 13, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Enterprise Systems: State-of-the-art and future trends. IEEE Trans. Ind. Infomat. 2011, 7, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W. A Survey on Internet of Things: Architecture, Enabling Technologies, Security and Privacy, and Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausenblas, M. Smart Phones and the Internet of Things. Available online: https://www.mapr.com/blog/smart-phones-and-internet-things (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Khaddar, M.A.E. Smartphone: The Ultimate IoT and IoE Device. IntechOpen. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/56113 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Simplifying IoT: Connecting, Commissioning, and Controlling with Near Field Communication (NFC). NFC Forum. Available online: http://nfc-forum.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/NFC_Forum_IoT_White_Paper_-v05.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Majumder, A.; Ghosh, S.; Goswami, J.; Bhattacharyya, B.K. NFC in IoT-Based Payment Architecture. Internet Things 2017, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, L.K.; Kadry, S. Internet of things (IOT). Blockchain Ind. Internet Things 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, A.A.; Wu, K.; Laghari, R.A.; Ali, M.; Khan, A.A. A review and state of art of internet of things (IOT). Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.; Occhiogrosso, B. Practical aspects for the integration of 5G networks and IoT applications in smart cities environments. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2019, 2019, 5710834. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, G. Bringing dark data into the light: Illuminating existing IoT data lost within your organization. Bus. Horiz. 2020, 63, 519–530. [Google Scholar]
- Quek, T. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Internet of Things (IoT). Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/advantages-disadvantages-internet-things-iot-tommy-quek (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Caesarendra, W.; Pappachan, B.; Wijaya, T.; Lee, D.; Tjahjowidodo, T.; Then, D.; Manyar, O. An AWS Machine Learning-Based Indirect Monitoring Method for Deburring in Aerospace Industries towards Industry 4.0. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antão, L.; Pinto, R.; Reis, J.P.; Gonçalves, G.M.; Naji, H.I.; Amer, W.; Maula, B.; Parkash, B.; Pai, A.; Tian, W.; et al. Fig. 1. Five Layer IOT Architecture. ResearchGate. 2018. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Five-Layer-IoT-Architecture_fig1_324797771 (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Muccini, H.; Moghaddam, M.T. IOT architectural styles. Softw. Archit. 2018, 11048, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D. The Internet of Thing (IoT) and Industrial Automation: A future perspective. World J. Model. Simul. 2019, 15, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, M.; Pascale, F.; Santaniello, D. Internet of things: A general overview between architectures, protocols and applications. Information 2021, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdmeziem, M.R.; Tandjaoui, D.; Romdhani, I. Architecting the Internet of Things: State of the art. Sens. Clouds 2015, 36, 55–75. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fuqaha, A.I.; Guizani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Aledhari, M.; Ayyash, M. Internet of Things: A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 2347–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colakovi’c, A.; Hadžiali’c, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A review of enabling technologies, challenges, and open research issues. Comput. Netw. 2018, 144, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinard, D.; Trifa, V.; Karnouskos, S.; Spiess, P.; Savio, D. Interacting with the SOA-based internet of things: Discovery, query, selection, and on-demand provisioning of web services. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2010, 3, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gama, K.; Touseau, L.; Donsez, D. Combining heterogeneous service technologies for building an internet of things middleware. Comput. Commun. 2012, 35, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermesan, O.; Eisenhauer, M.; Serrano, M.; Guillemin, P.; Sundmaeker, H.; Tragos, E.; Valiño, J.; Copigneaux, B.; Presser, M.; Aagaard, A.; et al. The Next Generation Internet of Things—Hyperconnectivity and Embedded Intelligence at the Edge. Available online: https://european-iot-pilots.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/SRIA-2018_The_Next_Generation_IoT_Hyperconnectivity_and_Embedded_Intelligence_at_the_Edge_Research_Trends_IERC_2018_Cluster_eBook_978-87-7022-007-1_P_Web.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Waldner, J.B. Nano-Informatique et Intelligence Ambiante; Hermes Science Publications: Paris, France, 2006; ISBN 10:2746215160. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, Q.M.; Rashid, T.A.; Al-Salihi, N.K.; Ismael, B.; Kist, A.A.; Zhang, Z. Low Power Wide Area Networks: A Survey of Enabling Technologies, Applications and Interoperability Needs. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 77454–77473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampropoulos, G.; Siakas, K.; Anastasiadis, T. Internet of Things in the Context of Industry 4.0: An Overview. Int. J. Entrep. Knowl. 2019, 7, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpakwu, G.A.; Silva, B.J.; Hancke, G.P.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. A Survey on 5G Networks for the Internet of Things: Communication Technologies and Challenges. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3619–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Fu, X.; Zhao, W. A Novel Dynamic En-Route Decision Real-Time Route Guidance Scheme in Intelligent Transportation Systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 35th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems ICDCS 2015, Columbus, OH, USA, 29 June–2 July 2015; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, M.S.; Chowdhury, B.D. About Us | Xantra. Available online: http://xantra.in/about.html (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Zhang, L. Applications of the Internet of Things in the Medical Industry (Part 1): Digital Hospitals. 24 June 2018. Available online: https://dzone.com/articles/applications-of-the-internet-of-things-in-the-medi-1 (accessed on 22 February 2020).
- Matthews, K. How IoT Is Enabling the Telemedicine of Tomorrow. 28 November 2018. Available online: https://www.iotforall.com/how-iot-enables-tomorrows-telemedicine/ (accessed on 16 March 2020).
- Vilamovska, A.M.; Hatziandreou, E.; Schindler, R.H.; Nassau, C.O.; Vries, H.; Krapelse, J. Study on the requirements and options for RFID application in healthcare Identifying areas for Radio Frequency Identification deployment in health care delivery: A review of relevant literature. Available online: https://www.rand.org/pubs/technical_reports/TR608.html (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Whitmore, A.; Agarwal, A.; Da Xu, L. The Internet of Things—A survey of topics and trends. Inf. Syst. Front. 2014, 17, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjagi, R.; Jindal, M. IoT in Healthcare Industry|IoT Applications in Healthcare—Wipro. Available online: https://www.wipro.com/business-process/what-can-iot-do-for-healthcare-/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Horwitz, L. Patient Health Data Is Increasingly Democratized–Despite Data Quality Issues. March 2020. Available online: https://www.iotworldtoday.com/2020/03/03/democratization-of-patient-health-data-empowers-despite-data-quality-issues/ (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Meola, A. IoT Healthcare in 2020: Companies, Devices, Use Cases and Market Stats. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/iot-healthcare?international=true&r=US&IR=T (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Work Apple Watch Series 5. Available online: https://www.apple.com/lae/apple-watch-series-5/workout/ (accessed on 11 September 2021).
- Guo, B.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, D. Opportunistic IoT: Exploring the social side of the internet of things. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, CSCWD 2012, Wuhan, China, 23–25 May 2012; pp. 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, D.; Gupta, M.; Attar, T.; Chavan, P.; Patel, V. An attempt to develop an IOT based vehicle security system. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Smart Electronic Systems (ISES) (Formerly INiS), Hyderabad, India, 17–19 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Health Organization Report about Air Pollution WHO; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/250141/9789241511353-eng.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2019).
- Kaivonen, S.; Ngai, E.C.-H. Real-time air pollution monitoring with sensors on City Bus. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2020, 6, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Bhunia, S.S.; Mukherjee, N. Vehicular pollution monitoring using IOT. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering, ICRAIE 2014, Jaipur, India, 9–11 May 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qadri, Y.A.; Nauman, A.; Zikria, Y.B.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Kim, S.W. The future of healthcare internet of things: A survey of emerging technologies. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1121–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Bhatt, S.; Gupta, M.; Tosun, A.S. Future smart connected communities to fight COVID-19 outbreak. Internet Things 2021, 13, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technology Networks. Using the Internet of Things to Fight Virus Outbreaks. Available online: https://www.technologynetworks.com/immunology/articles/using-the-internet-of-things-to-fight-virus-outbreaks-331992 (accessed on 21 March 2020).
- Perlstein, D. How Is IoT Helping to Fight the Coronavirus?—Axonize IoT and Coronavirus. Available online: https://www.axonize.com/blog/iot-automation/how-is-iot-helping-to-fight-the-coronavirus/?utm_source=trendemon&utm_medium=content&utm_campaign=flow (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- Das, C.K.D.; Alam, M.W.; Hoque, M.I. A wireless heartbeat and Temperature Monitoring System for Remote Patients. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Renewable Energy, ICMERE 2014, Chittagong, Bangladesh, 1–3 May 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nall, R. What Is a Normally Temperature Range? Health News—Medical News Today. Available online: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323819 (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Bellany, D.Y. Thermometer Guns’ on Coronavirus Front Lines are Notoriously Not Accurate. The New York Times. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/02/14/business/coronavirus-temperature-sensor-guns.html (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Yousif, M.; Hewage, C.; Nawaf, L. IOT technologies during and beyond COVID-19: A comprehensive review. Future Internet 2021, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocetta, S. Hands-Free Everything? The Coronavirus Impact on IoT. Available online: https://www.globalsign.com/en/blog/hands-free-everything-coronavirus-impact-iot (accessed on 23 March 2021).
- Western Shelter.COVID-19 Screening, Monitoring, and Isolation Part 1—Western Shelter. Available online: https://westernshelter.com/blog/2020/8/3/covid-19-screening-monitoring-and-isolation (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Koetsier, J. This Smart Home Gym Is the Future of Fitness. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/johnkoetsier/2020/10/13/this-smart-home-gym-is-the-future-of-fitness/?sh=68691ae414bd (accessed on 26 February 2021).
- Personal Use: Meet ADAMM—Health Care Originals. Available online: http://www.healthcareoriginals.com/personal (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Muthuramalingam, S.; Bharathi, A.; Kumar, S.R.; Gayathri, N.; Sathiyaraj, R.; Balamurugan, B. Iot based intelligent transportation system (iot-its) for global perspective: A case study. In Intelligent Systems Reference Library; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 154. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-W.; Gu, X.-W.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhu, H.-S. AIoT Used for COVID-19 Pandemic Prevention and Control. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2021, 2021, 3257035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasajpour, M.; Pouriyeh, S.; Parizi, R.M.; Dorodchi, M.; Valero, M.; Arabnia, H.R. Internet of things for current COVID-19 and future pandemics: An exploratory study. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2020, 4, 325–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A. Wearable Technology. Available online: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/w/wearable-technology.asp (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Smart Wearables Market to Generate $53bn Hardware Revenues by 2019. Available online: https://www.juniperresearch.com/press/smart-wearables-market-to-generate-53bn-hardware (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Berglund, M.E.; Duvall, J.; Dunne, L.E. A survey of the historical scope and current trends of wearable technology applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016; pp. 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyntanidou, B.; Zouka, M.; Apostolopoulou, A.; Bamidis, P.D. IoT-based smart triage of COVID-19 suspicious cases in the Emergency Department. In Proceedings of the IEEE Globecom Workshops, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al Bassam, N.; Hussain, S.A.; Al Qaraghuli, A.; Khan, J.; Sumesh, E.P.; Lavanya, V. IoT based wearable device to monitor the signs of quarantined remote patients of COVID-19. Inform. Med. Unlocked. 2021, 24, 100588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabella, A.; Lekshmi, K.S.; Thamizhvaani, E.P.; Vishali, S. IOT Based Emergency Medical Services. Int. J. Eng. Tech. 2018, 4, 199–202. [Google Scholar]
- Magurano, D. Development of a Scalable Architecture for Industrial Internet of Things. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/9ff6/7ba53c0fbaee90d5d27e43d5958b0ff4872f.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2020).
- Miorandi, D.; Sicari, S.; De Pellegrini, F.; Chlamtac, I. Internet of things: Vision, applications and research challenges. Ad Hoc Netw. 2012, 10, 1497–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, C. Implementing Smart Factory of Industrie 4.0: An Outlook. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2016, 12, 3159805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.; Wang, W.; Bi, Y.; Qiu, M.; Hassan, M.M. Human localization based on inertial sensors and fingerprints in the Industrial Internet of Things. Comput. Netw. 2016, 101, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Wan, J.; Lu, J.; Qiu, D. Security of the Internet of Things: Perspectives and challenges. Wirel. Netw. 2014, 20, 2481–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, M.; Rinn, T.; Thaden, G.; Thieulloy, G. Industry 4.0. The New Industrial Revolution. How Europe Will Succeed. Hg V Roland Berg. Strategy Consult; GmbH Münch. Abgerufen Am 1105 2014 Unter: Munich, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wollschlaeger, M.; Sauter, T.; Jasperneite, J. The Future of Industrial Communication: Automation Networks in the Era of the Internet of Things and Industry 4.0. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2017, 11, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodpour, M.; Lobov, A.; Lanz, M.; Makela, P.; Rundas, N. Role-based visualization of industrial IoT-based systems. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE/ASME International Conference on Mechatronic and Embedded Systems and Applications, MESA 2018, Oulu, Finland, 2–4 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SlideModel. Industry 4.0 PowerPoint Template. Available online: https://slidemodel.com/templates/industry-4-0-powerpoint-template/ (accessed on 16 March 2020).
- Lee, J.; Bagheri, B.; Kao, H.A. A Cyber-Physical Systems architecture for Industry 4.0-based manufacturing systems. Manuf. Lett. 2015, 3, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasi, H.; Fettke, P.; Kemper, H.G.; Feld, T.; Hoffmann, M. Industry 4.0. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2014, 4, 239–242. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12599-014-0334-4#auth-1 (accessed on 1 May 2020). [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, X.; Klotz, E.; Newman, S.T. Intelligent Manufacturing in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review. Engineering 2017, 3, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, N.C.; Melício, R.; Mendes, V.M.F. Services enabler architecture for smart grid and smart living services providers under industry 4.0. Energy Build. 2017, 141, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, F.; Sun, Z.; Jin, H. Topic-centric and semantic-aware retrieval system for internet of things. Inf. Fusion 2015, 23, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, Z.; Yang, L.T. Fusion–An aide to data mining in Internet of Things. Inf. Fusion 2015, 23, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsoom, T.; Ahmed, S.; Rafi-ul-Shan, P.M.; Azmat, M.; Akhtar, P.; Pervez, Z.; Imran, M.A.; Ur-Rehman, M. Impact of IOT on Manufacturing Industry 4.0: A new triangular systematic review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Nagi, R. A review of agile manufacturing systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2001, 39, 3561–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallasega, P.; Rauch, E.; Linder, C. Industry 4.0 as an enabler of proximity for construction supply chains: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. 2018, 99, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sharma, R. Analysis of the driving and dependence power of barriers to adopt Industry 4.0 in Indian manufacturing industry. Comput. Ind. 2018, 101, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottge, S.; Menzel, T.; Forslund, H. Industry 4.0 technologies in the purchasing process. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2020, 120, 730–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, S.; Sufian, A.; Pervaiz, S.; Tanveer, M. Smart Traffic Management System using internet of things. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, ICACT 2018, Chuncheon, Korea, 11–14 February 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumia, L.; Ranga, V. Intelligent traffic management system for prioritizing emergency vehicles in a smart city. Int. J. Eng. 2018, 31, 278–283. [Google Scholar]
- Pyykonen, P.; Laitinen, J.; Viitanen, J.; Eloranta, P.; Korhonen, T. IOT for intelligent traffic system. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing, ICCP 2013, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 5–7 September 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, B.; Umair, M.; Asadullah Shah, G.; Ahmed, E. Enabling IOT platforms for social IOT applications: Vision, feature mapping, and challenges. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, E.; Kfoury, E.; Khoury, D. An IOT approach to vehicle accident detection, reporting, and Navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Multidisciplinary Conference on Engineering Technology, IMCET 2016, Beirut, Lebanon, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.T.; Sankar, J. IOT based Smart School Bus Monitoring and Notification System. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference, R10-HTC 2017, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 21–23 December 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drath, R.; Horch, A. Industrie 4.0: Hit or Hype? [Industry Forum]. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2014, 8, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, R.; Chalamalasetti, S.R. Applicability of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) in Lean Manufacturing: A brief Study. Prod. Sched. 2019, 10, 22–26. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337286599_Applicability_of_Industrial_Internet_of_Things_IIoT_in_Lean_Manufacturing_A_brief_Study (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Harrell, C. The Internet of Things and Control System Architecture. Available online: http://blog.aac.advantech.com/the-internet-of-things-and-control-system-architecture/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Capello, F.; Toja, M.; Trapani, N. A Real-Time Monitoring Service based on Industrial Internet of Things to manage agrifood logistics. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information Systems, Logistics and Supply Chain ILS Conference, Bordeaux, France, 1–4 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hiter, S. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Market Size & Forecast. 2022. Available online: https://www.datamation.com/trends/industrial-internet-of-things-iiot-market/ (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Evans, D. The Internet of Things How the Next Evolution of the Internet Is Changing Everything. Cisco Internet Bus. Solut. Group (IBSG) 2011, 1, 1–11. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en_us/about/ac79/docs/innov/IoT_IBSG_0411FINAL.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Afshar, V. HuffPost Is Now a Part of Verizon Media. Available online: https://www.huffpost.com/entry/cisco-enterprises-are-leading-the-internet-of-things_b_59a41fcee4b0a62d0987b0c6 (accessed on 14 June 2020).
- Statista Research Department. IoT: Number of Connected Devices Worldwide 2012–2025. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/471264/iot-number-of-connected-devices-worldwide/ (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Patil, P.; Tawade, P.; Samudre, S.; Mali, S.; Pardeshi, S. Survey on Internet of Things (IoT): Tools and Technologies. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. (IJSRCSEIT) 2018, 3, 1108–1112. Available online: http://ijsrcseit.com/CSEIT1833352 (accessed on 3 April 2021).
- Heutger, M. A Shared Journey: Customer-Centric Innovation-Huawei Case Studies. Huawei Enterprise. Available online: https://e.huawei.com/en/case-studies/global/2017/201709070922 (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Cisco. Solutions-Cisco IOT Helps Nissan Transform Car Production Operations. Cisco. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/internet-of-things/nissan-motors-case-study.html (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Gartner Gartner Says 5.8 Billion Enterprise and Automotive IoT Endpoints Will Be in Use in 2020. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2019-08-29-gartner-says-5-8-billion-enterprise-and-automotive-io (accessed on 3 April 2020).
- Presser, M.; Gluhak, A. The Internet of things: Connecting the real world with the digital world. Eurescom Message—The Magazine for Telecom Insiders. 2009, Volume 2. Available online: http://www.eurescom.eu/message (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Ray, P.P. A survey on Internet of Things architectures. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 30, 291–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frost & Sullivan Best Practices Award. Radio-Frequency Identification for Retail Self Checkouts—Europe. 2019, pp. 1–19. Available online: https://www.nordicid.com/wp-content/uploads/Frost-Sullivan-Nordic-ID-New-Product-Innovation-2019-report.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Industrial Internet of Things Market Size Report. 2021–2028. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/industrial-internet-of-things-iiot-market (accessed on 16 December 2021).
- Shen, W.; Norrie, D.H. Agent-Based Systems for Intelligent Manufacturing: A State-of-the-Art Survey. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 1999, 1, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Wan, J.; Vasilakos, A.V.; Lai, C.-F.; Wang, S. A review of industrial wireless networks in the context of Industry 4.0. Wirel. Netw. 2015, 23, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, D.; Carrie, C.; Turner, V.; Morales, M. Worldwide and Regional Internet of Things (IoT) 2014–2020 Forecast: A Virtuous Circle of Proven Value and Demand. IDC Analyze the Future, 1–27. Available online: http://branden.biz/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/IoT-worldwide_regional_2014-2020-forecast.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Krishnamachari, B.; Power, J.; Shahabi, C.; Kim, S.H. IoT Marketplace: A Data and API Market for IoT Devices; University of Southern California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Saputhanthri, A.; Alwis, C.D.; Liyanage, M. Emergence of Blockchain Based IOT Marketplaces. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Madhusanka-Liyanage/publication/350835689_Emergence_of_Blockchain_based_IoT_Marketplaces/links/6080a4c8907dcf667bb5ae4f/Emergence-of-Blockchain-based-IoT-Marketplaces.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2021).









| Application Field | Area | Current Application |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Retail | Retail Center |
| Smart Environment and City | City Sense Smart Parking | |
| Smart Water | GBROOS | |
| Smart Houses | Security, Health | Smart Fridge, Smart Thermostat |
| Years | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1784 | 1870 | 1969 | Today | |
| Industrial Revolution | Industry 1.0 Mechanization Steam power Weaving loom | Industry 2.0 Mass production Assembly line Electrical energy | Industry 3.0 Automation Computers and electronics | Industry 4.0 Cyber-physical systems Internet of Things networks |
| Years | Utilities | Government | Building Automation | Physical Security | Manufacturing & Natural Resources | Automotive | Healthcare Providers | Retail & Wholesale Trade | Information | Transportation | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Segment | ||||||||||||
| 2018 | 0.98 | 0.4 | 0.23 | 0.83 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 3.96 | |
| 2019 | 1.17 | 0.53 | 0.31 | 0.95 | 0.4 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.07 | 4.81 | |
| 2020 | 1.37 | 0.7 | 0.44 | 1.09 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 5.81 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salih, K.O.M.; Rashid, T.A.; Radovanovic, D.; Bacanin, N. A Comprehensive Survey on the Internet of Things with the Industrial Marketplace. Sensors 2022, 22, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030730
Salih KOM, Rashid TA, Radovanovic D, Bacanin N. A Comprehensive Survey on the Internet of Things with the Industrial Marketplace. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030730
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalih, Kazhan Othman Mohammed, Tarik A. Rashid, Dalibor Radovanovic, and Nebojsa Bacanin. 2022. "A Comprehensive Survey on the Internet of Things with the Industrial Marketplace" Sensors 22, no. 3: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030730
APA StyleSalih, K. O. M., Rashid, T. A., Radovanovic, D., & Bacanin, N. (2022). A Comprehensive Survey on the Internet of Things with the Industrial Marketplace. Sensors, 22(3), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030730








